基于CIFAR10图像数据集和SVM的图像分类算法matlab仿真
Posted fpga和matlab
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于CIFAR10图像数据集和SVM的图像分类算法matlab仿真相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、理论基础
基于支持向量机(Support Vector Machines,SVM)的训练学习算法,其主要原理是通过统计学理论,使得其具备以较少数量的训练数据样本来完成分类器的训练。而传统的基于神经网络的学习理论,往往需要较大数量的样本作为训练数据,因此传统的神经网络学习方法其对样本数量的依赖性较大。所以,采用SVM支持向量机的分类方法优于采用神经网络的分类方法。通过SVM支持向量机的分类算法,其首先需要对数据进行预处理,将维度较高的特征数据转换为低维度的特征数据,然后通过一个非线性映射函数产生一个对数据进行分割的超平面。因此,基于SVM支持向量机的分类算法,其本质是通过样本数据对非线性映射函数的训练和学习,从而得到适用于当前训练样本的非线性映射函数。根据实现非线性映射函数的不同方式,SVM可以分为线性可分和非线性可分两种类型。下面对这两种SVM的基本原理进行介绍。

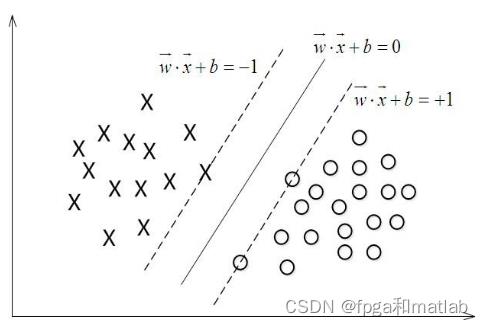


二、案例背景
图像是多媒体信息的最主要信息载体,其具有内容感受直观,信息丰富等优势,因此关于图像方面的研究也得到了越来越多的关注。其中图像图像的分类和识别是目前计算机视觉科学研究领域的一个重要环节,通过该计算可以对数字图像的信息进行分类,并得到正确的处理结果。目前关于图像分类识别的实际应用也有很多方面,各种科技设备不断得出现在人们的日常生活中,如网络支付,门禁系统,智能识别系统等。而这些设备基本都是基于生物学学特征分类技术实现的,比如其通过对比和分析人体的生物学特征与数据库中存储的特征的相似性来进行人体特征的分类和识别;还有各种应用在道路上的交通设备,进行车辆识别的,其主要根据车辆的特征进行匹配分类处理;此外还有应用在动物园监控设备方面的动物识别等。
因此,图像的分类识别技术是目前计算机图像视觉分类识别领域的一个重要研究方向,其主要设计的技术包括图像的预处理(图像的滤波,均衡,增强,明暗度调整等)、图像的特征提取(基于gabor滤波的特征提取,DCT变换特征提取,HOG特征提取等等)、特征数据的降维(PCA降维)以及图像的分类识别(SVM分类器,神经网络分类器等)。
三、matlab程序
训练部分:
clc;
clear;
close all;
warning off;
addpath 'func\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\java\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\java\\libsvm\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\matlab\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\matlab-implement[by faruto]\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\python\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\svm-toy\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\tools\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\windows\\'
%读取库
sel = 0;
if sel == 1
file_path = 'train\\0\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F1 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F1 = [F1;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\1\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F2 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F2 = [F2;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\2\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F3 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F3 = [F3;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\3\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F4 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F4 = [F4;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\4\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F5 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F5 = [F5;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\5\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F6 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F6 = [F6;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\6\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F7 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F7 = [F7;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\7\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F8 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F8 = [F8;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\8\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F9 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F9 = [F9;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
file_path = 'train\\9\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F10 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F10 = [F10;func_hog_feature(I)];
end
save feature.mat F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10
end
load feature.mat
C = 0.05;
gamma = 0.00025;
cmd = ['-s 1',' -t 3',[' -c ', num2str(C)],[' -g ',num2str(gamma)],' -p 0.0001'];
%SVM训练
%SVM训练
KK=5000;
T=[1*ones(KK,1);2*ones(KK,1);3*ones(KK,1);4*ones(KK,1);5*ones(KK,1);6*ones(KK,1);7*ones(KK,1);8*ones(KK,1);9*ones(KK,1);10*ones(KK,1)];
P=[F1(1:KK,:);F2(1:KK,:);F3(1:KK,:);F4(1:KK,:);F5(1:KK,:);F6(1:KK,:);F7(1:KK,:);F8(1:KK,:);F9(1:KK,:);F10(1:KK,:)];
% T=[1*ones(KK,1);2*ones(KK,1);3*ones(KK,1);4*ones(KK,1);5*ones(KK,1);6*ones(KK,1)];
% P=[F1(1:KK,:);F2(1:KK,:);F3(1:KK,:);;F4(1:KK,:);F5(1:KK,:);F6(1:KK,:);];
svm_models = svmtrain(T,P,cmd);
save svm_model3.mat svm_models
测试部分:
clc;
clear;
close all;
warning off;
addpath 'func\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\java\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\java\\libsvm\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\matlab\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\matlab-implement[by faruto]\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\python\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\svm-toy\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\tools\\'
addpath 'func\\func_SVM_toolbox\\windows\\'
%SVM测试
load svm_model3.mat
file_path = 'test\\0\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F1 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F1 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(1,F1,svm_models);
Rout1(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\1\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F2 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F2 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(2,F2,svm_models);
Rout2(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\2\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F3 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F3 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(3,F3,svm_models);
Rout3(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\3\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F4 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F4 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(4,F4,svm_models);
Rout4(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\4\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F5 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F5 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(5,F5,svm_models);
Rout5(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\5\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F6 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F6 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(6,F6,svm_models);
Rout6(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\6\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F7 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F7 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(7,F7,svm_models);
Rout7(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\7\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F8 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F8 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(8,F8,svm_models);
Rout8(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\8\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F9 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F9 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(9,F9,svm_models);
Rout9(i)=Predict1;
end
file_path = 'test\\9\\';% 图像文件夹路径
img_path_list = dir(strcat(file_path,'*.jpg'));
img_num = length(img_path_list);%获取图像总数量?
F10 = [];
for i = 1:img_num
i
image_name = img_path_list(i).name;
I = imread(strcat(file_path,image_name));
F10 = [func_hog_feature(I)];
[Predict1,error1] = svmpredict(10,F10,svm_models);
Rout10(i)=Predict1;
end
save hogresult_total.mat Rout1 Rout2 Rout3 Rout4 Rout5 Rout6 Rout7 Rout8 Rout9 Rout10
四、仿真结论
我们采用的测试图像库为CIFAR10图像数据集,下面对这两种数据进行介绍。CIFAR-10图像数据集是一种微小图像数据集,其中包括10个大类,共计60000个图片,每个图片的分辨率为32*32。该图像数据集是由他们由Alex Krizhevsky,Vinod Nair和Geoffrey Hinton收集的。CIFAR-10图像数据集如下图所示:

选择CIFAR10图像数据库作为测试图像库,并选择HOG的特征提取方式,SVM核函数选择径向基函数。采用其中的5万张图片作为训练图像,1万张图片作为测试图像,每一个分类目标为5000张训练图片,1000张测试图片。本实验中,SVM的参数为C=0.05,gamma=0.00025,HOG特征提取算法的参数为CELL单元分割大小8*8,位移像素为8,角度方向个数为9。通过MATLAB仿真得到如下的仿真结果:
| TP | FN | FP | P | R | F1 | |
| 第一类:飞机 | 593 | 407 | 355 | 0.6255 | 0.5930 | 0.6088 |
| 第二类:汽车 | 552 | 448 | 332 | 0.6244 | 0.5520 | 0.5860 |
| 第三类:鸟 | 604 | 396 | 233 | 0.7216 | 0.6040 | 0.6576 |
| 第四类:猫 | 593 | 407 | 328 | 0.6439 | 0.5930 | 0.6174 |
| 第五类:鹿 | 592 | 408 | 246 | 0.7064 | 0.5920 | 0.6442 |
| 第六类:狗 | 583 | 417 | 396 | 0.5955 | 0.5830 | 0.5892 |
| 第七类:青蛙 | 570 | 430 | 413 | 0.5799 | 0.5700 | 0.5749 |
| 第八类:马 | 611 | 389 | 323 | 0.6542 | 0.6110 | 0.6319 |
| 第九类:船 | 579 | 421 | 411 | 0.5848 | 0.5790 | 0.5819 |
| 第十类:货车 | 576 | 424 | 219 | 0.7245 | 0.5760 | 0.6418 |
| 均值 | 585 | 415 | 326 | 0.6461 | 0.5853 | 0.6134 |
A10-52
以上是关于基于CIFAR10图像数据集和SVM的图像分类算法matlab仿真的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章