android Input专题- Q/R/S 10/11/12 InputManager源码分析
Posted Android高级知识分享官
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了android Input专题- Q/R/S 10/11/12 InputManager源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android手机大厂Framework系统-Input系统专题实战课
https://ke.qq.com/course/4963459
[入门课,实战课,跨进程专题
ps需要学习深入framework课程和课程优惠
新课程优惠获取请加入qq群:422901085
1、SystemServer中InputManagerService创建与启动
base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startOtherServices()
//省略部分
traceBeginAndSlog("StartInputManagerService");
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("StartWindowManagerService");
// WMS needs sensor service ready
ConcurrentUtils.waitForFutureNoInterrupt(mSensorServiceStart, START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
mSensorServiceStart = null;
wm = WindowManagerService.main(context, inputManager, !mFirstBoot, mOnlyCore,
new PhoneWindowManager(), mActivityManagerService.mActivityTaskManager);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, wm, /* allowIsolated= */ false,
DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager,
/* allowIsolated= */ false, DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
traceEnd();
//省略部分
traceBeginAndSlog("StartInputManager");
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputManagerCallback());
inputManager.start();//这里再调用start
traceEnd();
//省略部分
这里以前讲过在SystemServer中会对系统中很多service进行启动,这里我们就发现有对InputManagerService进行对应的构造和添加
2、Native层面的InputManager启动
public InputManagerService(Context context)
this.mContext = context;
this.mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(DisplayThread.get().getLooper());
//省略部分
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());
//省略部分
这里InputManagerService构造方法中就是调用了nativeInit,这个方法是native方法
来看看对应的native方法:
base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jobject serviceObj, jobject contextObj, jobject messageQueueObj)
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
if (messageQueue == nullptr)
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "MessageQueue is not initialized.");
return 0;
NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj, serviceObj,
messageQueue->getLooper());
im->incStrong(0);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(im);
这里主要就是构造了一个NativeInputManager:
base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager(jobject contextObj,
jobject serviceObj, const sp<Looper>& looper) :
mLooper(looper), mInteractive(true)
//省略部分
mInputManager = new InputManager(this, this);
defaultServiceManager()->addService(String16("inputflinger"),
mInputManager, false);
这里主要就是对我们InputManager进行构造,然后把它添加到了servicemanager,而且传递的两个参数都是NativeInputManager类本身
这里它的类结构其实是实现了几个接口方便InputManager里面传递和调用:
base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
class NativeInputManager : public virtual RefBase,
public virtual InputReaderPolicyInterface,
public virtual InputDispatcherPolicyInterface,
public virtual PointerControllerPolicyInterface
那么接下来重点就分析我们的InputManager构造:
native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy)
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
mClassifier = new InputClassifier(mDispatcher);
mReader = createInputReader(readerPolicy, mClassifier);
initialize();
这里首先是进行了new InputDispatcher,再是把构造对象作为InputClassifier的构造参数,然后再是createInputReader,而且把InputClassifier对象也传递给了InputReader,看看createInputReader:
sp<InputReaderInterface> createInputReader(
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener)
return new InputReader(new EventHub(), policy, listener);
InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) :
mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy),
mNextSequenceNum(1), mGlobalMetaState(0), mGeneration(1),
mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0)
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);//listener是作为后面连接InputDispatcher纽带
// acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
//第一次执行时候,一般都是一些初始化的,还没获取到真正一些devices相关信息
refreshConfigurationLocked(0);
updateGlobalMetaStateLocked();
// release lock
这里就是构造出了InputReader,而且传递了一个EventHub,也是立即构造的,整个input系统其实就是InputReader和InputDispatcher最为重要。而且二者其实也是间接相连的:
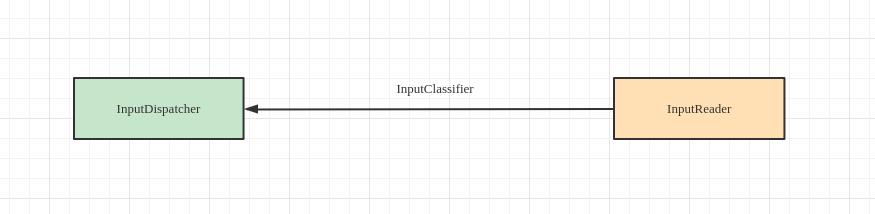
这样才方便后面InputReader读取加工好了数据就传递到InputDispatcher中,让InputDispatcher做下一步的传递工作。
再来看到有new一个EventHub,来看看它是干啥的:
native/services/inputflinger/EventHub.cpp
EventHub::EventHub(void) :
mBuiltInKeyboardId(NO_BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD), mNextDeviceId(1), mControllerNumbers(),
mOpeningDevices(nullptr), mClosingDevices(nullptr),
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan(false),
mNeedToReopenDevices(false), mNeedToScanDevices(true),
mPendingEventCount(0), mPendingEventIndex(0), mPendingINotify(false)
acquire_wake_lock(PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, WAKE_LOCK_ID);
mEpollFd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);
//省略部分
mINotifyFd = inotify_init();
mInputWd = inotify_add_watch(mINotifyFd, DEVICE_PATH, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE);
//省略部分
struct epoll_event eventItem;
memset(&eventItem, 0, sizeof(eventItem));
eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
eventItem.data.fd = mINotifyFd;
int result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mINotifyFd, &eventItem);
//省略部分
int wakeFds[2];
result = pipe(wakeFds);
mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];
mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
result = fcntl(mWakeReadPipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
result = fcntl(mWakeWritePipeFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
eventItem.data.fd = mWakeReadPipeFd;
result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, &eventItem);
//省略部分
我相信看到这里的EventHub,大家应该会有非常非常熟悉的想到getevent源码,二者其实本质的功能都是一样的,这里使用的epoll来监听各个fd的变化,getevent中使用是poll。
这里大概可以看出EventHub职责就是来获取/dev/input/路径设备的,及对数据进行获取,和getevent职责一样,后面再使用到的时候再进行具体分析。
接下来继续分析InputManager构造的最后一个方法initialize:
void InputManager::initialize()
mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader);
mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherThread(mDispatcher);
这里把mReaderThread和mDispatcherThread构造出来了,它们就是native层面的Thread对象,这里在入门课时候就已经讲解过了,但是这里只是创建了线程并没有启动,那么到这里构造部分就分析完成了,但是还没看到最关键的两个线程启动。其实这个启动是在文章一开始的SystemServer类中startOtherServices触发的,通过调用inputManager.start()方法:
base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
public void start()
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting input manager");
nativeStart(mPtr);
//省略部分
这里调用是nativeStart方法,有到了我们的native层:
base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jlong ptr)
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();
if (result)
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Input manager could not be started.");
这里其实只干了一件关键事情,调用了InputManager的start:
native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
status_t InputManager::start()
status_t result = mDispatcherThread->run("InputDispatcher",
PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY + PRIORITY_MORE_FAVORABLE);
//省略部分
result = mReaderThread->run("InputReader",
PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY + PRIORITY_MORE_FAVORABLE);
//省略部分
return OK;
这里其实就是干了把InputDispatcher和InputReader两个线程启动运行起来,那本节课就先分析到这里,目前就算把InputDispatcher和InputReader开始执行部分引出来了。
以上是关于android Input专题- Q/R/S 10/11/12 InputManager源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章