[OC学习笔记]分类和关联对象源码解析
Posted Billy Miracle
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[OC学习笔记]分类和关联对象源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我们平时在开发的时候经常会使用分类来添加方法、协议、属性,但在添加属性的时候属性是不会自动生成成员变量的,这时候我们就需要关联对象来动态存储属性值。
分类
@interface NSObject(Study)
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSObject *obj1;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSObject *obj2;
- (void)instanceMethod;
+ (void)classMethod;
@end
static const void *NSObjectObj1Name = "NSOBJECT_OBJ1";
@implementation NSObject(Study)
@dynamic obj2;
- (void)setObj1:(NSObject *)obj1
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &NSObjectObj1Name, obj1, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN);
- (NSObject *)obj1
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &NSObjectObj1Name);
- (void)instanceMethod
NSLog(@"-类名:%@,方法名:%s,行数:%d",NSStringFromClass(self.class), __func__, __LINE__);
+ (void)classMethod
NSLog(@"+类名:%@,方法名:%s,行数:%d",NSStringFromClass(self.class), __func__, __LINE__);
@end
我们将上面的代码重写成c++代码,我们看一看关键部分:
static struct _category_t _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_NSObject_$_Study __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) =
"NSObject",
0, // &OBJC_CLASS_$_NSObject,
(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_INSTANCE_METHODS_NSObject_$_Study,
(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_CLASS_METHODS_NSObject_$_Study,
0,
(const struct _prop_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_PROP_LIST_NSObject_$_Study,
;
可以看到其根本的实现是_category_t这个结构,那么我们可以在objc源码来查找关于category_t的定义:
struct category_t
const char *name;
classref_t cls;
WrappedPtr<method_list_t, method_list_t::Ptrauth> instanceMethods;
WrappedPtr<method_list_t, method_list_t::Ptrauth> classMethods;
struct protocol_list_t *protocols;
struct property_list_t *instanceProperties;
// Fields below this point are not always present on disk.
struct property_list_t *_classProperties;
method_list_t *methodsForMeta(bool isMeta)
if (isMeta) return classMethods;
else return instanceMethods;
property_list_t *propertiesForMeta(bool isMeta, struct header_info *hi);
protocol_list_t *protocolsForMeta(bool isMeta)
if (isMeta) return nullptr;
else return protocols;
;
根据category_t源码,我们可以总结:
- 分类里面即有实例方法列表又有类方法列表
- 分类没有成员变量列表
分类的加载
分类的加载是在objc中实现的。 在源码attachCategories的实现中:
// Attach method lists and properties and protocols from categories to a class.
// Assumes the categories in cats are all loaded and sorted by load order,
// oldest categories first.
static void
attachCategories(Class cls, const locstamped_category_t *cats_list, uint32_t cats_count,
int flags)
...
bool fromBundle = NO;
bool isMeta = (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS);
//新建rwe
auto rwe = cls->data()->extAllocIfNeeded();
//debug代码可以放这里
//遍历每个分类
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cats_count; i++)
auto& entry = cats_list[i];
//获取分类里面的方法
method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);
if (mlist)
if (mcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ)
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle, __func__);
rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);
mcount = 0;
mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++mcount] = mlist;
fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle();
...
if (mcount > 0)
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount,
NO, fromBundle, __func__);
//添加分类的方法到rwe中
rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount);
if (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING)
flushCaches(cls, __func__, [](Class c)
// constant caches have been dealt with in prepareMethodLists
// if the class still is constant here, it's fine to keep
return !c->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache();
);
rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - propcount, propcount);
rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - protocount, protocount);
我们在这个函数里加上:
//调试新增
const char *mangledName = cls->nonlazyMangledName();
//你添加分类的类名
const char *className = "MyObject";
if (strcmp(mangledName, className) == 0 && !isMeta)
printf("debug find it\\n");
打上断点,注意:分类和本类都需要实现+load方法才可以。我们看堆栈信息:
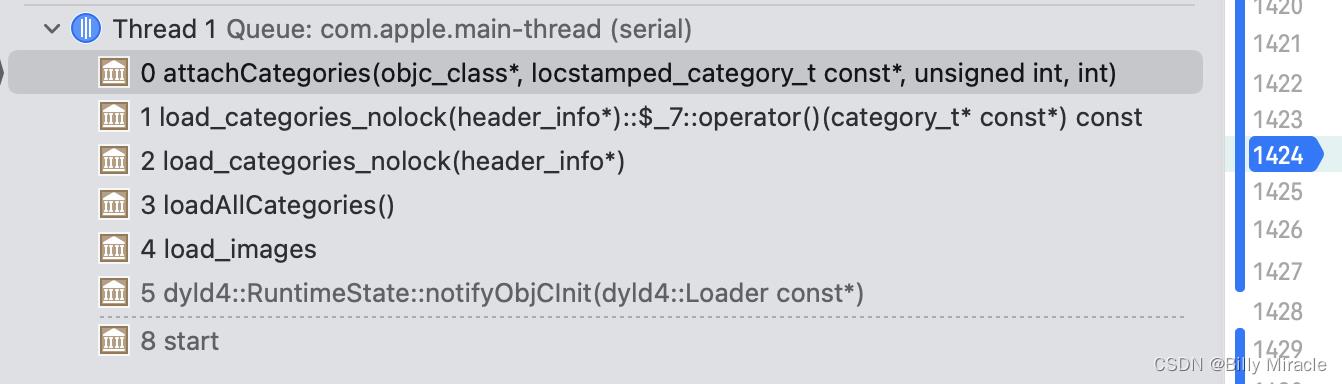
可以看到是load_images中调用的。前面的文章已经讲解过load_images的调用时机。在里面也可以最终找到attachCategories的调用时机(当然,这只是一种情况,还有一种情况是在realizeClassWithoutSwift最后的methodizeClass调用):
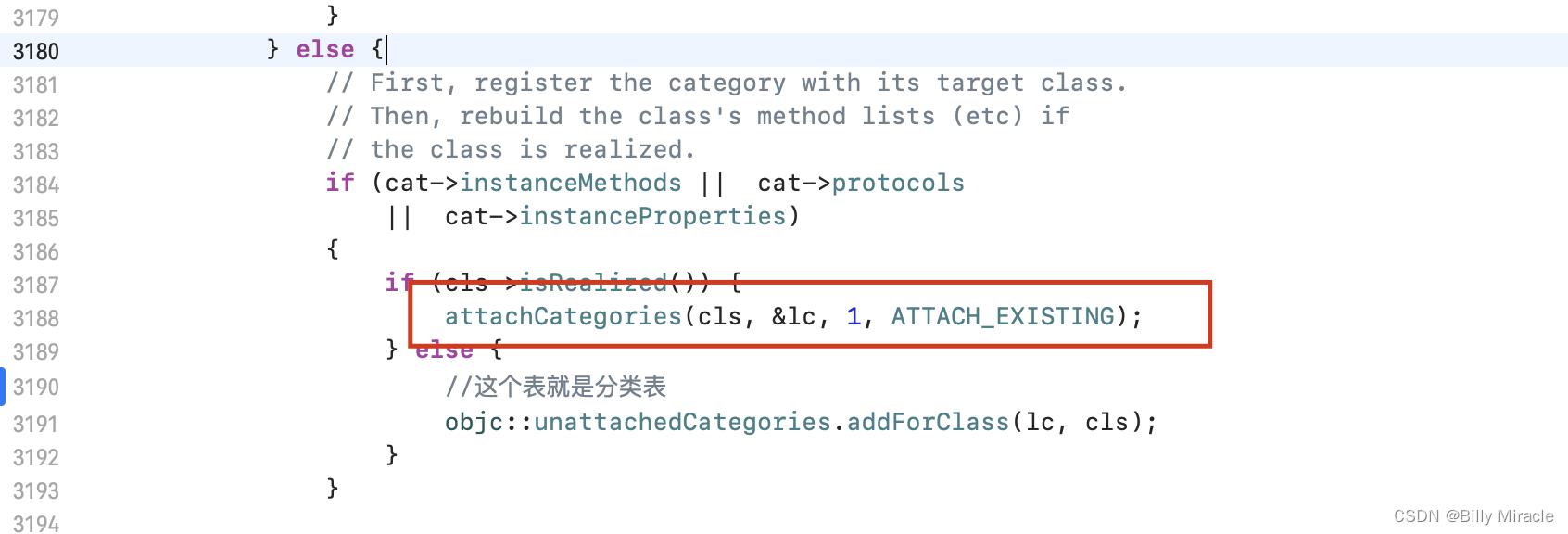
接下来我们通过lldb来调试。

在这里,我获得的方法列表里面方法数为0。越过断点,使用count()获取:

现在数量为3。因为我们写了三个实例方法,所以数量是3。
关联对象
回到我们一开始的代码,还有一个关联对象。我们先在objc源码中找到关联对象api的实现部分:
void
objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
_object_set_associative_reference(object, key, value, policy);
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object)
if (object && object->hasAssociatedObjects())
_object_remove_assocations(object, /*deallocating*/false);
objc_setAssociatedObject
可以看到是调用了内部函数_object_set_associative_reference,解析注解如下:
void
_object_set_associative_reference(id object, const void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy)
// This code used to work when nil was passed for object and key. Some code
// probably relies on that to not crash. Check and handle it explicitly.
// rdar://problem/44094390
if (!object && !value) return;
//isa有一位信息为禁止关联对象,如果设置了,直接报错
if (object->getIsa()->forbidsAssociatedObjects())
_objc_fatal("objc_setAssociatedObject called on instance (%p) of class %s which does not allow associated objects", object, object_getClassName(object));
//包装对象,转换类型
DisguisedPtr<objc_object> disguised(objc_object *)object;
//包装值和属性信息
ObjcAssociation associationpolicy, value;
// retain the new value (if any) outside the lock.
//设置属性信息
association.acquireValue();
bool isFirstAssociation = false;
//调用构造函数,构造函数内加锁操作
AssociationsManager manager;
//获取全局的HasMap
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get());
//如果值不为空
if (value)
//去关联对象表中找对象对应的二级表,如果没有内部会重新生成一个⚠️
auto refs_result = associations.try_emplace(disguised, ObjectAssociationMap);
//如果没有找到
if (refs_result.second)
/* it's the first association we make */
//说明是第一次设置关联对象,把是否关联对象设置为YES
isFirstAssociation = true;
/* establish or replace the association */
auto &refs = refs_result.first->second;
//在二级表中找key对应的内容,
auto result = refs.try_emplace(key, std::move(association));
//如果已经有内容了,没有内容上面根据association已经插入了值,所以啥也不用干
if (!result.second)
//替换掉
association.swap(result.first->second);
//如果value为空
else
//通过object找对应的二级表
auto refs_it = associations.find(disguised);
// 如果有
if (refs_it != associations.end())
auto &refs = refs_it->second;
//通过key再在二级表里面找对应的内容
auto it = refs.find(key);
//如果有
if (it != refs.end())
//删除掉
association.swap(it->second);
refs.erase(it);
if (refs.size() == 0)
associations.erase(refs_it);
// Call setHasAssociatedObjects outside the lock, since this
// will call the object's _noteAssociatedObjects method if it
// has one, and this may trigger +initialize which might do
// arbitrary stuff, including setting more associated objects.
// 第一次时候标记对象是否有关联对象
if (isFirstAssociation)
object->setHasAssociatedObjects();
// release the old value (outside of the lock).
// 释放
association.releaseHeldValue();
方法需要传入四个参数:
| 参数名称 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| id object | 需要关联的对象 |
| void *key | 对应的key |
| id value | 对应的值 |
| objc_AssociationPolicy policy | 内存管理策略 |
AssociationsManager
是一个构造函数,内部构造函数AssociationsManager()和析构函数~AssociationsManager()进行了加锁和解锁(不是单例)。 构造函数中加锁只是为了避免重复创建,在这里是可以初始化多个AssociationsManager变量。
// class AssociationsManager manages a lock / hash table singleton pair.
// Allocating an instance acquires the lock
// 类关联管理器管理锁/哈希表单例对。
// 分配实例获取锁
class AssociationsManager
using Storage = ExplicitInitDenseMap<DisguisedPtr<objc_object>, ObjectAssociationMap>;
static Storage _mapStorage;
public:
AssociationsManager() AssociationsManagerLock.lock();
~AssociationsManager() AssociationsManagerLock.unlock();
AssociationsHashMap &get()
return _mapStorage.get();
static void init()
_mapStorage.init();
;
通过观察代码和注释可以看出:其通过AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.get());获取的关联表是全局唯一的,_mapStorage是全局静态变量,获取的AssociationsHashMap是全局唯一的。
接下来,我们需要注意try_emplace这个方法。
try_emplace
当value有的情况下 try_emplace 会走2次。
- 第一次参数传入:
DisguisedPtr<objc_object> disguised(objc_object *)object闭包 - 第二次参数传入:
key, objc_setAssociatedObject(key为传进来的第二个参数:自定义的key)
// Inserts key,value pair into the map if the key isn't already in the map.
// The value is constructed in-place if the key is not in the map, otherwise
// it is not moved.
// 如果key不在map中,插入key,value进map
// 如果key不在map中,则会在适当的位置构造该value,否则不会移动该value
template <typename... Ts>
std::pair<iterator, bool> try_emplace(const KeyT &Key, Ts &&... Args)
// 创建BucketT通知
BucketT *TheBucket;
// 通过LookupBucketFor方法查询TheBucket值情况,要么有值走下面
if (LookupBucketFor(Key, TheBucket))
return std::make_pair(
makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true),
false); // Already in map.已经有值
// Otherwise, insert the new element.
// 没有值,给TheBucket插入新值
TheBucket = InsertIntoBucket(TheBucket, Key, std::forward<Ts>(Args)...);
return std::make_pair(
makeIterator(TheBucket, getBucketsEnd(), true),
true);
这里返回的是一个迭代器,如果有内容返回对应的迭代器,如果没有的话,添加一个,并返回迭代器。使用了两次try_emplace方法,可以得知他是嵌套两层的HashMap结构,根据代码的理解,可以得到以下结构图:
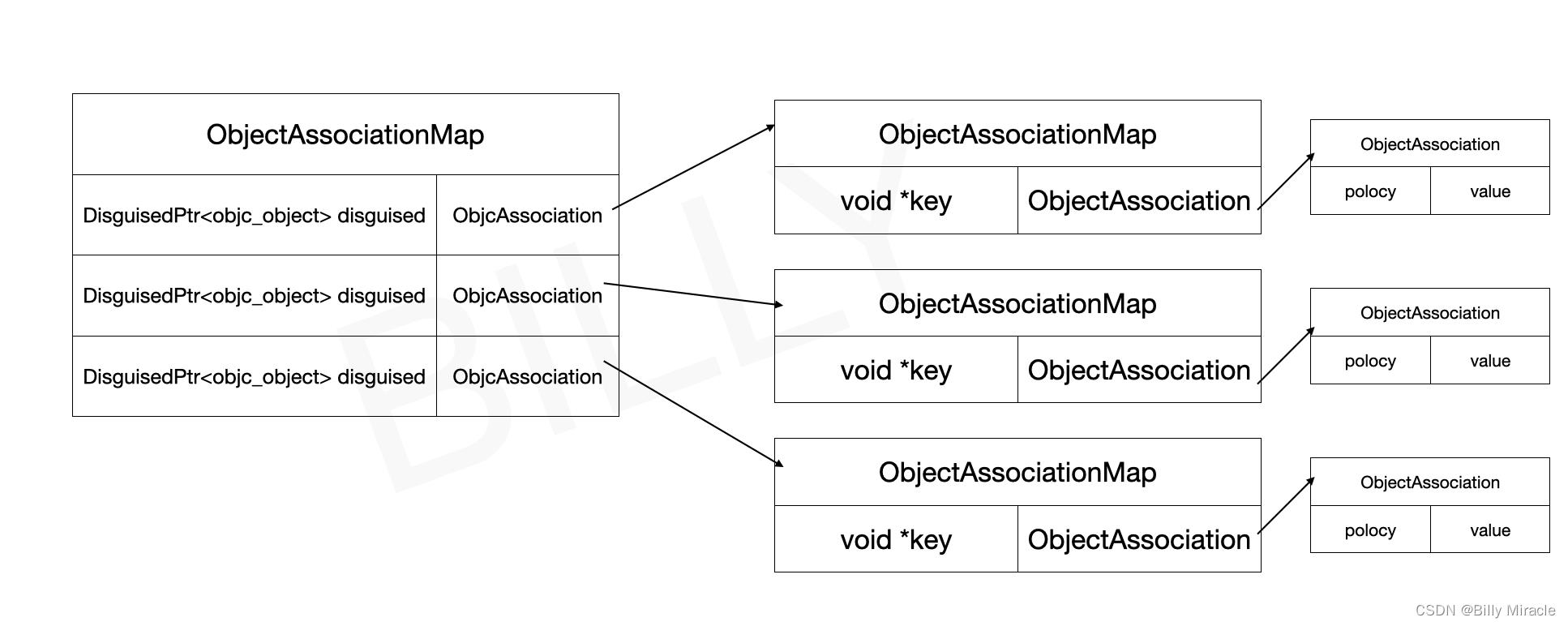
LookupBucketFor
/// LookupBucketFor - Lookup the appropriate bucket for Val, returning it in
/// FoundBucket. If the bucket contains the key and a value, this returns
/// true, otherwise it returns a bucket with an empty marker or tombstone and
/// returns false.
/// 查找 Val 的相应存储桶,将其返回到 FoundBucket 中。
/// 如果存储桶包含键和值,则返回 true,否则返回带有空标记或逻辑删除的存储桶并返回 false。
template<typename LookupKeyT>
bool LookupBucketFor(const LookupKeyT &Val,
const BucketT *&FoundBucket) const
// 获取buckets的首地址
const BucketT *BucketsPtr = getBuckets();
// 获取可存储的buckets的总数
const unsigned NumBuckets = getNumBuckets();
// 如果NumBuckets = 0 返回 false
if (NumBuckets == 0)
FoundBucket = nullptr;
return false;
// FoundTombstone - Keep track of whether we find a tombstone while probing.
// 在探查的时候留意我们是否找到了tombstone
const BucketT *FoundTombstone = nullptr;
const KeyT EmptyKey = getEmptyKey();
const KeyT TombstoneKey = getTombstoneKey();
assert(!KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, EmptyKey) &&
!KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, TombstoneKey) &&
"Empty/Tombstone value shouldn't be inserted into map!");
// 计算bucket的hash下标
unsigned BucketNo = getHashValue(Val) & (NumBuckets-1);
unsigned ProbeAmt = 1;
while (true)
// 内存平移:找到hash下标对应的Bucket
const BucketT *ThisBucket = BucketsPtr + BucketNo;
// Found Val's bucket? If so, return it.
if (LLVM_LIKELY(KeyInfoT::isEqual(Val, ThisBucket->getFirst())))
// 如果查询到`Bucket`的`key`和`Val`相等 返回当前的Bucket,说明查询到了
FoundBucket = ThisBucket;
return true;
// If we found an empty bucket, the key doesn't exist in the set.
// Insert it and return the default value.
// 如果bucket为空,说明当前key还不在表中,返回false
// 返回默认值
if (LLVM_LIKELY(KeyInfoT::isEqual(ThisBucket->getFirst(), EmptyKey)))
// If we've already seen a tombstone while probing, fill it in instead
// of the empty bucket we eventually probed to.
// 如果我们在探测时已经看到了tombstone,请将其填充,而不是我们最终探测到的空bucket。
FoundBucket = FoundTombstone ? FoundTombstone : ThisBucket;
return false;
// If this is a tombstone, remember it. If Val ends up not in the map, we
// prefer to return it than something that would require more probing.
// Ditto for zero values.
// 如果这是tombstone,记住它。如果Val最终不在map中,我们宁愿返回它,而不是需要更多探测的东西。
// 对于零值也是如此
if (KeyInfoT::isEqual(ThisBucket->getFirst(), TombstoneKey) &&
!FoundTombstone)
//记录发现的第一个tombstone
FoundTombstone = ThisBucket; // Remember the first tombstone found.
if (ValueInfoT::isPurgeable(ThisBucket->getSecond()) && !FoundTombstone)
FoundTombstone = ThisBucket;
// Otherwise, it's a hash collision or a tombstone, continue quadratic
// probing.
// 否则,它是一个哈希冲突或tombstone,继续二次探索。
if (ProbeAmt > NumBuckets)
FatalCorruptHashTables(BucketsPtr, NumBuckets);
// 重新计算hash下标
BucketNo += ProbeAmt++;
BucketNo &= (NumBuckets-1);
和在cache中的找bucket流程一样。
InsertIntoBucket
template <typename KeyArg, typename... ValueArgs>
BucketT *InsertIntoBucket(BucketT *TheBucket, KeyArg &&Key,
ValueArgs &&... Values)
// 根据Key 找到TheBucket的内存地址
TheBucket = InsertIntoBucketImpl(Key, Key, TheBucket);
// 将 Key 和 Values保存到TheBucket中
TheBucket->getFirst() = std::forward<KeyArg>(Key);
::new (&TheBucket->getSecond()) ValueT(std::forward<ValueArgs>(Values)...);
return TheBucket;
主要的插入工作都是在InsertIntoBucketImpl方法中完成的:
template <typename LookupKeyT>
BucketT *InsertIntoBucketImpl(const KeyT &Key, const LookupKeyT &Lookup,
BucketT *TheBucket)
// If the load of the hash table is more than 3/4, or if fewer than 1/8 of
// the buckets are empty (meaning that many are filled with tombstones),以上是关于[OC学习笔记]分类和关联对象源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章