C++栈和队列应用实验
Posted 康小庄
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++栈和队列应用实验相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 假设正读和反读都相同的字符序列为“回文”,例如,‘abba’和‘abcba’是回文,‘abcde’则不是回文。试写一个算法判别读入的一个以’@’为结束符的字符序列是否是“回文”。(利用栈和队列两种结构实现)。
运行结果如图所示:
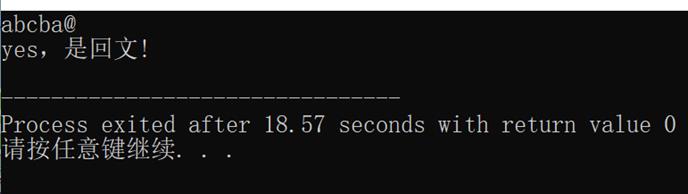
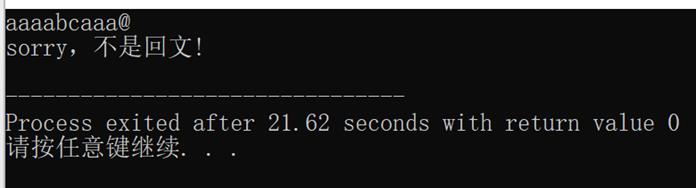
完整代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define null 0;
#define n 10;
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
using namespace std;
struct stack
char *base;
char *top;
int stacksize;
;
void initstack(struct stack *s)
s->base = (char *) malloc(20 * sizeof(char));
if (!s->base) exit(0);
s->top = s->base;
s->stacksize = 20;
return;
void push(struct stack *s, char e)
if (s->top - s->base >= s->stacksize)
s->base = (char *) realloc(s->base, (s->stacksize + 10) * sizeof(char));
if (!s->base) exit(0);
s->top = s->base + s->stacksize;
s->stacksize += n;
*(s->top)++ = e;
return;
char pop(struct stack *s)
char e;
if (s->top == s->base) return null;
e = *--s->top;
return e;
void clearstack(struct stack *s)
if (s->top == s->base) return;
s->top = s->base;
return;
int StackEmpty(struct stack *s)
if (s->top == s->base) return 1;
else return 0;
typedef int elemType;
/* 以下是关于队列链接存储操作的6种算法 */
struct sNode
elemType data; /* 值域 */
struct sNode *next; /* 链接指针 */
;
struct queueLK
struct sNode *front; /* 队首指针 */
struct sNode *rear; /* 队尾指针 */
;
/* 1.初始化链队 */
void initQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
hq->front = (sNode *) malloc(20 * sizeof(struct sNode));
if (!hq->front) exit(0);
hq->front = hq->rear = NULL; /* 把队首和队尾指针置空 */
return;
/* 2.向链队中插入一个元素x */
void enQueue(struct queueLK *hq, elemType x)
/* 得到一个由newP指针所指向的新结点 */
struct sNode *newP;
newP = (sNode *) malloc(sizeof(struct sNode));
if (newP == NULL)
printf("内存空间分配失败! ");
exit(1);
/* 把x的值赋给新结点的值域,把新结点的指针域置空 */
newP->data = x;
newP->next = NULL;
/* 若链队为空,则新结点即是队首结点又是队尾结点 */
if (hq->rear == NULL)
hq->front = hq->rear = newP;
else /* 若链队非空,则依次修改队尾结点的指针域和队尾指针,使之指向新的队尾结点 */
hq->rear->next = newP;
hq->rear = newP;/* 注意赋值顺序哦 */
return;
/* 3.从队列中删除一个元素 */
int outQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
struct sNode *p;
int temp;
/* 若链队为空则停止运行 */
if (hq->front == NULL)
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
temp = hq->front->data; /* 暂存队尾元素以便返回 */
p = hq->front; /* 暂存队尾指针以便回收队尾结点 */
hq->front = p->next; /* 使队首指针指向下一个结点 */
/* 若删除后链队为空,则需同时使队尾指针为空 */
if (hq->front == NULL)
hq->rear = NULL;
free(p); /* 回收原队首结点 */
return temp; /* 返回被删除的队首元素值 */
/* 4.检查链队是否为空,若为空则返回1, 否则返回0 */
int emptyQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
/* 判断队首或队尾任一个指针是否为空即可 */
if (hq->front == NULL)
return 1;
else
return 0;
/************************************************************************/
void useStack(struct stack s, char *a)
cout << "输入一串字符以@结尾" << endl;
cin >> a;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(a) - 1; i++)
if (a[i] != '\\@')
push(&s, a[i]);
int i = 0;
while (!StackEmpty(&s))
if (pop(&s) != a[i])
cout << "不是回文数" << endl;
break;
i++;
if (StackEmpty(&s))
cout << "是回文数" << endl;
void useStackAnDQueue(struct queueLK q, struct stack s, char *a)
cout << "输入一串字符以@结尾" << endl;
cin >> a;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(a) - 1; i++)
if (a[i] != '\\@')
push(&s, a[i]);
enQueue(&q, a[i]);
while (!StackEmpty(&s) && !emptyQueue(&q))
if (pop(&s) != outQueue(&q))
cout << "不是回文数" << endl;
break;
if (StackEmpty(&s) && emptyQueue(&q))
cout << "是回文数" << endl;
int main()
struct queueLK q;
struct stack s;
char a[10];
initQueue(&q);
initstack(&s);
useStackAnDQueue(q, s, a);
//利用栈和队列的操作特点写一段代码
//判别读入的一个以’@’为结束符的字符序列是否是“回文”。
运行截图
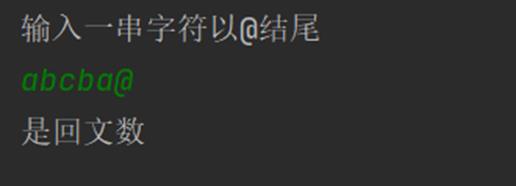

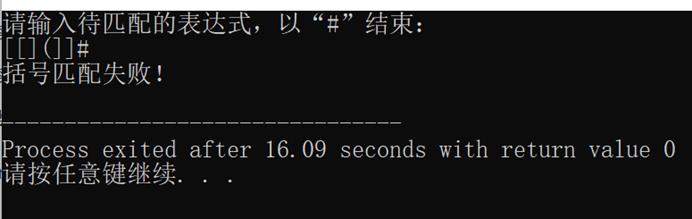
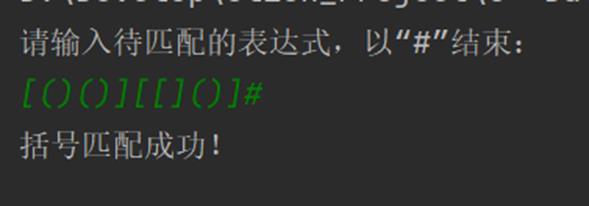
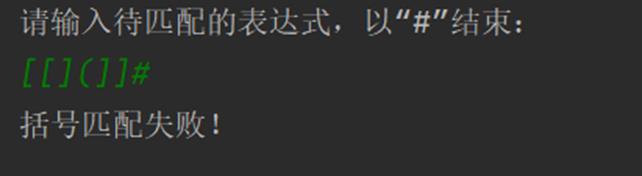
2. 利用栈的存储结构完成括号匹配程序。
运行结果如图所示:
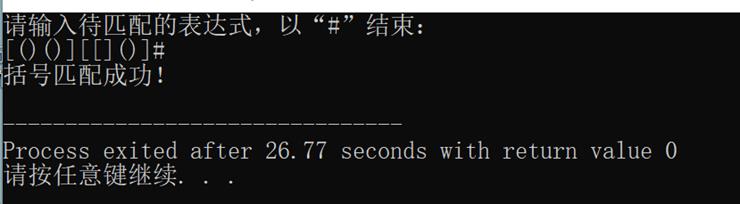
完整代码
/***链栈实现括号匹配***/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef char SElemType;
typedef int Status;
typedef struct SNode
int data;
struct SNode *next;
SNode, *LinkStack;
Status InitStack(LinkStack &S)
S = NULL;
return OK;
bool StackEmpty(LinkStack S)
if (!S)
return true;
return false;
Status Push(LinkStack &S, SElemType e)
SNode *p = new SNode;
if (!p)
return OVERFLOW;
p->data = e;
p->next = S;
S = p;
return OK;
Status Pop(LinkStack &S, SElemType &e)
SNode *p;
if (!S)
return ERROR;
e = S->data;
p = S;
S = S->next;
delete p;
return OK;
Status GetTop(LinkStack &S)
if (!S)
return ERROR;
return S->data;
//算法3.21 括号的匹配
Status Matching() //检验表达式中所含括号是否正确匹配,如果匹配,则返回true,否则返回false
//表达式以“#”结束
char ch;
SElemType x;
LinkStack S;
InitStack(S);
cin >> ch;
int flag = 1;
while (ch != '#' && flag)
switch (ch)
case '[':
case '(':
Push(S, ch);
break;
case ')':
if (!StackEmpty(S) && GetTop(S) == '(')
Pop(S, x);
else
flag = 0;
break;
case ']':
if (!StackEmpty(S) && GetTop(S) == '[')
Pop(S, x);
else
flag = 0;
break;
cin >> ch;
if (StackEmpty(S) && flag)
return true;
else
return false;
int main()
LinkStack S;
cout << "请输入待匹配的表达式,以“#”结束:" << endl;
int flag = (int) Matching();
if (flag)
cout << "括号匹配成功!" << endl;
else
cout << "括号匹配失败!" << endl;
return 0;
运行截图
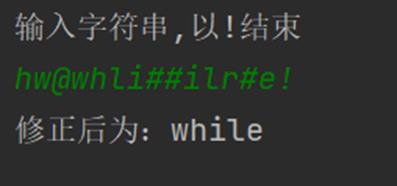
3. (选做)利用栈的存储结构完成行编辑程序,要求如下:
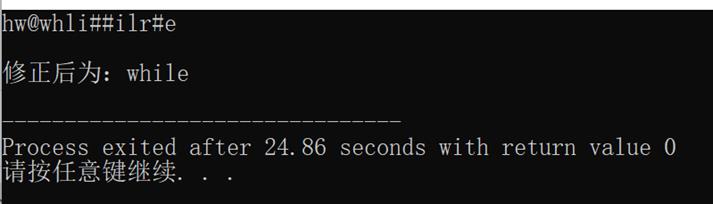
输入一行字符串,用户在输入错误时可以用#和@进行修正,其中#为退格符,@为退行符。要求输出修正后的字符串。如字符串“hw@whli##ilr#e”修正后输出为“while”。
运行结果如图所示:
完整代码
#include"stdio.h"
#include"stdlib.h"
#include"string.h"
#include <iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
#define null 0
#define n 10
struct stack
char *base;
char *top;
int stacksize;
;
void initstack(struct stack *s)
s->base = (char *) malloc(20 * sizeof(char));
if (!s->base) exit(0);
s->top = s->base;
s->stacksize = 20;
return;
void push(struct stack *s, char e)
if (s->top - s->base >= s->stacksize)
s->base = (char *) realloc(s->base, (s->stacksize + n) * sizeof(char));
if (!s->base) exit(0);
s->top = s->base + s->stacksize;
s->stacksize += n;
*(s->top)++ = e;
return;
char pop(struct stack *s)
char e;
//if(s->top==s->base) return 0;
e = *(--s->top);
return e;
void clearstack(struct stack *s)
if (s->top == s->base) return;
s->top = s->base;
return;
int main()
//输入一行字符串,用户在输入错误时可以用#和@进行修正,
//其中#为退格符,@为退行符。要求输出修正后的字符串。
char ch;
struct stack s;
struct stack t;
initstack(&s);
initstack(&t);
cout << "输入字符串,以!结束" << endl;
ch = getchar();
while (ch != '!')
switch (ch)
case '#':
// 出栈
pop(&s);
break;
case '@':
clearstack(&s);
break;
default:
push(&s, ch);
ch = getchar();
// hw@whli##ilr#e!
cout << s.base;
运行截图
以上是关于C++栈和队列应用实验的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章