Windows系统编译GSL2.7用于C语言编程(2022.5.8)
Posted jing_zhong
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Windows系统编译GSL2.7用于C语言编程(2022.5.8)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Windows系统编译GSL2.7用于C语言编程(2022.5.8)
- 1、 GSL(GNU Scientific Library)
- 2、Windows下利用MSYS2编译GSL库
- 3、基于GSL库编写C语言代码(CodeBlocks / Visual Studio)
- 4、总结
- 5、参考WIki
1、 GSL(GNU Scientific Library)
1.1 GSL简介
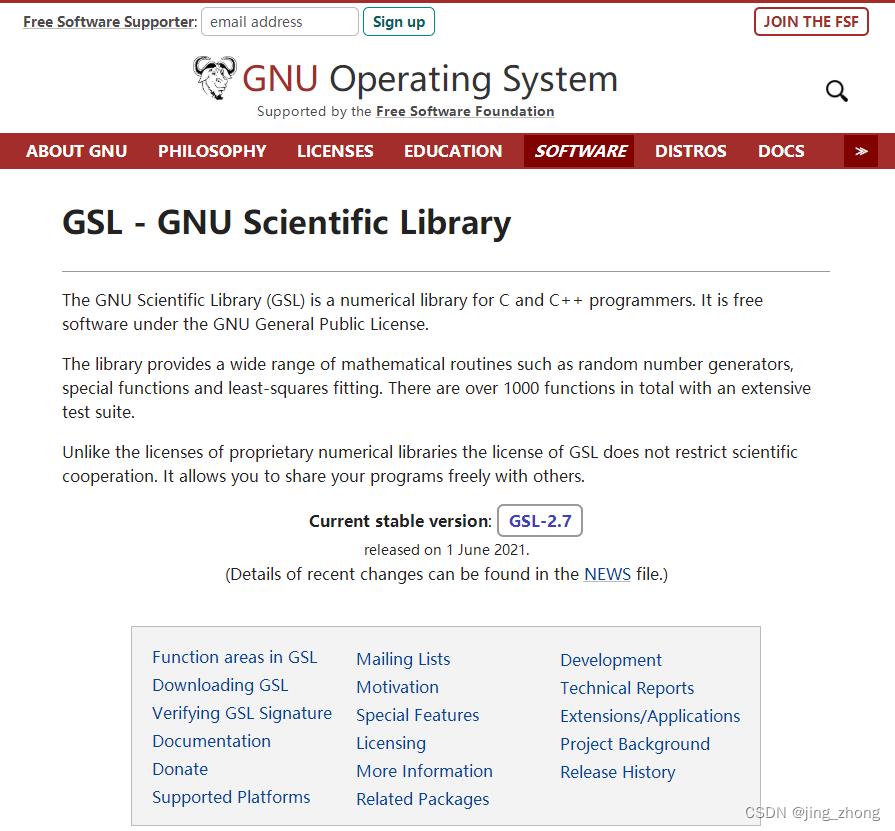
GSL(GNU Scientific Library)是一个面向C和C++编程语言的数值计算库,它是GNU General Public License通用公共许可下的开放软件。GSL库提供了大量的数学日常运算函数,涉及领域如随机数生成器、复数、向量、矩阵、排序、快速傅里叶变换、随机分布、统计、插值、离散小波变换、稀疏矩阵、线性代数、最小二乘拟合等,还允许自己与他人自由分享程序,代码开源,开发者可对用户社区贡献改进代码。GSL是在GNU/Linux平台上由gcc编译器所开发,满足GNU Coding Standards标准,同时其源码已被证实可以在Linux(gcc编译器)、Unix(gcc编译器) 和 Microsoft Windows等平台进行编译使用,但Window系统下编译较为困难,最好还是选择Linux系统编译,便捷快速。
GSL库具有以下五个特点:
- 采用面向对象的设计,不同的算法可以很容易地插入或在运行时更改,而无需重新编译程序;
- 面向普通用户,任何了解
C编程的人都可立即开始使用该库; - 界面设计简单,可链接到非常高级的语言,如
GNU Guile或Python; - 具有线程安全性;
- 易于编译,且不依赖于其他包。
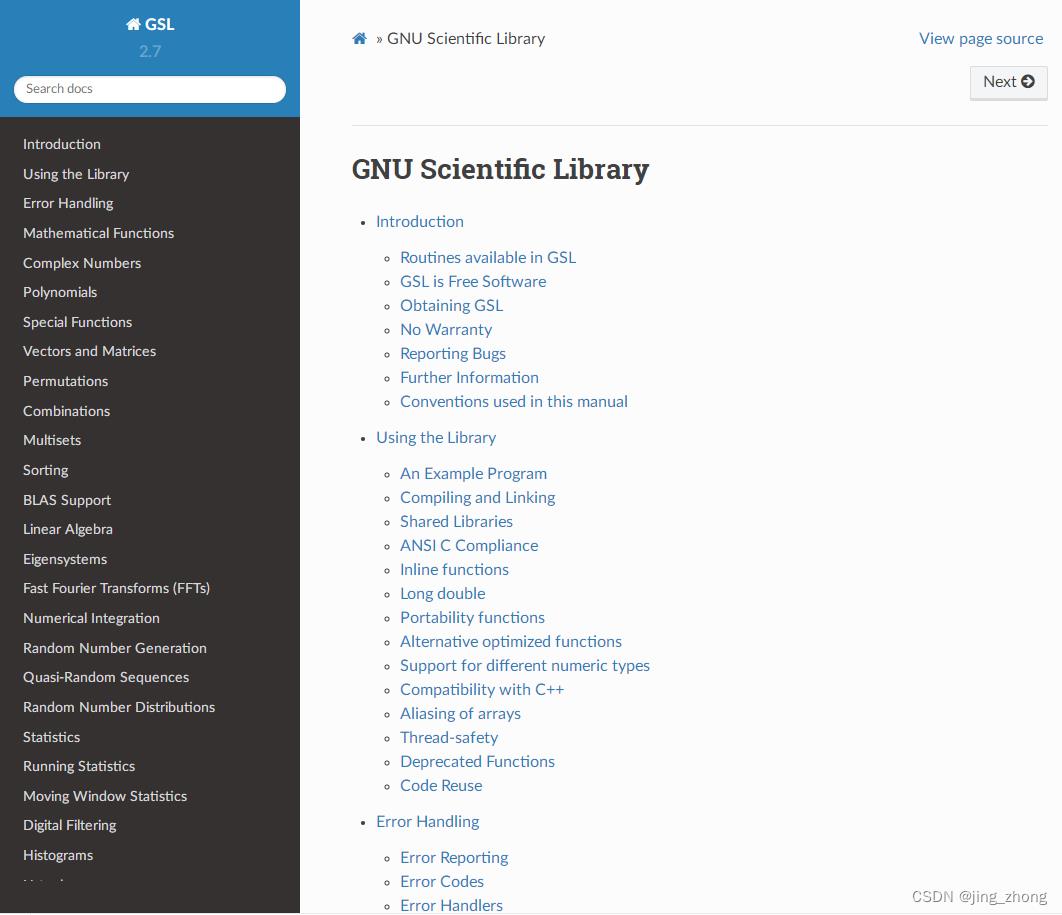
截至目前,GSL已经发布了很多版本,从gsl-1.0到gsl-2.7,当前最新且稳定的版本为gsl-2.7,各版本的下载地址有两个:https://mirrors.tripadvisor.com/gnu/gsl/和https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gsl/。官网的帮助文档地址有html 帮助文档、pdf 帮助文档和技术报告。

| 
|

| 
|
1.2 前人在Windows平台下已编译好的GSL库(版本太低)
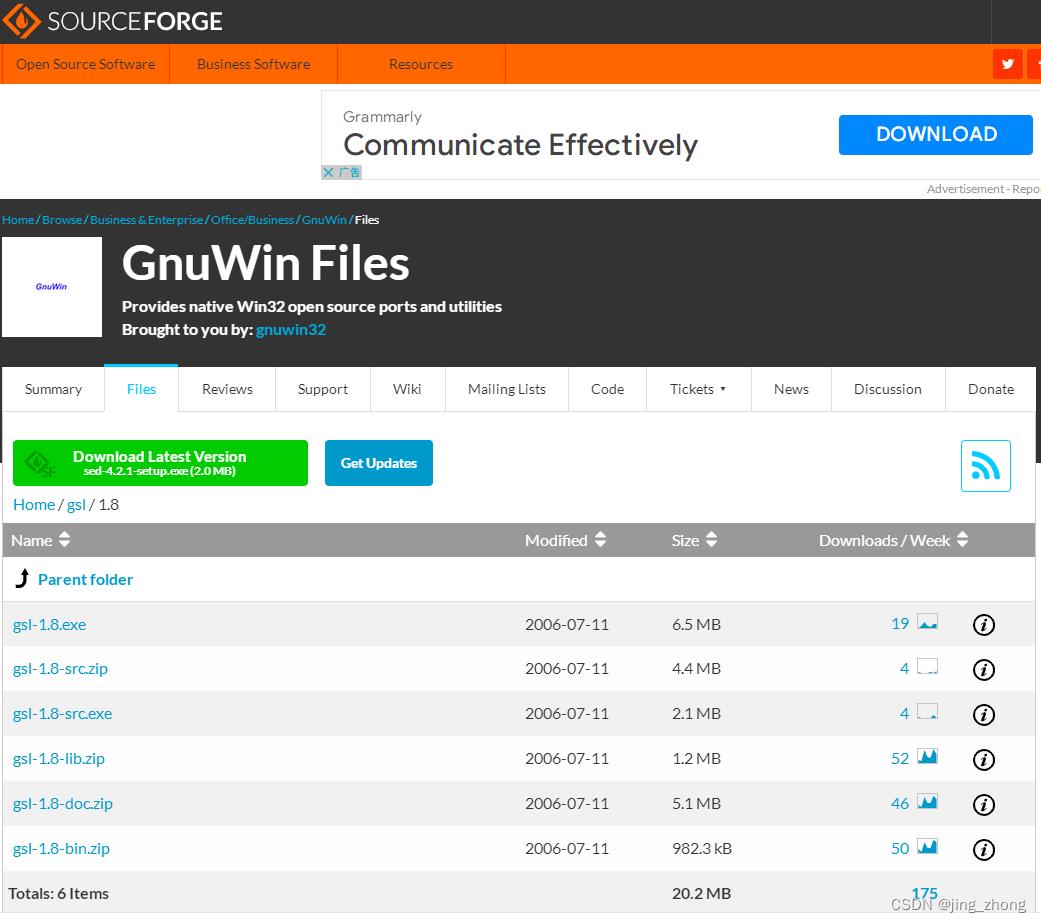
进入Gsl for Windows网站可看到1.8版本的GSL编译库,在该页面点击Complete package, except sources右侧的Setup,进入Gnu Win Files,下载gsl-1.8.exe后安装并配置成功后应该就可使用了。

| 
|
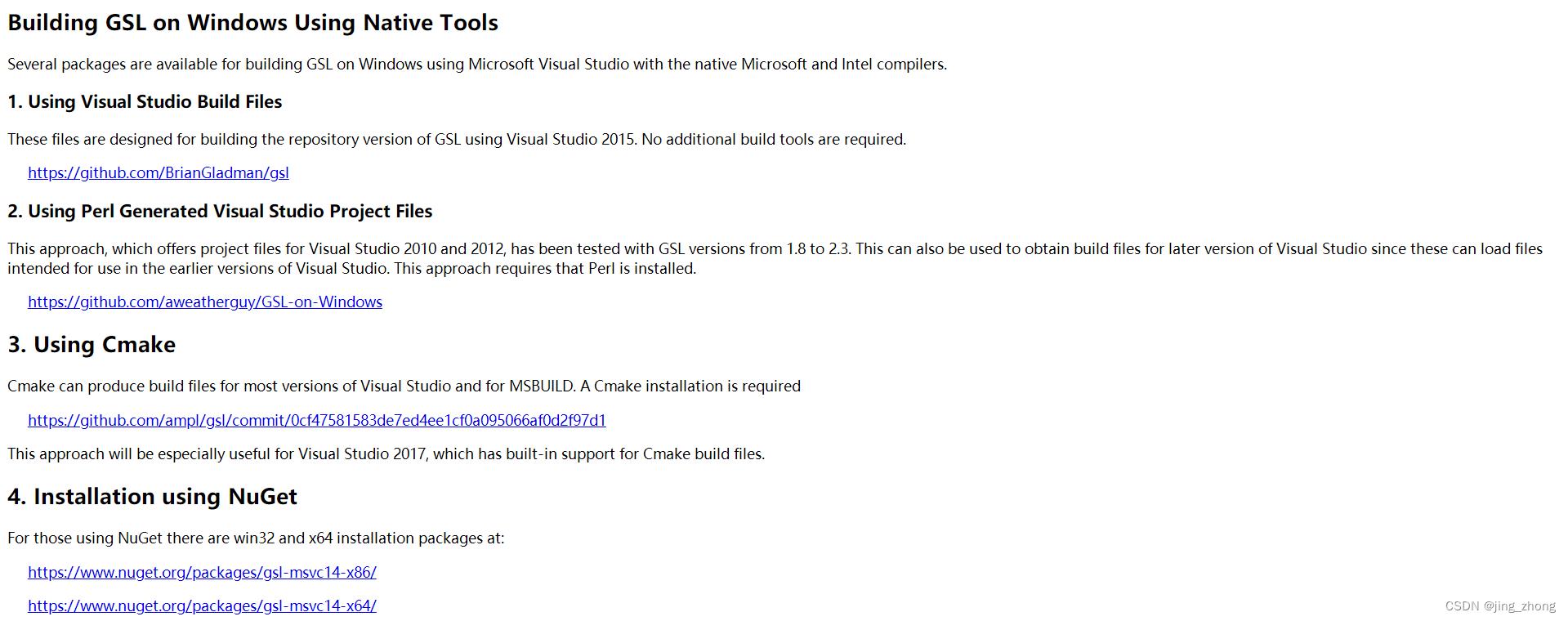
另外GSL官网也明确指出一些开发者提供了一些方法可轻松地在Windows平台上构建GSL库,详情见Building GSL on Windows Using Native Tools中的四种方法。个人感觉前两种方法过于陈旧,而NuGet安装包的方法版本只到GSL2.3.0,如果觉得版本还可以接受则可采用;个人感觉基于CMake的方法可以尝试,毕竟其Star数不少。
| 
|
| 
|
曾经的开发者们尽管采用了众多方法在Windows上构建GSL库,但这些方法已经编译的GSL库版本太低,没有及时更新,或许无法满足个人对新版本GSL库的需求,因此还是需要自己动手编译最新版本的GSL库(看个人喜好)。
2、Windows下利用MSYS2编译GSL库
2.1 MSYS2 简介
MSYS2并不是“一个统治所有人的工具”,而是试图专注于它擅长的东西。它提供了一个基于开源软件的本地构建环境,当用户已经熟悉Linux时,它会让您感到宾至如归。有充分的理由在Windows上为不同的任务使用多种不同的环境和工具。MSYS2是一个工具和库的集合,能为构建、安装和运行本机Windows软件提供一个易于使用的Linux环境。它包括一个名为mintty、bash的命令行终端、git和subversion等版本控制系统、tar和awk等工具,甚至还有autotools等构建系统,所有这些都是基于Cygwin的修改版本。尽管其中一些核心部件基于Cygwin,但MSYS2的重点是为本机Windows软件提供构建环境,并且使用Cygwin的部件保持在最低限度。
MSYS2的包管理器为pacman。MSYS2软件发行版使用pacman来管理(安装、删除和更新)二进制软件包,并首先构建这些软件包。MSYS2中的包与流行的Linux发行版中的包类似。软件包是包含一段软件的存档,这通常意味着可执行文件、运行库、数据、共享和静态链接库、头文件、配置文件和手册页。软件包还包含元数据,如软件名称、用途描述、版本号、供应商、校验和,以及软件正常运行所需的依赖项列表。
MSYS2为GCC、mingw-w64、CPython、CMake、Meson、OpenSSL、FFmpeg、Rust、Ruby等提供了最新的本机版本。为了方便安装软件包并保持更新,它提供了一个名为Pacman的软件包管理系统,Arch Linux用户应该熟悉该系统。它带来了许多强大的功能,如依赖解析和简单的完整系统升级,以及直接和可复制的包构建,软件包存储库包含2500多个准备安装的预构建软件包。安装后,包含的文件将被提取到MSYS2安装目录中,元数据存储在本地数据库中。它有6个软件包存储库,如经典的msys2、mingw32和mingw64,以及更新的ucrt64、clang32和clang64。msys2中的包与Linux发行版中的包一样命名,其他版本中的包的前缀为mingw-w64-i686(适用于32位包)或mingw-w64-x86_64(适用于带有辅助前缀clang或ucrt的64位包)。
2.2 Windows系统安装MSYS2

首先到MSYS2官网下载安装包msys2-x86_64-20220503.exe,双击进行安装,在安装程序窗口点击下一步,选择安装文件夹为D:\\msys64后直接安装即可。
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
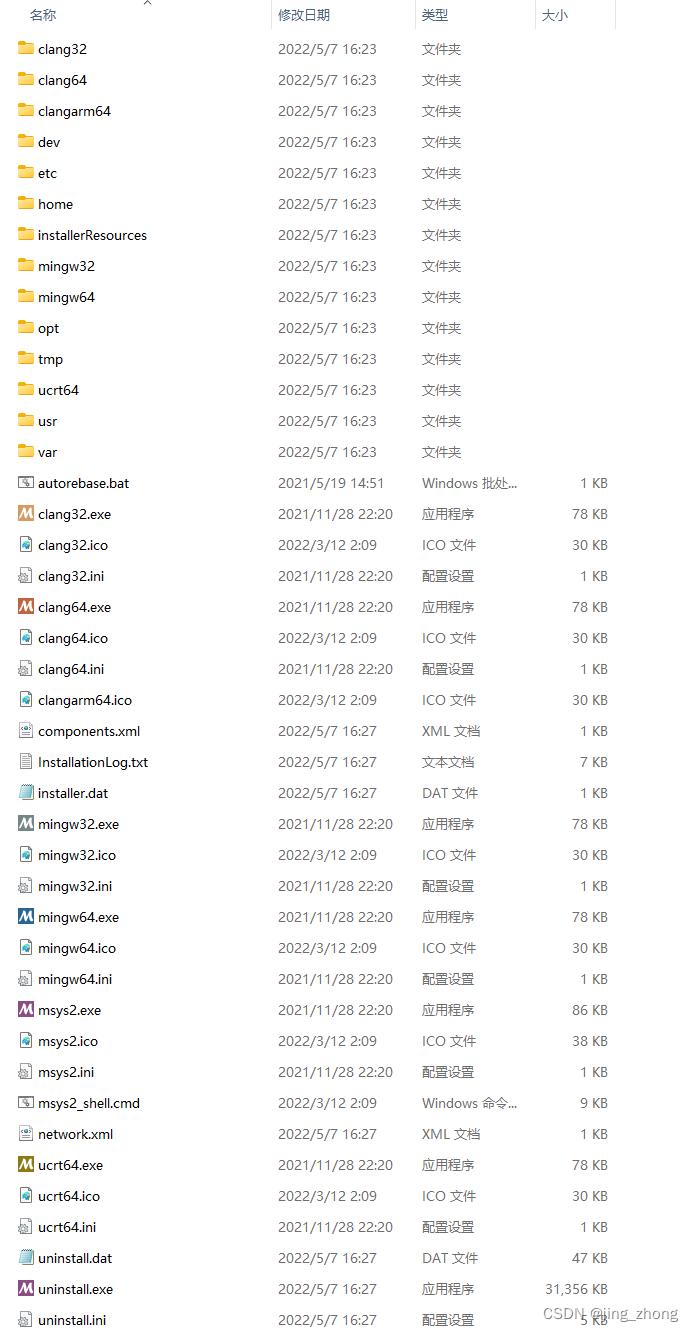
| 
|
安装完成后,由于MSYS2需要安装依赖库,考虑到网络访问等原因,将MSYS2镜像改为清华源镜像,也就是说,所有依赖库都优先从国内清华源镜像网站下载。具体设置步骤为:(1)打开/etc/pacman.conf文件,分别设置mingw32、mingw64、ucrt64、clang32、clang64、msys的Include路径为各自对应的/etc/pacman.d下的mirrorlist文件名;(2)分别打开这6个mirrorlist文件,将清华源镜像网址放在第一行,如下图所示。
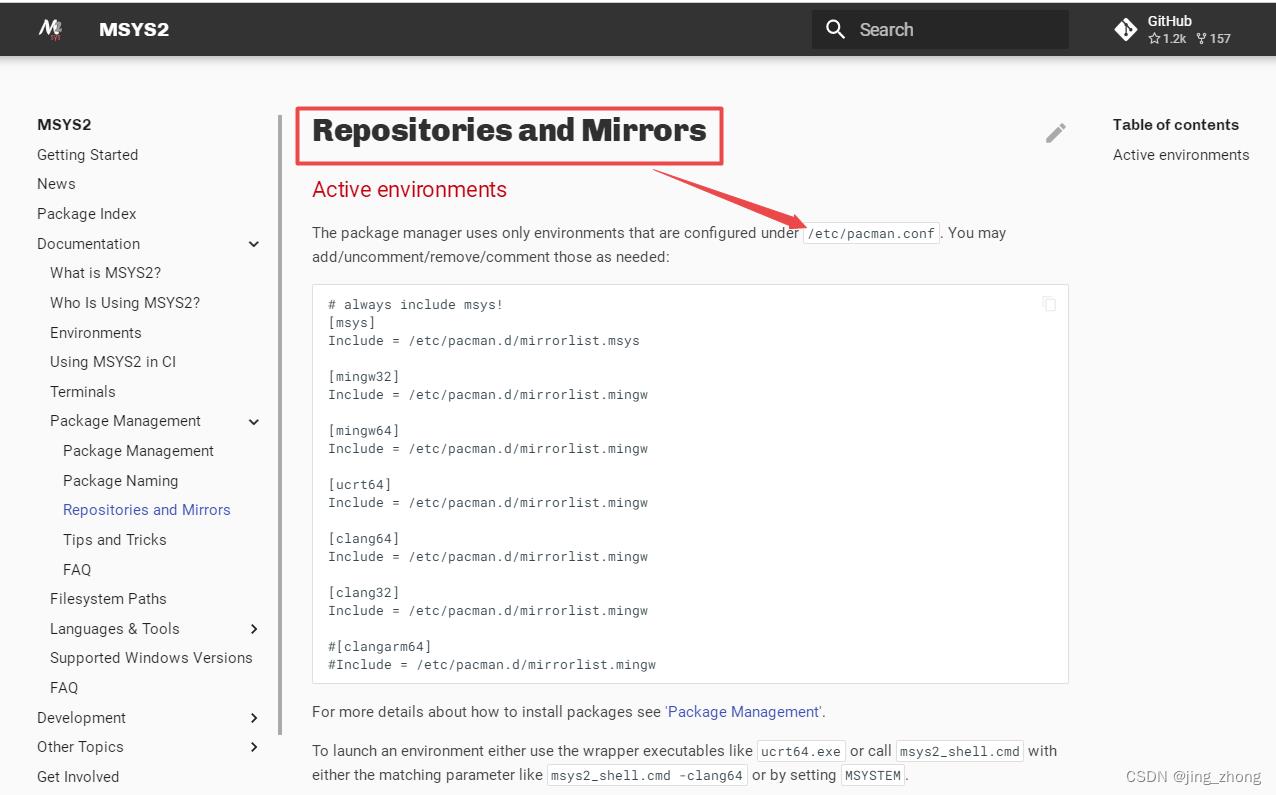 | 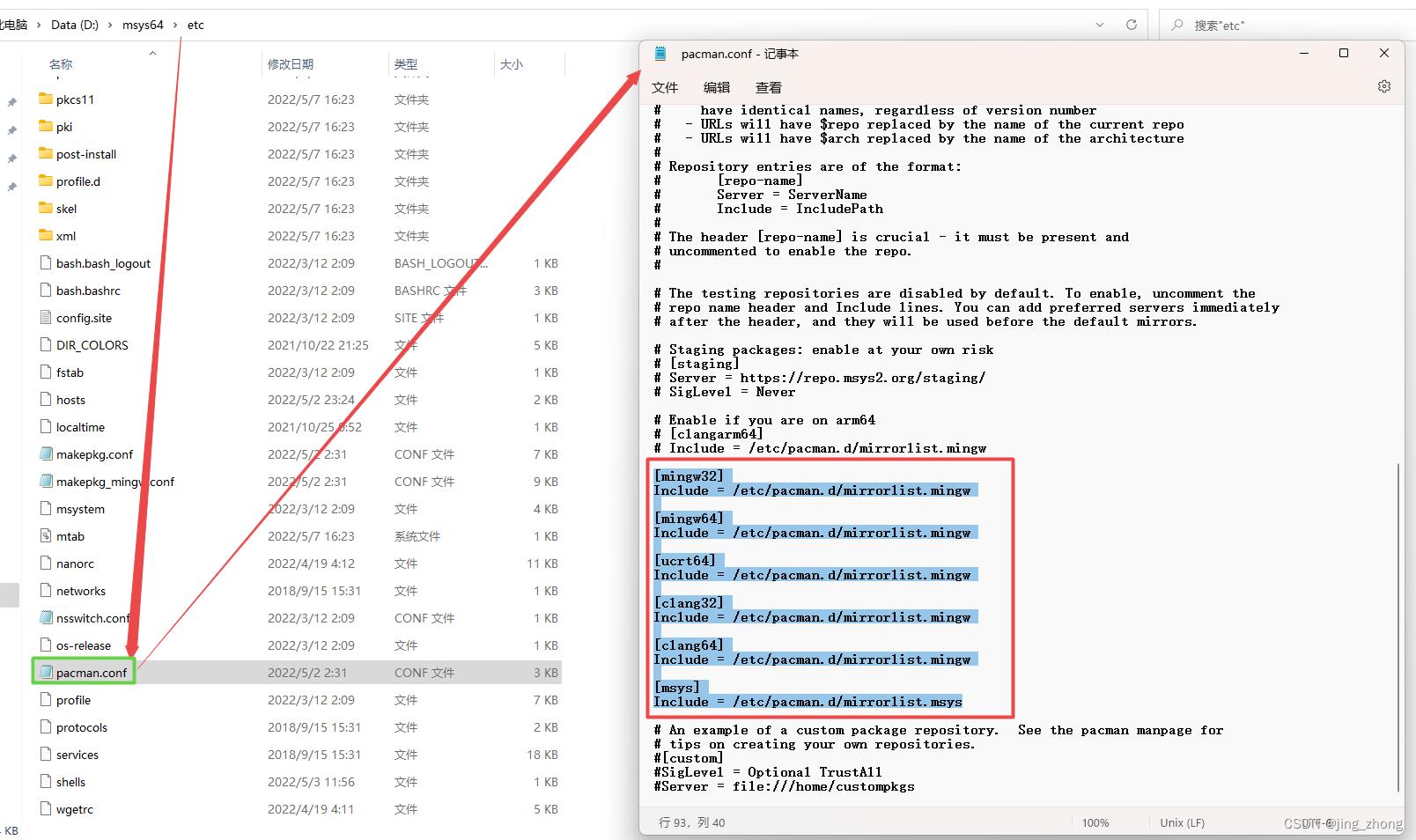 |
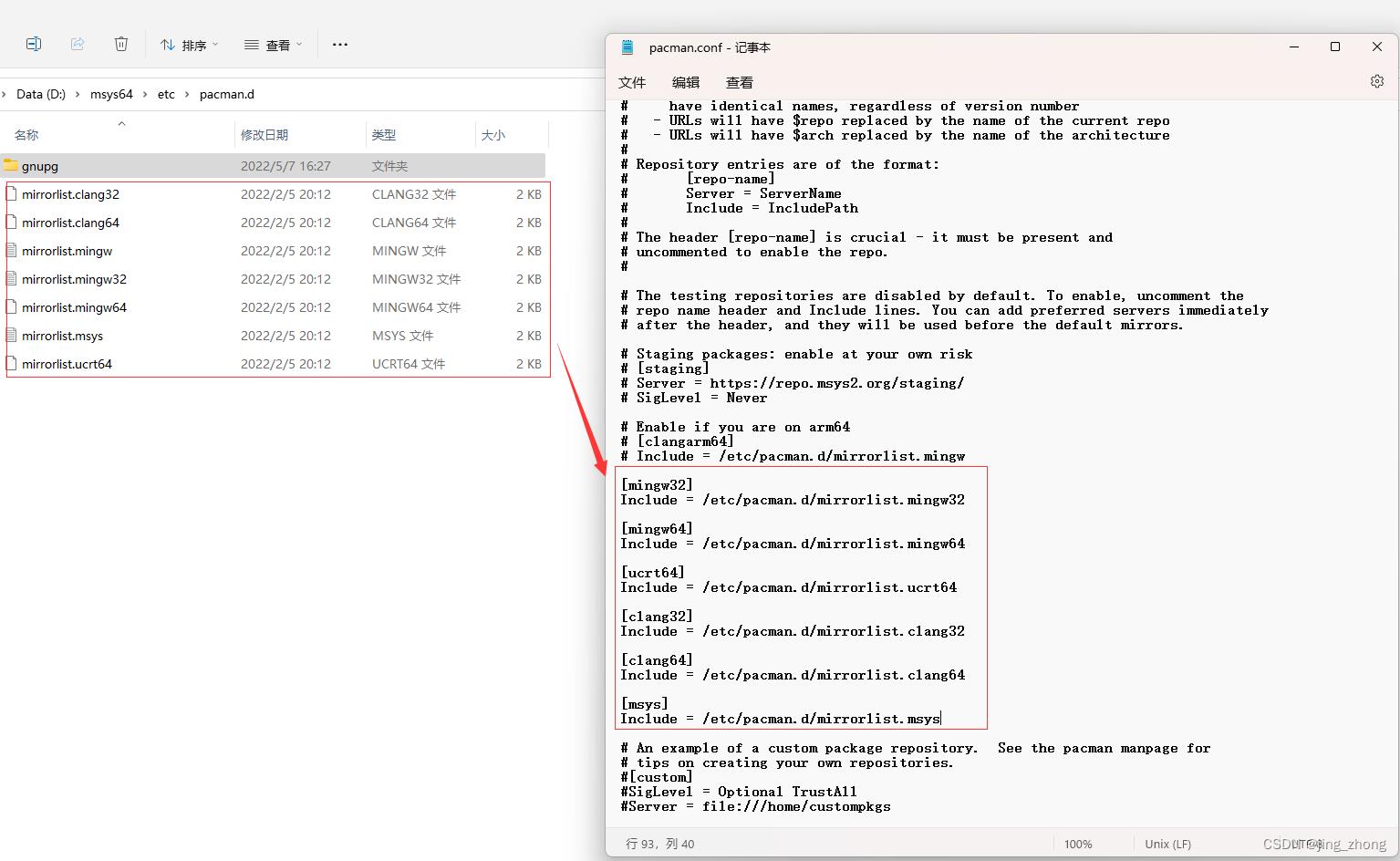 | 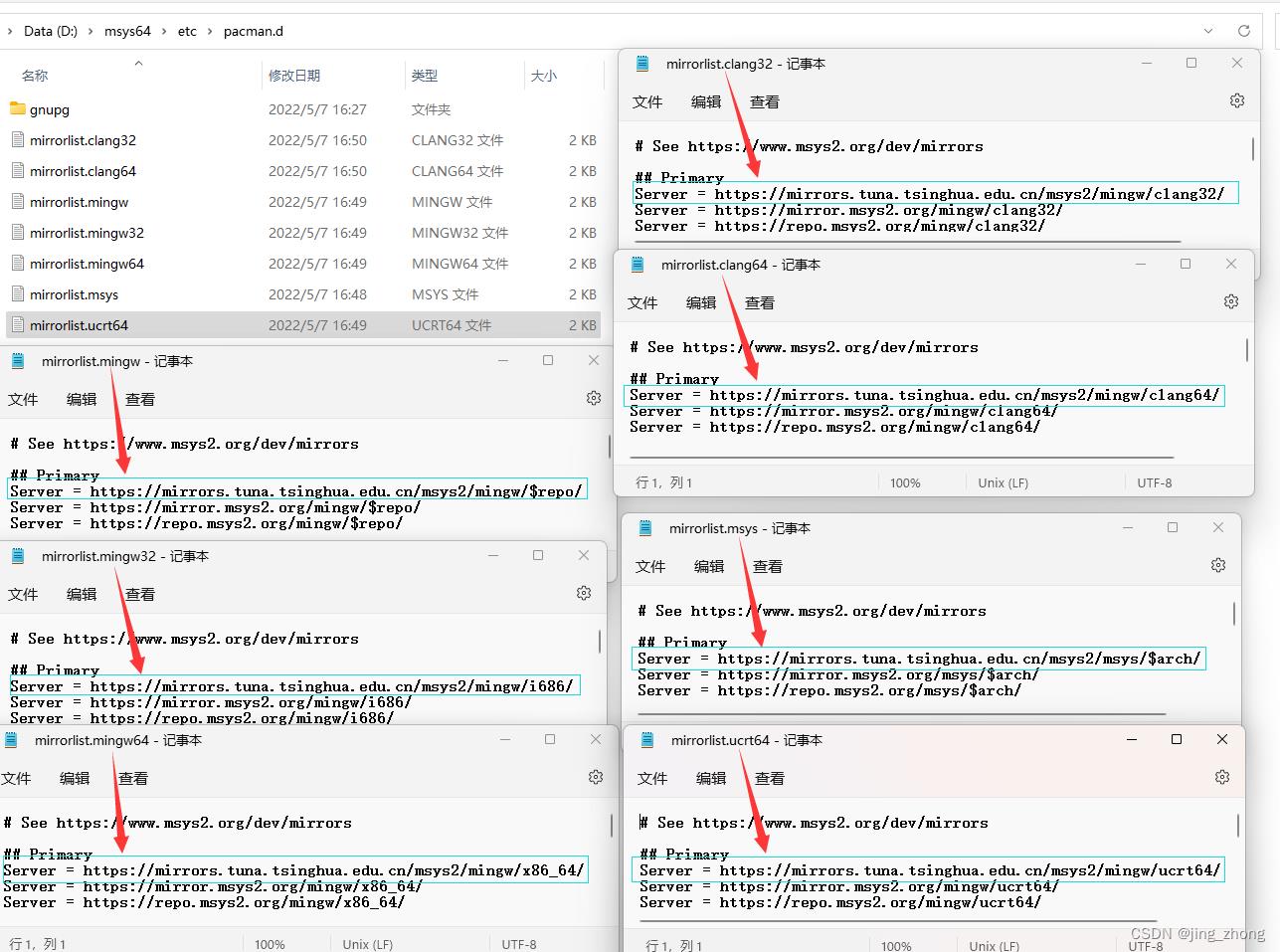 |
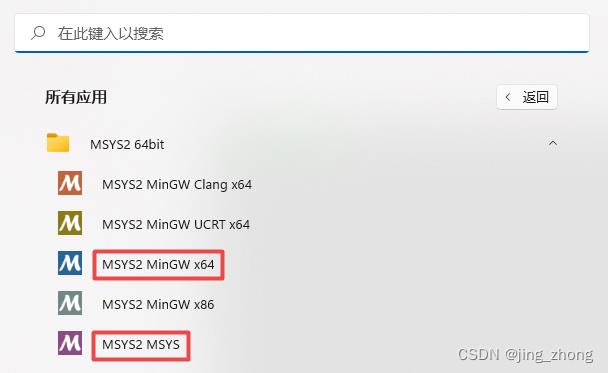
然后为了在MSYS2中安装相关的依赖,打开开始菜单,可以看到MSYS 2 64bit文件夹下有5个快捷方式,运行MSUS2 MSYS后弹出bash窗口,依次输入如下命令:
pacman -help
pacman -Syu
pacman -Syu
pacman -Su
pacman -S mingw-w64-x86_64-gcc
pacman -S make
pacman -S vim
pacman -S git
pacman -S python
pacman -S winpty
which g++
which gcc
which make
which vim
which git
which python
which winpty

现在MSYS2的基本环境就搭建好了,如下图所示,在D:\\msys64\\mingw64\\bin文件夹下可以看到有c++.exe、g++.exe、gcc.exe和一些dll等文件,这也能表明mingw64下的gcc环境搭建成功。
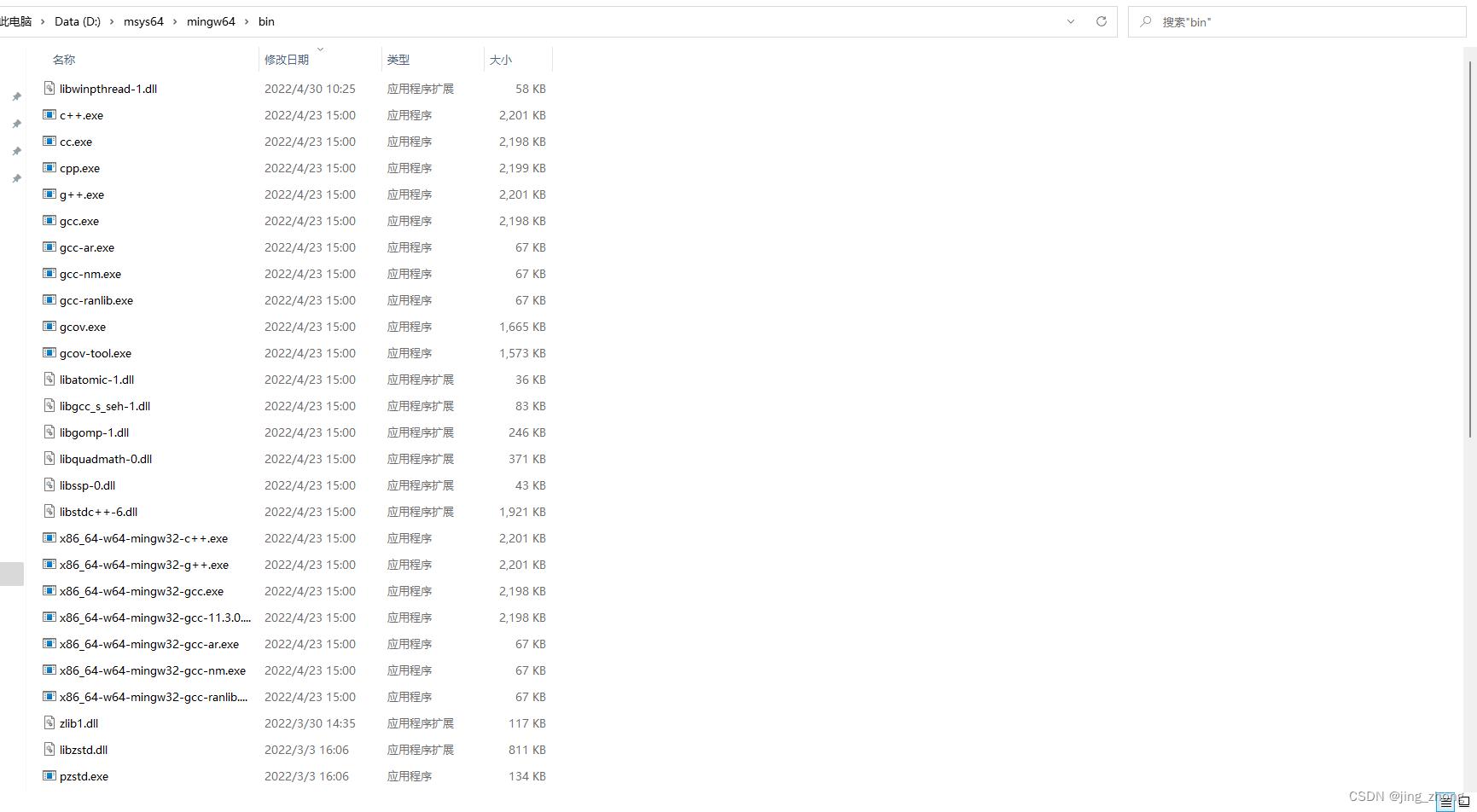
2.3 下载GSL源码进行编译构建

在MSYS2环境搭建成功后,为了编译GSL源码,首先需要获得GSL较新版本的源码,下载gsl-2.7.tar.gz压缩包并解压,解压后的文件夹为D:\\搜狗高速下载\\gsl-2.7\\gsl-2.7,该文件夹下的文件如图所示,其中需要重点关注两个文件:INSTALL文件和README文件,可以选中文件点击鼠标右键选择用记事本打开查看文件内容。
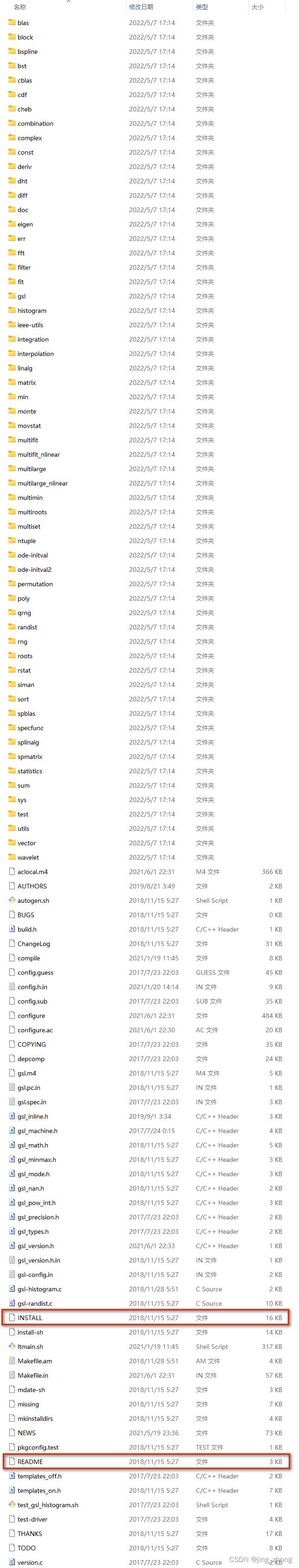
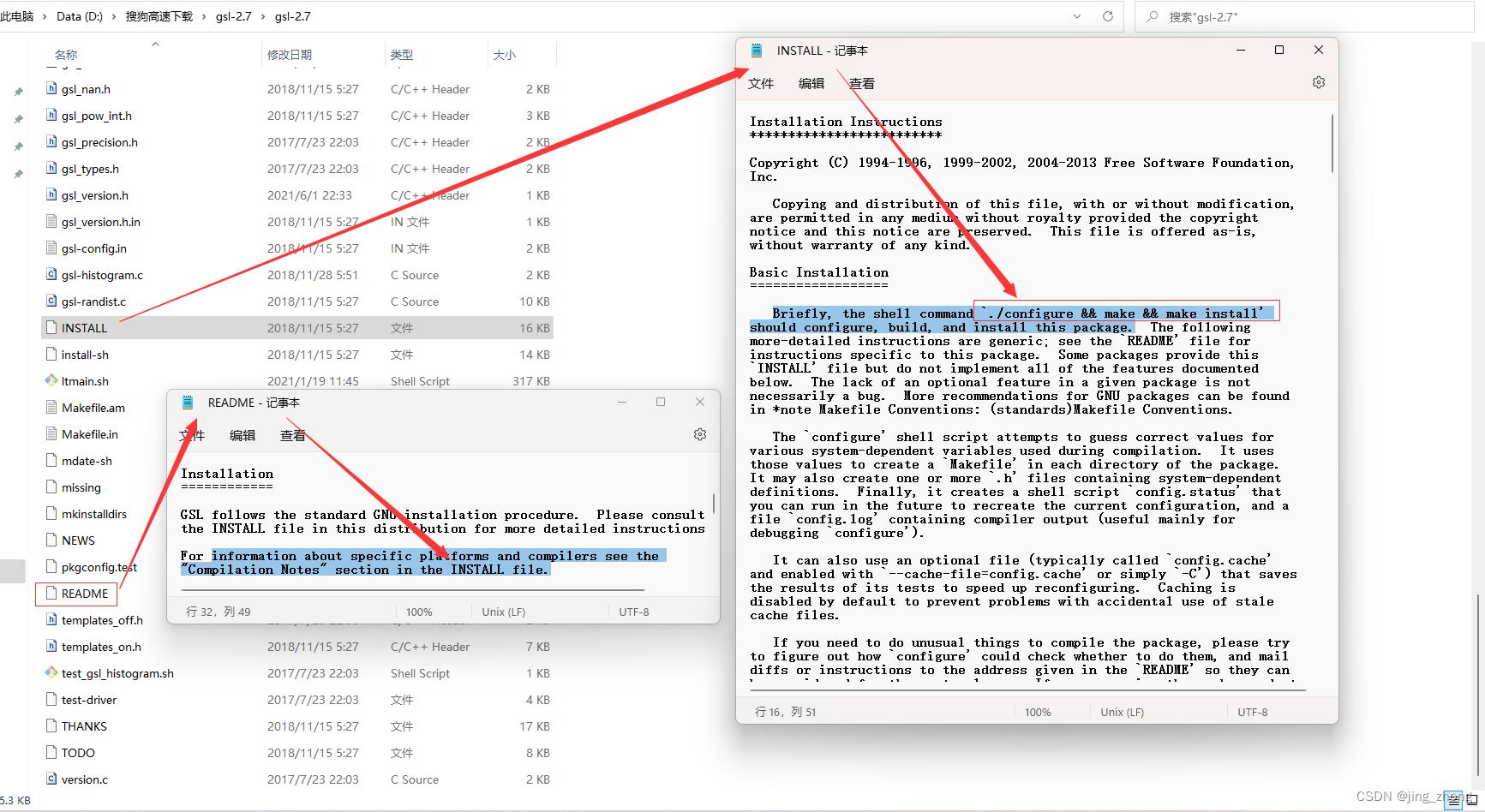 |  |  |
通过查看INSTALL和README这两个文件中的说明内容,可知GSL的编译最好使用gcc编译器,需要依次输入./configure、make、make install这三个命令来完成GSL的编译、构建和安装。如果直接使用上述三个命令,那么默认会将GSL编译后的bin、include文件放到/usr/local/bin和/usr/local/include目录下。为了将GSL安装到其他目录,这里新建文件夹D:\\搜狗高速下载\\gsl-2.7\\gsl-2.7-build作为GSL的安装目录,需要利用./configure --prefix=/D/搜狗高速下载/gsl-2.7/gsl-2.7-build命令来进行设置。具体的configure命令帮助如下,可参考:
$ ./configure --help
`configure' configures gsl 2.7 to adapt to many kinds of systems.
Usage: ./configure [OPTION]... [VAR=VALUE]...
To assign environment variables (e.g., CC, CFLAGS...), specify them as
VAR=VALUE. See below for descriptions of some of the useful variables.
Defaults for the options are specified in brackets.
Configuration:
-h, --help display this help and exit
--help=short display options specific to this package
--help=recursive display the short help of all the included packages
-V, --version display version information and exit
-q, --quiet, --silent do not print `checking ...' messages
--cache-file=FILE cache test results in FILE [disabled]
-C, --config-cache alias for `--cache-file=config.cache'
-n, --no-create do not create output files
--srcdir=DIR find the sources in DIR [configure dir or `..']
Installation directories:
--prefix=PREFIX install architecture-independent files in PREFIX
[/usr/local]
--exec-prefix=EPREFIX install architecture-dependent files in EPREFIX
[PREFIX]
By default, `make install' will install all the files in
`/usr/local/bin', `/usr/local/lib' etc. You can specify
an installation prefix other than `/usr/local' using `--prefix',
for instance `--prefix=$HOME'.
For better control, use the options below.
Fine tuning of the installation directories:
--bindir=DIR user executables [EPREFIX/bin]
--sbindir=DIR system admin executables [EPREFIX/sbin]
--libexecdir=DIR program executables [EPREFIX/libexec]
--sysconfdir=DIR read-only single-machine data [PREFIX/etc]
--sharedstatedir=DIR modifiable architecture-independent data [PREFIX/com]
--localstatedir=DIR modifiable single-machine data [PREFIX/var]
--runstatedir=DIR modifiable per-process data [LOCALSTATEDIR/run]
--libdir=DIR object code libraries [EPREFIX/lib]
--includedir=DIR C header files [PREFIX/include]
--oldincludedir=DIR C header files for non-gcc [/usr/include]
--datarootdir=DIR read-only arch.-independent data root [PREFIX/share]
--datadir=DIR read-only architecture-independent data [DATAROOTDIR]
--infodir=DIR info documentation [DATAROOTDIR/info]
--localedir=DIR locale-dependent data [DATAROOTDIR/locale]
--mandir=DIR man documentation [DATAROOTDIR/man]
--docdir=DIR documentation root [DATAROOTDIR/doc/gsl]
--htmldir=DIR html documentation [DOCDIR]
--dvidir=DIR dvi documentation [DOCDIR]
--pdfdir=DIR pdf documentation [DOCDIR]
--psdir=DIR ps documentation [DOCDIR]
Program names:
--program-prefix=PREFIX prepend PREFIX to installed program names
--program-suffix=SUFFIX append SUFFIX to installed program names
--program-transform-name=PROGRAM run sed PROGRAM on installed program names
System types:
--build=BUILD configure for building on BUILD [guessed]
--host=HOST cross-compile to build programs to run on HOST [BUILD]
Optional Features:
--disable-option-checking ignore unrecognized --enable/--with options
--disable-FEATURE do not include FEATURE (same as --enable-FEATURE=no)
--enable-FEATURE[=ARG] include FEATURE [ARG=yes]
--enable-silent-rules less verbose build output (undo: "make V=1")
--disable-silent-rules verbose build output (undo: "make V=0")
--enable-maintainer-mode
enable make rules and dependencies not useful (and
sometimes confusing) to the casual installer
--enable-dependency-tracking
do not reject slow dependency extractors
--disable-dependency-tracking
speeds up one-time build
--enable-shared[=PKGS] build shared libraries [default=yes]
--enable-static[=PKGS] build static libraries [default=yes]
--enable-fast-install[=PKGS]
optimize for fast installation [default=yes]
--disable-libtool-lock avoid locking (might break parallel builds)
Optional Packages:
--with-PACKAGE[=ARG] use PACKAGE [ARG=yes]
--without-PACKAGE do not use PACKAGE (same as --with-PACKAGE=no)
--with-pic[=PKGS] try to use only PIC/non-PIC objects [default=use
both]
--with-aix-soname=aix|svr4|both
shared library versioning (aka "SONAME") variant to
provide on AIX, [default=aix].
--with-gnu-ld assume the C compiler uses GNU ld [default=no]
--with-sysroot[=DIR] Search for dependent libraries within DIR (or the
compiler's sysroot if not specified).
Some influential environment variables:
CC C compiler command
CFLAGS C compiler flags
LDFLAGS linker flags, e.g. -L<lib dir> if you have libraries in a
nonstandard directory <lib dir>
LIBS libraries to pass to the linker, e.g. -l<library>
CPPFLAGS (Objective) C/C++ preprocessor flags, e.g. -I<include dir> if
you have headers in a nonstandard directory <include dir>
CPP C preprocessor
LT_SYS_LIBRARY_PATH
User-defined run-time library search path.
Use these variables to override the choices made by `configure' or to help
it to find libraries and programs with nonstandard names/locations.
Report bugs to the package provider.
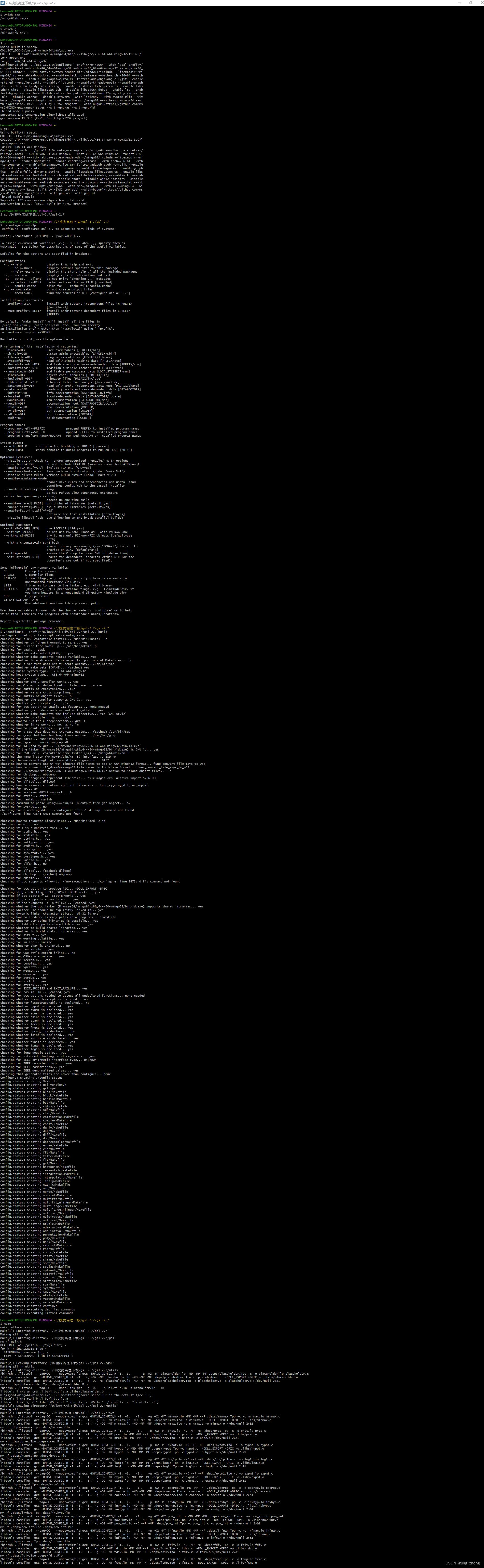
然后打开MSYS2 MinGW x64窗口,依次输入如下bash命令来编译GSL源码:
which gcc
which g++
gcc -v
g++ -v
cd /D/搜狗高速下载/gsl-2.7/gsl-2.7
./configure --help
./configure --prefix=/D/搜狗高速下载/gsl-2.7/gsl-2.7-build
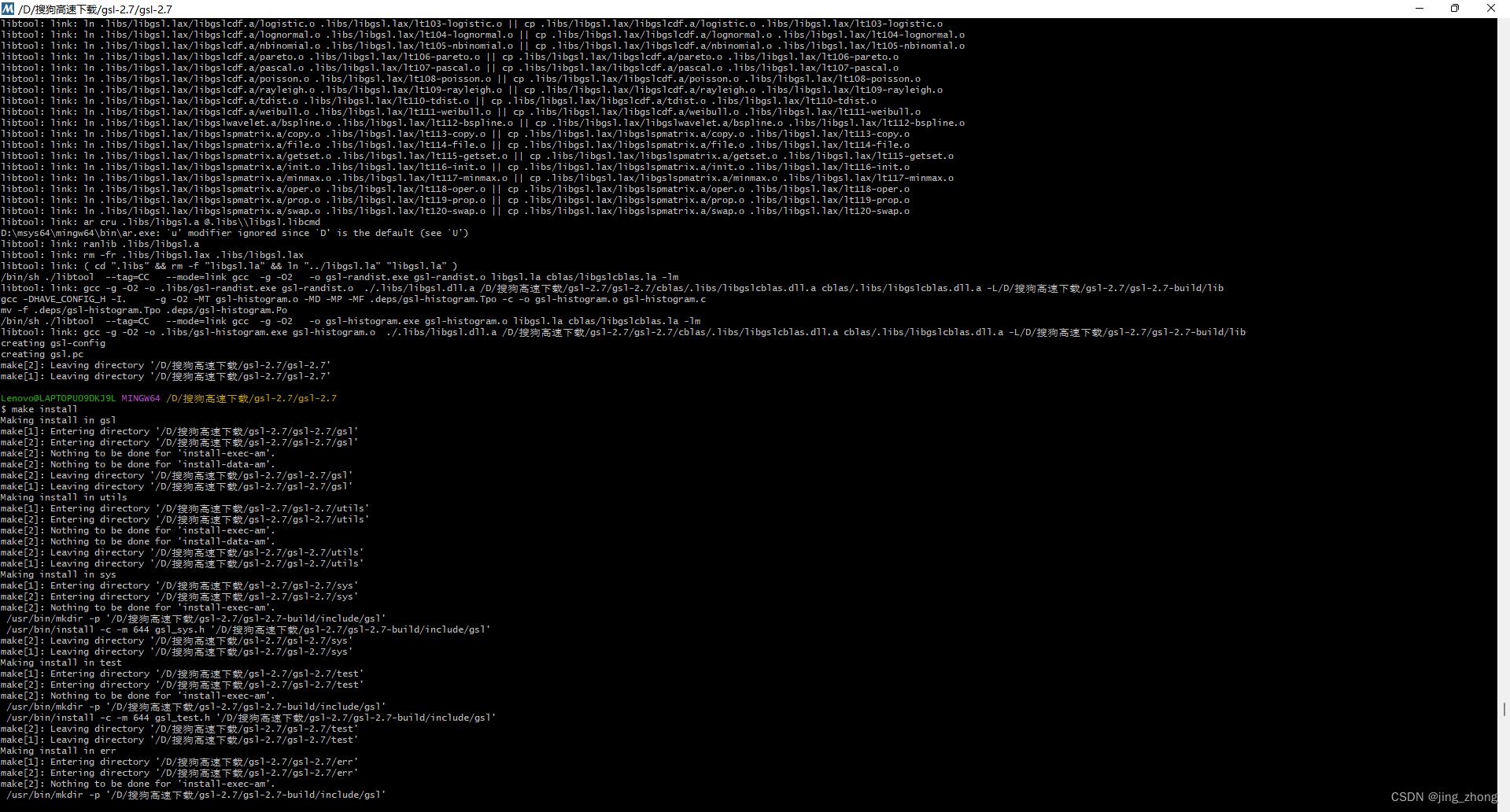
make
make install
GSL编译过程中的执行界面如下图所示:
 | 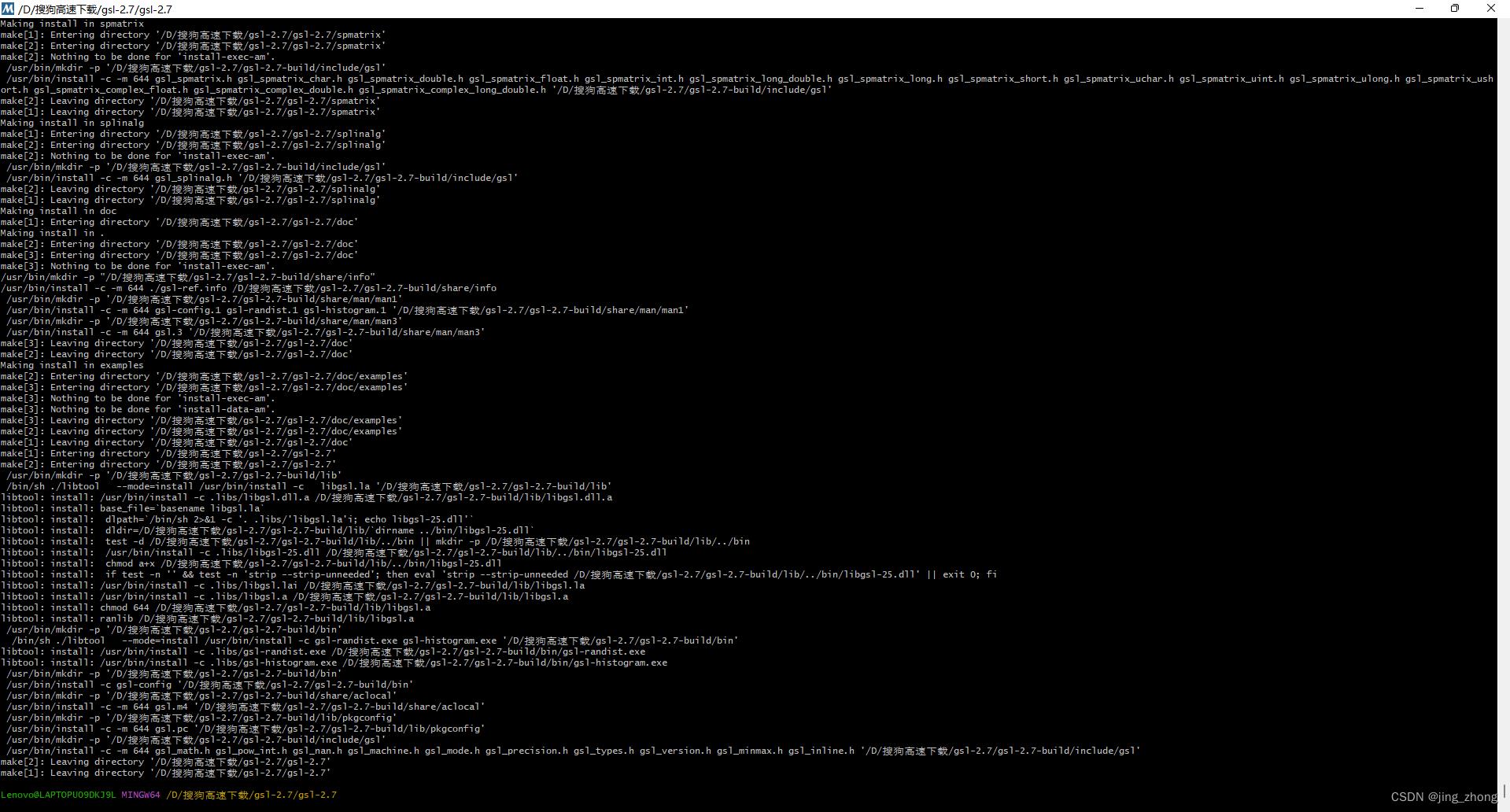 |
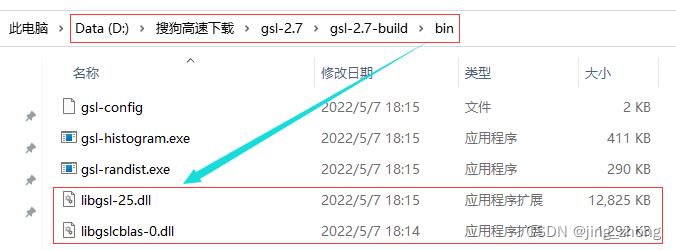
最终GSL编译构建成功后,在安装目录D:\\搜狗高速下载\\gsl-2.7\\gsl-2.7-build下可看到bin、include、lib和share四个文件夹,各个文件夹中的文件如下图所示,至此gsl-2.7编译构建成功。
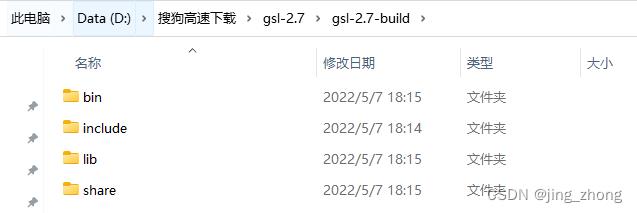
| 
|
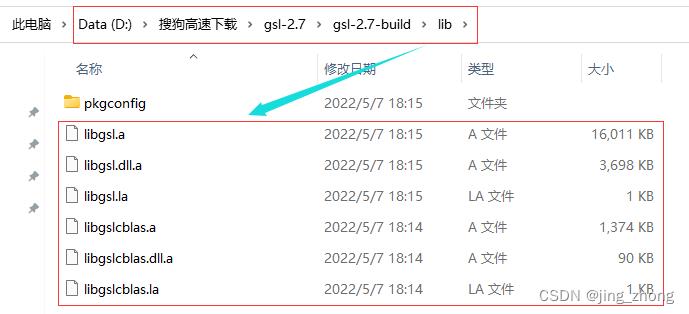
|

3、基于GSL库编写C语言代码(CodeBlocks / Visual Studio)
下面分别采用CodeBlocks和Visual Studio这两种IDE来编写利用GSL库的C项目,主要对GSL库在两种IDE中的配置过程进行简单介绍。
3.1 在CodeBlocks中基于GSL库编写C语言代码
3.1.1 安装CodeBlocks(自带gcc编译器)
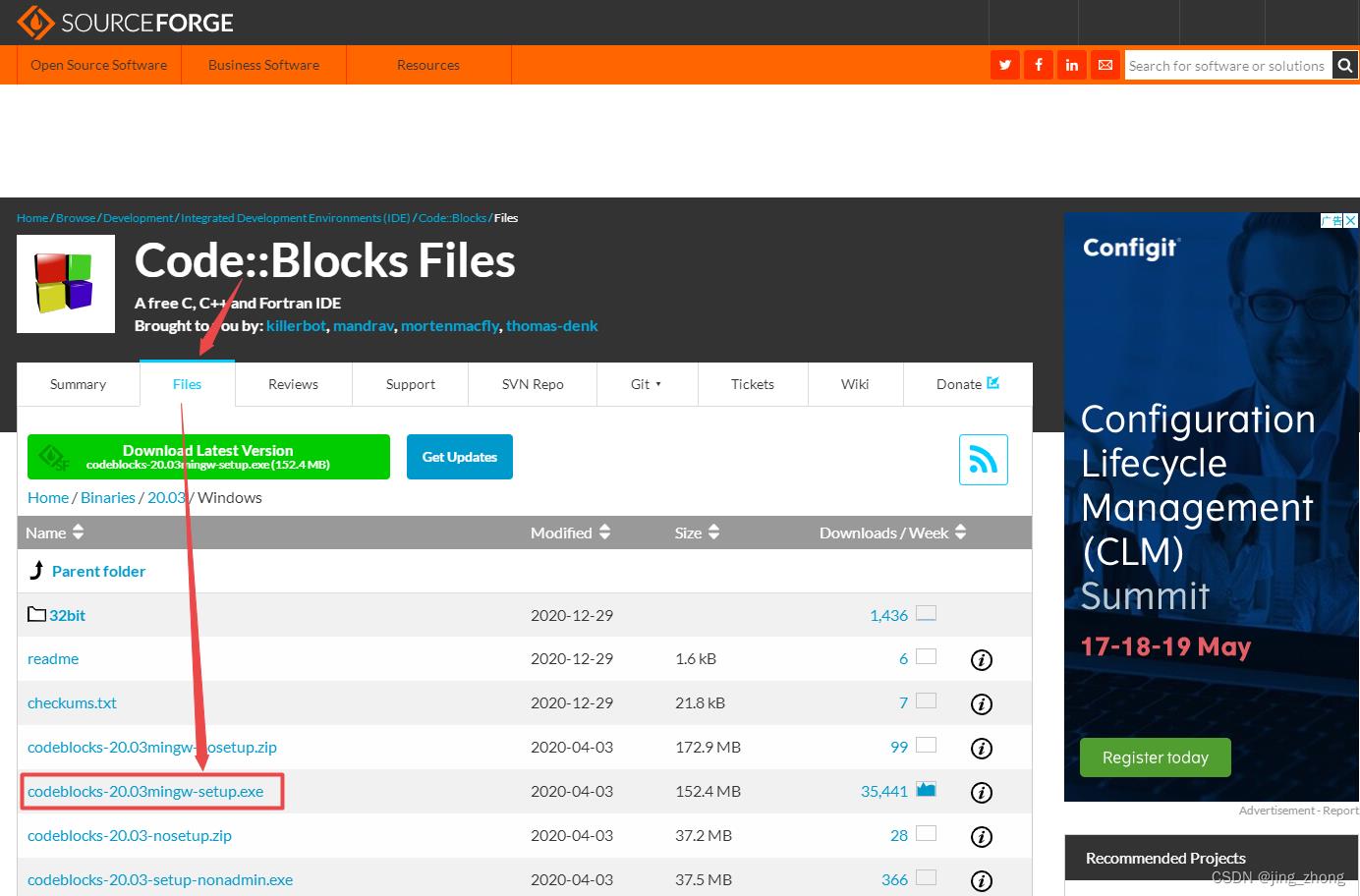
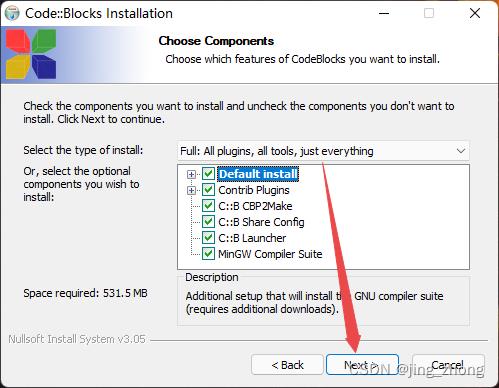
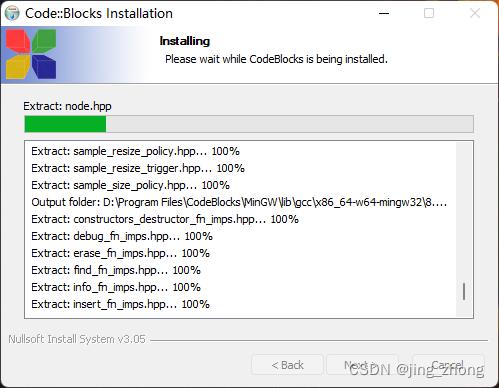
首先CodeBlocks作为一种开源的IDE,可用来编写C、C++和Fortran语言,且跨平台具有良好的扩展性,能安装插件,可满足大多开发者的需求。下载codeblocks-20.03mingw-setup.exe后,双击进行安装,接受GPL许可协议,选择安装目录为D:\\program files\\CodeBlocks,之后一直点击Next默认安装即可,安装过程如下图所示。

 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |

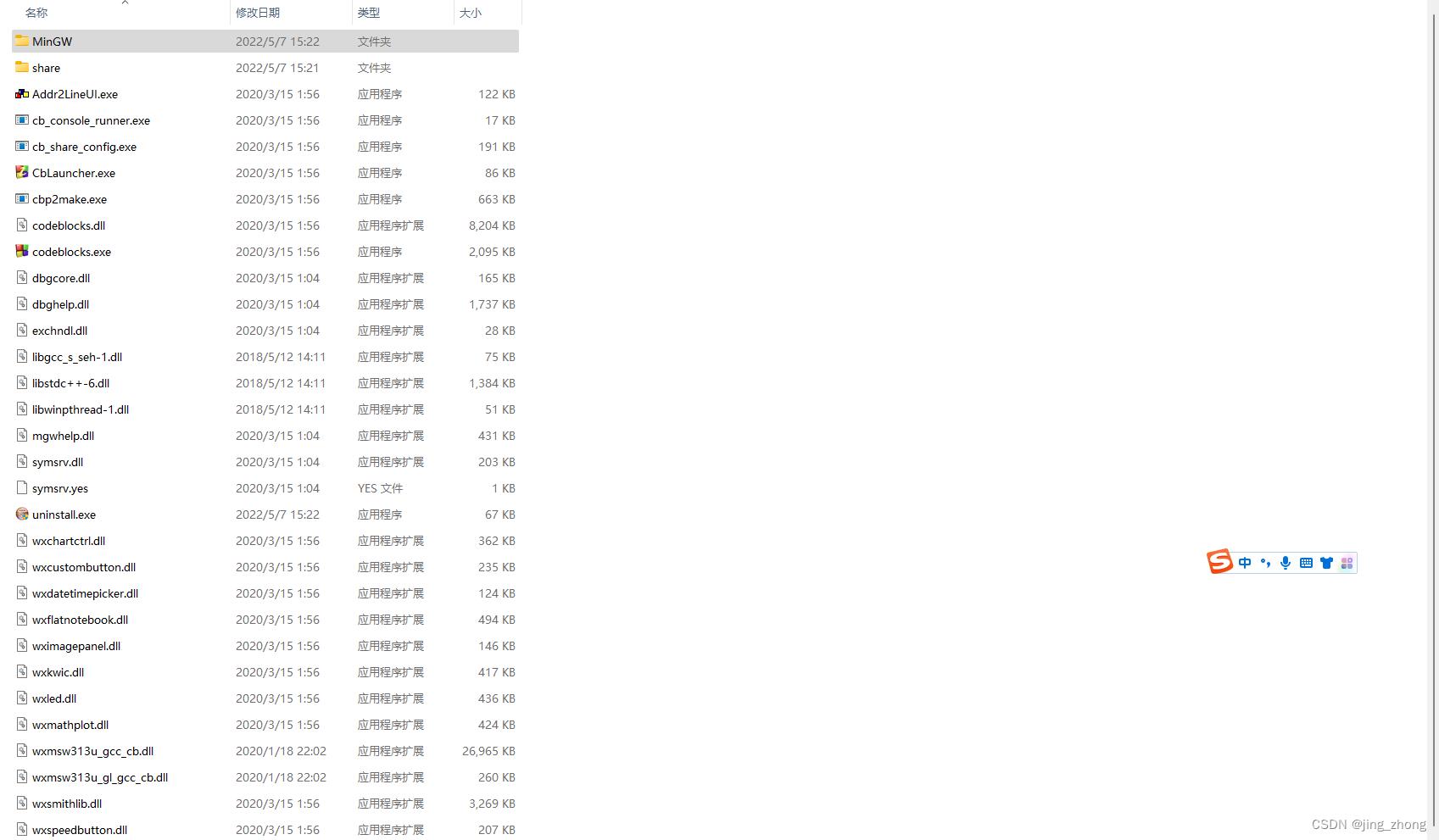
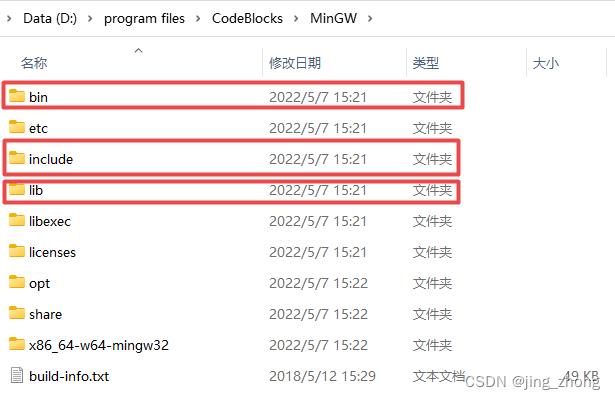
安装结束后,在桌面会看到CodeBlocks快捷方式,同时对应安装目录D:\\program files\\CodeBlocks下的文件包含MinGW文件夹,该文件夹下有bin、include和lib目录,bin目录下g++.exe、gcc.exe和mingw32-make.exe,可见MinGW自带gcc环境。
 |  |
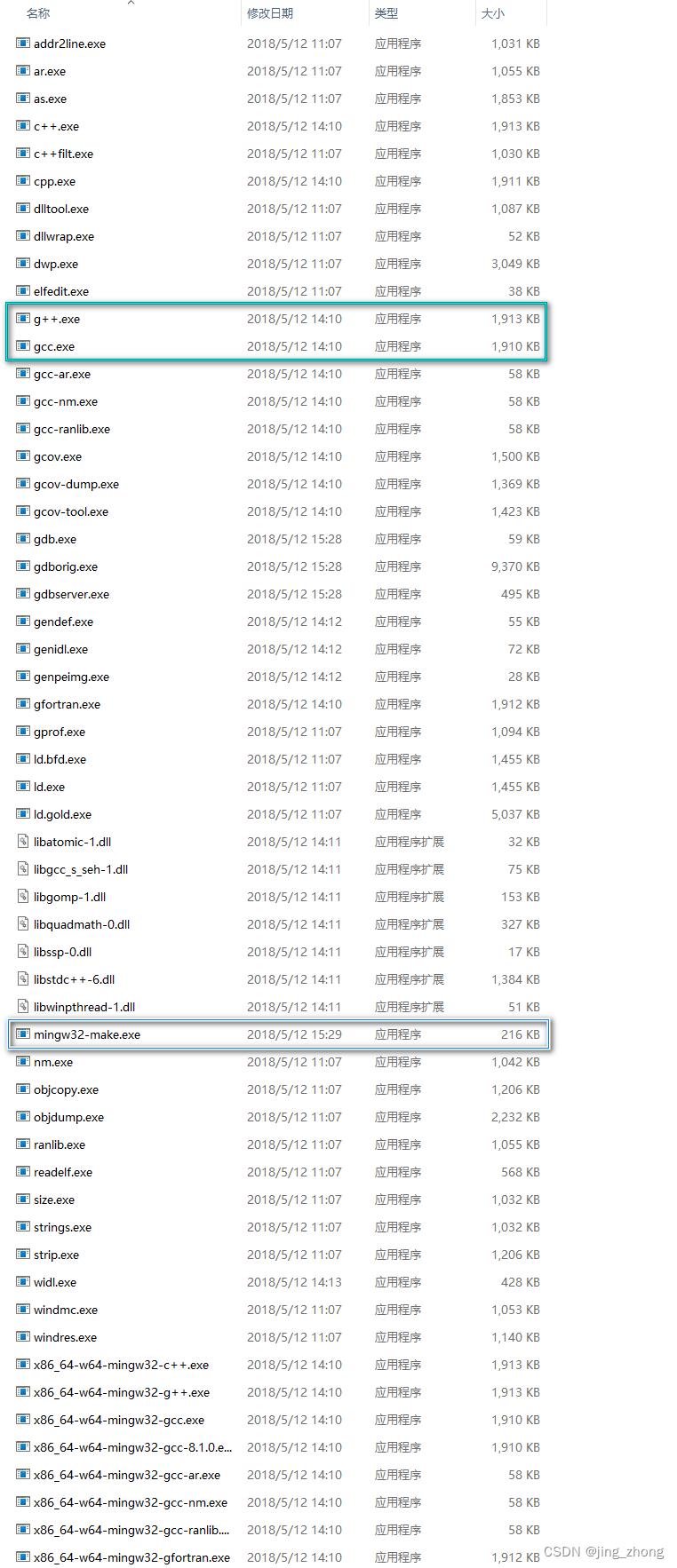
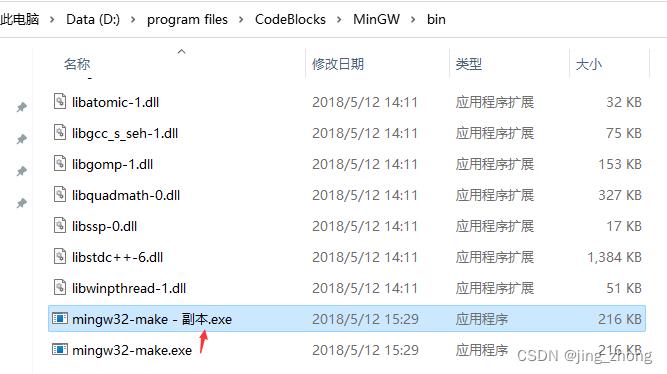
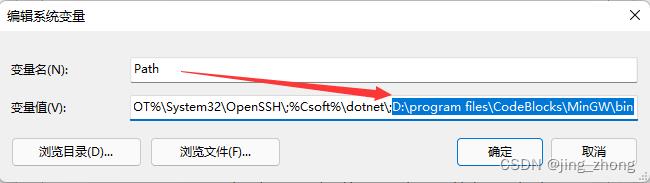
当然,如果想要配置make命令,需要将D:\\program files\\CodeBlocks\\MinGW\\bin文件夹下的mingw32-make.exe复制一份并重命名为make.exe,同时将D:\\program files\\CodeBlocks\\MinGW\\bin添加到系统的环境变量Path中。
| 
|
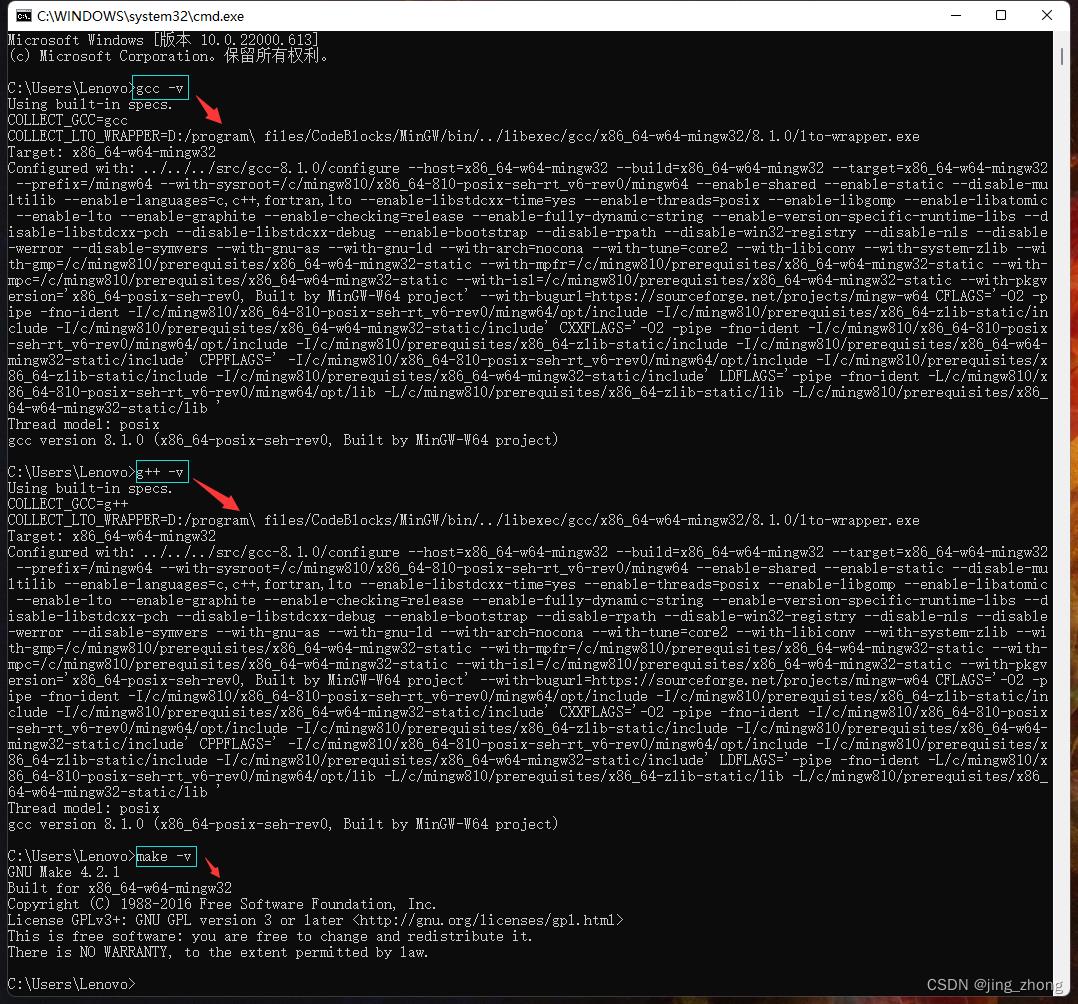
最后Win+R打开cmd命令行窗口,依次输入如下命令检验gcc编译器环境,结果如下图所示则配置成功。
gcc -v
g++ -v
make -v
3.1.2 利用CodeBlocks新建C项目
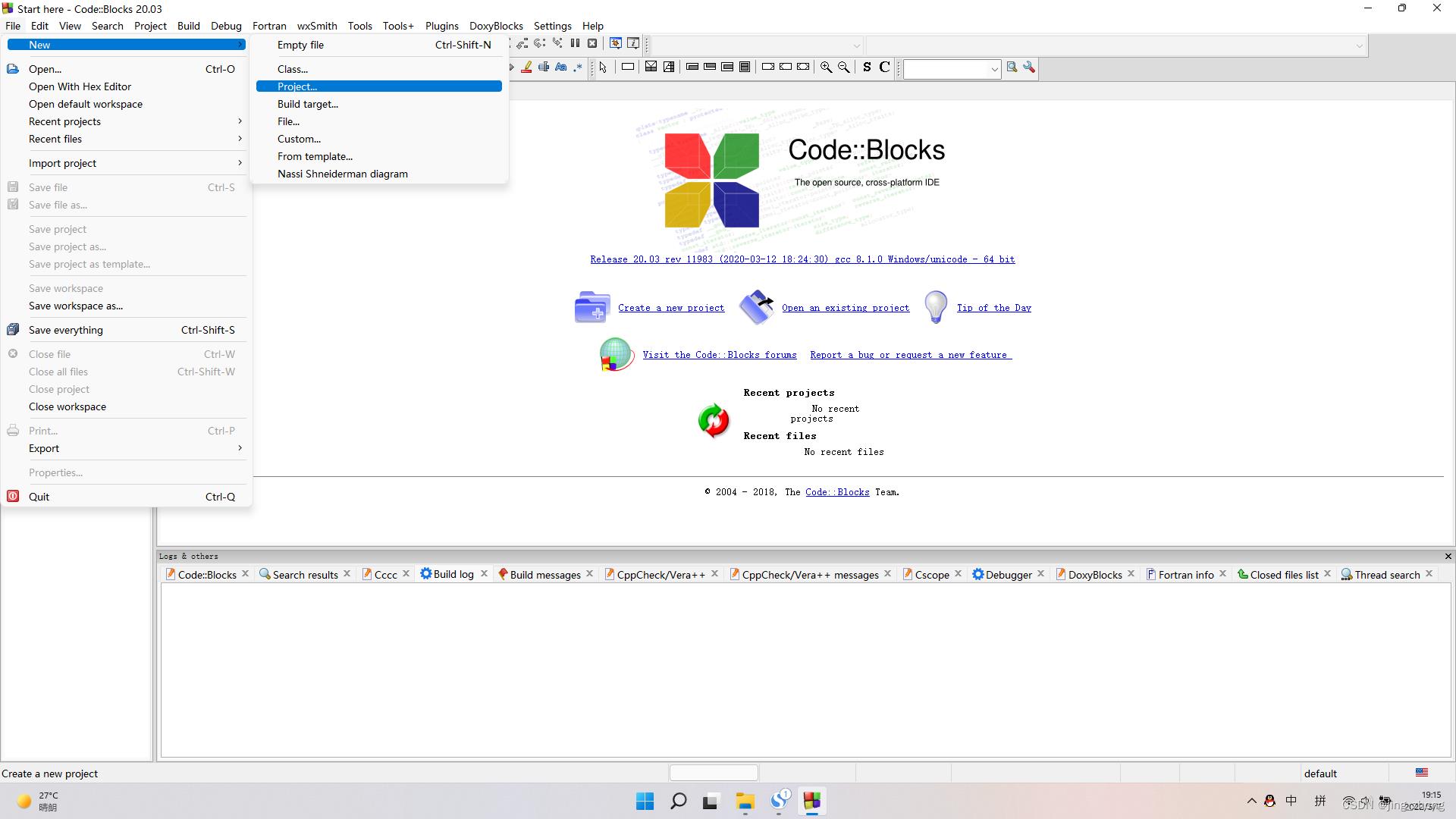
打开CodeBlocks软件,点击File->New->Project,选择Projects->Console->Console application后点击go,编程语言选择C,之后输入项目名称和项目文件夹,编译器选择GNU GCC Compiler后点击Finish,这样就成功创建了一个C项目。
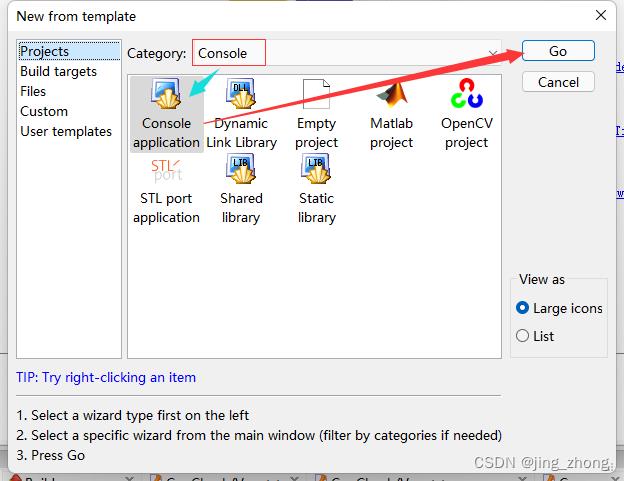 | 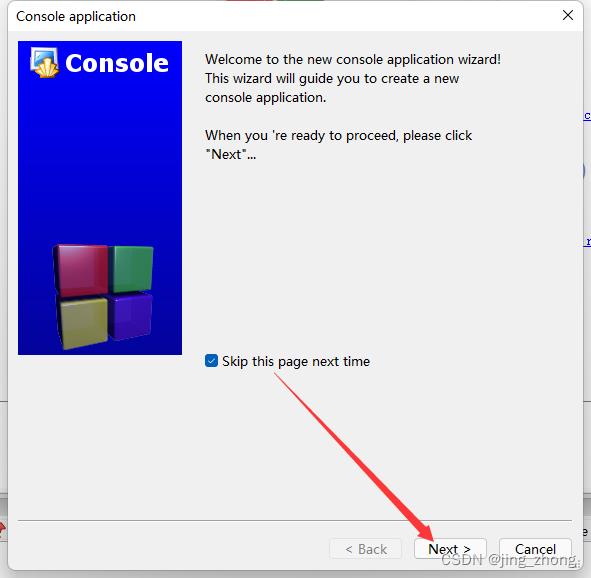 | |
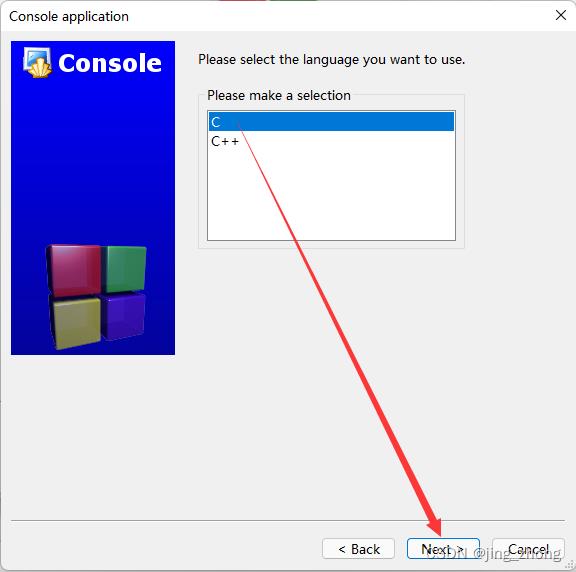 | 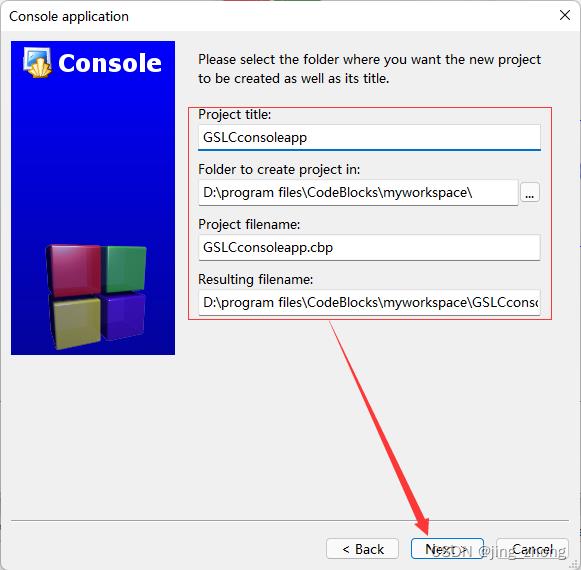 | |
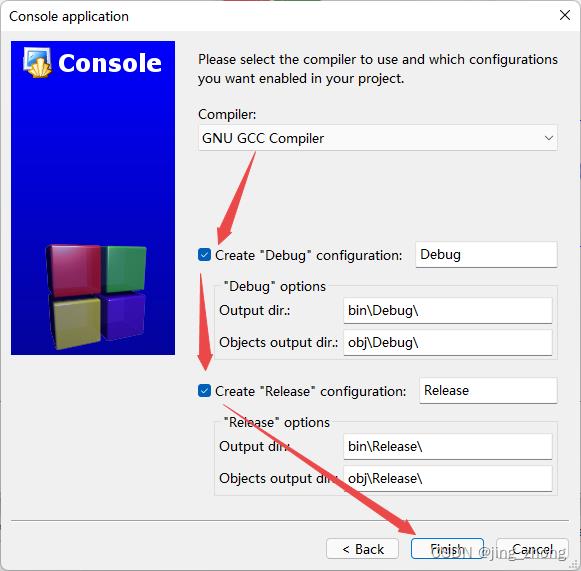 |
新建的C项目会自动生成main.c文件,将里面的代码替换为GSL相关的代码(注:自己可以到GSL文档中找Examples中的例子代码)。
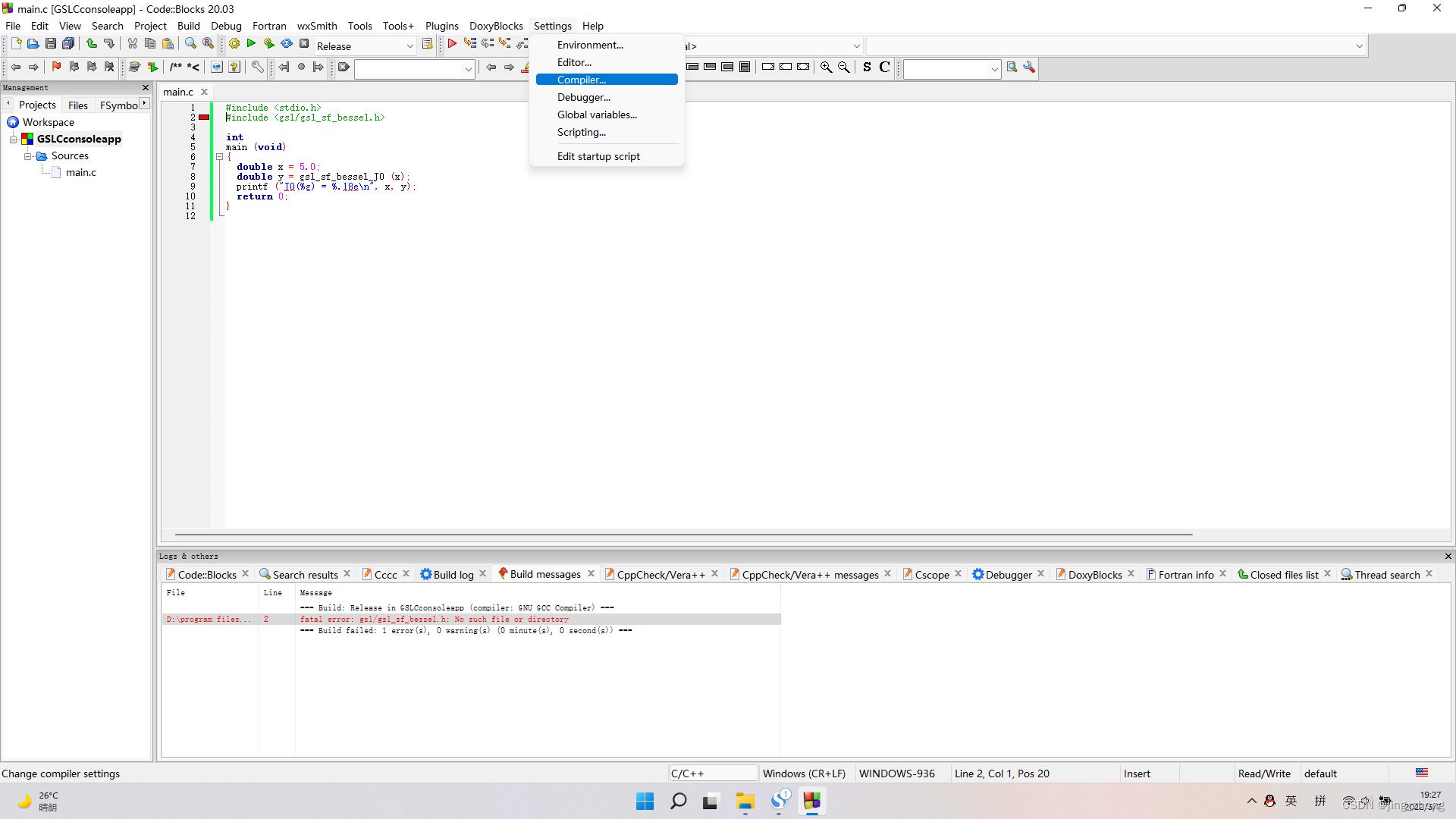
main.c代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_sf_bessel.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_fit.h>
int main (void)
int i, n = 4;
double x[4] = 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000 ;
double y[4] = 12, 11, 14, 13 ;
double w[4] = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 ;
double c0, c1, cov00, cov01, cov11, chisq;
gsl_fit_wlinear (x, 1, w, 1, y, 1, n,
&c0, &c1, &cov00, &cov01, &cov11,
&chisq);
printf ("# best fit: Y = %g + %g X\\n", c0, c1);
printf ("# covariance matrix:\\n");
printf ("# [ %g, %g\\n# %g, %g]\\n",cov00, cov01, cov01, cov11);
printf ("# chisq = %g\\n", chisq);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf ("data: %g %g %g\\n",
x[i], y[i], 1/sqrt(w[i]));
printf ("\\n");
for (i = -30; i < 130; i++)
double xf = x[0] + (i/100.0) * (x[n-1] - x[0]);
double yf, yf_err;
gsl_fit_linear_est (xf,
c0, c1,
cov00, cov01, cov11,
&yf, &yf_err);
printf ("fit: %g %g\\n", xf, yf);
printf ("hi : %g %g\\n", xf, yf + yf_err);
printf ("lo : %g %g\\n", xf, yf - yf_err);
double x1 = 5.0;
double y1 = gsl_sf_bessel_J0 (x1);
printf ("J0(%g) = %.18e\\n", x1, y1);
return 0;
另外,为了让GCC编译器找到GSL相关的头文件和库文件,还需要在CodeBlocks中设置GCC编译器的链接库目录、搜索包含目录,即在Compiler settings窗口设置Linker settings为GSL安装目录下lib文件夹中的所有.a文件,设置Search Directories为GSL安装目录下的include文件夹,检查GCC编译器的位置为CodeBlocks下的MinGW文件夹。
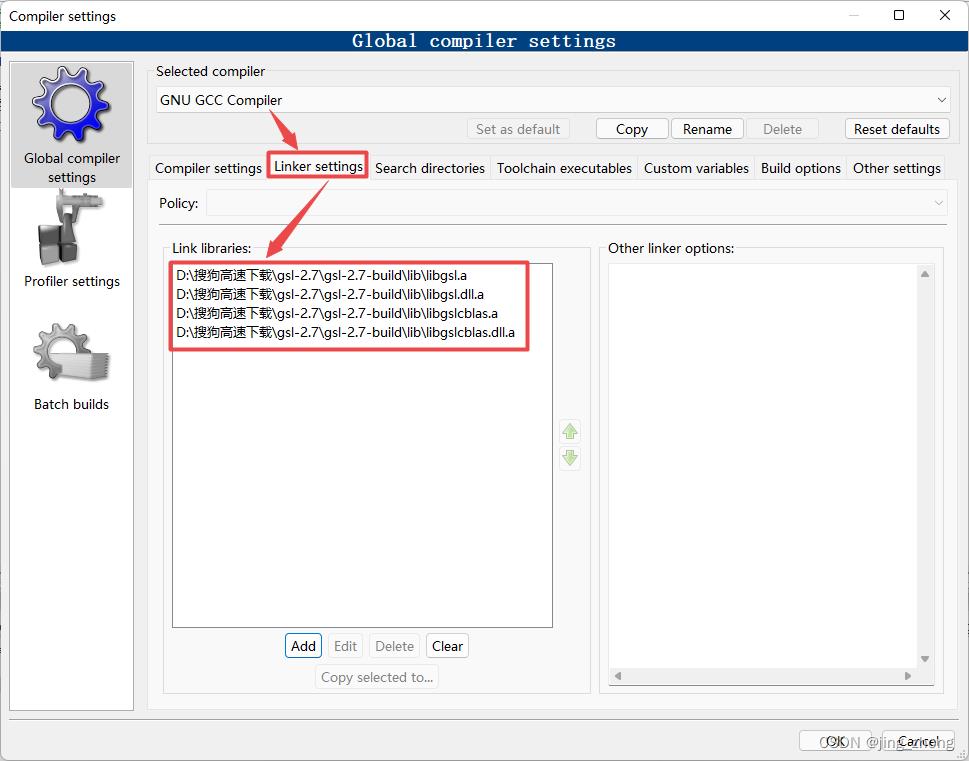
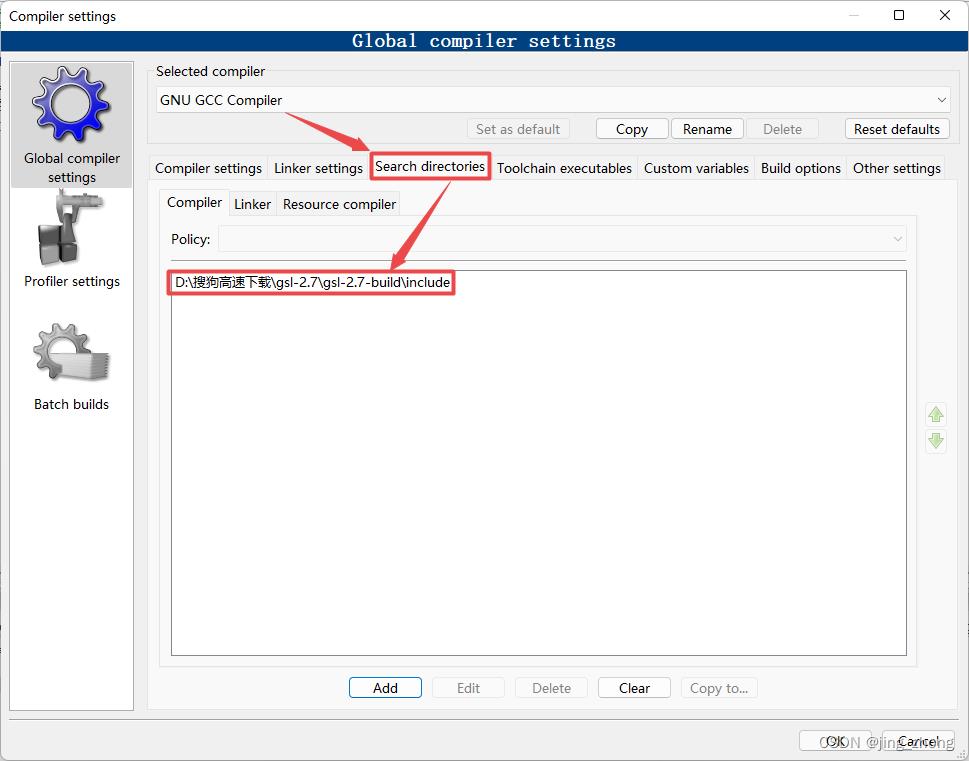
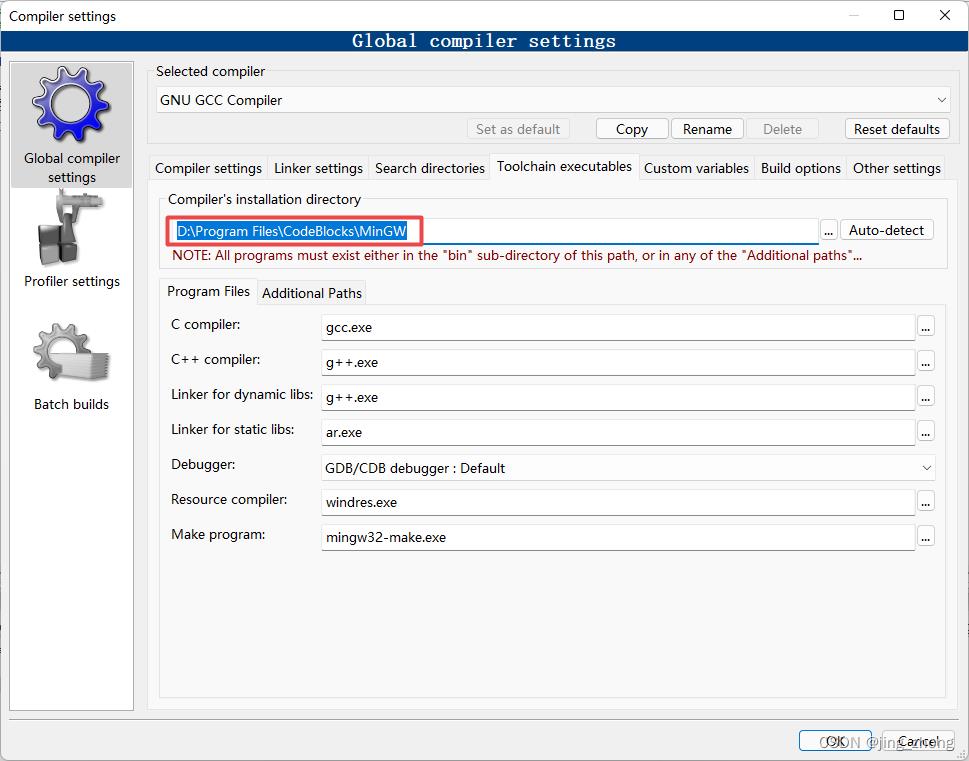
最后,在CodeBlocks的菜单栏中点击Build下的Build来编译生成项目,编译成功后点击Run对应的绿色朝右三角形按钮即可运行,在弹出的控制台窗口中查看运行结果。
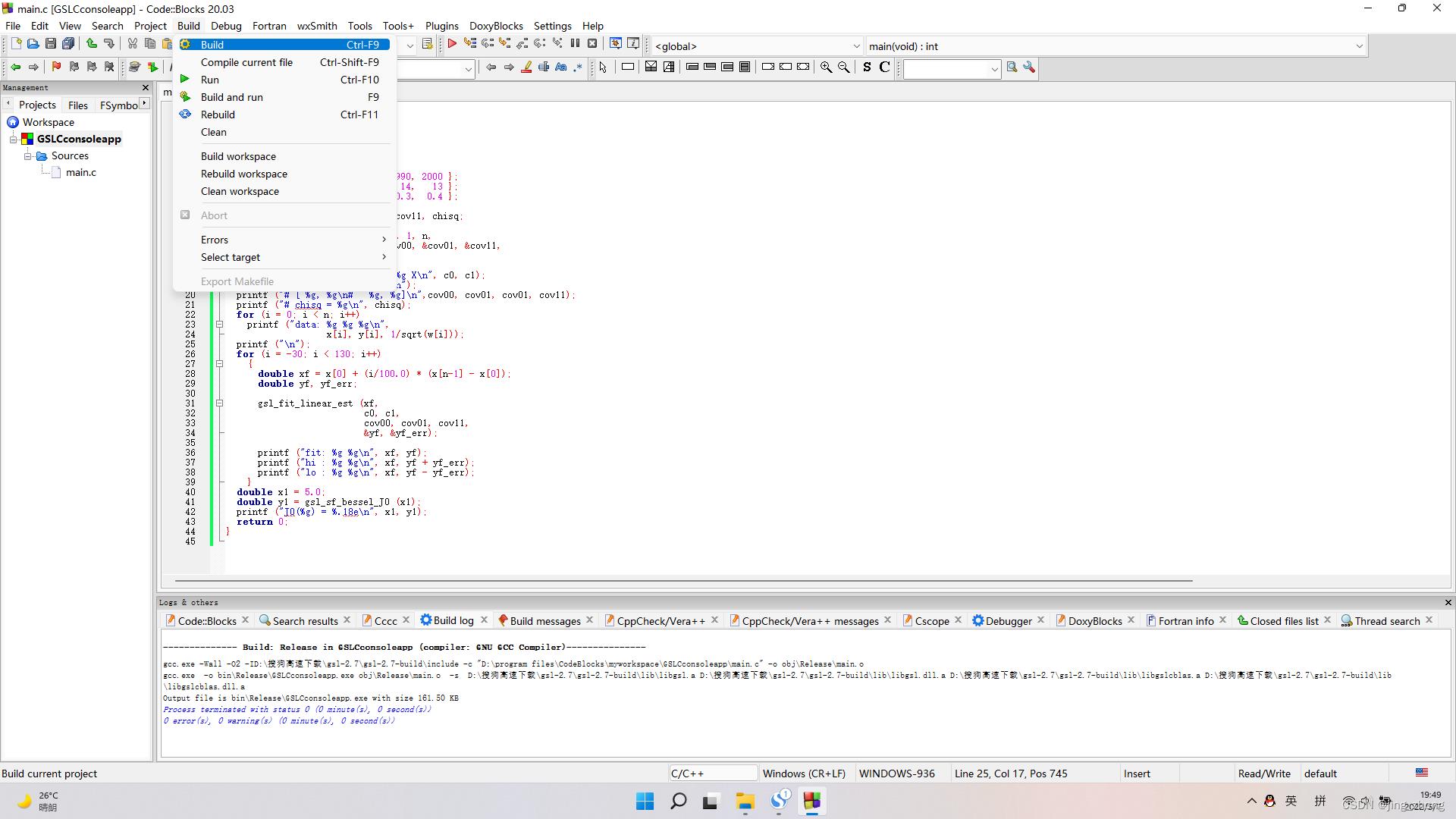
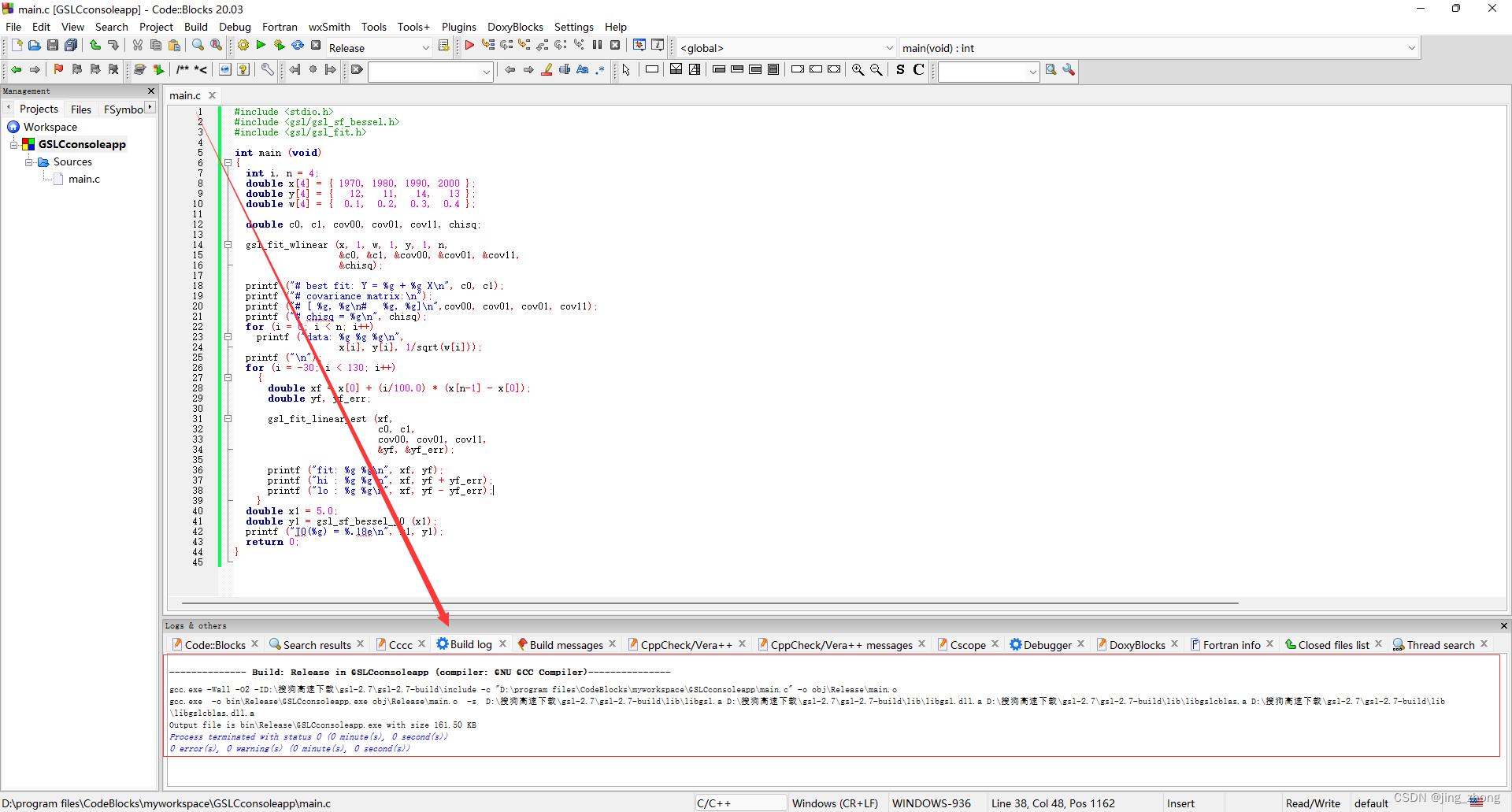
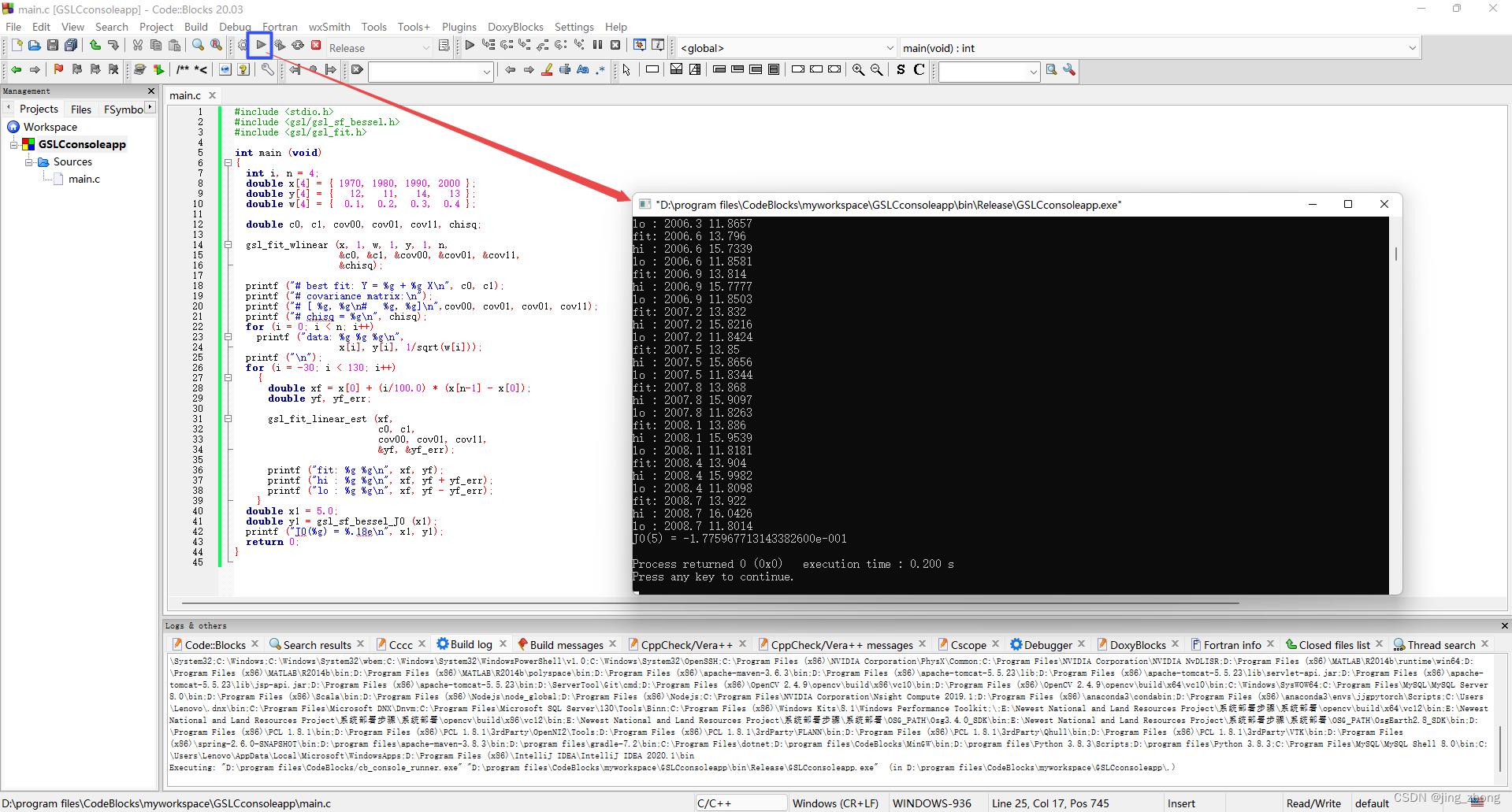
3.2 dll转lib用于VS 2015 中编写C项目调用(pexports + dlltool)
为了在Visual Studio中利用编译好的GSL库,则需要GSL安装目录lib文件夹下存在.lib文件,而上述编译的lib文件夹下仅存在.a文件(gcc编译器所用的lib文件),因此需要考虑将GSL安装目录bin文件夹下的.dll文件转换为.lib文件。而目前已知的转换方式主要有两种:(1)pexports.exe + MinGW自带的dlltool.exe;(2)pexports.exe +VS自带的lib.exe。
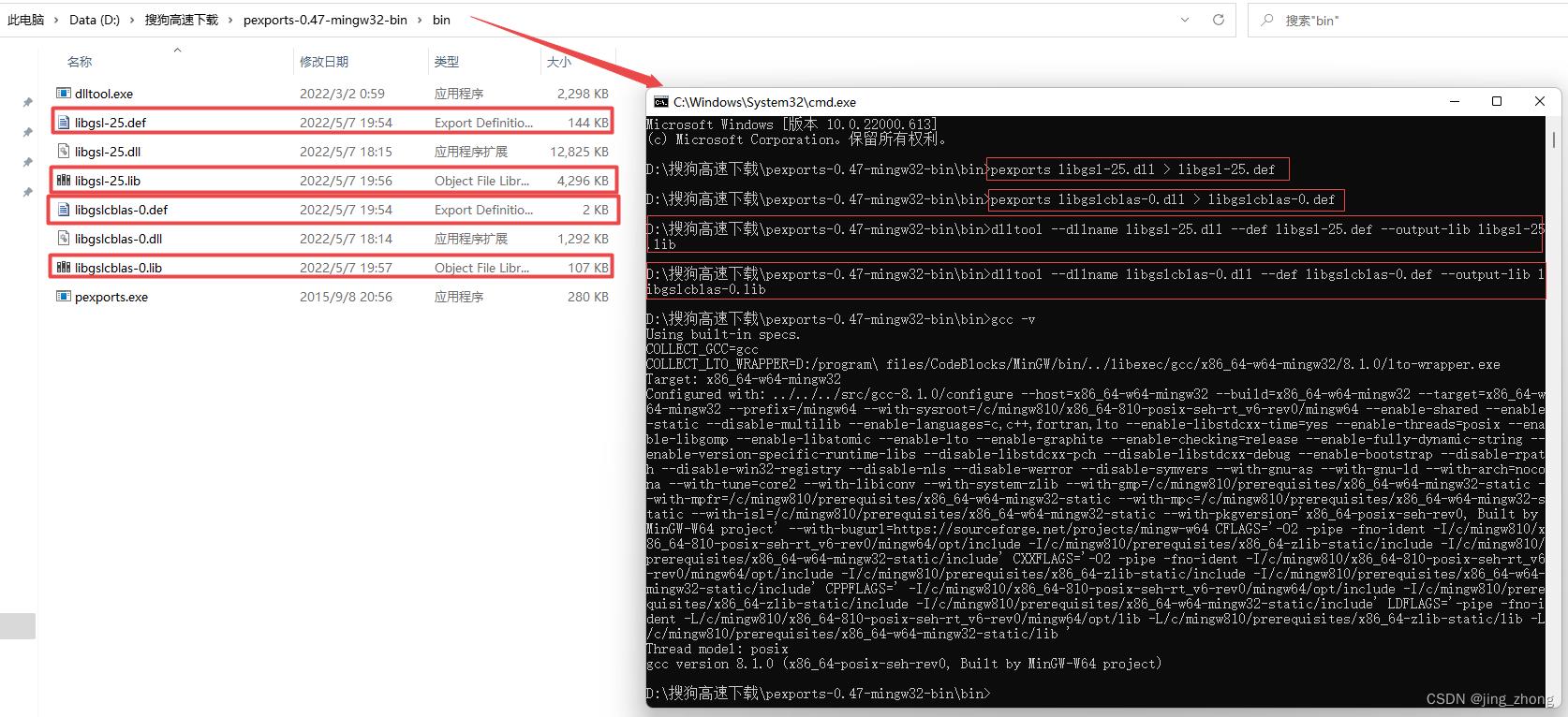
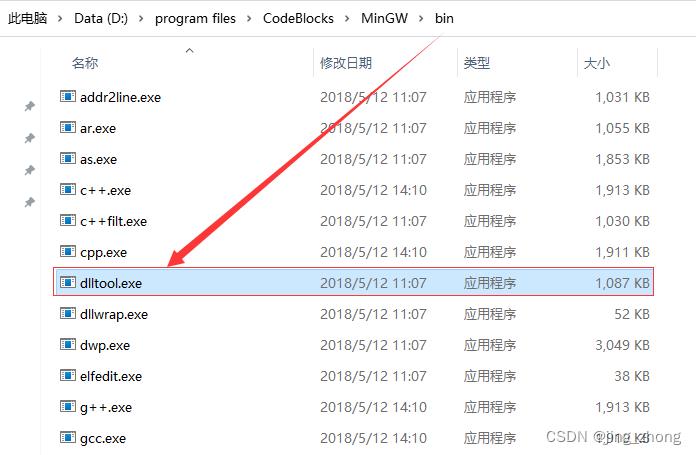
方式一:需要下载pexports.exe,dlltool.exe可在CodeBlocks安装目录下的MinGW\\bin文件夹 或 MSYS2安装目录下的MinGW\\bin文件夹下找到,将这两个exe文件复制到同一个目录下,然后将要转换的dll文件复制到该目录,并执行以下命令进行转换:
pexports libgls-25.dll >libgsl-25.def
pexports libgslcblas-0.dll >libgslcblas-0.def
dlltool --dllname libgsl-25.dll --def libgsl-25.def --output-lib libgsl-25.lib
dlltool --dllname libgslcblas-0.dll --def libgslcblas-0.def --output-lib libgslcblas-0.lib
可见,pexports负责将dll转换为def文件,而dlltool负责将dll和def一起转换为lib文件,具体执行过程如下图所示:
 |
 |
 |
 |  |
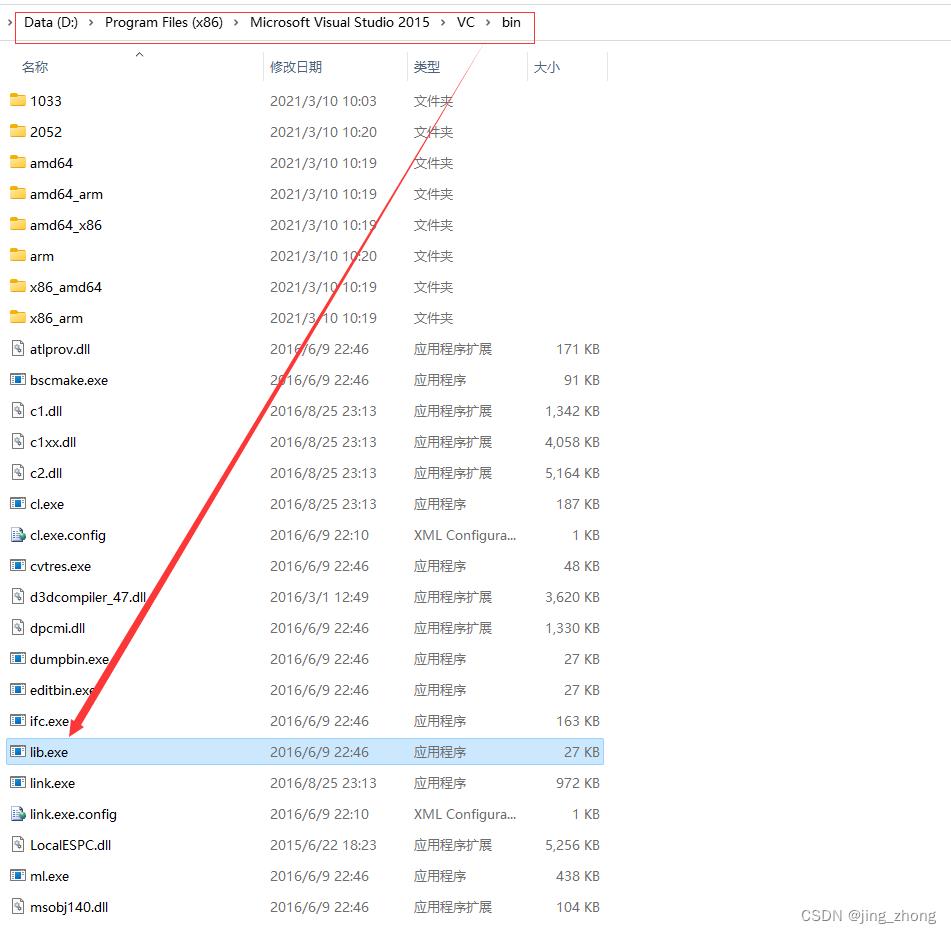
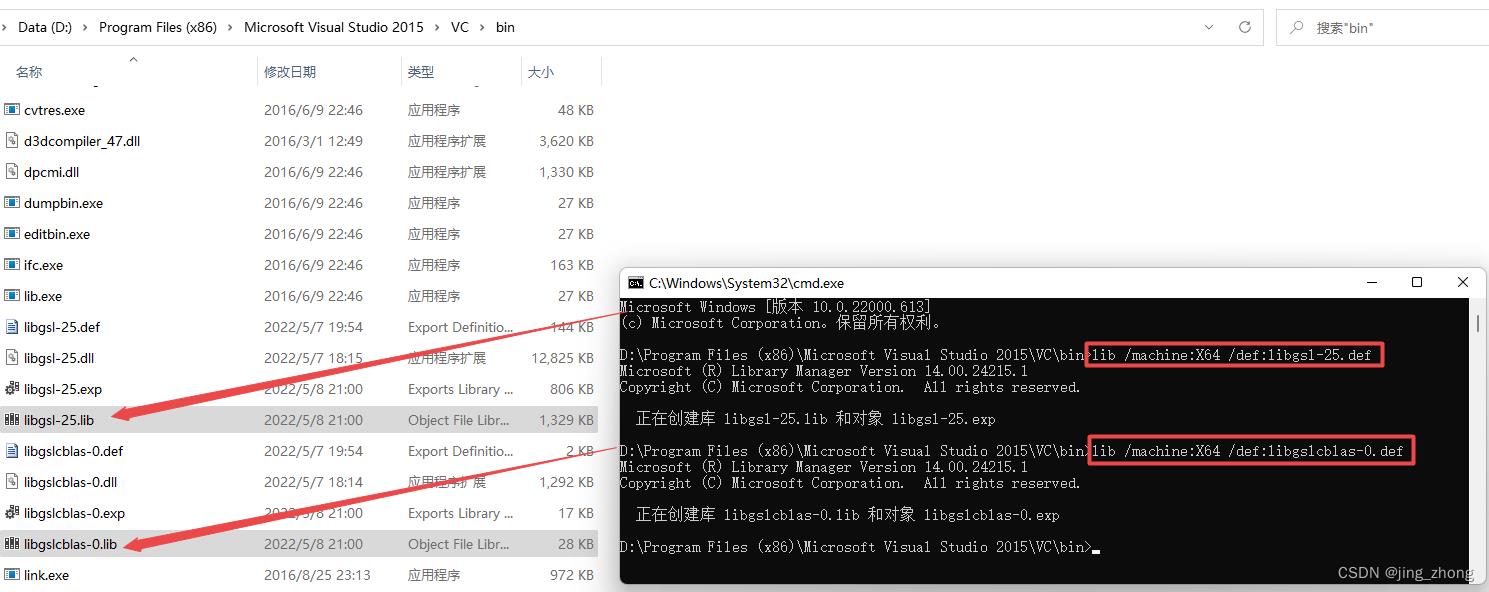
方式二:在VS安装目录下的VC\\bin文件夹下可以找到lib.exe文件(这里以VS 2015为例),将要转换的dll文件复制到此文件夹,然后在此文件夹处打开cmd窗口,输入的具体命令如下(32位和64位自己对应),将生成的两个lib文件放到GSL安装目录下的lib文件夹下。
lib /machine:i386 /def:libgsl-27.def # 32位
lib /machine:i386 /def:libgslcblas-0.def # 32位
# 由于电脑是64位,这里选择64位的进行转换
lib /machine:X64 /def:libgsl-27.def # 64位
lib /machine:X64 /def:libgslcblas-0.def # 64位
考虑到GSL库的底层实现是基于C语言,这里打开VS 2015,新建C++控制台项目,将项目配置为Release和64位后,在右侧的解决方案资源管理器窗口中,在项目名称上右键选择属性,在弹出的属性窗口中分别对附加包含目录、附加库目录、链接器->输入->附加依赖项进行设置。
 | 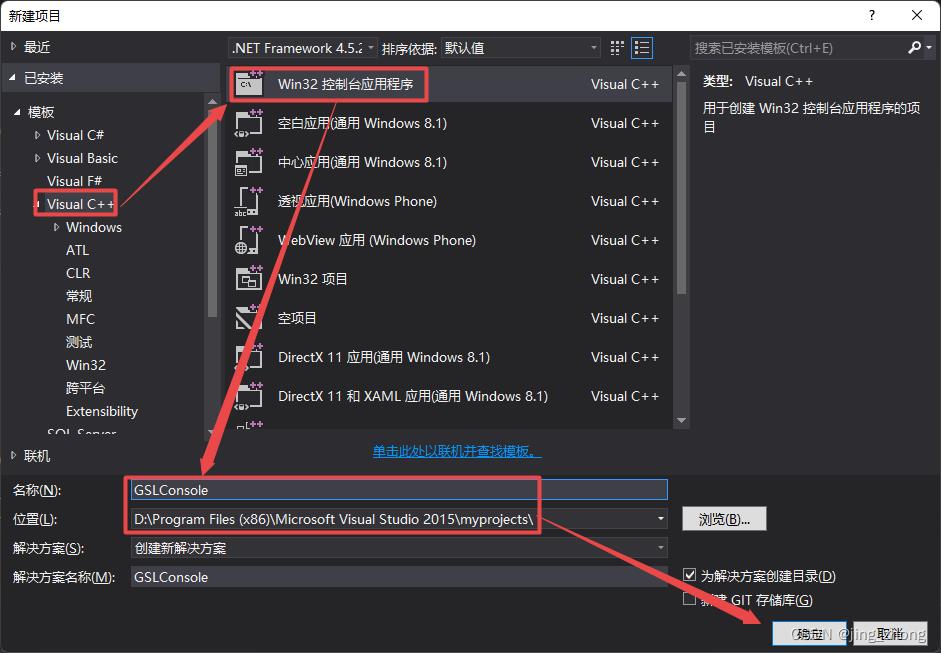 |
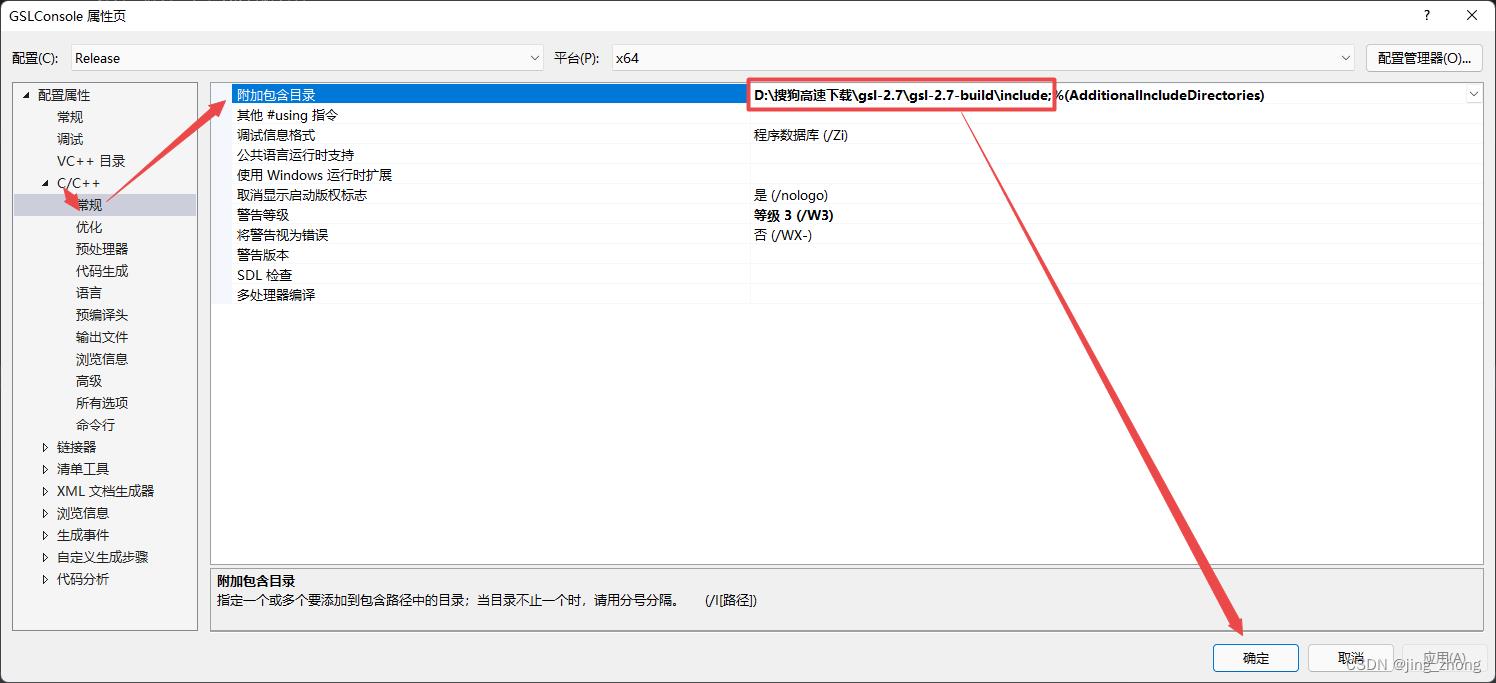
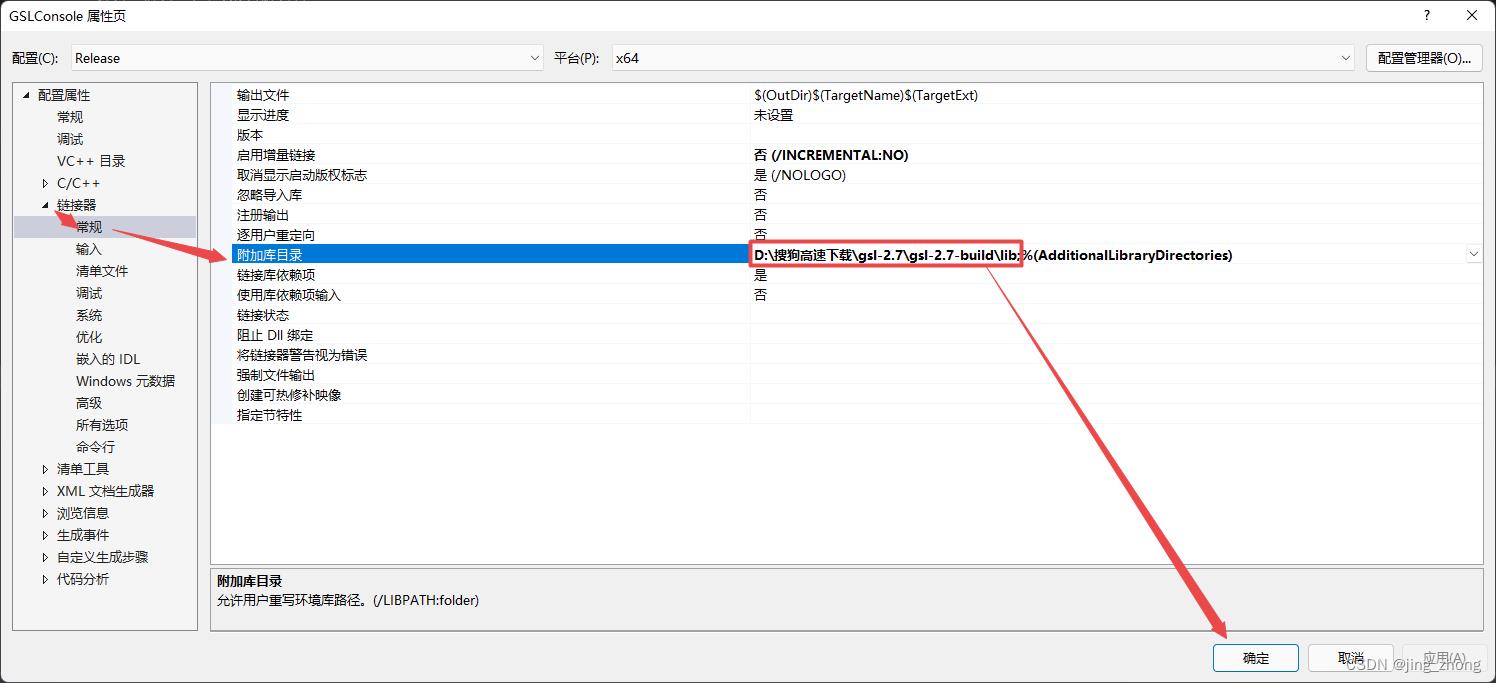
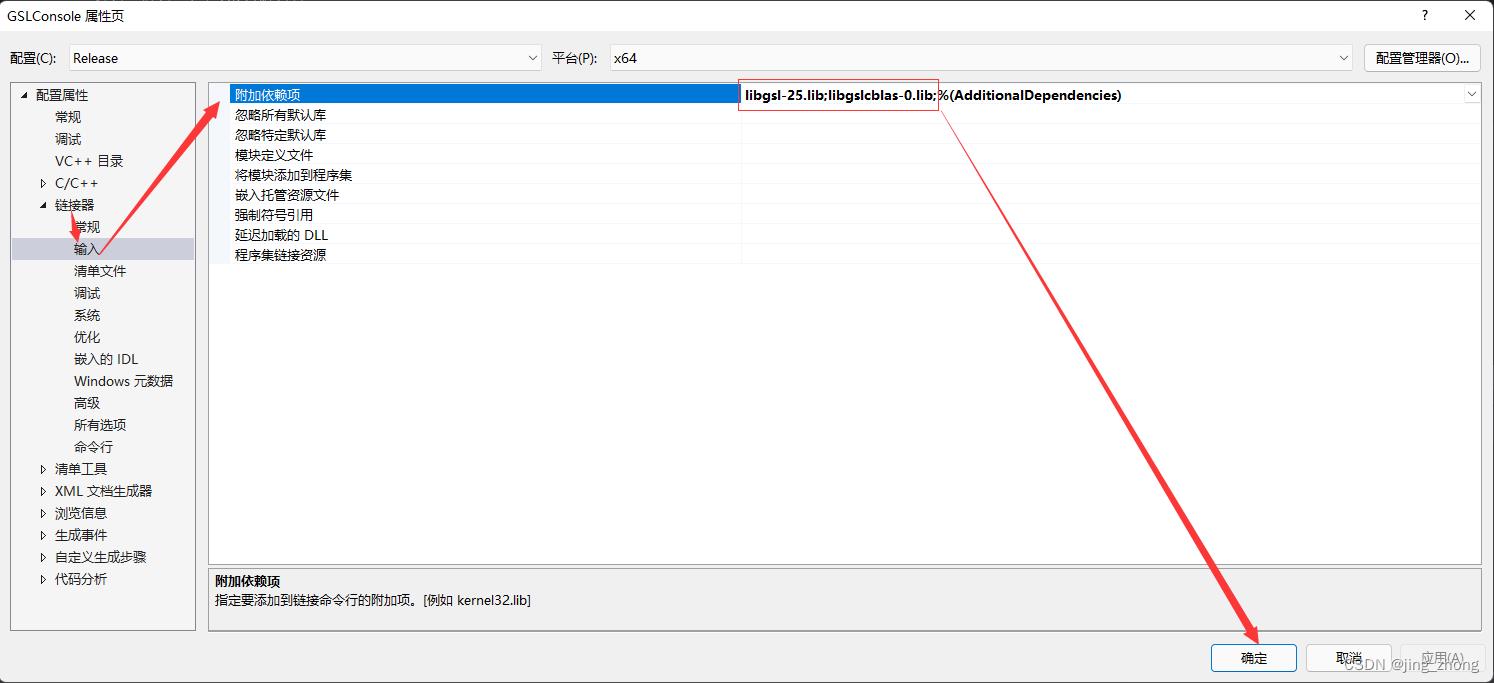
之后在源文件上右键选择添加->新建项,在弹出的添加新项窗口中点击C++文件,在文本框中输入main.c作为文件名后点击添加即可,然后打开main.c文件,输入以下代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_sf_bessel.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_fit.h>
int main(void)
int i, n = 4;
double x[4] = 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000 ;
double y[4] = 12, 11, 14, 13 ;
double w[4] = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 ;
double c0, c1, cov00, cov01, cov11, chisq;
gsl_fit_wlinear(x, 1, w, 1, y, 1, n,&c0, &c1, &cov00, &cov01, &cov11,&chisq);
printf("# best fit: Y = %g + %g X\\n", c0, c1);
printf("# covariance matrix:\\n");
printf("# [ %g, %g\\n# %g, %g]\\n", cov00, cov01, cov01, cov11);
printf("# chisq = %g\\n", chisq);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("data: %g %g %g\\n",
x[i], y[i], 1 / sqrt(w[i]));
printf("\\n");
for (i = -30; i < 130; i++)
double xf = x[0] + (i / 100.0) * (x[n - 1] - x[0]);
double yf, yf_err;
gsl_fit_linear_est(xf,c0, c1,cov00, cov01, cov11,&yf, &yf_err);
printf("fit: %g %g\\n", xf, yf);
printf("hi : %g %g\\n", xf, yf + yf_err);
printf("lo : %g %g\\n", xf, yf - yf_err);
double x1 = 5.0;
double y1 = gsl_sf_bessel_J0(x1);
以上是关于Windows系统编译GSL2.7用于C语言编程(2022.5.8)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章