kubernetes集群搭建efk日志收集平台
Posted 江湖有缘
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了kubernetes集群搭建efk日志收集平台相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
kubernetes集群搭建efk日志收集平台
- 一、efk介绍
- 二、检查本地kubernetes集群状态
- 三、配置默认存储
- 四、安装helm工具
- 五、配置helm仓库
- 六、安装Elasticsearch
- 七、安装filebeat
- 八、安装metricbeat
- 九、安装kibana
- 十、访问kibana的web
一、efk介绍
1.efk简介
Kubernetes 开发了一个 Elasticsearch 附加组件来实现集群的日志管理。这是一个 Elasticsearch、Filebeat(或者Fluentd)和 Kibana 的组合。
2.Elasticsearch介绍
①Elasticsearch简介
Elasticsearch是一个基于Apache Lucene™的开源搜索和数据分析引擎引擎,Elasticsearch使用Java进行开发,并使用Lucene作为其核心实现所有索引和搜索的功能。
②Elasticsearch的特点
1.Elasticsearch是一个实时的,分布式的,可扩展的搜索引擎。
2.Elasticsearch允许进行全文本和结构化搜索以及对日志进行分析。
3.Elasticsearch 是一个搜索引擎,负责存储日志并提供查询接口。
4.Elasticsearch通常用于索引和搜索大量日志数据,也可以用于搜索许多不同种类的文档。
3.Filebeat介绍
①Filebeat简介
Filebeat是用于转发和集中日志数据的轻量级传送工具。Filebeat监视您指定的日志文件或位置,收集日志事件,并将它们转发到Elasticsearch或 Logstash进行索引。
②Fluentd简介
Fluentd是一个开源数据收集器,通过它能对数据进行统一收集和消费,能够更好地使用和理解数据。
③Fluentd作用
1.在kubernetes集群中每个节点安装Fluentd。
2.通过获取容器日志文件、过滤和转换日志数据
3.将数据传递到 Elasticsearch 集群,在该集群中对其进行索引和存储
4. Kibana介绍
Kibana是一个开源的分析与可视化平台,被设计用于和Elasticsearch一起使用的。通过kibana可以搜索、查看和交互存放在Elasticsearch中的数据,利用各种不同的图表、表格和地图等,Kibana能够对数据进行分析与可视化。
5、efk的架构图
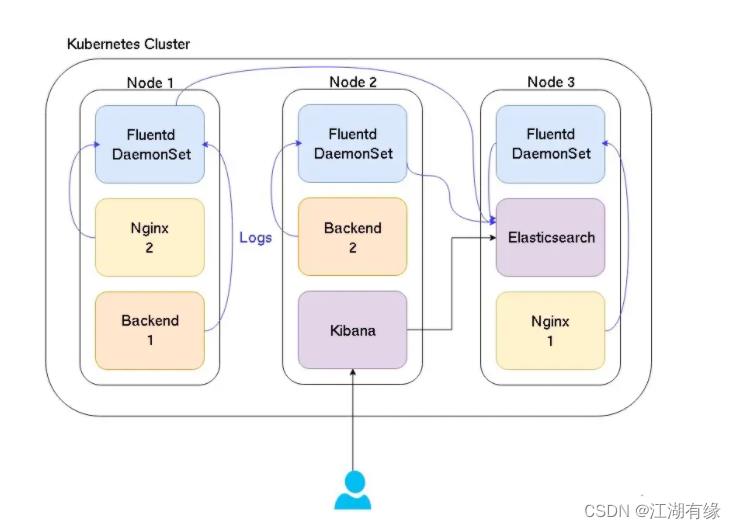
二、检查本地kubernetes集群状态
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes -owide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
k8s-master Ready control-plane,master 10d v1.23.1 192.168.3.201 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 containerd://1.6.6
k8s-node01 Ready <none> 10d v1.23.1 192.168.3.202 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 containerd://1.6.6
k8s-node02 Ready <none> 10d v1.23.1 192.168.3.203 <none> CentOS Linux 7 (Core) 3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 containerd://1.6.6
三、配置默认存储
1.检查nfs
[root@k8s-master efk]# showmount -e 192.168.3.201
Export list for 192.168.3.201:
/nfs/data *
2.编辑sc.yaml文件
[root@k8s-master efk]# cat sc.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: nfs-storage
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
provisioner: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "true" ## 删除pv的时候,pv的内容是否要备份
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/lfy_k8s_images/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.2
# resources:
# limits:
# cpu: 10m
# requests:
# cpu: 10m
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: k8s-sigs.io/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 192.168.3.201 ## 指定自己nfs服务器地址
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /nfs/data ## nfs服务器共享的目录
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 192.168.3.201
path: /nfs/data
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3.应用sc.ymal文件
[root@k8s-master efk]# kubectl apply -f sc.yaml
4.检查sc相关pod
[root@k8s-master efk]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nfs-client-provisioner-779b7f4dfd-zpqmt 1/1 Running 0 8s
5.测试pv
①编写pv.yaml
[root@k8s-master efk]# cat pv.yaml
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 200Mi
②运行pv
kubectl apply -f pv.yaml
③检查pv和pvc状态
[root@k8s-master efk]# kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
pvc-939faa36-9c19-4fd9-adc9-cb30b270de75 200Mi RWX Delete Bound default/nginx-pvc nfs-storage 40s
[root@k8s-master efk]# kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
nginx-pvc Bound pvc-939faa36-9c19-4fd9-adc9-cb30b270de75 200Mi RWX nfs-storage 44
四、安装helm工具
1.下载helm二进制包
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.9.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
2.解压下载的helm压缩包
tar -xzf helm-v3.9.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
3.复制helm文件
cp -a linux-amd64/helm /usr/bin/helm
4.查看helm版本
[root@k8s-master addons]# helm version
version.BuildInfoVersion:"v3.9.0", GitCommit:"7ceeda6c585217a19a1131663d8cd1f7d641b2a7", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.17.5"
五、配置helm仓库
1.添加efk相关组件的helm源
[root@k8s-master ~]# helm repo add stable https://apphub.aliyuncs.com
"stable" has been added to your repositories
[root@k8s-master ~]# helm repo add elastic https://helm.elastic.co
"elastic" has been added to your repositories
[root@k8s-master ~]# helm repo add azure http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts/
"azure" has been added to your repositories
[root@k8s-master ~]#
2.查看helm仓库
[root@k8s-master ~]# helm repo list
NAME URL
stable https://apphub.aliyuncs.com
elastic https://helm.elastic.co
azure http://mirror.azure.cn/kubernetes/charts/
六、安装Elasticsearch
1.下载Elasticsearch的chart包
[root@k8s-master efk]# helm pull elastic/elasticsearch
2.解压tar包
[root@k8s-master efk]# tar -xzf elasticsearch-7.17.3.tgz
3.修改yaml文件
①修改replicas
vim elasticsearch/values.yaml
replicas: 2
minimumMasterNodes: 1
esMajorVersion: ""
②关闭持久存储(可选)
##
persistence:
enabled: false
labels:
# Add default labels for the volumeClaimTemplate of the StatefulSet
enabled: false
annotations:
4.安装Elasticsearch应用
helm install elastic elasticsearch
5.查看运行pod
[root@k8s-master efk]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cirror-28253 1/1 Running 0 135m
elasticsearch-master-0 1/1 Running 0 2m11s
elasticsearch-master-1 1/1 Running 0 2m11s
nfs-client-provisioner-779b7f4dfd-p7xsz 1/1 Running 0 3h31m
七、安装filebeat
1.下载filebeat
[root@k8s-master efk]# helm pull elastic/filebeat
2.解压tar包
[root@k8s-master efk]# tar -xzf filebeat-7.17.3.tgz
3查看values.yaml文件
[root@k8s-master filebeat]# cat values.yaml -n
1 ---
2 daemonset:
3 # Annotations to apply to the daemonset
4 annotations:
5 # additionals labels
6 labels:
7 affinity:
8 # Include the daemonset
9 enabled: true
10 # Extra environment variables for Filebeat container.
11 envFrom: []
12 # - configMapRef:
13 # name: config-secret
14 extraEnvs: []
15 # - name: MY_ENVIRONMENT_VAR
16 # value: the_value_goes_here
17 extraVolumes:
18 []
19 # - name: extras
20 # emptyDir:
21 extraVolumeMounts:
22 []
23 # - name: extras
24 # mountPath: /usr/share/extras
25 # readOnly: true
26 hostNetworking: false
27 # Allows you to add any config files in /usr/share/filebeat
28 # such as filebeat.yml for daemonset
29 filebeatConfig:
30 filebeat.yml: |
31 filebeat.inputs:
32 - type: container
33 paths:
34 - /var/log/containers/*.log
35 processors:
36 - add_kubernetes_metadata:
37 host: $NODE_NAME
38 matchers:
39 - logs_path:
40 logs_path: "/var/log/containers/"
41
42 output.elasticsearch:
43 host: '$NODE_NAME'
44 hosts: '$ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS:elasticsearch-master:9200'
45 # Only used when updateStrategy is set to "RollingUpdate"
46 maxUnavailable: 1
47 nodeSelector:
48 # A list of secrets and their paths to mount inside the pod
49 # This is useful for mounting certificates for security other sensitive values
50 secretMounts: []
51 # - name: filebeat-certificates
52 # secretName: filebeat-certificates
53 # path: /usr/share/filebeat/certs
54 # Various pod security context settings. Bear in mind that many of these have an impact on Filebeat functioning properly.
55 #
56 # - User that the container will execute as. Typically necessary to run as root (0) in order to properly collect host container logs.
57 # - Whether to execute the Filebeat containers as privileged containers. Typically not necessarily unless running within environments such as OpenShift.
58 securityContext:
59 runAsUser: 0
60 privileged: false
61 resources:
62 requests:
63 cpu: "100m"
64 memory: "100Mi"
65 limits:
66 cpu: "1000m"
67 memory: "200Mi"
68 tolerations: []
69
70 deployment:
71 # Annotations to apply to the deployment
72 annotations:
73 # additionals labels
74 labels:
75 affinity:
76 # Include the deployment
77 enabled: false
78 # Extra environment variables for Filebeat container.
79 envFrom: []
80 # - configMapRef:
81 # name: config-secret
82 extraEnvs: []
83 # - name: MY_ENVIRONMENT_VAR
84 # value: the_value_goes_here
85 # Allows you to add any config files in /usr/share/filebeat
86 extraVolumes: []
87 # - name: extras
88 # emptyDir:
89 extraVolumeMounts: []
90 # - name: extras
91 # mountPath: /usr/share/extras
92 # readOnly: true
93 # such as filebeat.yml for deployment
94 filebeatConfig:
95 filebeat.yml: |
96 filebeat.inputs:
97 - type: tcp
98 max_message_size: 10MiB
99 host: "localhost:9000"
100
101 output.elasticsearch:
102 host: '$NODE_NAME'
103 hosts: '$ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS:elasticsearch-master:9200'
104 nodeSelector:
105 # A list of secrets and their paths to mount inside the pod
106 # This is useful for mounting certificates for security other sensitive values
107 secretMounts: []
108 # - name: filebeat-certificates
109 # secretName: filebeat-certificates
110 # path: /usr/share/filebeat/certs
111 #
112 # - User that the container will execute as.
113 # Not necessary to run as root (0) as the Filebeat Deployment use cases do not need access to Kubernetes Node internals
114 # - Typically not necessarily unless running within environments such as OpenShift.
115 securityContext:
116 runAsUser: 0
117 privileged: false
118 resources:
119 requests:
120 cpu: "100m"
121 memory: "100Mi"
122 limits:
123 cpu: "1000m"
124 memory: "200Mi"
125 tolerations: []
126
127 # Replicas being used for the filebeat deployment
128 replicas: 1
129
130 extraContainers: ""
131 # - name: dummy-init
132 # image: busybox
133 # command: ['echo', 'hey']
134
135 extraInitContainers: []
136 # - name: dummy-init
137
138 # Root directory where Filebeat will write data to in order to persist registry data across pod restarts (file position and other metadata).
139 hostPathRoot: /var/lib
140
141 dnsConfig:
142 # options:
143 # - name: ndots
144 # value: "2"
145 hostAliases: []
146 #- ip: "127.0.0.1"
147 # hostnames:
148 # - "foo.local"
149 # - "bar.local"
150 image: "docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat"
151 imageTag: "7.17.3"
152 imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
153 imagePullSecrets: []
154
155 livenessProbe:
156 exec:
157 command:
158 - sh
159 - -c
160 - |
161 #!/usr/bin/env bash -e
162 curl --fail 127.0.0.1:5066
163 failureThreshold: 3
164 initialDelaySeconds: 10
165 periodSeconds: 10
166 timeoutSeconds: 5
167
168 readinessProbe:
169 exec:
170 command:
171 - sh
172 - -c
173 - |
174 #!/usr/bin/env bash -e
175 filebeat test output
176 failureThreshold: 3
177 initialDelaySeconds: 10
178 periodSeconds: 10
179 timeoutSeconds: 5
180
181 # Whether this chart should self-manage its service account, role, and associated role binding.
182 managedServiceAccount: true
183
184 clusterRoleRules:
185 - apiGroups:
186 - ""
187 resources:
188 - namespaces
189 - nodes
190 - pods
191 verbs:
192 - get
193 - list
194 - watch
195 - apiGroups:
196 - "apps"
197 resources:
198 - replicasets
199 verbs:
200 - get
201 - list
202 - watch
203
204 podAnnotations:
205
206 # iam.amazonaws.com/role: es-cluster
207
208 # Custom service account override that the pod will use
209 serviceAccount: ""
210
211 # Annotations to add to the ServiceAccount that is created if the serviceAccount value isn't set.
212 serviceAccountAnnotations:
213
214 # eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::111111111111:role/k8s.clustername.namespace.serviceaccount
215
216 # How long to wait for Filebeat pods to stop gracefully
217 terminationGracePeriod: 30
218 # This is the PriorityClass settings as defined in
219 # https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
220 priorityClassName: ""
221
222 updateStrategy: RollingUpdate
223
224 # Override various naming aspects of this chart
225 # Only edit these if you know what you're doing
226 nameOverride: ""
227 fullnameOverride: ""
228
229 # DEPRECATED
230 affinity:
231 envFrom: []
232 extraEnvs: []
233 extraVolumes: []
234 extraVolumeMounts: []
235 # Allows you to add any config files in /usr/share/filebeat
236 # such as filebeat.yml for both daemonset and deployment
237 filebeatConfig:
238 nodeSelector:
239 podSecurityContext:
240 resources:
241 secretMounts: []
242 tolerations: []
243 labels:
4.安装filebeat
[root@k8s-master efk]# helm install fb filebeat
NAME: fb
LAST DEPLOYED: Sun Jul 3 13:03:21 2022
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
1. Watch all containers come up.
$ kubectl get pods --namespace=default -l app=fb-filebeat -w
5.查看filebeat相关pod
[root@k8s-master efk]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cirror-28253 1/1 Running 0 151m
elasticsearch-master-0 1/1 Running 0 18m
elasticsearch-master-1 1/1 Running 0 18m
fb-filebeat-8fhg7 1/1 Running 0 5m17s
fb-filebeat-lj5p7 1/1 Running 0 5m17s
nfs-client-provisioner-779b7f4dfd-p7xsz 1/1 Running 0 3h47m
八、安装metricbeat
1.下载metricbeat
helm pull stable/metricbeat
2.解压tar包
[root@k8s-master efk]# tar -xzf metricbeat-1.7.1.tgz
3.安装metricbeat
[root@k8s-master efk]# helm install metric metricbeat
4.查看metricbeat相关pod
[root@k8s-master efk]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cirror-28253 1/1 Running 0 3h26m
elasticsearch-master-0 1/1 Running 0 73m
elasticsearch-master-1 1/1 Running 0 73m
fb-filebeat-8fhg7 1/1 Running 0 60m
fb-filebeat-lj5p7 1/1 Running 0 60m
metric-metricbeat-4jbkk 1/1 Running 0 22s
metric-metricbeat-5h5g5 1/1 Running 0 22s
metric-metricbeat-758c5c674-ldgg4 1/1 Running 0 22s
metric-metricbeat-bdth2 1/1 Running 0 22s
nfs-client-provisioner-779b7f4dfd-p7xsz 1/1 Running 0 4h42m
九、安装kibana
1.下载安装kibana
helm pull elastic/kibana
2.解压kibana的tar包
tar -xzf kibana-7.17.3.tgz
3.修改服务类型
[root@k8s-master kibana]# vim values.yaml
##
service:
port: 80
type: NodePort
## Specify the nodePort value for the LoadBalancer and NodePort service types.
## ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/#type-nodeport
4.配置Elasticsearch地址
## Properties for Elasticsearch
##
elasticse以上是关于kubernetes集群搭建efk日志收集平台的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
DEVOPS架构师 -- 04Kubernetes集群的日志及监控-更新版