阿里云RDS PostgreSQL时序数据的优化
Posted chszs
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了阿里云RDS PostgreSQL时序数据的优化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
阿里云RDS PostgreSQL时序数据的优化
- 2008年6月8日
- 版权声明:本文为博主chszs的原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
PostgreSQL是最流行的开源数据库之一。PostgreSQL的一个优势是它可以通过多种方式进行优化,例如数据合并和数据清理。而数据合并和数据清理在一些应用场景下是必需的。
例如:
- 当数据表的具体内容被更新(插入、更新、删除)时,我们需要先合并,然后迅速得到每个主键的最新值。
- 当我们有大量连续不断地报告数据的传感器时,我们需要及时收集每个传感器的最新读数。
- 我们可以使用窗口查询进行这种操作,但我们需要快速检索批量数据。
通常有四种优化时序数据的方法:
- 当只有很少的唯一值和一个未知的范围时,我们可以使用递归(recursion)。
- 当只有很少的唯一值并且它们的范围已经确定,我们可以使用子查询(subquery)。
- 当有许多唯一值时,窗口查询(Window query)比上述方法更合适。
- 流计算(Stream computing)是所有场景中最好的。
本文只会比较前三种方法。流计算不需要进行比较,因为它是所有场景中最强大的方法。
递归 vs. 子查询 vs. 窗口查询
在比较中,将使用一个包含500万条唯一值的数据库作为数据源,并在以下情况下比较这些方法。
递归
情景1、有大量有效的唯一值(100万个唯一值)
第1步:创建一个表
\\timing
drop table test;
create unlogged table test(id int , info text, crt_time timestamp);
第2步:构建数据
insert into test select ceil(random()*1000000), md5(random()::text), clock_timestamp() from generate_series(1,5000000);
第3步:创建一个索引
create index idx_test_1 on test (id, crt_time desc);
第4步:递归查询效率
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) with recursive skip as (
(
select test as v from test where id in (select id from test where id is not null order by id,crt_time desc limit 1) limit 1
)
union all
(
select (
select t as v from test t where t.id>(s.v).id and t.id is not null order by id,crt_time desc limit 1
) from skip s where (s.v).id is not null
) -- The "where (s.v).id is not null" must be included. Else you will be stuck in an infinite loop.
)
select (t.v).id, (t.v).info, (t.v).crt_time from skip t where t.* is not null;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CTE Scan on skip t (cost=54.35..56.37 rows=100 width=44) (actual time=0.042..6626.084 rows=993288 loops=1)
Output: (t.v).id, (t.v).info, (t.v).crt_time
Filter: (t.* IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 1
Buffers: shared hit=3976934
CTE skip
-> Recursive Union (cost=0.91..54.35 rows=101 width=69) (actual time=0.034..6006.615 rows=993289 loops=1)
Buffers: shared hit=3976934
-> Limit (cost=0.91..0.93 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=0.033..0.033 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test.*
Buffers: shared hit=8
-> Nested Loop (cost=0.91..10.19 rows=500 width=69) (actual time=0.032..0.032 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test.*
Buffers: shared hit=8
-> HashAggregate (cost=0.48..0.49 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.021..0.021 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test_1.id
Group Key: test_1.id
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> Limit (cost=0.43..0.47 rows=1 width=12) (actual time=0.016..0.016 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test_1.id, test_1.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> Index Only Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test test_1 (cost=0.43..173279.36 rows=5000002 width=12) (actual time=0.015..0.015 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test_1.id, test_1.crt_time
Index Cond: (test_1.id IS NOT NULL)
Heap Fetches: 1
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test (cost=0.43..9.64 rows=6 width=73) (actual time=0.009..0.009 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test.*, test.id
Index Cond: (test.id = test_1.id)
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> WorkTable Scan on skip s (cost=0.00..5.14 rows=10 width=32) (actual time=0.006..0.006 rows=1 loops=993289)
Output: (SubPlan 1)
Filter: ((s.v).id IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 0
Buffers: shared hit=3976926
SubPlan 1
-> Limit (cost=0.43..0.49 rows=1 width=81) (actual time=0.005..0.005 rows=1 loops=993288)
Output: t_1.*, t_1.id, t_1.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=3976926
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test t_1 (cost=0.43..102425.17 rows=1666667 width=81) (actual time=0.005..0.005 rows=1 loops=993288)
Output: t_1.*, t_1.id, t_1.crt_time
Index Cond: ((t_1.id > (s.v).id) AND (t_1.id IS NOT NULL))
Buffers: shared hit=3976926
Planning time: 0.354 ms
Execution time: 6706.105 ms
(45 rows)
情景二、只有很少有效的唯一值(1,000个唯一值)
第1步:创建一个表
\\timing
drop table test;
create unlogged table test(id int , info text, crt_time timestamp);
第2步:构建数据
insert into test select ceil(random()*1000), md5(random()::text), clock_timestamp() from generate_series(1,5000000);
第3步:创建一个索引
create index idx_test_1 on test (id, crt_time desc);
第4步:递归查询效率
Query statement stays unchanged
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CTE Scan on skip t (cost=55.09..57.11 rows=100 width=44) (actual time=0.046..8.859 rows=1000 loops=1)
Output: (t.v).id, (t.v).info, (t.v).crt_time
Filter: (t.* IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 1
Buffers: shared hit=4007
CTE skip
-> Recursive Union (cost=0.91..55.09 rows=101 width=69) (actual time=0.039..8.203 rows=1001 loops=1)
Buffers: shared hit=4007
-> Limit (cost=0.91..1.67 rows=1 width=69) (actual time=0.038..0.038 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test.*
Buffers: shared hit=8
-> Nested Loop (cost=0.91..6335.47 rows=8333 width=69) (actual time=0.038..0.038 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test.*
Buffers: shared hit=8
-> HashAggregate (cost=0.48..0.49 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.021..0.021 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test_1.id
Group Key: test_1.id
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> Limit (cost=0.43..0.47 rows=1 width=12) (actual time=0.016..0.017 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test_1.id, test_1.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> Index Only Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test test_1 (cost=0.43..173279.55 rows=5000002 width=12) (actual time=0.015..0.015 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test_1.id, test_1.crt_time
Index Cond: (test_1.id IS NOT NULL)
Heap Fetches: 1
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test (cost=0.43..6284.98 rows=5000 width=73) (actual time=0.015..0.015 rows=1 loops=1)
Output: test.*, test.id
Index Cond: (test.id = test_1.id)
Buffers: shared hit=4
-> WorkTable Scan on skip s (cost=0.00..5.14 rows=10 width=32) (actual time=0.008..0.008 rows=1 loops=1001)
Output: (SubPlan 1)
Filter: ((s.v).id IS NOT NULL)
Rows Removed by Filter: 0
Buffers: shared hit=3999
SubPlan 1
-> Limit (cost=0.43..0.49 rows=1 width=81) (actual time=0.007..0.007 rows=1 loops=1000)
Output: t_1.*, t_1.id, t_1.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=3999
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test t_1 (cost=0.43..102425.80 rows=1666667 width=81) (actual time=0.007..0.007 rows=1 loops=1000)
Output: t_1.*, t_1.id, t_1.crt_time
Index Cond: ((t_1.id > (s.v).id) AND (t_1.id IS NOT NULL))
Buffers: shared hit=3999
Planning time: 0.353 ms
Execution time: 8.980 ms
(45 rows)
子查询
情景1、有大量有效的唯一值(100万个唯一值)
第1步:子查询查询效率
如果ID的值范围过宽,子查询效率会很低下。
需要维护一个唯一的ID表。这里我们使用generate_series作为测试的替代。
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select (select test from test where id=t.id order by crt_time desc limit 1) from generate_series(1,1000000) t(id);
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Function Scan on pg_catalog.generate_series t (cost=0.00..1976.65 rows=1000 width=32) (actual time=70.682..2835.109 rows=1000000 loops=1)
Output: (SubPlan 1)
Function Call: generate_series(1, 1000000)
Buffers: shared hit=3997082
SubPlan 1
-> Limit (cost=0.43..1.97 rows=1 width=77) (actual time=0.002..0.002 rows=1 loops=1000000)
Output: test.*, test.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=3997082
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test (cost=0.43..9.64 rows=6 width=77) (actual time=0.002..0.002 rows=1 loops=1000000)
Output: test.*, test.crt_time
Index Cond: (test.id = t.id)
Buffers: shared hit=3997082
Planning time: 0.119 ms
Execution time: 2892.712 ms
(14 rows)
情景二、只有很少有效的唯一值(1,000个唯一值)
第1步:子查询查询效率
查询语句更改为
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select (select test from test where id=t.id order by crt_time desc limit 1) from generate_series(1,1000) t(id);
QUERY PLAN
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Function Scan on pg_catalog.generate_series t (cost=0.00..1699.41 rows=1000 width=32) (actual time=0.107..7.041 rows=1000 loops=1)
Output: (SubPlan 1)
Function Call: generate_series(1, 1000)
Buffers: shared hit=4000
SubPlan 1
-> Limit (cost=0.43..1.69 rows=1 width=77) (actual time=0.006..0.007 rows=1 loops=1000)
Output: test.*, test.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=4000
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test (cost=0.43..6284.98 rows=5000 width=77) (actual time=0.006..0.006 rows=1 loops=1000)
Output: test.*, test.crt_time
Index Cond: (test.id = t.id)
Buffers: shared hit=4000
Planning time: 0.131 ms
Execution time: 7.126 ms
(14 rows)
窗口查询
情景1、有大量有效的唯一值(100万个唯一值)
第1步:窗口查询效率
explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select id,info,crt_time from (select row_number() over (partition by id order by crt_time desc) as rn, * from test) t where rn=1;
postgres=# explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select id,info,crt_time from (select row_number() over (partition by id order by crt_time desc) as rn, * from test) t where rn=1;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Subquery Scan on t (cost=0.43..310779.41 rows=25000 width=45) (actual time=0.027..6398.308 rows=993288 loops=1)
Output: t.id, t.info, t.crt_time
Filter: (t.rn = 1)
Rows Removed by Filter: 4006712
Buffers: shared hit=5018864
-> WindowAgg (cost=0.43..248279.39 rows=5000002 width=53) (actual time=0.026..5973.497 rows=5000000 loops=1)
Output: row_number() OVER (?), test.id, test.info, test.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=5018864
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test (cost=0.43..160779.35 rows=5000002 width=45) (actual time=0.019..4058.476 rows=5000000 loops=1)
Output: test.id, test.info, test.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=5018864
Planning time: 0.121 ms
Execution time: 6446.901 ms
(13 rows)
情景二、只有很少有效的唯一值(1,000个唯一值)
第1步:窗口查询效率
查询语句保持不变
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Subquery Scan on t (cost=0.43..310779.61 rows=25000 width=45) (actual time=0.027..6176.801 rows=1000 loops=1)
Output: t.id, t.info, t.crt_time
Filter: (t.rn = 1)
Rows Removed by Filter: 4999000
Buffers: shared hit=4744850 read=18157
-> WindowAgg (cost=0.43..248279.58 rows=5000002 width=53) (actual time=0.026..5822.576 rows=5000000 loops=1)
Output: row_number() OVER (?), test.id, test.info, test.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=4744850 read=18157
-> Index Scan using idx_test_1 on public.test (cost=0.43..160779.55 rows=5000002 width=45) (actual time=0.020..4175.082 rows=5000000 loops=1)
Output: test.id, test.info, test.crt_time
Buffers: shared hit=4744850 read=18157
Planning time: 0.108 ms
Execution time: 6176.924 ms
(13 rows)
横向效率比较图
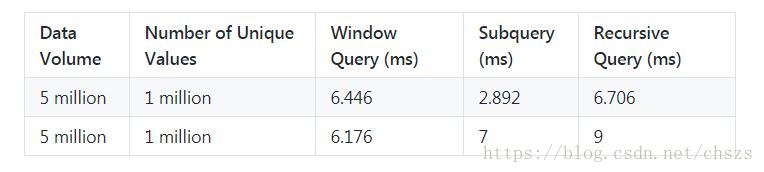
结论
随着物联网的兴起,越来越多的业务会使用时序数据,在必须根据这些数据提供服务的情况下,计算数据中的最新值和滑动窗口中的值是至关重要的。
PostgreSQL是开源数据库的最佳选择,因为它为相同的问题提供了几种解决方案。参考数据优化方法,我们可以得出结论:
- 递归适用于只有少量唯一值但范围未知的情况。
- 子查询适用于唯一值很少且范围已确定的情况。
- 当有大量唯一值时,窗口查询比子查询更合适。
- 流计算是所有场景的最佳选择。
以上是关于阿里云RDS PostgreSQL时序数据的优化的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章