实现STL(SGI)的string(深拷贝)
Posted -YIN
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了实现STL(SGI)的string(深拷贝)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实现string
解决浅拷贝问题
如题:

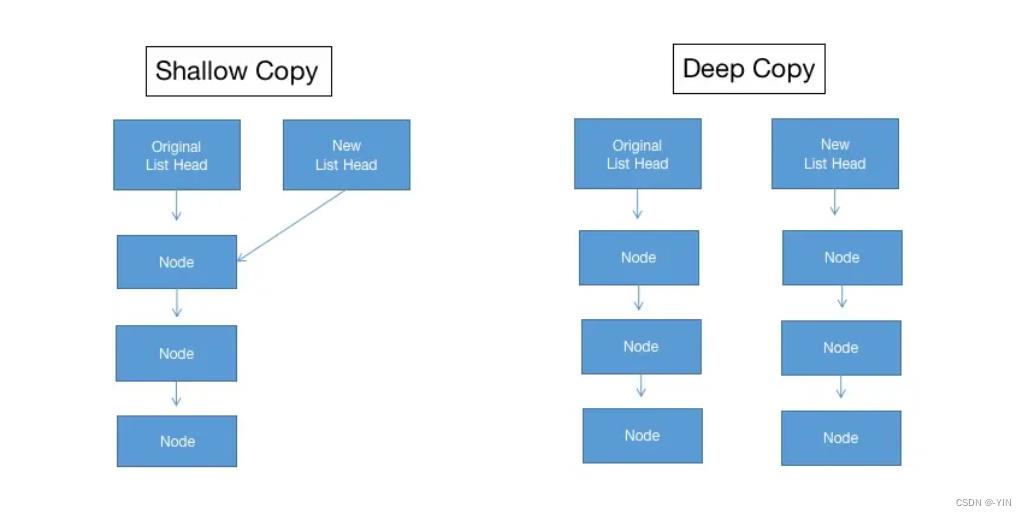
什么是浅拷贝
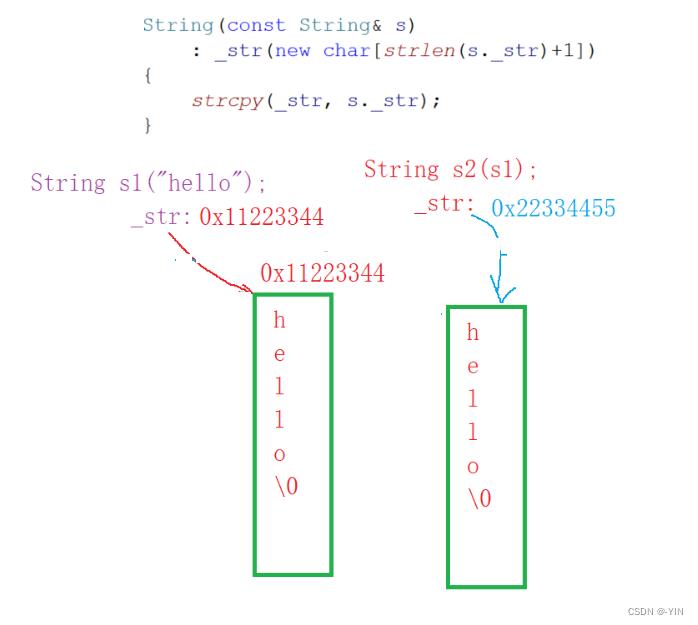
浅拷贝:也称位拷贝,编译器只是将对象中的值拷贝过来。如果对象中管理资源,最后就会导致多个对象共享同一份资源,当一个对象销毁时就会将该资源释放掉,而此时其余对象不知道该资源已经被释放,以为还有效,所以 当继续对资源进项操作时,就会发生发生了错误。要解决浅拷贝问题,通过深拷贝来解决。
浅拷贝 深拷贝
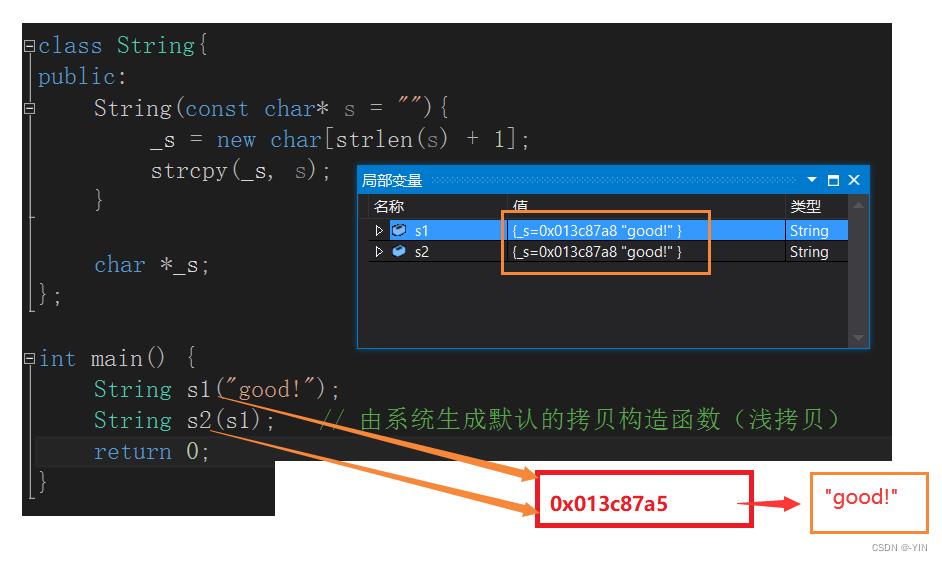
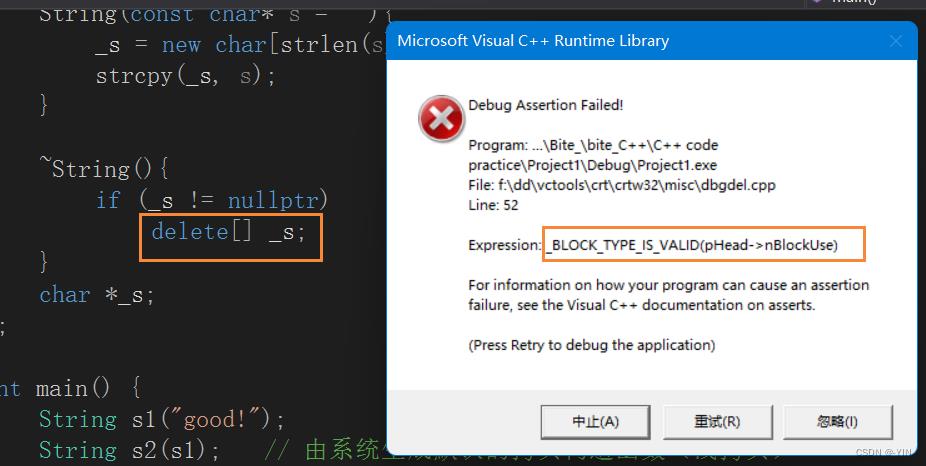
而在进行析构释放堆上new出来的资源时候就会出现重复释放的错误,如下图所示,当s1 destory,_s申请的空间被释放,但是!!因为s1和s2中是同一个资源,当s2释放时改空间已经是一块被释放的空间,再进行释放就会造成非法访问。
浅拷贝问题:
- 可能会造成内存泄漏
- 资源重复释放会使程序运行崩溃
所以当类中涉及动态内存管理时,一定要预防浅拷贝发生,使用深拷贝
深拷贝
实现代码:
class String
public:
String(const char *str = NULL); // 通用构造函数
String(const String &another); // 拷贝构造函数
~ String(); // 析构函数
String & operater =(const String &rhs); // 赋值函数
private:
char *m_data; // 用于保存字符串
;
有几种深拷贝的方法如下:
- 深拷贝 1.0
// 通用构造函数
String::String(const char *str = NULL)
m_data = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(m_data, str);
// 深拷贝 1.0
String::String(const String &another)
m_data = new char[strlen(another) + 1]; //+1加上字符串结尾的'/0'
strcpy(m_data, str);
// 析构函数
String::~String()
if (m_data != nullptr)
delete[] m_data;
// 赋值运算符重载函数
String::String& operator=(const String& rhs)
if (this != &rhs) //不是给自己赋值
// 申请新空间
char* temp = new char[strlen(rhs.m_data) + 1];
// 拷贝元素
strcpy(temp, rhs.m_data);
// 释放旧空间
delete[] m_data;
// 使用新空间
m_data = temp;
return *this;
- 深拷贝 2.0
// 深拷贝 2.0
String::String(const String &another)
if(this != &another)
String temp(another.m_data);
swap(m_data, temp.m_data);
// 赋值运算符重载函数
String::String& operator=(const String& rhs)
if(this != &another)
String temp(another.m_data);
swap(m_data, temp.m_data);
return *this;
2.0 简化版
// 深拷贝 2.1
String::String(const String &another)
String temp(another.m_data);
swap(m_data, temp.m_data);
// 赋值运算符重载函数
String::String& operator=(const String& rhs)
swap(m_data,rhs.m_data); // 传参时拷贝构造临时对象
return *this;
或通过写时拷贝解决
写时拷贝就是一种拖延症,是在浅拷贝的基础之上增加了引用计数的方式来实现的。
引用计数:用来记录资源使用者的个数。在构造时,将资源的计数给成1,每增加一个对象使用该资源,就给计数增加1,当某个对象被销毁时,先给该计数减1,然后再检查是否需要释放资源,如果计数为1,说明该对象时资源的最后一个使用者,将该资源释放;否则就不能释放,因为还有其他对象在使用该资源
(智能指针思想)
实现string
https://cplusplus.com/reference/string
源代码
#ifndef _STRING_H_
#define _STRING_H_
#include "stdhead.h"
namespace my_stl
class string
public:
// 迭代器(原生指针)
typedef char* iterator;
typedef char* reverse_iterator;
/* Member functions */
// 构造函数
string(const char* str = "")
if (str == NULL) assert(false);
_size = strlen(str);
_str = new char[_size + 1]; //+1加上字符串结尾的'/0'
strcpy(_str, str);
_capacity = _size;
string(size_t n, char ch)
_str = new char[n + 1];
_str[n] = '\\0';
_size = _capacity = n;
// 拷贝构造
string(const string& s) :_str(NULL)
string temp(s._str);
this->swap(temp);
// 赋值运算符重载
string& operator=(string s)
swap(s); // 传参时拷贝构造临时对象
return *this;
~string()
if (_str != NULL)
delete[] _str;
_str = NULL;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
/* Iterators: */
iterator begin() return _str;
iterator end() return _str + _size;
reverse_iterator rbegin() return end();
reverse_iterator rend() return begin();
/* Capacity: */
size_t size()const return _size;
size_t length()const return _size;
size_t capacity()const return _capacity;
bool empty()const return _size == 0;
void clear()
_str[0] = '\\0';
_size = 0;
return;
void resize(size_t newsize, char ch)
size_t oldsize = _size;
if (oldsize > newsize) _str[newsize] = '\\0';
else
if (newsize > _capacity)
// 扩容
reserve(2 * _capacity); // 以2倍方式进行扩容
append(newsize - oldsize, ch);
_size = newsize;
void resize(size_t newsize)
resize(newsize, char());
void reserve(size_t newcapacity)
size_t oldcapacity = _capacity;
if (oldcapacity < newcapacity)
char* temp = new char[newcapacity + 1];
strcpy(temp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = temp;
_capacity = newcapacity;
/* Element access: */
char& operator[](size_t index)
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
const char& operator[](size_t index)const
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
char& back() return _str[_size - 1];
const char& back() const return _str[_size - 1];
char& front() return _str[0];
const char& front() const return _str[0];
/* Modifiers: */
string& operator+=(char ch)
push_back(ch);
return *this;
string& operator+=(const char* str)
append(str);
return *this;
string& operator+=(const string& s)
append(s.c_str());
return *this;
string& append(size_t n, char ch)
if (n + _size > _capacity)
reserve(n + _size);
memset(_str + _size, ch, n);
_size += n;
_str[_size] = '\\0';
return *this;
string& append(const char* str)
size_t size = strlen(str);
if (size + _size > _capacity)
reserve(size + _size);
strcat(_str, str);
_size += size;
return *this;
void push_back(char ch) append(1, ch);
string& insert(size_t pos, const string& s)
if (_size + s._size > _capacity)
reserve(_size + s._size);
// 搬移元素
for (int i = _size; i >= (int)pos; --i)
_str[i+s._size] = _str[i];
strncpy(_str + pos, s._str, s._size);
_size += s._size;
return *this;
string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t n = npos)
if (pos == npos || pos + n >= _size)
_str[pos] = '\\0';
_size = pos;
else
_str[pos] = '\\0';
strcat(_str + pos, _str + pos + n);
/* String operations: */
const char* c_str()const
return _str;
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0)
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i)
if (ch == _str[i]) return i;
return npos;
size_t rfind(char ch, size_t pos = npos)
if (pos == npos) pos = _size - 1;
for (size_t i = pos; i >= 0; --i)
if (ch == _str[i]) return i;
return npos;
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t n = npos)
if (n == npos) n = _size - pos;
char* temp = new char[n + 1];
strncpy(temp, _str + pos, n);
temp[n] = '\\0';
return temp;
int compare(const string& s) strcmp(_str,s._str);
int compare(const char* s) strcmp(_str, s);
/* Non-member function overloads */
void swap(string&s)
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
// 重载输入输出流运算符时会报参数过多,所以重载成友元或是全局函数
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& _cin, string& s)
s.clear();
char ch = _cin.get();
while (ch != '\\n' || ch != ' ')
s += ch;
ch = _cin.get();
return _cin;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& _cout, const string& s)
_cout << s._str;
return _cout;
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size; // 有效元素
size_t _capacity; // 容量
/* vs下维护了长度16的数组,如果长度较小直接使用数组,长度超过在扩容;
vs STL与Linux下SGI STL扩容方式不一样 */
static size_t npos;
;
size_t string::npos = -1;
#endif
以上是关于实现STL(SGI)的string(深拷贝)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章