Java Annotation —— 注解实战
Posted 福州-司马懿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java Annotation —— 注解实战相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Annotation是Java5、6只后的新特征(中文称之为注解),并且越来越多的得到了应用,比如Spring、Hibernate3、Struts2、iBatis3、JPA、JUnit等等都得到了广泛应用,通过使用注解,代码的灵活性大大提高。这些都是使用别人定义的注解,一般注解的使用都是在一些基础框架或者类库中来定义的,因此很少见过有人自己去写一个注解出来并使用在程序中。
一、注解的好处在于
通过类似注释的方式,可以控制程序的一些行为,运行时的状态,可以为成员赋值,做配置信息等等,与常规编码思维大相径庭。只用别人定义好的注解是搞不懂这些问题的,要想真正知道注解内部的秘密,要自己定义注解,然后在程序中获取注解信息,拿到注解信息后,就可以为我所用了。
下面我简单演示下三类注解的用法:类注解、方法注解、字段(也称之域)注解的定义与适用,并看看如何获取注解的信息。
二、使用注意点
(1)自定义注解,注意注解的时空范围,简单说就是注解针对的目标(类、方法、字段),以及注解的时效(运行时、或者源码中有效)。
(2)要获取注解的信息,必须通过Java的反射技术来获取Annotation对象,因为你除此之外没有别的获取注解对象的方法。
(3)获取了注解对象,就可以调用注解的方法来获取相对应的值了。为基础框架所用。
(4)当然,注解也可以没有定义成员,这样注解就成了一个标记符号了。
三、代码实战:
(1)AnnotationInterfaceFIELD.java
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface AnnotationInterfaceFIELD
public String descriptionFIELD();
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD
public String descriptionMETHOD();
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//@Retention(value=RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
//@Target(ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface AnnotationInterfaceTYPE
String name() default "bob";
int age() default 24;
package com.demo.annotation;
@AnnotationInterfaceTYPE(name="chy龙神的博客",age=24)
public class AnnotationTestClass
@AnnotationInterfaceFIELD(descriptionFIELD="annotation private field")
private String privateField;
@AnnotationInterfaceFIELD(descriptionFIELD="annotation protected field")
protected String protectedField;
@AnnotationInterfaceFIELD(descriptionFIELD="annotation public field")
public String publicField;
@AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD(descriptionMETHOD="annotation private method")
public void privateMethod()
@AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD(descriptionMETHOD="annotation protected method")
public void protectedMethod()
@AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD(descriptionMETHOD="annotation public method")
public void publicMethod()
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AnnotationTestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
AnnotationTestClass cls = new AnnotationTestClass();
try
Class annotationCls = Class.forName("com.demo.annotation.AnnotationInterfaceTYPE");
if(cls.getClass().isAnnotationPresent(annotationCls))
System.out.println("\\nAnnotation Type=====================");
AnnotationInterfaceTYPE annotationType = cls.getClass().getAnnotation(AnnotationInterfaceTYPE.class);
System.out.println("annotationType.name = " + annotationType.name());
System.out.println("annotationType.name = " + annotationType.age());
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("\\nAnnotation Field====================");
//getField只能获取类的public字段
Field[] fields = cls.getClass().getFields();
System.out.println("1、getField"+"("+fields.length+")");
dumpFields(fields);
//getDeclaredField是可以获取一个类的所有字段
Field[] declardFields = cls.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
System.out.println("\\n2、getDeclaredField"+"("+declardFields.length+")");
dumpFields(declardFields);
try
Field mField = cls.getClass().getDeclaredField("publicField");
AnnotationInterfaceFIELD mAnnotationField = mField.getAnnotation(AnnotationInterfaceFIELD.class);
System.out.println(mAnnotationField.descriptionFIELD());
catch (NoSuchFieldException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("\\nAnnotation Method===================");
Method[] methods = cls.getClass().getMethods();
System.out.println("1、getMethod"+"("+methods.length+")");
dumpMethods(methods);
Method[] declardMethods = cls.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println("\\n2、getDeclaredMethod"+"("+declardMethods.length+")");
dumpMethods(declardMethods);
try
Method mMethod = cls.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("publicMethod");
AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD mAnnotatMethod = mMethod.getAnnotation(AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD.class);
System.out.println(mAnnotatMethod.descriptionMETHOD());
catch (NoSuchMethodException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (SecurityException e)
e.printStackTrace();
public static void dumpFields(Field[] fields)
for(int i=0;i<fields.length;i++)
System.out.println("("+i+")"+fields[i].getName());
public static void dumpMethods(Method[] methods)
for(int i=0;i<methods.length;i++)
System.out.println("("+i+")"+methods[i].getName());
Annotation是Java5、6只后的新特征(中文称之为注解),并且越来越多的得到了应用,比如Spring、Hibernate3、Struts2、iBatis3、JPA、JUnit等等都得到了广泛应用,通过使用注解,代码的灵活性大大提高。这些都是使用别人定义的注解,一般注解的使用都是在一些基础框架或者类库中来定义的,因此很少见过有人自己去写一个注解出来并使用在程序中。
一、注解的好处在于
通过类似注释的方式,可以控制程序的一些行为,运行时的状态,可以为成员赋值,做配置信息等等,与常规编码思维大相径庭。只用别人定义好的注解是搞不懂这些问题的,要想真正知道注解内部的秘密,要自己定义注解,然后在程序中获取注解信息,拿到注解信息后,就可以为我所用了。
下面我简单演示下三类注解的用法:类注解、方法注解、字段(也称之域)注解的定义与适用,并看看如何获取注解的信息。
二、使用注意点
(1)自定义注解,注意注解的时空范围,简单说就是注解针对的目标(类、方法、字段),以及注解的时效(运行时、或者源码中有效)。
(2)要获取注解的信息,必须通过Java的反射技术来获取Annotation对象,因为你除此之外没有别的获取注解对象的方法。
(3)获取了注解对象,就可以调用注解的方法来获取相对应的值了。为基础框架所用。
(4)当然,注解也可以没有定义成员,这样注解就成了一个标记符号了。
三、代码实战:
(1)AnnotationInterfaceFIELD.java
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface AnnotationInterfaceFIELD
public String descriptionFIELD();
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD
public String descriptionMETHOD();
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//@Retention(value=RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
//@Target(ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface AnnotationInterfaceTYPE
String name() default "bob";
int age() default 24;
package com.demo.annotation;
@AnnotationInterfaceTYPE(name="chy龙神的博客",age=24)
public class AnnotationTestClass
@AnnotationInterfaceFIELD(descriptionFIELD="annotation private field")
private String privateField;
@AnnotationInterfaceFIELD(descriptionFIELD="annotation protected field")
protected String protectedField;
@AnnotationInterfaceFIELD(descriptionFIELD="annotation public field")
public String publicField;
@AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD(descriptionMETHOD="annotation private method")
public void privateMethod()
@AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD(descriptionMETHOD="annotation protected method")
public void protectedMethod()
@AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD(descriptionMETHOD="annotation public method")
public void publicMethod()
package com.demo.annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AnnotationTestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
AnnotationTestClass cls = new AnnotationTestClass();
try
Class annotationCls = Class.forName("com.demo.annotation.AnnotationInterfaceTYPE");
if(cls.getClass().isAnnotationPresent(annotationCls))
System.out.println("\\nAnnotation Type=====================");
AnnotationInterfaceTYPE annotationType = cls.getClass().getAnnotation(AnnotationInterfaceTYPE.class);
System.out.println("annotationType.name = " + annotationType.name());
System.out.println("annotationType.name = " + annotationType.age());
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("\\nAnnotation Field====================");
//getField只能获取类的public字段
Field[] fields = cls.getClass().getFields();
System.out.println("1、getField"+"("+fields.length+")");
dumpFields(fields);
//getDeclaredField是可以获取一个类的所有字段
Field[] declardFields = cls.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
System.out.println("\\n2、getDeclaredField"+"("+declardFields.length+")");
dumpFields(declardFields);
try
Field mField = cls.getClass().getDeclaredField("publicField");
AnnotationInterfaceFIELD mAnnotationField = mField.getAnnotation(AnnotationInterfaceFIELD.class);
System.out.println(mAnnotationField.descriptionFIELD());
catch (NoSuchFieldException e)
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("\\nAnnotation Method===================");
Method[] methods = cls.getClass().getMethods();
System.out.println("1、getMethod"+"("+methods.length+")");
dumpMethods(methods);
Method[] declardMethods = cls.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println("\\n2、getDeclaredMethod"+"("+declardMethods.length+")");
dumpMethods(declardMethods);
try
Method mMethod = cls.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("publicMethod");
AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD mAnnotatMethod = mMethod.getAnnotation(AnnotationInterfaceMETHOD.class);
System.out.println(mAnnotatMethod.descriptionMETHOD());
catch (NoSuchMethodException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (SecurityException e)
e.printStackTrace();
public static void dumpFields(Field[] fields)
for(int i=0;i<fields.length;i++)
System.out.println("("+i+")"+fields[i].getName());
public static void dumpMethods(Method[] methods)
for(int i=0;i<methods.length;i++)
System.out.println("("+i+")"+methods[i].getName());
四、运行截图:
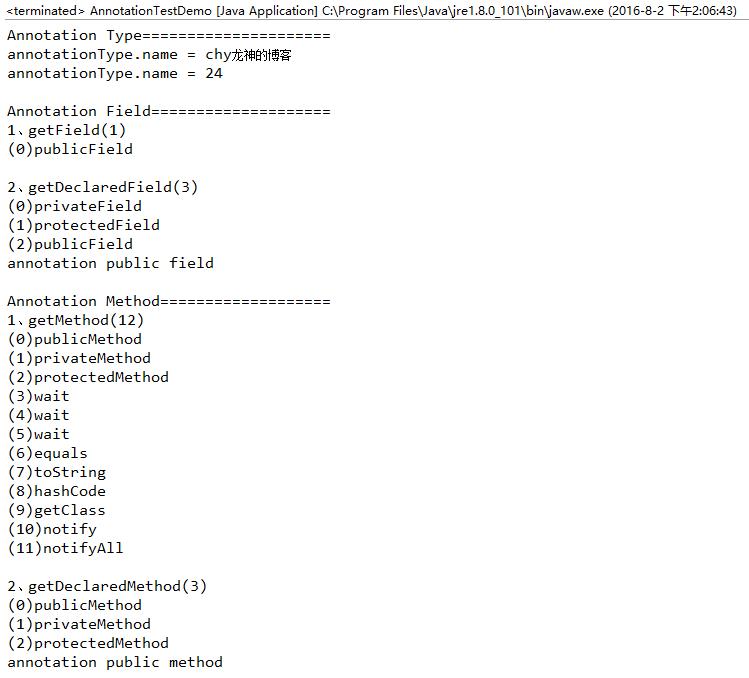
补充:个人感觉其实对于“class的注解”与“添加基类的共有方法”无异。
以上是关于Java Annotation —— 注解实战的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章