Spring的ioc的扫描器与bean的作用域与生命周期
Posted 韶光不负
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring的ioc的扫描器与bean的作用域与生命周期相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
1、设置自动化扫描的范围(如果bean对象未在指定包范围,即使声明了注解,也无法实例化)
2、使用指定的注解(声明在类级别,bean对象的id属性默认是类的首字母小写)
扫描器作用:bean对象统一进行管理,简化开发配置,提高开发效率
方式一(在配置文档中通过指定init-method 属性来完成。):
方式二(实现org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean接口):
步骤一(实现销毁方式(Spring容器会维护bean对象的管理,可以指定bean对象的销毁所要执行的方法)):
步骤二(通过AbstractApplicationContext对象,调用其close方法实现bean的销毁过程):
IOC扫描器
在实际的开发中,bean的数量非常多,采用手动配置bean的方式已无法满足生产需要,Spring这时候同样提供了扫描的方式,对扫描到的bean对象统一进行管理,简化开发配置,提高开发效率。
扫描器的配置
1、设置自动化扫描的范围(如果bean对象未在指定包范围,即使声明了注解,也无法实例化)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--
使用注解方式进行创建对象
1.开启注解扫描
含义:开启注解扫描,指定了 base-package 扫描指定的包,扫描包与子包中所有的类
查看类上是否有指定的注解, 如果类上有指定的注解,那么就创建给类对象,
放到spring容器中
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.package"/>
</beans>
2、使用指定的注解(声明在类级别,bean对象的id属性默认是类的首字母小写)
Dao层:
package com.lsf.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
//Dao层使用扫描器
@Repository
public class AccountDao
public void test()
System.out.println("AccountDao....");
service层:
package com.lsf.service;
import com.lsf.conteoller.AccountController;
import com.lsf.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
//Service层使用扫描器
@Service
public class AccountService
//bean自动注入
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void test()
System.out.println("AccountService....");
accountDao.test();
controller层:
package com.lsf.conteoller;
import com.lsf.service.AccountService;
import com.lsf.util.PropertyUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
//Controller层扫描器
@Controller
public class AccountController
//bean自动注入方式一 Resource
@Resource
private AccountService accountService;
//bean自动注入方式二 Autowired
@Autowired
private PropertyUtil propertyUtil;
public void test()
System.out.println("AccountController....");
propertyUtil.test();
accountService.test();
econtroller任意类(工具类):
package com.lsf.util;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//工具类使用扫描器
@Component
public class PropertyUtil
public void test()
System.out.println("PropertyUtil....");
注:开发过程中建议按照指定规则声明注解
现象证明:
package com.lsf;
import com.lsf.conteoller.AccountController;
import com.lsf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Starter
public static void main(String[] args)
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
//bean对象的id属性默认是类的首字母小写
AccountController accountController = (AccountController) factory.getBean("accountController");
accountController.test();
扫描器作用:bean对象统一进行管理,简化开发配置,提高开发效率
遇到错误:Injection of resource dependencies failed; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type
解答:设置自动化扫描的范围小了,导致不能生成需要的bean对象,所有报错,扩大扫描包的范围
<context:component-scan base-package="扩大包范围位置"/>
bean的作用域
默认情况下,我们从spring容器中拿到的对象均是单例的,对于bean的作用域类型如下:

默认情况下,被管理的bean只会loC容器中存在一个实例,对于所有获取该Bean的操作Spring容器将只返回同一个Bean。
容器在启动的情况下就实例化所有singleton的bean对象,并缓存与容器中
lazy-init属性
lazy-init是懒加载,如果等于true时作用是指spring容器启动的时候不会去实例化这个bean,而是在程序调用时才去实例化.默认是false即spring容器启动时实例化.
如果为false,则在IOC容器启动时会实例化bean对象,默认false
如果为true,则oc容器启动时不会实例化Bean对象,在使用bean对象时才会实例化
lazy-init属性好处:
- 可以提前发现潜在的配置问题
- Bean对象存在于缓存中,使用时不用再去实例化bean,加快程序运行效率
什么对象适合作为单例对象(什么对象适合IOC维护?)
一般来说对于无状态或状态不可改变的对象适合使用单例模式。(不存在会改变对象状态的成员变量)比如: controller层、 service层、dao层。
什么是无状态或状态不可改变的对象?
实际上对象状态的变化往往均是由于属性值的变化而引起的,比如user类姓名属性会有变化,属性姓名的变化一般会引起user对象状态的变化。对于我们的程序来说,无状态对象没有实例变量的存在,保证了线程的安全性,service层业务对象即是无状态对象。线程安全的。
单例作用域与原型作用域
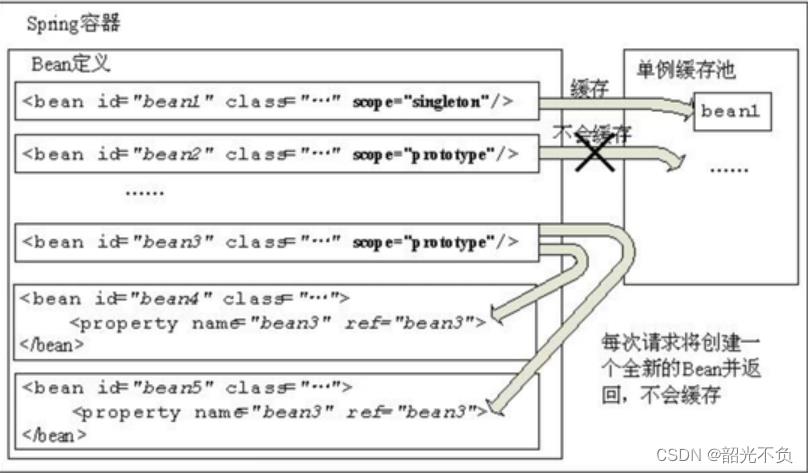
scope属性:
singleton 该bean为单例,作用在单例缓存池中(默认情况)
prototype 该bean为原型,Spring容器在启动时会实例化Bean对象,不会将对象设置到单例缓存池中,每次请求都会重新创建一个新的Bean
bean生命周期
在spring中,Bean的生命周期包括Bean的定义、初始化、使用和销毁4个阶段
bean的定义
在Spring中,通常是通过配置文档的方式来定义Bean的。在一个配置文档中,可以定义多个Bean。(在配置文件中定义bean标签,设置对应的id与class属性值)
bean的初始化
默认在IOC容器加载时,实例化对象。Spring bean初始化有两种方式:
方式一(在配置文档中通过指定init-method 属性来完成。):
package com.lsf.service;
public class AccountService
public void test()
System.out.println("AccountService....");
accountDao.test();
xml配置
<bean id="accountService" class="com.lsf.service.AccountService" init-method="test"></bean>
方式二(实现org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean接口):
public class RoleService implements InitializingBean
@override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception
System. out.println( "RoleService init. .."):
//xml配置
<bean id="roleService" class="com . xxxx,service.RoleService" ></bean>
bean的使用
方式一(使用BeanFactory):
package com.lsf;
import com.lsf.conteoller.AccountController;
import com.lsf.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Starter
public static void main(String[] args)
//bean的使用
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
AccountController accountController = (AccountController) factory.getBean("accountController");
方式二(使用ApplicationContext):
package com.lsf;
import com.lsf.conteoller.AccountController;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Starter
public static void main(String[] args)
//bean的使用
ApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
AccountController accountController = (AccountController) factory.getBean("accountController");
accountController.test();
bean的销毁
实现销毁方式(Spring容器会维护bean对象的管理,可以指定bean对象的销毁所要执行的方法)。
步骤一(实现销毁方式(Spring容器会维护bean对象的管理,可以指定bean对象的销毁所要执行的方法)):
<bean id="accountService" class="com.lsf.service.AccountService" destroy-method="自己写销毁方法"></bean>
步骤二(通过AbstractApplicationContext对象,调用其close方法实现bean的销毁过程):
AbstractApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
ac.close();以上是关于Spring的ioc的扫描器与bean的作用域与生命周期的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
