PyTorch笔记 - GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit)网络结构
Posted SpikeKing
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了PyTorch笔记 - GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit)网络结构相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
LSTM with peephole connections
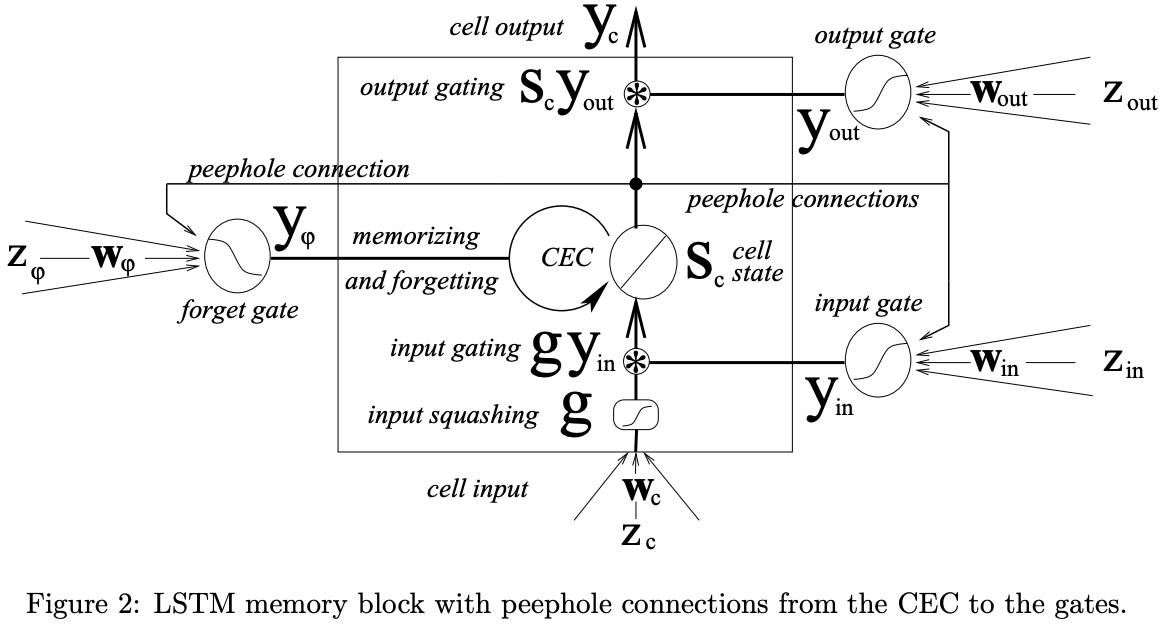
即 w*x + w*h_(t-1) + w*c_(t-1),t-1为下标的,都是初始状态。
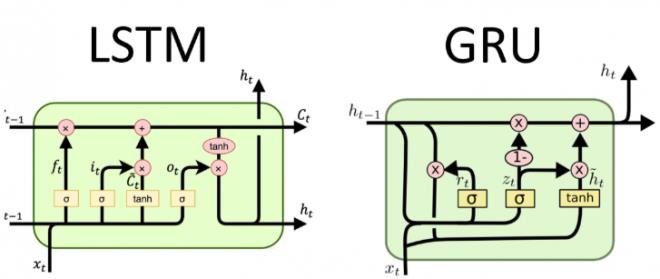
- r是reset,重置门
- z是update,更新门
- n是new,最新门

参数量:LSTM的0.75倍,计算量也是LSTM的0.75倍
- GRU的图中,缺少“+”,即
h_(t-1) * r + x_t,同时z_t和1-z_t写反了。
Paper:Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling
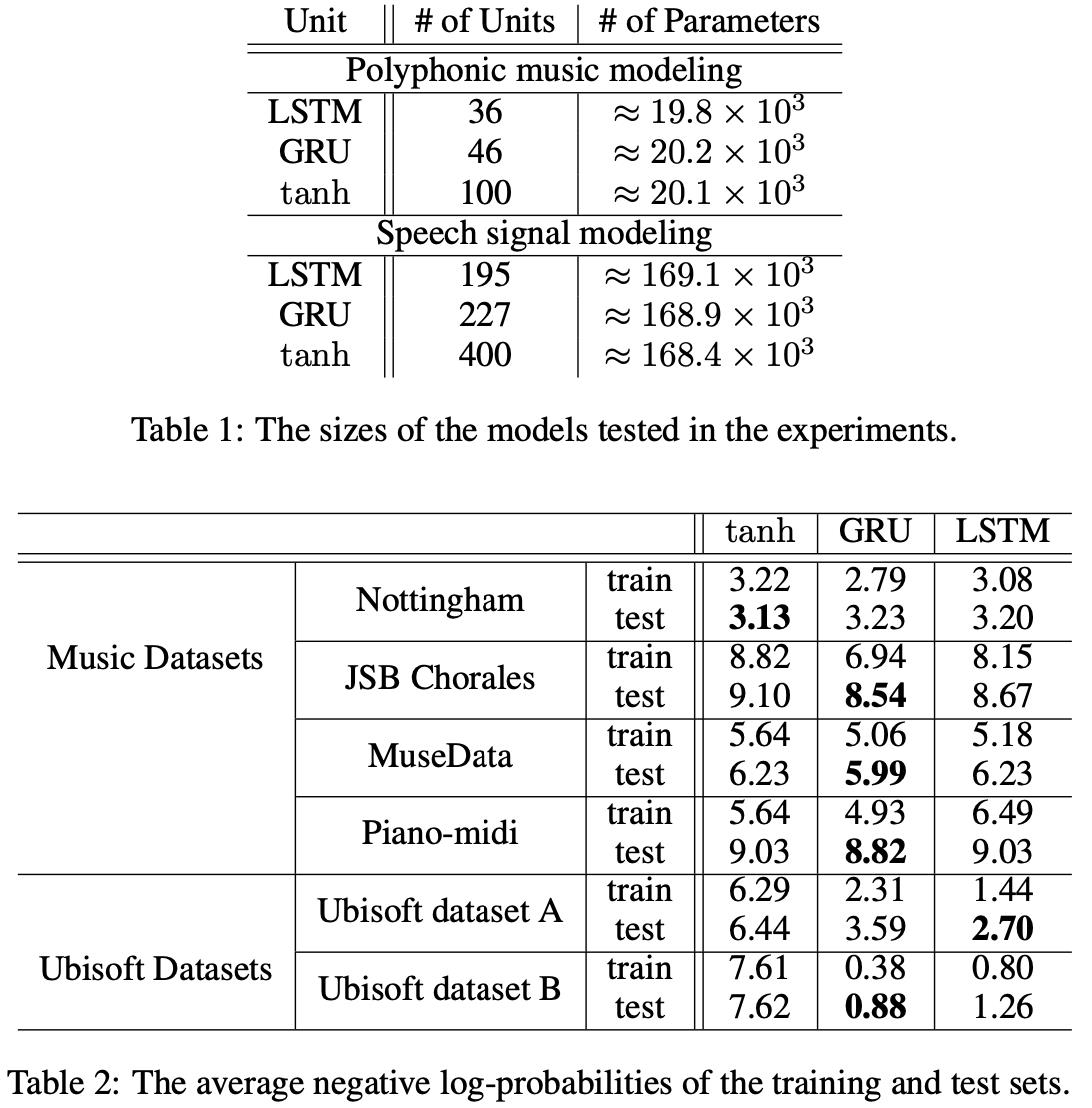
参数数目对比,LSTM vs. GRU:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
lstm_layer = nn.LSTM(3, 5)
gru_layer = nn.GRU(3, 5)
print(sum(p.numel() for p in lstm_layer.parameters()))
print(sum(p.numel() for p in gru_layer.parameters()))
GRU只有h_0,没有c_0
# step5 逐行实现GRU网络
def gru_forward(input, initial_state, w_ih, w_hh, b_ih, b_hh):
prev_h = initial_state
bs, T, i_size = input.shape
h_size = w_ih.shape[0] // 3 # GPU只有3组,LSTM有4组
# 对权重扩维,复制batch_size倍
batch_w_ih = w_ih.unsqueeze(0).tile(bs, 1, 1) # 复制bs倍
batch_w_hh = w_hh.unsqueeze(0).tile(bs, 1, 1)
output = torch.zeros(bs, T, h_size) # GRU网络的输出状态序列
for t in range(T):
x = input[:, t, :] # t时刻GRU cell的输入特征向量, [bs, i_size]
w_times_x = torch.bmm(batch_w_ih, x.unsqueeze(-1)) # [bs, 3*h_size, 1]
w_times_x = w_times_x.squeeze(-1) # [bs, 3*h_size]
w_times_h_prev = torch.bmm(batch_w_hh, prev_h.unsqueeze(-1)) # [bs, 3*h_size, 1]
w_times_h_prev = w_times_h_prev.squeeze(-1) # [bs, 3*h_size]
r_t = torch.sigmoid(w_times_x[:, :h_size] + w_times_h_prev[:, :h_size] + \\
b_ih[:h_size] + b_hh[:h_size]) # 重置门
z_t = torch.sigmoid(w_times_x[:, h_size:h_size*2] + w_times_h_prev[:, h_size:h_size*2] + \\
b_ih[h_size:h_size*2] + b_hh[h_size:h_size*2]) # 更新门
n_t = torch.tanh(w_times_x[:, h_size*2:h_size*3] + b_ih[h_size*2:h_size*3] + \\
r_t*(w_times_h_prev[:, h_size*2:h_size*3] + b_hh[h_size*2:h_size*3])) # 最新门
prev_h = (1-z_t)*n_t + z_t*prev_h # 增量更新隐含状态
output[:, t, :] = prev_h
return output, prev_h
# 测试函数的正确性
bs, T, i_size, h_size = 2, 3, 4, 5
input = torch.randn(bs, T, i_size) # 输入序列
h_0 = torch.randn(bs, h_size) # proj是对h进行压缩
# 调用官方GRU API
gru_layer = nn.GRU(i_size, h_size, batch_first=True)
# input带batch, h_0也需要增加1维
output, h_final = gru_layer(input, h_0.unsqueeze(0))
print(f'[Info] output: \\noutput')
for k, v in gru_layer.named_parameters():
print(k, v.shape)
output_custom, h_final_custom = gru_forward(input, h_0, gru_layer.weight_ih_l0, gru_layer.weight_hh_l0, \\
gru_layer.bias_ih_l0, gru_layer.bias_hh_l0)
print(f'[Info] output_custom: \\noutput_custom')
以上是关于PyTorch笔记 - GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit)网络结构的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章