quasi-maximum likelihood decoder一种有效的PSK信号准最大似然译码器matlab性能仿真
Posted fpga和matlab
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了quasi-maximum likelihood decoder一种有效的PSK信号准最大似然译码器matlab性能仿真相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.软件版本
matlab2013b
2.本算法实现
本算法主要参考文献:
《[1] Luo Z Q , Luo X , Kisialiou M . An efficient quasi-maximum likelihood decoder for PSK signals[C]// IEEE. IEEE, 2003.》
Since exact maximum likelihood (ML) detection is computationally intractable in general, approximate ML approaches are needed to reduce the computation time while maintaining low bit error rate (BER). In this work, we develop an efficient approximate ML decoder for constant modulus signals based on a simple nonlinear programming relaxation. Unlike the existing sphere decoder whose expected complexity is cubic in problem size and whose performance deteriorates with increasing problem size and noise level, our proposed new decoder enjoys a worst case quadratic complexity and scales gracefully with problem dimension and noise level. Our initial testing and analysis suggests that this new decoder is capable of delivering ML like BER performance for PSK signals while requiring substantially lower computational complexity. In this sense, our new decoder is similar to the sphere decoder which is an effective method for QAM signals.
算法流程图如下所示:

3.部分源码
clc;
clear all;
close all;
warning off;
SNR = 1:8;
%统计无码数
Times = 500;
%m
Tm = 10;
%n
Rn = 10;
%仿真序列帧长度
data_Numbers = 300;
for i=1:length(SNR)
Bit_err(i) = 0;
Num_err = 0;
Numbers = 0; %误码率累加器
N0 = 10/(10^(SNR(i)/10));
while Num_err <= Times
Num_err
fprintf('SNR = %f\\n', SNR(i));
%产生需要发送的随机数
Trans_data = round(rand(1,data_Numbers));
%BPSK
Trans_BPSK = 2*Trans_data-1;
%作为发送信源
MIMO_Tx(1,:) = Trans_BPSK;
for send_loop = 2:Tm
MIMO_Tx(send_loop,:) = MIMO_Tx(1,:);
end
%信道
H_Ray = (randn(Rn,Tm)+sqrt(-1)*randn(Rn,Tm))/sqrt(2);
H_Ray = abs(H_Ray);
%QUASI-ML PSK decoder算法
for k=1:data_Numbers
y = H_Ray*MIMO_Tx(:,k) + 2*N0*randn(size(H_Ray*MIMO_Tx(:,k)));
y = y/max(max(abs(y)));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
e0 = 0.5;
beta0 = 0.4;
n1 = 10;
n2 = 10;
ee = zeros(n1,1);
%STEP1
for i1 = 1:n1
ee(i1) = -i1*e0/(n1-1) + n1*e0/(n1-1);
x1s = [-1-ee(i1)+(2+2*ee(i1))/Tm:(2+2*ee(i1))/Tm:1+ee(i1)];
for k1 = 1:Tm
x1 = x1s(k1)*ones(Tm,1);
f1(k1) = x1'*H_Ray'*H_Ray*x1 - y'*H_Ray*x1 - x1'*H_Ray'*y + y'*y;
end
[g1(i1),xk1(i1)] = min(f1);
end
[g11,xk11] = min(g1);
XK1 = y(xk1(xk11));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%STEP2
M = 64;
for i2 = 1:n2
beta(i2) = -i1*beta0/(n2-1) + n2*e0/(n2-1);
deltaa(i2) = 2*pi*(i2-1)/(M*(n2-1));
x2s = [-1-beta(i2)+(2+2*beta(i2))/Tm:(2+2*beta(i2))/Tm:1+beta(i2)];
for k2 = 1:Tm
x2 = x2s(k2)*ones(Tm,1);
f2(i2,k2) = x2'*H_Ray'*H_Ray*x2 - y'*H_Ray*x2 - x2'*H_Ray'*y + y'*y;
end
end
for k2 = 1:Tm
[g2,xk2] = min(f2(:,k2));
XK2(k2) = y(xk2);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%STEP3
a5(:,k) = XK2;
end
%接收
MIMO_Rx = a5;
MIMO_Rx2 = ones(1,Tm)*MIMO_Rx(:,:);
Rec_data =(sign(MIMO_Rx2)+1)/2;
[nberr,rat] = biterr(Trans_data,Rec_data);
Num_err = Num_err+nberr;
Numbers = Numbers+1;
end
Bit_err(i)=Num_err/(data_Numbers*Numbers);
end
figure;
semilogy(SNR,Bit_err,'o-r');
xlabel('SNR(dB)');
ylabel('BER');
grid on;
% save BPSK_10_err.mat SNR Bit_err
clc;
clear all;
close all;
warning off;
SNR = 5;
%统计无码数
Times = 5000;
%m
NN = [2:2:16];
complexity = zeros(1,length(NN));
for jjj = 1:length(NN)
tic;
Tm = NN(jjj);
%n
Rn = Tm;
%仿真序列帧长度
data_Numbers = 300;
for i=1:length(SNR)
Bit_err(i) = 0;
Num_err = 0;
Numbers = 0; %误码率累加器
N0 = 10/(10^(SNR(i)/10));
while Num_err <= Times
Num_err
Tm
%产生需要发送的随机数
Trans_data = round(rand(1,2*data_Numbers));
%QPSK
QPSK_IQ = [-1 1];
QPSK_input_I = QPSK_IQ(Trans_data(1:2:end)+1);
QPSK_input_Q = QPSK_IQ(Trans_data(2:2:end)+1);
Trans_QPSK =(QPSK_input_I + sqrt(-1) * QPSK_input_Q)/sqrt(2);
%作为发送信源
MIMO_Tx(1,:) = Trans_QPSK;
for send_loop = 2:Tm
MIMO_Tx(send_loop,:) = MIMO_Tx(1,:);
end
%信道
H_Ray = (randn(Rn,Tm)+sqrt(-1)*randn(Rn,Tm))/sqrt(2);
H_Ray = abs(H_Ray);
%QUASI-ML PSK decoder算法
for k=1:data_Numbers
y = H_Ray*MIMO_Tx(:,k) + 2*N0*randn(size(H_Ray*MIMO_Tx(:,k)));
y = y/max(max(abs(y)));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
e0 = 0.5;
beta0 = 0.4;
n1 = 10;
n2 = 10;
ee = zeros(n1,1);
%STEP1
for i1 = 1:n1
ee(i1) = -i1*e0/(n1-1) + n1*e0/(n1-1);
x1s = [-1-ee(i1)+(2+2*ee(i1))/Tm:(2+2*ee(i1))/Tm:1+ee(i1)];
for k1 = 1:Tm
x1 = x1s(k1)*ones(Tm,1);
f1(k1) = x1'*H_Ray'*H_Ray*x1 - y'*H_Ray*x1 - x1'*H_Ray'*y + y'*y;
end
[g1(i1),xk1(i1)] = min(f1);
end
[g11,xk11] = min(g1);
XK1 = y(xk1(xk11));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%STEP2
M = 64;
for i2 = 1:n2
beta(i2) = -i1*beta0/(n2-1) + n2*e0/(n2-1);
deltaa(i2) = 2*pi*(i2-1)/(M*(n2-1));
x2s = [-1-beta(i2)+(2+2*beta(i2))/Tm:(2+2*beta(i2))/Tm:1+beta(i2)];
for k2 = 1:Tm
x2 = x2s(k2)*ones(Tm,1);
f2(i2,k2) = x2'*H_Ray'*H_Ray*x2 - y'*H_Ray*x2 - x2'*H_Ray'*y + y'*y;
end
end
for k2 = 1:Tm
[g2,xk2] = min(f2(:,k2));
XK2(k2) = y(xk2);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%STEP3
a5(:,k) = XK2;
end
%接收
MIMO_Rx = a5;
MIMO_Rx2 = ones(1,Tm)*MIMO_Rx(:,:);
%QPSK解调
QPSK_input_I = real(MIMO_Rx2);
QPSK_input_Q = imag(MIMO_Rx2);
QPSK_Demodu_IQ = [0,1]; %f(m)=(m+1)/2 + 1, so I=-1 ---> 1, I=1 ---> 2
idx = find(QPSK_input_I>1);
QPSK_input_I(idx) = 1;
idx = find(QPSK_input_I<-1);
QPSK_input_I(idx) = -1;
idx = find(QPSK_input_Q>1);
QPSK_input_Q(idx) = 1;
idx = find(QPSK_input_Q<-1);
QPSK_input_Q(idx) = -1;
Rec_data = zeros(1,length(MIMO_Rx2)*2);
Rec_data(1:2:end) = QPSK_Demodu_IQ(round((QPSK_input_I+1)/2) + 1);
Rec_data(2:2:end) = QPSK_Demodu_IQ(round((QPSK_input_Q+1)/2) + 1);
[nberr,rat] = biterr(Trans_data,Rec_data);
Num_err = Num_err+nberr;
Numbers = Numbers+1;
end
Bit_err(i)=Num_err/(data_Numbers*Numbers);
end
complexity(jjj)=toc/Numbers;
clear MIMO_Tx H_Ray y ee x1s x1 f1 g1 xk11 XK1 beta deltaa x2s x2 f2 XK2 a5
end
figure;
plot(NN,complexity,'b-o');
xlabel('size');
ylabel('complexity');
save CSNR5.mat NN complexity4.仿真结论
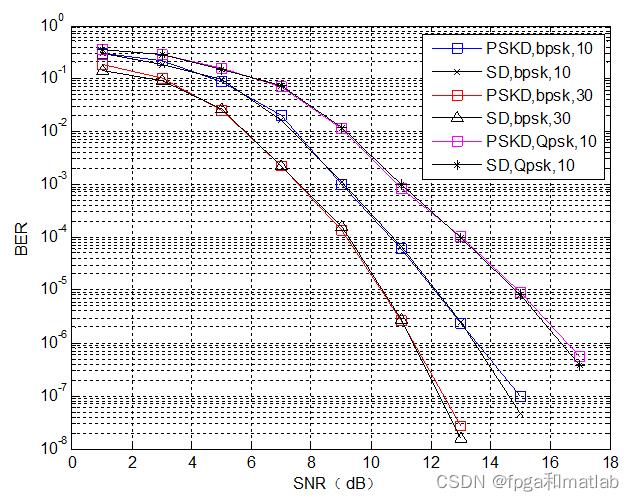
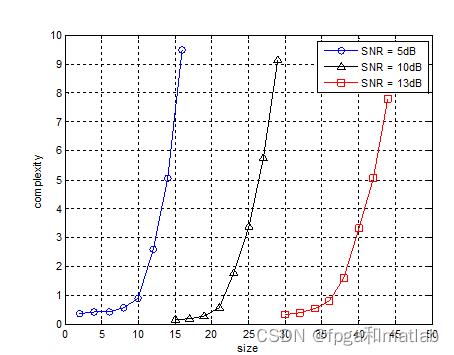
4.参考文献
[1] Luo Z Q , Luo X , Kisialiou M . An efficient quasi-maximum likelihood decoder for PSK signals[C]// IEEE. IEEE, 2003.A01-108
以上是关于quasi-maximum likelihood decoder一种有效的PSK信号准最大似然译码器matlab性能仿真的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章