ES6 从入门到精通 # 20:async 的用法
Posted 凯小默
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ES6 从入门到精通 # 20:async 的用法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
说明
ES6 从入门到精通系列(全23讲)学习笔记。
async
作用:使得异步操作更加方便
async 它会返回一个 promise 对象,它是 generator 的语法糖
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
async function f()
console.log(f())
</script>
</body>
</html>

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
async function f()
return await "hello kaimo";
f().then(res =>
console.log(res);
).catch(err =>
console.log(err);
)
</script>
</body>
</html>

如果 async 函数中有多个 await 那么then 函数会等待所有的 await 指令运行完才去执行
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
async function f()
let k = await "hello kaimo";
let data = await k.split("");
return data;
f().then(res =>
console.log(res);
).catch(err =>
console.log(err);
)
</script>
</body>
</html>
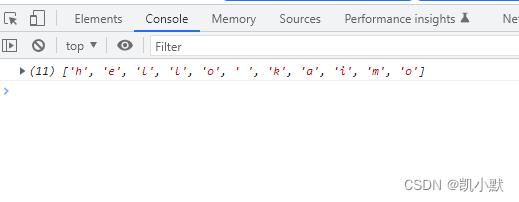
错误的情况:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
async function f()
let k = await "hello kaimo";
let data = await k.split("");
return data;
f().then(res =>
console.log(res);
).catch(err =>
console.log(err);
)
async function f2()
throw new Error("报错了");
f2().then(res =>
console.log(res);
).catch(err =>
console.log(err);
)
</script>
</body>
</html>
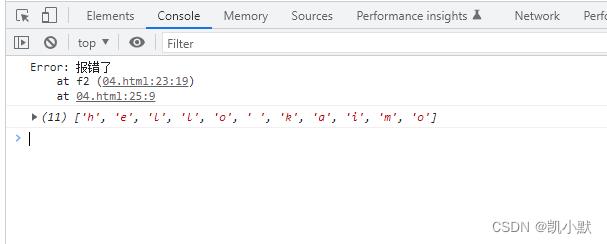
如果 await 有多个,里面有错误跟成功的,有错误就会停止。
async function f2()
// throw new Error("报错了");
await Promise.reject("报错了");
await Promise.resolve("hello kaimo2");
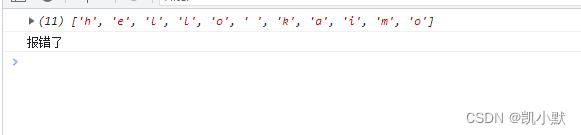
上面这种可以采用 try catch 处理
async function f2()
// throw new Error("报错了");
try
await Promise.reject("报错了");
catch (error)
return await Promise.resolve("hello kaimo2");

例子
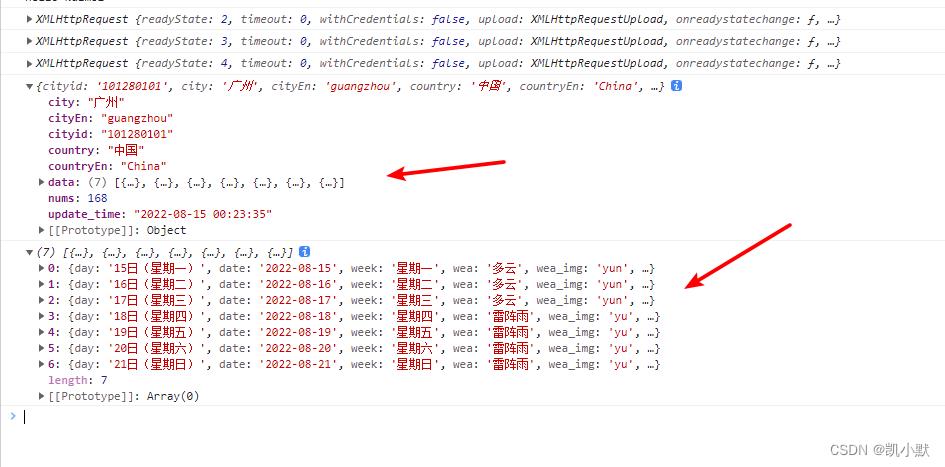
获取广州天气的 datalist 数据
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const getData = function(url)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.onreadystatechange = handler;
xhr.responseType = "json";
xhr.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/json");
xhr.send();
function handler()
console.log(this);
if(this.readyState === 4)
if(this.status === 200)
resolve(this.response);
else
reject(new Error(this.statusText));
)
async function getDataList(url)
let res = await getData(url);
console.log(res);
// 获取 datalist 数据
return await res.data;
getDataList("https://v0.yiketianqi.com/api?unescape=1&version=v91&appid=43656176&appsecret=I42og6Lm&ext=&cityid=&city=广州")
.then(res =>
console.log(res)
, err =>
console.log(err)
)
</script>
</body>
</html>
以上是关于ES6 从入门到精通 # 20:async 的用法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章