图像重建基于matlab SIDER算法图像压缩重建含Matlab源码 2170期
Posted 海神之光
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了图像重建基于matlab SIDER算法图像压缩重建含Matlab源码 2170期相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、获取代码方式
获取代码方式1:
完整代码已上传我的资源:【图像重建】基于matlab SIDER算法图像压缩重建【含Matlab源码 2170期】
点击上面蓝色字体,直接付费下载,即可。
获取代码方式2:
付费专栏图像处理(Matlab)
备注:
点击上面蓝色字体付费专栏图像处理(Matlab),扫描上面二维码,付费299.9元订阅海神之光博客付费专栏,凭支付凭证,私信博主,可免费获得5份本博客上传CSDN资源代码(有效期为订阅日起,三天内有效);
点击CSDN资源下载链接:5份本博客上传CSDN资源代码
二、压缩感知图像重建算法的基本思想
压缩感知(Compressive Sensing)理论指出,对于可压缩信号能以远低于奈奎斯特的频率进行采样[8],将采样和压缩过程结合起来,然后在后期可通过高性能的计算机对信号进行精确恢复。设Φ∈RM×N(MN)为测量矩阵,考虑某未知信号x在该矩阵下的测量值y∈RN,有:

而信号的精确重构过程是由y解析生成x,由于y的维数远小于x的维数,对式(1)的求解是一个欠定过程。然而Candes等证明[9],如果原始信号x是K稀疏的,测量次数满足M=O(Klg N),且Φ满足RIP(Restricted Isometry Property)条件,就可将信号x恢复转化为l0最优范数的问题进行精确重构:
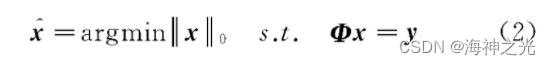
但实际工程应用中所需处理信号在其采样空间几乎都非常冗余,不能直接应用以上过程进行采样与重构,因而需要利用某种变换基Ψ对原始信号进行稀疏表示,即x=Ψf,则有:

其中,A=ΦΨ为M×N矩阵,称为感知矩阵。如果A满足RIP条件,就可以将f的稀疏性作为先验条件,通过求解类似式(2)的最优l0范数问题重构出f,进而得到原始信号x。
具体的压缩感知流程如图1所示。图像高分辨率重构是指从低分辨率图像重建生成高分辨率图像,本质上是一个从低维到高维的解析延拓过程。一般而言,直接从低分辨率图像进行图像高分辨率重构是非适定的[10]。然而在压缩感知中,由式(3)可知通过稀疏变换表示,当图像足够稀疏,即x仅需极少的f便可表示时,从少量的测量值y解算f,并由此重建高分辨率原始信号x便不再是非适定问题,因此借鉴压缩感知的思想进行图像的稀疏表示与高分辨率图像的重构研究具有重要的理论价值与实际意义。
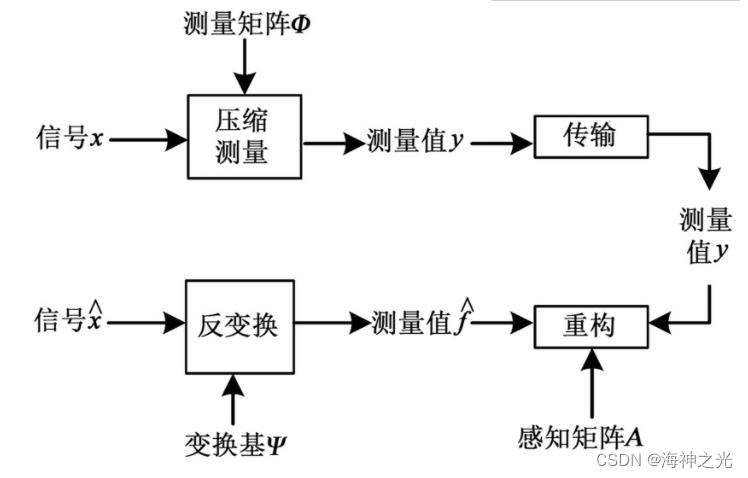
图1 压缩感知理论中信号采样与重建流程图
三、部分源代码
function [u,errAll] = SIDER(Dest,Alphaest,b,f,R,N,mu,lambda,gamma,alpha,beta,nBreg,mask,varargin)
% function [u,errAll] =
% SIDER(Dest,Alphaest,b,f,R,N,mu,lambda,gamma,alpha,beta,nBreg,mask,var
% argin)
%
% The proposed method incorporates the knowledge of the signal decay into
% the reconstruction (SIDER) to accelerate the acquisition of MR diffusion
% data by undersampling in both spatial and b-value dimensions.
%
% SIDER combines total variation (TV) with a
% penalty function that promotes sparsity across the b-direction as follows
% min_u beta|grad_x,y u|_1 + gamma|M u|_1 st. ||Fu-f||^2 < delta, where the
% first term corresponds to spatial TV and M is is an operator that encodes
% the relationship between ventilation images for consecutives values of b,
% based on a stretched exponential model.
%
% Code downloaded from repository:
% https://github.com/HGGM-LIM/compressed-sensing-diffusion-lung-MRI
%
% If you use this code, please, cite the following paper:
% JFPJ Abascal, M Desco, J Parra-Robles. Incorporation of prior knowledge
% of the signal behavior into the reconstruction to accelerate the
% acquisition of MR diffusion data,(submitted for publication) 2016.
%
% Departamento de Bioingenier韆 e Ingenier韆 Aeroespacial
% Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
% juanabascal78@gmail.com, jmparra@hggm.es, desco@hggm.es
switch nargin
case 14
uTarget = varargin1;
end % nargin
tolKrylov = 1e-2;% 1e-2 % Krylov convergence criterion
rows = N(1);
cols = N(2);
numTime = N(3);
Nf = size(f);
R = reshape(R,Nf);
f = f.*R;
% Normalize data
normFactor = getNormalizationFactor(R,f);
f = normFactorf;
uTarget = uTargetnormFactor;
% Calculate the norm of the target on the given mask
% for ip = 1:numTime
% uTargetNorm(ip) = norm(reshape(uTarget(:,:,ip),[],1));
% end
for ip = 1:numTime
tmp = uTarget(:,:,ip);
uTargetNorm(ip) = norm(tmp(mask));
end
% Signal decay operator
dm = -[exp(-( (Destb(2:end)).^Alphaest - (Destb(1:end-1)).^Alphaest )) 0]';
L = spdiags([dm ones(N(3),1)],[-1 0],N(3),N(3));
LT = L’;
LTL = LT*L;
LMat = @(x)reshape((Lreshape(x,[prod(N(1:2)),N(3)])‘)’,N);
LTMat = @(x)reshape((LTreshape(x,[prod(N(1:2)),N(3)])‘)’,N);
LTLMat = @(x)reshape((LTL*reshape(x,[prod(N(1:2)),N(3)])‘)’,N);
uBest = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
errBest = inf;
% Reserve memory for the auxillary variables
f0 = f;
v = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
u = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
x = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
y = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
bx = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
by = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
dx = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
dy = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
p = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
bp = zeros(rows,cols,numTime);
murf = mu*ifft2(f);
h = waitbar(0,‘SIDER’);
h2 = figure;
% Do the reconstruction
for outer = 1:nBreg
rhs_wt = gammau;
rhs_p = lambdaLTMat(p-bp);
rhs_tv = lambda*(Dxt(x-bx)+Dyt(y-by));
rhs = murf+rhs_wt+rhs_p+rhs_tv;
u = reshape(krylov(rhs(😃),N);
% Derivatives
dx = Dx(u);
dy = Dy(u);
dp = LMat(u);
% update x and y
[x,y] = shrink2(dx+bx, dy+by,alpha/lambda);
p = shrink1(dp+bp, beta/lambda);
% update bregman parameters
bx = bx+dx-x;
by = by+dy-y;
bp = bp+dp-p;
% Bregman iteration for the data constraint
fForw = fft2(u).*R;
f = f + f0-fForw;
murf = mu*(ifft2(f));
% for ip = 1:numTime
% % Solution error norm
% tmp = u(:,:,ip)-uTarget(:,:,ip);
% errAll(outer,ip) = norm(tmp(😃)/uTargetNorm(ip);
% end
% Solution error norm in a mask
for ip = 1:numTime
tmp = u(:,:,ip);
tmp2 = uTarget(:,:,ip);
errAll(outer,ip) = norm(tmp(mask)-tmp2(mask))/uTargetNorm(ip);
end
if nargin >= 14
if any([outer ==1, outer == 100, outer == 500, rem(outer,250)==0])
figure(h); waitbar(outer/nBreg,h);
ip = 1;
close(h2);
h2=figure;
subplot(2,2,1);
imagesc(abs(u(:,:,ip))); colorbar; title(['Iter ' num2str(outer)]);
subplot(2,2,2);
imagesc(abs(x(:,:,1))); colorbar; title(['x, nnz(x) % ' num2str(ceil(100*nnz(x(:))/prod(N)))]); colorbar;
subplot(2,2,3);
imagesc(abs(p(:,:,ip))); colorbar; title(['p, nnz(p) % ' num2str(ceil(100*nnz(p(:))/prod(N)))]); colorbar;
subplot(2,2,4); plot(errAll(1:outer,:)); axis tight; title(['Sol. error' ]);
colormap hot;
drawnow;
end % rem
end % plots
if (mean(errAll(outer,:)) <= errBest)
uBest = u;
errBest = mean(errAll(outer,:));
end %errThis
end % outer
四、运行结果
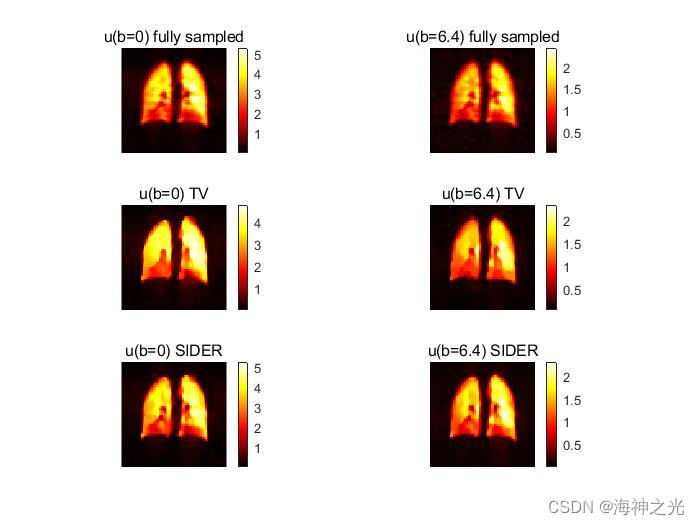
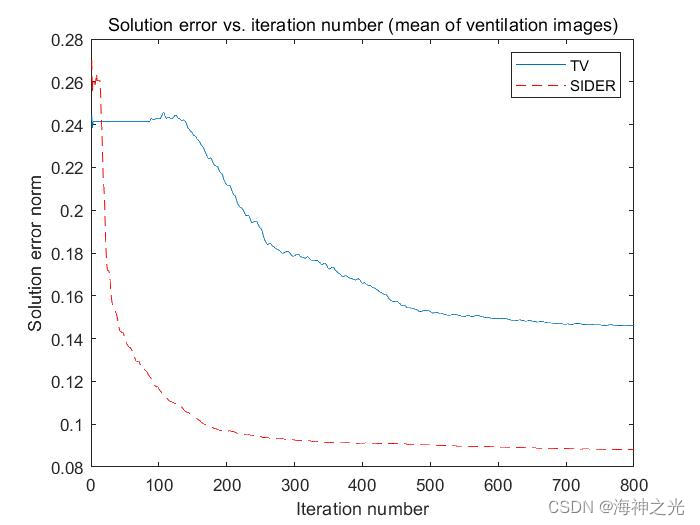

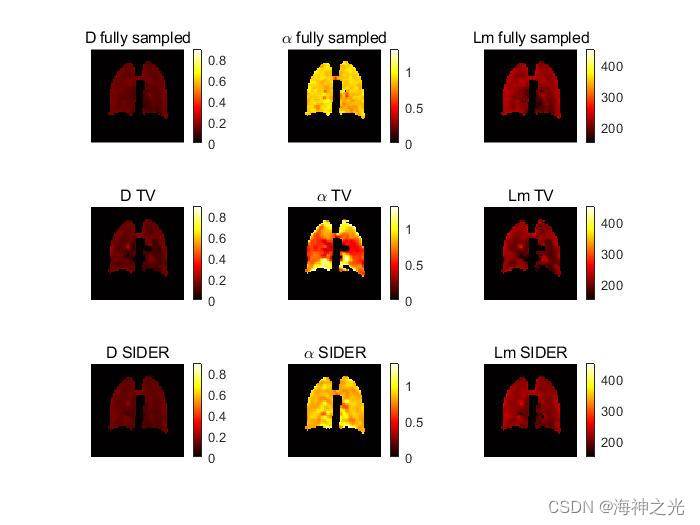
五、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 胡浩,张建林,李斌成,徐智勇.基于稀疏优化的图像压缩感知重建算法[J].半导体光电. 2021,42(02)
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除
以上是关于图像重建基于matlab SIDER算法图像压缩重建含Matlab源码 2170期的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章