SpringAop 流程源码阅读
Posted 看写写
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringAop 流程源码阅读相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
AOP的核心概念
由来
AOP是切面的意思,面向对象的思想,设计出来的结构都是树状的,最大程度的提升代码的复用率、扩展性、易读性。但是这里有个问题,树状结构大家都是知道是一种关系型结构,擅长处理关系结构,扩展等方面适合业务功能核心代码的开发。但是对于一些重复的、每个功能都需要用到的功能比如,日志、监控、权限、统计、事务等横向的功能(所有功能都需要的),使用面向对象的思想处理起来的结果就是导致代码重复率高、不易扩展、阅读体验比较差,每次都要看非业务代码。这种情况就适合用切面来处理。因为这个过程和织布机,横向织入横线的过程一样,所以这个过程被称为织入。
关键点
切面的核心点,就是切入点,point,我们需要一个切入点 point cut,围绕这个点进行一些增强处理,可能是前,后,或者环绕式的,这些具体的增强就是advice,而切面 aspect 是包含这两个部分的。但是切面生成之后,如果放到合适的地方,就是需要织入 weaving。
spring中的应用
面向对象的设计中,一个类有两部分组成,成员变量,成员方法。成员变量是属性,运行时标识当前对象的状态,成员方法是action,标识这个类可以做哪些事情。所以AOP增强的最小单位就是成员方法,是对方法的增强。但是方法属于类,所以切入点的通过规则表达式(可以理解过正则表达式)来选定类+方法,具体规则看
所以增强的单位肯定也是方法,可以理解为方法增强。最后的织入过程,我们都知道设计模式中的代理模式,这里就是基于代理模式的思想,通过spring的IOC机制生成代理对象,spring通过IOC获取的都是代理对象,所以很方便的就完成了织入过程。
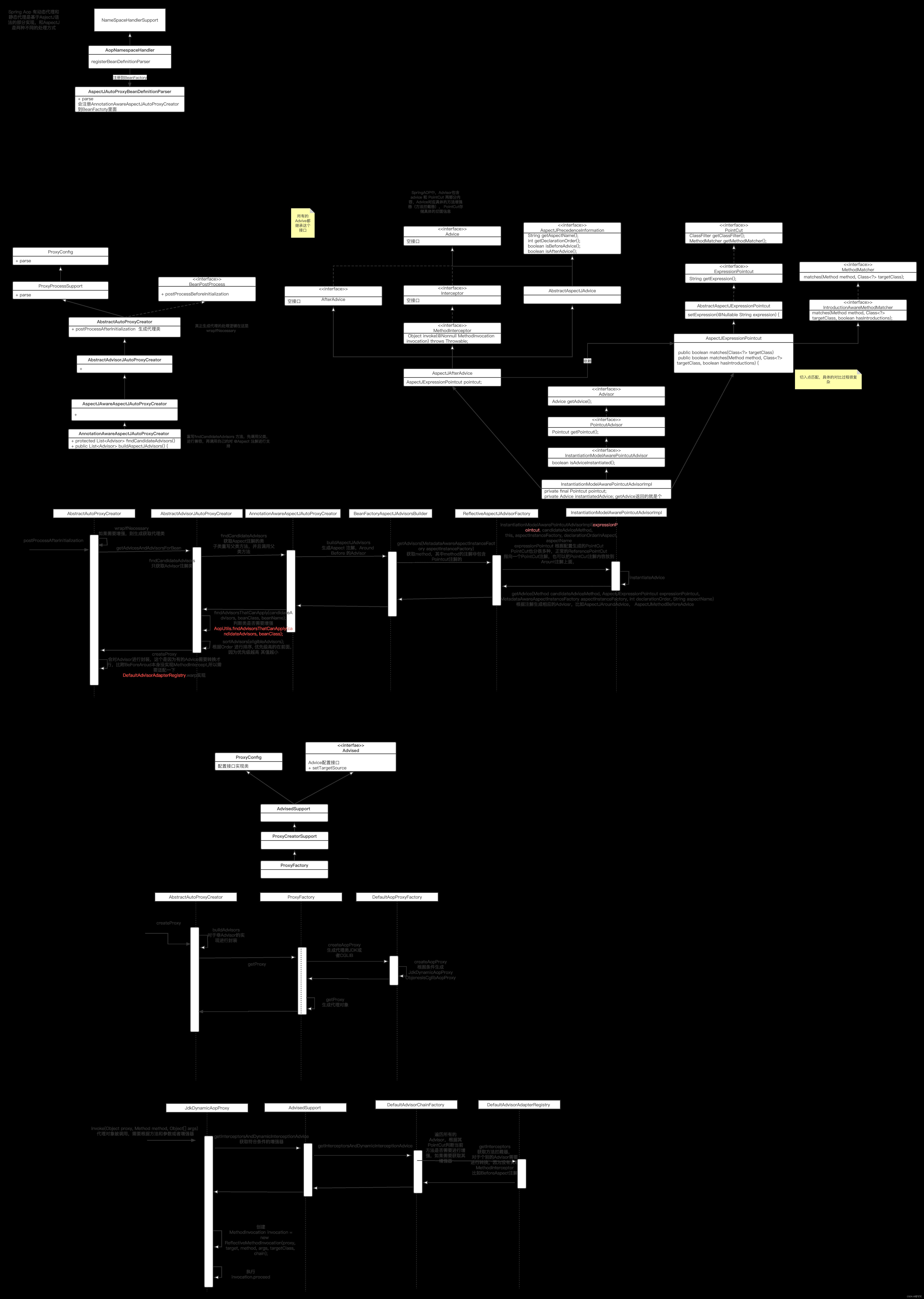
基于以上的概念,spring aop是分开设计了4种接口
spring中的设计
切入点,主要是用来解析表达式,并且进行类、方法的 match操作,PointCut
增强器,主要用来对方法进行增强:Advice
切面,切入点和增强器的组合具体是流程控制: PointCutAdvisor
织入,获取目标对象是否需要进行代理,如果需要则获取需要进行代理的切面(可能有多个),生成代理对象放入到容器中替换目标对象,AutoProxyCreator
类图
Demo
主入口 main
public class InstalmentApiServer
public static void main(String[] args)
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");
log.info("starting main");
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]
"classpath:context/applicationContext.xml",
, false);
IHello testA = (IHello) context.getBean("testA");
testA.sayHello();
xml 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"
default-lazy-init="false">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="testA" class="com.xiaomi.mifi.instalment.api.server.TestA" init-method="initMethod"> </bean>
<bean id="logAspect" class="com.xiaomi.mifi.instalment.api.server.LogAspect" />
<!--注册annotation-->
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>
切面 LogAspect
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class LogAspect
@Around("execution(* com..*(..))")
private Object errorHandlerAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable
System.out.println("-----------> LogAspect before");
Object rs = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("-----------> LogAspect After");
return rs;
HelloImpl
public class HelloImpl implements IHello
@Override
public void sayHello()
System.out.println("hello world");
TestA
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
public class TestA implements InitializingBean , IHello
public TestA()
System.out.println("---->TestA constructor this is ");
@PostConstruct
public void init()
System.out.println("PostConstruct");
public void initMethod()
System.out.println("initMethod");
public void fooA()
System.out.println("----> TestA.fooA this is ");
public void foo()
System.out.println("----> TestA.foo this is ");
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception
System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet");
@Override
public void sayHello()
System.out.println("----> TestA sayHello implement ");
开启aop配置
这个触发操作是由于配置
// spring 配置文件, 启动spring AOP
<beans // aop 命令空间
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"
default-lazy-init="false">
// 开启 aop配置
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
aop地址空间映射
org.springframework.aop.config.AopNamespaceHandler
这个类用来解析xml配置文件中,aop开头的配置
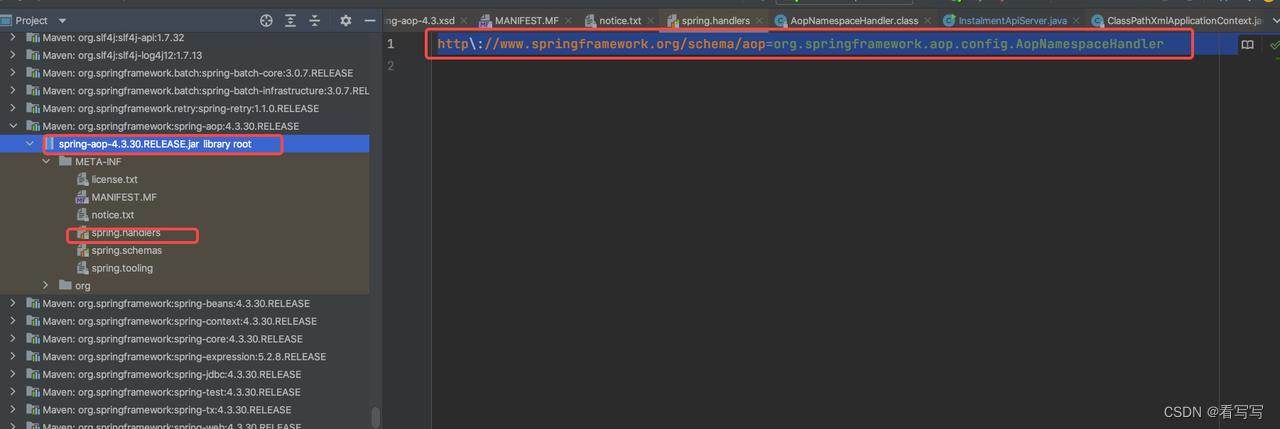
这个aop命令空间(http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop) 是如何映射到这个类是通过配置文件spring.handlers,来完成的,这个文件在
srping-aop-4.3.30.jar包的,META-INF 目录下面的,spring会加载所有这个名称的文件,用来解析xml文件中的命令空间的
文件内容
http\\://www.springframework.org/schema/aop=org.springframework.aop.config.AopNamespaceHandler
aop属性解析
org.springframework.aop.config.AopNamespaceHandler
@Override
public void init()
// In 2.0 XSD as well as in 2.5+ XSDs
registerBeanDefinitionParser("config", new ConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
// 属性 aspectj-autoproxy 的解析
registerBeanDefinitionParser("aspectj-autoproxy", new AspectJAutoProxyBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionDecorator("scoped-proxy", new ScopedProxyBeanDefinitionDecorator());
// Only in 2.0 XSD: moved to context namespace in 2.5+
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
aop解析细节
具体的细节就是使用AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类,去向
BeanDefinitionRegistry把beanDefinition注册到工厂类中,bean的创建过程是先创建bena的定义,通过bean的定义再生成的对象。
通过下面的方法完成类:AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的注册,所有aop的增强都是通过这个类来完成的如果是通过@Aspect注解,注解的切面。
该类的优先级别是最高级别的,先执行
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
生成代理类
AbstractAutoProxyCreator
是 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 的祖先类的,实现对类的增强是流程主入口。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator本身只处理和Aspect注解相关的事情,充分体现面向对象
抽象、继承,的特点,体现了高扩展能力。
主流程
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean
->applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
开始执行 .postProcessAfterInitialization
// spring 解决单例循环依赖的时候,会提前注册一个BeanFactory,这里会提前生成代理类
@Override
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 写入这个map的原因,是为了保证单例,这里提前生成了代理类(因为循环依赖),
// A->B->A , 这种情况下,在创建B的时候,会调用这里提前生成A的代理类,
// 这个时候B里面的对A的引用已经是新的代理类了,但是A本身的还在初始化的过程中还没完成
// 需要完成A的初始化,但是还不能重新生成新的代理类否则就不是单例了,所以这里记录
// 在postProcessAfterInitialization的时候,对比引用,如果一样,就不重新生成代理类了
// 同时这个方法只会被调用一次,因为单例对象生成过成中会加锁,而且进行缓存,保证创建完成之后
// 只会从缓存里面取。同时最终A初始化完成之后,会把最终返回的引用对象体会为这里生成的代理对象,保证单例
this.earlyProxyReferences.put(cacheKey, bean);
// 生成代理类的具体实现
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
// 正常的非循环依赖的对象,都从这里进行AOP的增强
// 这里的循环依赖指的是单例循环依赖(非构造函数依赖)
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
if (bean != null)
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 1, 如果是循环依赖则remove返回的bean ,和 当前是bean地址一样,这里是false,直接结束
// 2, 非循环依赖,那这里remove返回的是null,而bean不为空是先决条件,所以这里返回 true,进行类的增强,生成代理类
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean)
// 生成代理类的具体实现
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
return bean;
// 生成代理类
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey)
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName))
return bean;
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey)))
return bean;
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName))
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//获取需要增强的切面
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY)
// 缓存该类,需要 AOP 增强
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 生成代理类对象
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors
// 被代理的对象,在代理类最后调用
, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
// 缓存
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
// 缓存该类,不需要 AOP 增强
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
// 生成代理类
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource)
// 设置属性,把原始类名称,设置到 BeanDefiniiton的属性中
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// 检查类,是需要代理类,还是代理接口,因为有的类没有接口,只能代理类
// java JDK proxy只能代理接口,如果是代理类需要使用cgLib生成子类才行
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass())
// 检查类属性是否有生命
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName))
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
else
// 如果实现的类是内部类,最后也会代理类
// proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
// 生成最终的增强器
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered())
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
// 生成代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
// 检查是否需要代理类
protected void evaluateProxyInterfaces(Class<?> beanClass, ProxyFactory proxyFactory)
Class<?>[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, getProxyClassLoader());
boolean hasReasonableProxyInterface = false;
for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces)
if (!isConfigurationCallbackInterface(ifc) && !isInternalLanguageInterface(ifc) &&
ifc.getMethods().length > 0)
hasReasonableProxyInterface = true;
break;
// 有需要代理的接口,则添加代理接口,这里有个问题,就是只能代理接口的方法,
// 非接口方法无法代理,即使符合pointCut的条件
if (hasReasonableProxyInterface)
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the target's interfaces only.
for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces)
proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc);
else
// 否则只能代理类
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
// 生成最终的advisor
protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors)
// Handle prototypes correctly...
// 通过配置文件配置的,目前都是通过注解,所以这里一般都是空的
Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames();
List<Object> allInterceptors = new ArrayList<Object>();
if (specificInterceptors != null)
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(specificInterceptors));
if (commonInterceptors.length > 0)
if (this.applyCommonInterceptorsFirst)
allInterceptors.addAll(0, Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
else
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
Advisor[] advisors = new Advisor[allInterceptors.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < allInterceptors.size(); i++)
// wrap 是进行一次适配的过程,因为要兼容老的切面,所以进行一次兼容处理
advisors[i] = this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(allInterceptors.get(i));
return advisors;
获取该对象需要增强的切面
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
是 org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator
的子类,提供和切面相关的逻辑
@Override
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource)
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty())
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
return advisors.toArray();
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
// 获取所有的切面, 注意是逻辑见AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 取出符合该对象的切面
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 扩展切面,这个是因为有一些切面比较老,需要去兼容一些,做一些适配
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty())
// 切面排序,决定执行先后顺序
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
return eligibleAdvisors;
获取Aspect所有的切面
对Aspect注解,进行解析,获取所有的Aspect注解,切面
以及表达式
org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
主流程
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors()
// 先调用父类接口,兼容父类
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// 获取Aspect注解的切面
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
return advisors;
// 获取增强列表,
// 来自类:org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors()
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null)
// 加锁,防止重复操作
synchronized (this)
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
// double check
if (aspectNames == null)
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
aspectNames = new LinkedList<String>();
// 由于Aspect注解本身无法直接识别,所以通过这种方式获取所有的已经
// 这个地方会获取所有的bean,包含继承Object的子类,由于Asject注解,的类本身是没有类型的
// 所以这里使用Object获取所有的,调用这个方法会进行缓存
//所以没有直接调用this.beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames 这个方法
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames)
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName))
continue;
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null)
continue;
// 判断是否有Aspect注解
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType))
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON)
// 创建工厂类,这个工厂类只包含当前aspect一个beanName,为了后续生成advice使用
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 解析Aspect注解的类,获取方法上面的注解,每个增强方法都是一个切面增强
// 具体的可以看下代码细节,比较简单就是解析 Around After before这些注解
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName))
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
else
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
else
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
if (aspectNames.isEmpty())
return Collections.emptyList();
List<Advisor> advisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames)
// 单例
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null)
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
else
// 非单例的每次都需要通过工厂类生成新的对象
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
return advisors;
获取类里面的增强器
// 获取@aspect 注解类中的 advice
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory)
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
// 为了延迟初始化对象
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<Advisor>();
// 过滤掉pointCut 切面注解,
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass))
// 获取所有的注解方法, @around @before等
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null)
advisors.add(advisor);
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated())
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields())
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null)
advisors.add(advisor);
return advisors;
//
@Override
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName)
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null)
return null;
// 这里会根据注解 @around before after 生成不同的advice实现类
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
//
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName)
this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut;
this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass();
this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName();
this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes();
this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod;
this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory;
this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory;
this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder;
this.aspectName = aspectName;
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
// 这里进行advice的初始化
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
// 实例化增强器 advice
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pcut)
return this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
// 根据不同的注解,生成不同的advice实例,代理的时候调用的是这个实例
@Override
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName)
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null)
return null;
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass))
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType())
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
return null;
// around 注解,
case AtAround:
// 这里把facotyr作为参数放进去,是为了延迟获取实例化对象,等需要的时候再生成
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning()))
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing()))
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null)
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
获取符合当前bean的切面
// 匹配符合条件的切面
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
// 设置到 ThrealLocal里面,其他地方会调用这个来进行切面的匹配,从这里获取要增强的类
// 决定是否要进行增强以上是关于SpringAop 流程源码阅读的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章