IO流知识点
Posted 技术很low的瓜贼
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了IO流知识点相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
IO流
概念:
- IO就是Input和Output的简写,也就是输入和输出的含义
- IO流就是指读写数据时像流水一样从一端流到另外一端,因此得名为“流"
分类:
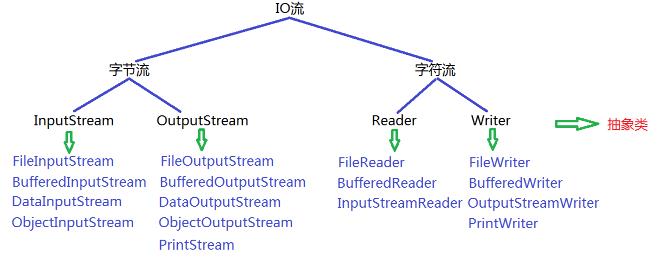
- 按照读写数据的基本单位不同,分为 字节流 和 字符流
- 字节流主要指以字节为单位进行数据读写的流,可以读写任意类型的文件
- 字符流主要指以字符(2个字节)为单位进行数据读写的流,只能读写文本文件
- 按照读写数据的方向不同,分为 输入流 和 输出流
- 输入流主要指从文件中读取数据内容输入到程序中,也就是读文件
- 输出流主要指将程序中的数据内容输出到文件中,也就是写文件
- 按照流的角色不同分为 节点流 和 处理流
- 节点流主要指直接和输入输出源对接的流
- 处理流主要指需要建立在节点流的基础之上的流
体系结构:

相关流解析:
FileWriter类
- 概念:
- java.io.FileWriter类主要用于将文本内容写入到文本文件
- 常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| FileWriter(String fileName) | 根据参数指定的文件名构造对象 |
| FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) | 以追加的方式根据参数指定的文件名来构造对象 |
| void write(int c) | 写入单个字符 |
| void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 将指定字符数组中从偏移量off开始的len个字符写入此文件输出流 |
| void write(char[] cbuf) | 将cbuf.length个字符从指定字符数组写入此文件输出流中 |
| void flush() | 刷新流 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
代码:
public class FileWriterTest
public static void write()
FileWriter fw = null;
try
// 构造FileWriter类型的对象与文件进行关联
// 若文件不存在自动创建新的文件
// 若文件存在清空文件中的原有内容
// fw = new FileWriter("g:/a.txt");
// 以追加的方式创建对象关联文件
fw = new FileWriter("g:/a.txt", true);
// 通过流对象写入数据内容
fw.write('f');
// 准备一个字符数组,写入文件
char[] crr = new char[] 'a', 'b', 'x', 'y';
// 写入固定位置范围内的元素
fw.write(crr, 1, 3);
// 写入整个数组内容
fw.write(crr);
System.out.println("字符写入成功");
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
if (null != fw)
fw.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
public static void main(String[] args)
FileWriterTest.write();
FileReader类
- 概念:
- java.io.FileReader类主要用于从文本文件读取文本数据内容
- 常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| FileReader(String fileName) | 根据参数指定的文件名构造对象 |
| int read() | 读取单个字符的数据并返回,返回-1表示读取到末尾 |
| int read(char[] cbuf, int offset, int length) | 从输入流中将最多len个字符的数据读入一个字符数组中,返回读取到的字符个数,返回-1表示读取到末尾 |
| int read(char[] cbuf) | 从此输入流中将最多 cbuf.length 个字符的数据读入字符数组中,返回读取到的字符个数,返回-1表示读取到末尾 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
代码:
/**
* 字符输入流
* 读取
*/
public class FileReaderTest
/**
* 单个字符读取文件内容
*/
public static void test1()
FileReader fr = null;
try
fr = new FileReader("g:/a.txt");
// 读取单个字符
//int read = fr.read();
//System.out.println((char)read);
int res = 0;
while((res = fr.read()) != -1)
System.out.println((char)res);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
if (fr != null)
try
fr.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
/**
* 通过数组读取文件内容
*/
public static void test2()
FileReader fr = null;
try
fr = new FileReader("g:/a.txt");
char[] arr = new char[10];
//int read = fr.read(arr, 2, 3);
int read = fr.read(arr);
System.out.println("读取到的字符个数为" + read);
for (char c : arr)
System.out.println((char)c);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
if (fr != null)
try
fr.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
public static void main(String[] args)
//FileReaderTest.test1();
FileReaderTest.test2();
FileOutputStream类
- 概念:
- java.io.FileOutputStream类主要用于将图像数据之类的原始字节流写入到输出流中
- 常用方法:
| FileOutputStream(String name) | 根据参数指定的文件名来构造对象 |
|---|---|
| FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) | 以追加的方式根据参数指定的文件名来构造对象 |
| void write(int b) | 将指定字节写入此文件输出流 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 将指定字节数组中从偏移量off开始的len个字节写入此文件输出流 |
| void write(byte[] b) | 将 b.length 个字节从指定字节数组写入此文件输出流中 |
| void flush() | 刷新此输出流并强制写出任何缓冲的输出字节 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
FileInputStream类
- 概念:
- java.io.FileInputStream类主要用于从输入流中以字节流的方式读取图像数据等
- 常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| FileInputStream(String name) | 根据参数指定的文件路径名来构造对象 |
| int read() | 从输入流中读取单个字节的数据并返回,返回-1表示读取到末尾 |
| int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 从此输入流中将最多len个字节的数据读入字节数组中,返回读取到的字节个数,返回-1表示读取到末尾 |
| int read(byte[] b) | 从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入字节数组中,返回读取到的字节个数,返回-1表示读取到末尾 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
| int available() | 获取输入流所关联文件的大小 |
BufferedOutputStream类
-
概念:
- java.io.BufferedOutputStream类主要用于描述缓冲输出流,此时不用为写入的每个字节调用底层系统
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) | 根据参数指定的引用和缓冲区大小来构造对象 |
| void write(int b) | 写入单个字节 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 写入字节数组中的一部分数据 |
| void write(byte[] b) | 写入参数指定的整个字节数组 |
| void flush() | 刷新流 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
BufferedInputStream类
-
概念:
- java.io.BufferedInputStream类主要用于描述缓冲输入流
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) | 根据参数指定的引用构造对象 |
| BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) | 根据参数指定的引用和缓冲区大小构造对象 |
| int read() | 读取单个字节 |
| int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 读取len个字节 |
| int read(byte[] b) | 读取b.length个字节 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
BufferedWriter类
-
概念:
- java.io.BufferedWriter类主要用于写入单个字符、字符数组以及字符串到输出流中
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| BufferedWriter(Writer out) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) | 根据参数指定的引用和缓冲区大小来构造对象 |
| void write(int c) | 写入单个字符到输出流中 |
| void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 将字符数组cbuf中从下标off开始的len个字符写入输出流中 |
| void write(char[] cbuf) | 将字符串数组cbuf中所有内容写入输出流中 |
| void write(String s, int off, int len) | 将参数s中下标从off开始的len个字符写入输出流中 |
| void write(String str) | 将参数指定的字符串内容写入输出流中 |
| void newLine() | 用于写入行分隔符到输出流中 |
| void flush() | 刷新流 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
BufferedReader类
-
概念:
- java.io.BufferedReader类用于从输入流中读取单个字符、字符数组以及字符串
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| BufferedReader(Reader in) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) | 根据参数指定的引用和缓冲区大小来构造对象 |
| int read() | 从输入流读取单个字符,读取到末尾则返回-1,否则返回实际读取到的字符内容 |
| int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 从输入流中读取len个字符放入数组cbuf中下标从off开始的位置上,若读取到末尾则返回-1,否则返回实际读取到的字符个数 |
| int read(char[] cbuf) | 从输入流中读满整个数组cbuf |
| String readLine() | 读取一行字符串并返回,返回null表示读取到末尾 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
PrintStream类
- 概念:
- java.io.PrintStream类主要用于更加方便地打印各种数据内容
- 常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| PrintStream(OutputStream out) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| void print(String s) | 用于将参数指定的字符串内容打印出来 |
| void println(String x) | 用于打印字符串后并终止该行 |
| void flush() | 刷新流 |
| void close() | 用于关闭输出流并释放有关的资源 |
代码:
/**
* 案例题目
* 不断地提示用户输入要发送的内容,若发送的内容是"bye"则聊天结束,否则将用户输入的内容写
* 入到文件d:/a.txt中。
* 要求使用BufferedReader类来读取键盘的输入 System.in代表键盘输入
* 要求使用PrintStream类负责将数据写入文件
*/
public class PrintWriterChatTest
public static void chat()
BufferedReader br = null;
PrintStream ps = null;
//PrintWriter ps = null;
try
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("g:/chat.txt"));
//ps = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("g:/char.txt"));
while (true)
System.out.println("请输入想要发送的内容");
String str = br.readLine();
if ("bye".equals(str))
System.out.println("聊天结束");
break;
ps.println(str);
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
if (null != ps)
ps.close();
if (null != br)
try
br.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
public static void main(String[] args)
PrintWriterChatTest.chat();
PrintWriter类
-
概念:
- java.io.PrintWriter类主要用于将对象的格式化形式打印到文本输出流
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| PrintWriter(Writer out) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| void print(String s) | 将参数指定的字符串内容打印出来 |
| void println(String x) | 打印字符串后并终止该行 |
| void flush() | 刷新流 |
| void close() | 关闭流对象并释放有关的资源 |
OutputStreamWriter类
-
概念:
- java.io.OutputStreamWriter类主要用于实现从字符流到字节流的转换
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName) | 根据参数指定的引用和编码构造对象 |
| void write(String str) | 将参数指定的字符串写入 |
| void flush() | void flush() |
| void close() | 用于关闭输出流并释放有关的资源 |
InputStreamReader类
-
概念:
- java.io.InputStreamReader类主要用于实现从字节流到字符流的转换
-
常用方法
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) | 根据参数指定的引用和编码来构造对象 |
| int read(char[] cbuf) | 读取字符数据到参数指定的数组 |
| void close() | 用于关闭输出流并释放有关的资源 |
DataOutputStream类
-
概念:
- java.io.DataOutputStream类主要用于以适当的方式将基本数据类型写入输出流中
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 根据参数指定的引用构造对象 OutputStream类是个抽象类,实参需要传递子类对象 |
| void writeInt(int v) | 用于将参数指定的整数一次性写入输出流,优先写入高字节 |
| void close() | 用于关闭文件输出流并释放有关的资源 |
DataInputStream类
-
概念:
- java.io.DataInputStream类主要用于从输入流中读取基本数据类型的数据
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| DataInputStream(InputStream in) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 InputStream类是抽象类,实参需要传递子类对象 |
| int readInt() | 用于从输入流中一次性读取一个整数数据并返回 |
| void close() | 用于关闭文件输出流并释放有关的资源 |
ObjectOutputStream类
-
概念:
- java.io.ObjectOutputStream类主要用于将一个对象的所有内容整体写入到输出流中
- 只能将支持 java.io.Serializable 接口的对象写入流中
- 类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能
- 所谓序列化主要指将一个对象需要存储的相关信息有效组织成字节序列的转化过程
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| void writeObject(Object obj) | 用于将参数指定的对象整体写入到输出流中 |
| void close() | 用于关闭输出流并释放有关的资源 |
代码:
public class Person implements Serializable
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8810212400968907736L;
private String username;
private String password;
private String phone;
public Person()
public Person(String username, String password, String phone)
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.phone = phone;
public String getUsername()
return username;
public void setUsername(String username)
this.username = username;
public String getPassword()
return password;
public void setPassword(String password)
this.password = password;
public String getPhone()
return phone;
public void setPhone(String phone)
this.phone = phone;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Person" +
"username='" + username + '\\'' +
", password='" + password + '\\'' +
", phone='" + phone + '\\'' +
'';
public class ObjectOutputStreamTest
public static void write()
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try
System.out.println("正在写入");
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("g:/a.txt"));
Person p1 = new Person("张三", "123456", "153654");
Person p2= new Person("李四", "223154", "45641321");
Person p3 = new Person("王五", "123456", "110");
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(p1);
list.add(p2);
list.add(p3);
for (Person person : list)
// 可以写入单个对象
// 当有多个对象的时候,可以直接写入一个集合
oos.writeObject(list);
//oos.writeInt(10);
System.out.println("写入成功");
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
if (null != oos)
try
oos.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
public static void main(String[] args)
ObjectOutputStreamTest.write();
ObjectInputStream类
-
概念:
- java.io.ObjectInputStream类主要用于从输入流中一次性将对象整体读取出来
- 所谓反序列化主要指将有效组织的字节序列恢复为一个对象及相关信息的转化过程
-
序列化版本号
- 序列化机制是通过在运行时判断类的serialVersionUID来验证版本一致性的。在进行反序列化时,JVM会把传来的字节流中的serialVersionUID与本地相应实体类的serialVersionUID进行比较,如果相同就认为是一致的,可以进行反序列化,否则就会出现序列化版本不一致的异常(InvalidCastException)
-
transient关键字
- transient是Java语言的关键字,用来表示一个域不是该对象串行化的一部分。当一个对象被串行化的时候,transient型变量的值不包括在串行化的表示中,然而非transient型的变量是被包括进去的。
-
常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) | 根据参数指定的引用来构造对象 |
| Object readObject() | 主要用于从输入流中读取一个对象并返回 无法通过返回值来判断是否读取到文件的末尾 |
| void close() | 用于关闭输入流并释放有关的资源 |
代码:
public class ObjectInputStreamTest
public static void read()
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("g:/a.txt"));
try
System.out.println(ois.readObject());
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
e.printStackTrace();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
if (null != ois)
try
ois.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
public static void main(String[] args)
ObjectInputStreamTest.read();
RandomAccessFile类
- 概念:
- java.io.RandomAccessFile类主要支持对随机访问文件的读写操作
- 常用方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| RandomAccessFile(String name, String mode) | 根据参数指定的名称和模式构造对象 r: 以只读方式打开 rw:打开以便读取和写入 rwd:打开以便读取和写入,同步文件内容的更新 rws:打开以便读取和写入,同步文件内容和元数据的更新 |
| int read() | 读取单个字节的数据 |
| void seek(long pos) | 用于设置从此文件的开头开始测量的文件指针偏移量 |
| void write(int b) | 将参数指定的单个字节写入以上是关于IO流知识点的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章 |