RecyclerView的好朋友 — SnapHelpter
Posted Ever69
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了RecyclerView的好朋友 — SnapHelpter相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SnapHelpter,相信很多人可能都不知道它或者没怎么关注过它,但是通过它实现的效果肯定都见过。比如短视频应用中切换视频时一划划一页的效果,这可不是ViewPager实现的啊,使用ViewPager实现的话成本太高,所以这类效果都是通过RecyclerVIew + SnapHelper来实现的,拿刚才讲的短视频切换效果来说,使用的就是RecyclerVIew和SnapHelper的子类PagerSnapHelper来实现的。
目录
一、SnapHelper初解
说了这些,那么SnapHelper到底是什么东西呢?见名思意,Snap,翻译成中文有‘移到某位置’的意思,那么SnapHelper可以理解为‘移到某位置的帮手’,而这个被移到某位置的东西显然就是RecyclerVIew中的Item。
public abstract class SnapHelper extends RecyclerView.OnFlingListener
//....
@Nullable
public abstract int[] calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(@NonNull LayoutManager layoutManager,
@NonNull View targetView);
@Nullable
public abstract View findSnapView(LayoutManager layoutManager);
public abstract int findTargetSnapPosition(LayoutManager layoutManager, int velocityX,int velocityY);
可以看到SnapHelper是一个抽象类,并继承了RecyclerView.OnFlingListener这个类,其中还包括三个抽象方法,我们通过实现这三个方法,就可以帮助RecyclerView移动item到‘某位置’。
为了更好理解SnapHelper的这三个方法,先说说RecyclerView.OnFlingListener这个类。
public abstract static class OnFlingListener
/**
* 可用于实现自定义投掷行为
*
* @param velocityX X轴上的抛掷速度
* @param velocityY Y轴上的抛掷速度
*
* @return 如果处理了投掷,则为 true,否则为 false。
*/
public abstract boolean onFling(int velocityX, int velocityY);
这也是个抽象类,并且里面只有一个抽象方法,那这个类又是干啥的呢?我们都知道RecyclerView是可以滑动的,在我们手指离开屏幕后,RecyclerView还会继续顺着我们手指的方向再滑动一段距离,这个操作就是通过实现OnFlingListener接口来做到的。
SnapHelper继承了OnFlingListener实现了onFling方法,并在调用attachToRecyclerView()方法的时候将OnFlingListener设置给了RecyclerView。
public void attachToRecyclerView(@Nullable RecyclerView recyclerView)
throws IllegalStateException
if (mRecyclerView == recyclerView)
return; // nothing to do
if (mRecyclerView != null)
destroyCallbacks();
mRecyclerView = recyclerView;
if (mRecyclerView != null)
setupCallbacks();
mGravityScroller = new Scroller(mRecyclerView.getContext(),
new DecelerateInterpolator());
snapToTargetExistingView();
/**
* Called when an instance of a @link RecyclerView is attached.
*/
private void setupCallbacks() throws IllegalStateException
if (mRecyclerView.getOnFlingListener() != null)
throw new IllegalStateException("An instance of OnFlingListener already set.");
mRecyclerView.addOnScrollListener(mScrollListener);
mRecyclerView.setOnFlingListener(this);
二、三个方法
接着我们继续看SnapHelper中的三个抽象方法。
1、calculateDistanceToFinalSnap()
/**
* 计算将目标item移动到最终位置所需距离
*
* @param layoutManager
* @param targetView 需要被移动的item
*
* @return 输出坐标将结果,out[0] 是水平轴上的距离,out[1] 是垂直轴上的距离。
*/
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
@Nullable
public abstract int[] calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(@NonNull LayoutManager layoutManager,
@NonNull View targetView);public abstract int[] calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(@NonNull RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager,@NonNull View targetView);
这个方法是SnapHelper中另外两个抽象方法findSnapView()和findTargetSnapPosition()的下游方法,其参数中的targetView就是这两个方法提供的
通过findSnapView()提供
void snapToTargetExistingView()
/***/
View snapView = findSnapView(layoutManager);
if (snapView == null)
return;
int[] snapDistance = calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(layoutManager, snapView);
if (snapDistance[0] != 0 || snapDistance[1] != 0)
mRecyclerView.smoothScrollBy(snapDistance[0], snapDistance[1]);
通过findTargetSnapPosition()提供
private boolean snapFromFling(@NonNull RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, int velocityX,
int velocityY)
/**/
RecyclerView.SmoothScroller smoothScroller = createScroller(layoutManager);
if (smoothScroller == null)
return false;
int targetPosition = findTargetSnapPosition(layoutManager, velocityX, velocityY);
if (targetPosition == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION)
return false;
smoothScroller.setTargetPosition(targetPosition);
layoutManager.startSmoothScroll(smoothScroller);
return true;
findTargetSnapPosition()被调用后,将找到的位置设置给smoothScroller,然后再通过layoutManager调用startSmoothScroll()方法启动smoothScroller
public void startSmoothScroll(SmoothScroller smoothScroller)
if (mSmoothScroller != null && smoothScroller != mSmoothScroller
&& mSmoothScroller.isRunning())
mSmoothScroller.stop();
mSmoothScroller = smoothScroller;
mSmoothScroller.start(mRecyclerView, this);
在smoothScroller的start()方法中找到targetView
void start(RecyclerView recyclerView, LayoutManager layoutManager)
/***/
mTargetView = findViewByPosition(getTargetPosition());
onStart();
mRecyclerView.mViewFlinger.postOnAnimation();
mStarted = true;
最后回调到SnapHelper中创建的SmoothScroller中的onTargetFound()方法
@Nullable
@Deprecated
protected LinearSmoothScroller createSnapScroller(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager)
/***/
return new LinearSmoothScroller(mRecyclerView.getContext())
@Override
protected void onTargetFound(View targetView, RecyclerView.State state, Action action)
/***/
int[] snapDistances = calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(mRecyclerView.getLayoutManager(),
targetView);
final int dx = snapDistances[0];
final int dy = snapDistances[1];
final int time = calculateTimeForDeceleration(Math.max(Math.abs(dx), Math.abs(dy)));
if (time > 0)
action.update(dx, dy, time, mDecelerateInterpolator);
@Override
protected float calculateSpeedPerPixel(DisplayMetrics displayMetrics)
return MILLISECONDS_PER_INCH / displayMetrics.densityDpi;
;
2、findSnapView()
/**
* 找到需要被移动的item.
* 如果返回 @code null, 则SnapHelper 不需要移动任何item.
*
* @param layoutManager
*
* @return 需要被移动的item
*/
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
@Nullable
public abstract View findSnapView(LayoutManager layoutManager);
这个方法会在SnapHelper绑定到RecyclerView时和RecyclerView停止滑动时被调用
void snapToTargetExistingView()
/***/
View snapView = findSnapView(layoutManager);
/***/
//绑定RecyclerView时被调用
public void attachToRecyclerView(@Nullable RecyclerView recyclerView)
throws IllegalStateException
/***/
if (mRecyclerView != null)
/***/
snapToTargetExistingView();
//RecyclerView停止滑到时被调用
private final RecyclerView.OnScrollListener mScrollListener =
new RecyclerView.OnScrollListener()
boolean mScrolled = false;
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(RecyclerView recyclerView, int newState)
super.onScrollStateChanged(recyclerView, newState);
if (newState == RecyclerView.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE && mScrolled)
mScrolled = false;
snapToTargetExistingView();
@Override
public void onScrolled(RecyclerView recyclerView, int dx, int dy)
/***/
;
3、findTargetSnapPosition()
/**
* 找到需要被移动的目标item在adapter中的位置
*
* @param layoutManager
* @param 水平轴上的抛掷速度
* @param 纵轴上的抛掷速度
*
* @return 返回需要被移动的目标item在adapter中的位置或者无需移动时返回 @link RecyclerView#NO_POSITION
*/
public abstract int findTargetSnapPosition(LayoutManager layoutManager, int velocityX,int velocityY);
这个方法会在RecyclerView触发fling操作时被调用
private boolean snapFromFling(@NonNull RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, int velocityX,
int velocityY)
/***/
int targetPosition = findTargetSnapPosition(layoutManager, velocityX, velocityY);
if (targetPosition == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION)
return false;
smoothScroller.setTargetPosition(targetPosition);
layoutManager.startSmoothScroll(smoothScroller);
return true;
@Override
public boolean onFling(int velocityX, int velocityY)
/***/
return (Math.abs(velocityY) > minFlingVelocity || Math.abs(velocityX) > minFlingVelocity)
&& snapFromFling(layoutManager, velocityX, velocityY);
三、自定义SnapHelper实战
了解了SnapHelper三个方法的作用以及何时会调用后,我们趁热打铁,自己实现一个SnapHelper,如果想更多了解关于SnapHelper的实现,可以去看看官方实现的LinearSnapHelper和PagerSnapHelper。
这次我们继承SnapHelper,实现对RecyclerView一滑滑一页的效果,类似官方的PagerSnapHelper,但是比它更灵活,因为它的一页是一条item,我们的一页可以是多个item。
其实这次要实现的效果在很多App中都能看到,尤其是应用商城类的App。
光说还是有点懵,先看看实现的最终效果吧~
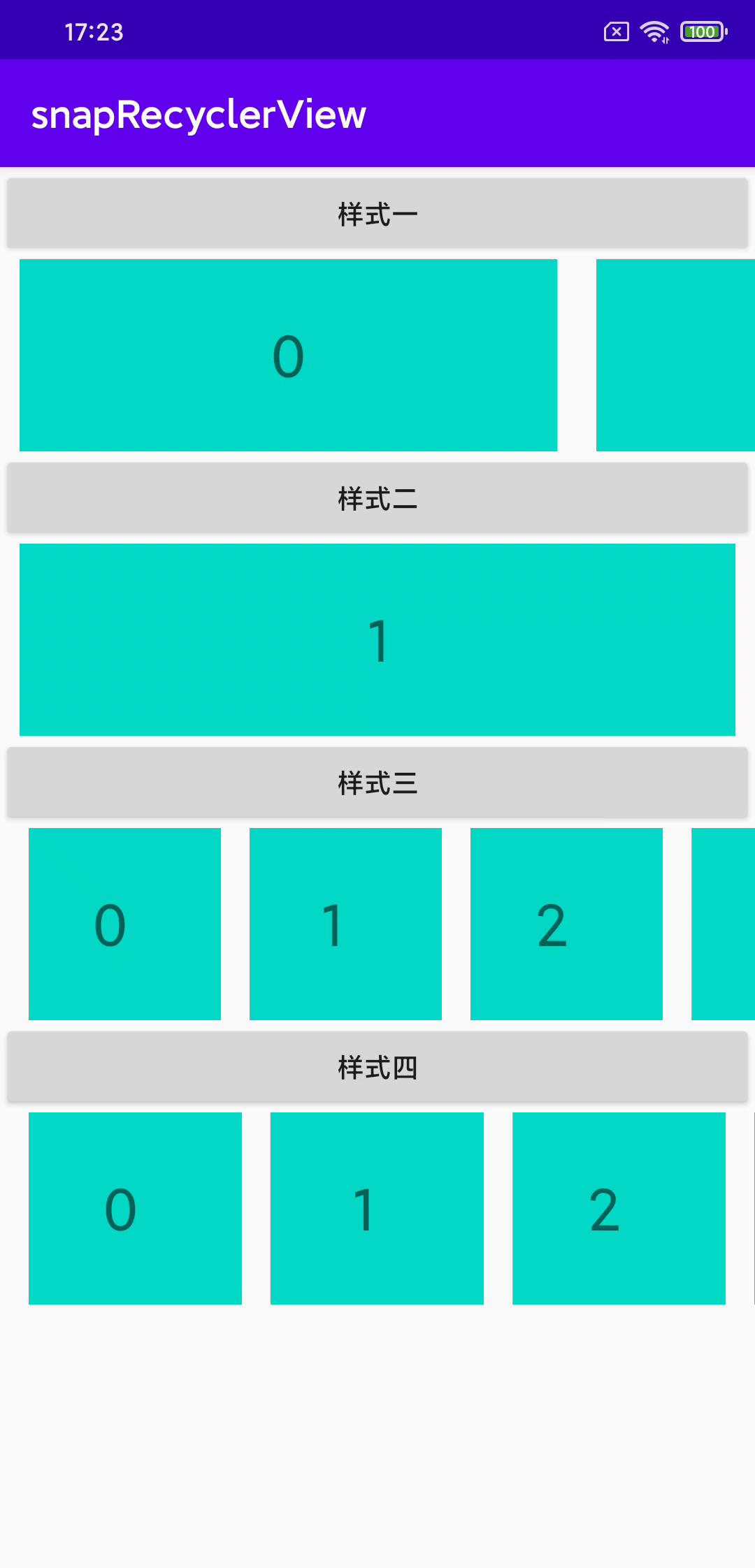
public class MyGallerySnapHelper extends SnapHelper
protected RecyclerView mRecyclerView;
@Nullable
private OrientationHelper mHorizontalHelper;
private int pageSize;
@Override
public void attachToRecyclerView(@Nullable RecyclerView recyclerView) throws IllegalStateException
mRecyclerView = recyclerView;
super.attachToRecyclerView(recyclerView);
@Nullable
@Override
public int[] calculateDistanceToFinalSnap(@NonNull RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, @NonNull View view)
int[] out = new int[2];
//RecyclerView为横向方向时
if (layoutManager.canScrollHorizontally())
out[0] = distance2Start(layoutManager, view,
getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager));
return out;
private int distance2Start(@NonNull RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, @NonNull View targetView, OrientationHelper helper)
//获取item的宽度
int columnWidth = helper.getDecoratedMeasurement(targetView);
//获取item的下标
int position = layoutManager.getPosition(targetView);
//计算RecyclerView一屏可以展示多少item
pageSize = (mRecyclerView.getWidth() - mRecyclerView.getPaddingStart() - mRecyclerView.getPaddingEnd()) / getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager).getDecoratedMeasurement(targetView);
//计算item处于第几屏
int pageIndex = position / pageSize;
//计算上一步所得屏数中第一个item的下标
int currentPageStart = pageIndex * pageSize;
//计算传入item和它所属屏数第一个item的距离
int distance = ((position - currentPageStart)) * columnWidth;
//获取传入item的顶部在RecyclerView中的位置(像素)
final int childStart = helper.getDecoratedStart(targetView);
return childStart - distance;
@Nullable
@Override
public View findSnapView(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager)
return findStartView(layoutManager, getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager));
private View findStartView(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, OrientationHelper helper)
int childCount = layoutManager.getChildCount();
if (childCount == 0) return null;
int lastPosition = 0;
//获取最后一个完整可见item的下标
if (layoutManager instanceof LinearLayoutManager)
lastPosition = ((LinearLayoutManager) layoutManager).findLastCompletelyVisibleItemPosition();
int absClosest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
View snapView = null;
//如最后一个完整可见item的下标等于列表最后一个item的下标
if (lastPosition == layoutManager.getItemCount() - 1)
snapView = layoutManager.getChildAt(lastPosition);
else
//找到距离RecyclerView顶部最近的item
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++)
View child = layoutManager.getChildAt(i);
int absDistance = helper.getDecoratedStart(child);
if (absDistance < absClosest)
absClosest = absDistance;
snapView = child;
return snapView;
@Override
public int findTargetSnapPosition(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager, int velocityX, int velocityY)
//找到距离RecyclerView顶部最近的item
View snapView = findSnapView(layoutManager);
if (snapView == null) return RecyclerView.NO_POSITION;
//得到距离RecyclerView顶部最近的item的下标
int startMostPosition = layoutManager.getPosition(snapView);
if (startMostPosition == RecyclerView.NO_POSITION) return RecyclerView.NO_POSITION;
//滑动方向,ture为正方向滑动 false为反方向滑动
final boolean forwardDirection;
if (layoutManager.canScrollHorizontally())
forwardDirection = velocityX > 0;
else
forwardDirection = velocityY > 0;
View childAt = layoutManager.getChildAt(0);
//计算RecyclerView一屏可以展示多少item
if (childAt != null)
pageSize = (mRecyclerView.getWidth() - mRecyclerView.getPaddingStart() - mRecyclerView.getPaddingEnd()) / getHorizontalHelper(layoutManager).getDecoratedMeasurement(childAt);
//计算item处于第几屏
int pageIndex = startMostPosition / pageSize;
//计算上一步所得屏数中第一个item的下标
int currentPageStart = pageIndex * pageSize;
//根据滑动方向,在当前屏首的下标上加减数量
return forwardDirection ? Math.min(currentPageStart + pageSize, layoutManager.getItemCount() - 1) : Math.max(0, currentPageStart + pageSize - 1);
@Nullable
@Override
protected RecyclerView.SmoothScroller createScroller(RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager)
return !(layoutManager instanceof RecyclerView.SmoothScroller.ScrollVectorProvider) ? null : new LinearSmoothScroller(this.mRecyclerView.getContext())
protected void onTargetFound(View targetView, RecyclerView.State state, RecyclerView.SmoothScroller<以上是关于RecyclerView的好朋友 — SnapHelpter的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章