笔记:基于keras的不同神经网络模型Minst手写体识别
Posted Lil_D603
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了笔记:基于keras的不同神经网络模型Minst手写体识别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基于keras的不同神经网络模型MNIST手写体识别
1.CNN版
1.导入数据
相关库(导入plt是为了看数据集的图)
import keras
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPool2D,Activation,Dropout
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
以下是keras里的原装数据集mnist的源码
def load_data(path='mnist.npz'):
# Returns
Tuple of Numpy arrays: `(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)`.
"""
path = get_file(path,
origin='https://s3.amazonaws.com/img-datasets/mnist.npz',
file_hash='8a61469f7ea1b51cbae51d4f78837e45')
with np.load(path, allow_pickle=True) as f:
x_train, y_train = f['x_train'], f['y_train']
x_test, y_test = f['x_test'], f['y_test']
return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
这个load_data就相当于一个爬虫,函数得到(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test)
的返回值。
所以我们导入mnist的数据的时候,要这样来导入
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
接下来可以看看mnist数据集的数据特征(x_train和x_test是图像img,而x_test和y_test是图片的标签值 0~9)
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
plt.imshow(x_train[5]) x代表的都是手写体的图
plt.show()
# print(y_train)
# plt.imshow(x_test[0])
# plt.show()
# print(y_test)
(60000, 28, 28) (60000,) (10000, 28, 28) (10000,)
这是输出的数据特征(x_train是三维的矩阵,60000张/每张像素点28*28)
然后这个就是输出来的图像

2.数据处理:转换数据格式和归一化
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)
然后就是归一化 normalization
数据灰度最大就是255 归一化操作就是除255
x_train = x_train / 255
x_test = x_test / 255
再对标签值做个one_hot处理(独热处理可以应对0~9的多分类问题)
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test)
到这里 我们就基本把数据处理做好了
再来看看处理后的数据集的数据特征
print(x_train.shape) (60000, 28, 28, 1)
print(y_train.shape) (60000, 10)
print(x_test.shape) (10000, 28, 28, 1)
print(y_test.shape) (10000, 10)
思考:区别在哪?
3.建模(这里用的lenet5)
基本上是:卷积池化—再卷积池化—平铺—全连接*2—输出softmax
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(6, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding='same', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2))
model.add(Conv2D(16, kernel_size=5, strides=1, padding='valid'))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add((MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2)))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(120))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Dense(84))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
4.配置模型参数再训练
model.compile(optimizer='Adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=64, epochs=50, validation_split=0.2)

训练的时候就能体现出CNN相对于传统深层神经网络的优势了
耗时短,准确率也比较搞
5.评估模型
#做出训练集上loss同步变化的情况
plt.plot(model.history.history['loss'])
plt.title('loss')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.show()
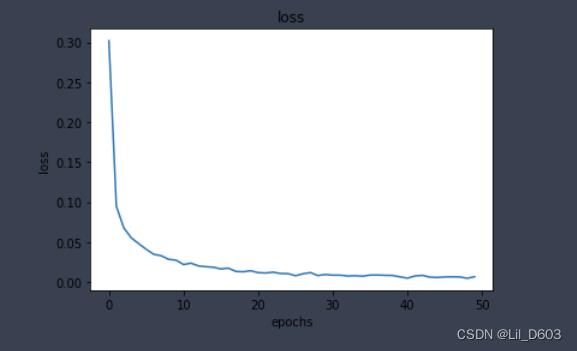
#做出训练集上accuracy同步变化的情况
plt.plot(model.history.history['accuracy'])
plt.title('loss')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.show()

以上是用lenet5(cnn)进行mnist手写体识别模型
后面还会继续更其他模型的
以上是关于笔记:基于keras的不同神经网络模型Minst手写体识别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章