Polygon zkEVM Memory Align状态机
Posted mutourend
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Polygon zkEVM Memory Align状态机相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 引言
前序博客有:
Memory Align状态机为Polygon zkEVM的六个二级状态机之一,该状态机内包含:
- executor part:sm_mem_align.js:负责生成execution trace,为常量多项式和隐私多项式赋值。
- 验证规则集PIL:mem_align.pil:定义了约束系统。
Polygon zkEVM Memory状态机通过使用a 32-byte word access来检查内存读写,而EVM支持对单个byte级别的offset进行读写。
如下图,分别表示了相同内容在 byte级别 和 32-byte级别的内存布局:
Table 7: Sample memory layouts for byte and 32-byte access.A D D R E S S B Y T E 0 0 x c 4 1 0 x 17 ⋮ ⋮ 30 0 x 81 31 0 x a 7 32 0 x 88 33 0 x d 1 ⋮ ⋮ 62 0 x b 7 63 0 x 23 \\beginarray|c|c| \\hline \\mathbfADDRESS &\\mathbfBYTE \\\\ \\hline \\mathtt0 &\\mathtt0xc4 \\\\ \\mathtt1 &\\mathtt0x17 \\\\ \\mathtt\\vdots &\\mathtt\\vdots \\\\ \\mathtt30 &\\mathtt0x81 \\\\ \\mathtt31 &\\mathtt0xa7 \\\\ \\mathtt32 &\\mathtt0x88 \\\\ \\mathtt33 &\\mathtt0xd1 \\\\ \\mathtt\\vdots &\\mathtt\\vdots \\\\ \\mathtt62 &\\mathtt0xb7 \\\\ \\mathtt63 &\\mathtt0x23 \\\\ \\hline \\endarray ADDRESS01⋮30313233⋮6263BYTE0xc40x17⋮0x810xa70x880xd1⋮0xb70x23
ADDRESS 32-BYTE WORD 0 0 x c 417...81 a 7 1 0 x 88 d 1... b 723 \\beginarray|c|c| \\hline \\textbfADDRESS & \\textbf32-BYTE WORD \\\\ \\hline \\mathtt0 &\\mathtt0xc417...81a7 \\\\ \\mathtt1 &\\mathtt0x88d1...b723 \\\\ \\hline \\endarray ADDRESS0132-BYTE WORD0xc417...81a70x88d1...b723
32-byte与byte级别布局之间的关系称为“memory alignment”,而Memory Align状态机负责检查二者之间关系的正确性。
EVM支持3种内存操作:
- 1)MLOAD:按指定offset地址读取内存,返回内存中自该offset开始的32字节word。【注意,MLOAD可读取2个不同words的bytes。】【对应zkasm中的
MEM_ALIGN_WR】 - 2)MSTORE:按指定offset地址存储32byte。【对应zkasm中的
MEM_ALIGN_RD】 - 3)MSTOREE:将某单个byte数据存入指定offset地址。【注意,MSTOREE为按单个byte写入。】【对应zkasm中的
MEM_ALIGN_WR8】
EVM是按byte级别操作的,仍以上表为例,对应2个word:
m
0
=
0
x
88
d
11
f
⋯
b
723
,
m
1
=
0
x
6
e
21
f
f
⋯
54
f
9
.
\\mathttm_0 = \\mathtt0x \\mathtt88d11f \\cdots \\mathttb723, \\quad \\mathttm_1 = \\mathtt0x \\mathtt6e21ff \\cdots \\mathtt54f9.
m0=0x88d11f⋯b723,m1=0x6e21ff⋯54f9.
当MLOAD 0x22时,返回的结果为:
v
a
l
=
0
x
1
f
⋯
b
7236
e
21
.
\\mathttval = \\mathtt0x1f \\cdots b7236e21.
val=0x1f⋯b7236e21.
跨越了2个word,将该读操作的结果标记为:
m
0
∣
m
1
\\mathttm_0 \\mid \\mathttm_1
m0∣m1:
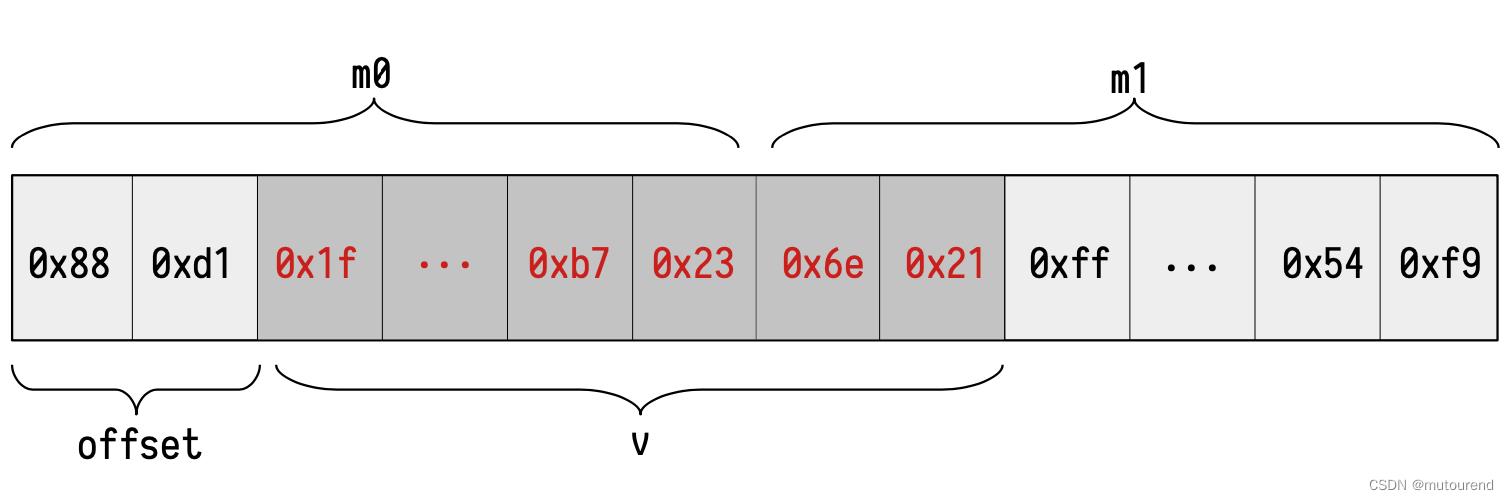
验证MLOAD 0x22返回的结果
0
x
1
f
⋯
7236
e
21
\\mathtt0x1f\\dotsb7236e21
0x1f⋯7236e21是否正确的流程为:
- 1)Main状态机需查询获得 m 0 \\mathttm_0 m0 和 m 1 \\mathttm_1 m1值;
- 2)Main状态机需调用Memory状态机来验证所查询的结果有效;
- 3)Main状态机可很容易extract the memory positions to query from the address 0x22。事实上,若
a
a
a为
MLOAD操作的内存位置,则 m 0 \\mathttm_0 m0总是存储在内存位置 ⌊ a 32 ⌋ \\lfloor \\fraca32 \\rfloor ⌊32a⌋ 且 m 1 \\mathttm_1 m1 存储在内存位置 ⌊ a 32 ⌋ + 1 \\lfloor \\fraca32 \\rfloor + 1 ⌊32a⌋+1。本例中 a = 0 x 22 = 34 a = \\mathtt0x22 = 34 a=0x22=34,从而 m 0 \\mathttm_0 m0 存储在位置 ⌊ 32 34 ⌋ = 0 x 01 \\lfloor \\frac3234 \\rfloor = \\mathtt0x01 ⌊3432⌋=0x01 且 m 1 \\mathttm_1 m1 存储在位置 ⌊ 32 34 ⌋ + 1 = 0 x 02 \\lfloor \\frac3234 \\rfloor + 1= \\mathtt0x02 ⌊3432⌋+1=0x02。 - 4)应从正确的offset提取,offset应为0-31的index,表示从 m 0 \\mathttm_0 m0的读取 v a l \\mathttval val的偏移位置。如本例中,offset为2(即offset为 a m o d 32 a \\mod 32 amod32)。可借助Plookup来验证已知 m 0 , m 1 \\mathttm_0,\\mathttm_1 m0,m1和 o f f s e t \\mathttoffset offset,所读取的 v a l \\mathttval val值是正确的。
同理,对于
M
S
T
O
R
E
\\mathttMSTORE
MSTORE为write bytes in two words。假设
w
0
,
w
1
\\mathttw_0,\\mathttw_1
w0,w1为
m
0
,
m
1
\\mathttm_0,\\mathttm_1
m0,m1进行
M
S
T
O
R
E
\\mathttMSTORE
MSTORE操作之后的值。
如MSTORE 0x22 0xe201e6...662b,想要向基于单个字节布局的以太坊内存中的0x22地址写入:
v
a
l
=
0
x
e
201
e
6
…
662
b
\\mathttval = \\mathtt0xe201e6\\dots662b
val=0xe201e6…662b
写入成功之后,相应的
w
0
,
w
1
\\mathttw_0,\\mathttw_1
w0,w1值为:
w
0
=
0
x
88
d
1
e
201
e
6
…
,
w
1
=
0
x
662
b
f
f
…
54
f
9
\\mathttw_0 = \\mathtt0x88d1\\mathtte201e6\\dots,\\quad \\mathttw_1 = \\mathtt0x\\mathtt662b\\mathttff\\dots54f9
w0=0x88d1e201e6…,w1=0x662bff…54f9
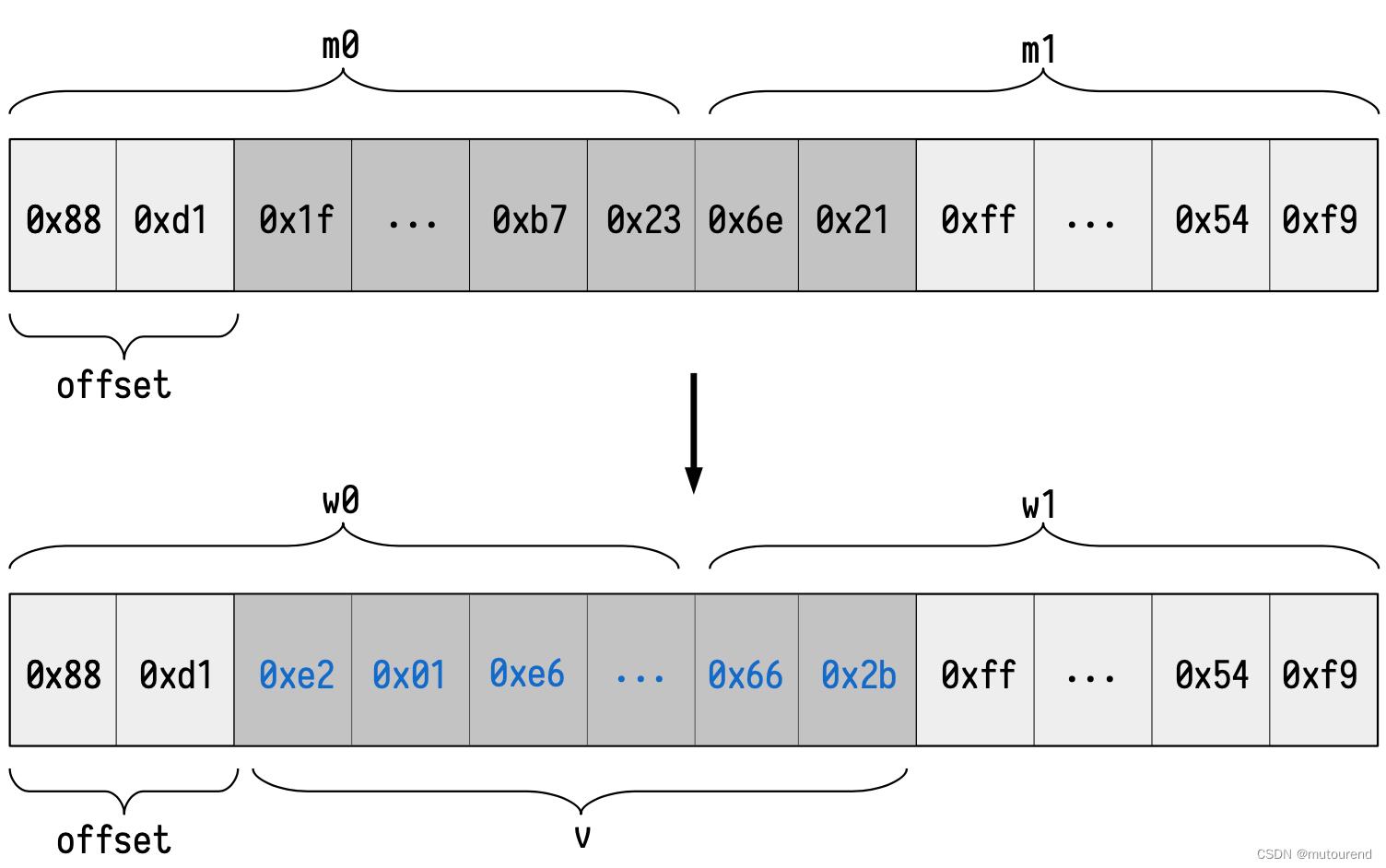
已知:
- 1)an address a d d r \\mathttaddr addr
- 2)an offset value o f f s e t \\mathttoffset offset
- 3)待写入的值 v a l \\mathttval val
Main状态机的操作与上面MLOAD类似,只是改为需要检查
w
0
,
w
1
\\mathttw_0,\\mathttw_1
w0,w1确实是根据已知的
v
a
l
,
m
0
,
m
1
,
o
f
f
s
e
t
\\mathttval,\\mathttm_0,\\mathttm_1,\\mathttoffset
val,m0,m1以上是关于Polygon zkEVM Memory Align状态机的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章