关于手写实现Spring注解实现自定义配置功能
Posted 前进道路上的程序猿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于手写实现Spring注解实现自定义配置功能相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
前言
我们在使用Spring中,常常使用注解来进行配置,例如用@Controller来注解这个类为控制器类,用@Service来注解这个是Service层类,@Autowired来表示对象注入,@RequestParam来表示对象为一个参数等等,那这些功能在Spring中是怎么实现的呢,我们就手动来实现一下
配置准备
配置application.properties
我们需要在src目录下准备一个application.properties文件,并且里面写上scanPackage=com.mvcframework
配置web.xml
我们在web.xml中配置相应的servlet,并且将application.properties作为参数加入到到这servlet里
<servlet>
<servlet-name>gpmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.mvcframework.v1.servlet.GPDispatchServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>application.properties</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>gpmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
自定义注解
@GPController
GPController :
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface GPController
String value() default "";
@GPService
GPService:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface GPService
String value() default "";
@GPAutowired
GPAutowired:
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface GPAutowired
String value() default "";
@GPRequestMapping
GPRequestMapping :
@Target(ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface GPRequestMapping
String value() default "";
@GPRequestParam
GPRequestParam:
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface GPRequestParam
String value() default "";
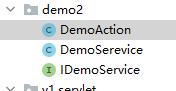
应用代码
应用的代码如下
DemoAction :
@GPController
@GPRequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoAction
@GPAutowired
private IDemoService demoService;
@GPRequestMapping("/query")
public void query(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, @GPRequestParam("name") String name)
String result = demoService.get(name);
try
resp.getWriter().write(result);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
@GPService
public class DemoSerevice implements IDemoService
public String get(String name)
return "My name is "+name;
public interface IDemoService
public String get(String name);
这些代码中DemoAction 使用@GPController定义其为GPController,然后注解@GPRequestMapping("/demo")定义其类路径,里面有一个IDemoService 属性使用@GPAutowired进行注解,一个方法query使用@GPRequestMapping("/query")定义其方法路径,方法中参数name使用@GPRequestParam(“name”)定义其参数
DemoSerevice 类使用@GPService定义其为GPService,同时实现IDemoService接口
容器初始化
接下来我们就要设计实现Spring注解访问资源的核心功能,这里我们就需要用到容器
在最早没有Spring的时候,我们实现MVC的时候,一般是通过从web.xml配置中,进入到相应的servlet,这里实现的功能核心就是在servlet的init方法里实现的
主要步骤包括:
1、加载配置文件
2、扫描相关的类
3、初始化扫描到的类,并且将它们放入容器中
4、完成依赖注入
5、初始化HandlerMapping,实现url与访问方法的匹配
然后就是在访问的时候根据url从HandlerMapping中获取相应的方法并执行
话不多说,我们用代码来看看
声明全局变量
首先我们在Servlet开头定义各种变量
//保存application.properties配置文件的内容
private Properties contextConfig= new Properties();
//保存扫描的所有类名
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<>();
//ioc容器,用于保存扫描到的类
private Map<String,Object> ioc = new HashMap<String,Object>();
//保存url和Method的对应关系
private Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<String,Method>();
init中定义调用方法的步骤
这里使用到了模板方法模式,定义了初始化时各种方法的使用步骤
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException
//1.加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
//2、扫描相关的类
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//初始化扫描到的类,并存入Ioc容器
doInstance();
//依赖注入
doAutowired();
//初始化HandlerMapping,实现url与访问方法的匹配
initHandlerMapping();
下面我们一步一步完成每个相关方法
加载配置文件
private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation)
InputStream fis = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation);
try
contextConfig.load(fis);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
if(null != fis)
try
fis.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
这个方法中,我们我们将配置的application.properties内容加载进contextConfig变量
扫描相关的类
private void doScanner(String scanPackage)
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/"+scanPackage.replaceAll("\\\\.","/"));
File classPath = new File(url.getFile());
for(File file:classPath.listFiles())
if(file.isDirectory())
doScanner(scanPackage+"."+file.getName());
else
if(!file.getName().endsWith(".class")) continue;
String className = (scanPackage+"."+file.getName().replace(".class",""));
classNames.add(className);
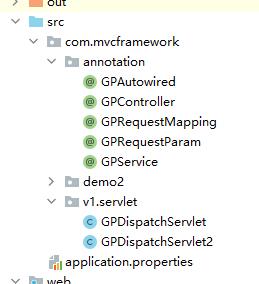
这个类中,通过递归不断的将application.properties中配置的路径下的类路径扫描入classNames中
初始化扫描到的类,并存入Ioc容器
private void doInstance()
if(classNames.isEmpty()) return;
try
for(String className:classNames)
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(GPController.class))
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
String beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
ioc.put(beanName,instance);
else if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(GPService.class))
GPService service = clazz.getAnnotation(GPService.class);
String beanName = service.value();
if("".equals(beanName.trim()))
beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName,instance);
for(Class<?> i:clazz.getInterfaces())
if(ioc.containsKey(i.getName()))
throw new Exception("The “"+ i.getName() +"” is exists!! ");
ioc.put(i.getName(),instance);
else
continue;
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
在这里面判断注释类型使用了isAnnotationPresent,这是一个很重要的方法
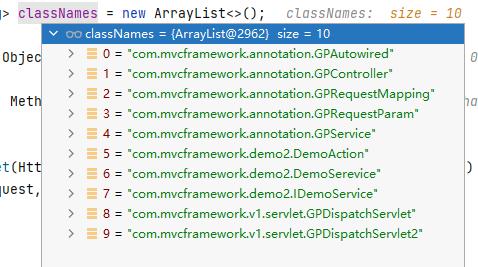
这个方法中,通过不断循环classNames中的类名,然后根据其类的相应注释来进行判断,从而使用反射来生成相应的对象,并且里面判断其注释类型,如果为GPController则存放到Ioc里的key使用类名首字母小写;如果为GPService则判断有没有写value,没有则使用类名首字母小写作为key,并且,Service的接口类也要存放,其key为接口类路径
执行这个方法后,ioc容器内情况如下:
类名首字母小写方法:
private String toLowerFirstCase(String simpleName)
char[] chars = simpleName.toCharArray();
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
依赖注入
private void doAutowired()
if(ioc.isEmpty()) return;
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> entry:ioc.entrySet())
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field:fields)
if(!field.isAnnotationPresent(GPAutowired.class))continue;
GPAutowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(GPAutowired.class);
String beanName = autowired.value().trim();
if("".equals(beanName))
beanName = field.getType().getName();
field.setAccessible(true);
try
field.set(entry.getValue(),ioc.get(beanName));//TODO
catch (IllegalAccessException e)
e.printStackTrace();
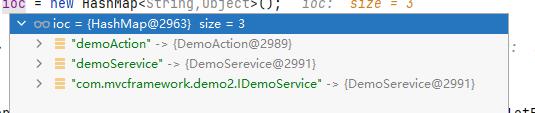
在这个方法中,我们会轮行取出ioc容器中的对象,然后轮训对象中的属性,如果属性以GPAutowired注释,则利用其备注的Value或者类型名称去ioc容器里查找对应的对象注入该属性中
执行完这个方法后,ioc容器状态如下
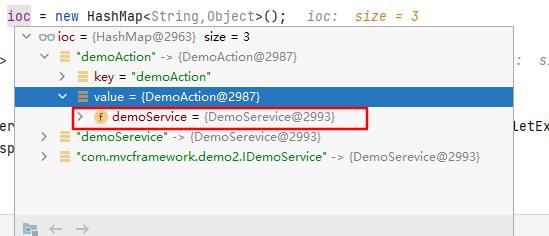
初始化HandlerMapping
private void initHandlerMapping()
if(ioc.isEmpty())
return;
for(Map.Entry<String,Object> entry:ioc.entrySet())
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
if(!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(GPController.class))
continue;
String baseUrl = "";
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(GPRequestMapping.class))
GPRequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(GPRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = requestMapping.value();
for (Method method:clazz.getMethods())
if(!method.isAnnotationPresent(GPRequestMapping.class))continue;
GPRequestMapping requestMapping = method.getAnnotation(GPRequestMapping.class);
String url = ("/"+baseUrl+"/"+requestMapping.value()).replaceAll("/+","/");
handlerMapping.put(url,method);
System.out.println("Mapped :"+url+","+method);
在这个方法中,我们从ioc容器中拿出GPController修饰的对象,然后其类上注释的GPRequestMapping路径叠加方法上叠加的GPRequestMapping路径,然后生成url作为key,method作为value存放到handlerMapping中
执行完这个方法handlerMapping状态如下:
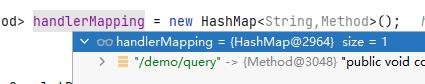
访问时调用
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
this.doPost(request,response);
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
try
doDispatch(request,response);
catch (Exception e)
response.getWriter().write("500 Exception "+ Arrays.toString(e.getStackTrace()));
我们在servlet中定义doGet和doPost如上面,然后doPost里调用doDispatch,
doDispatch方法如下
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception
String url = request.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = request.getContextPath