LeetCode 310. 最小高度树(找树中的最长路径) / 796. 旋转字符串 / 429. N 叉树的层序遍历
Posted Zephyr丶J
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode 310. 最小高度树(找树中的最长路径) / 796. 旋转字符串 / 429. N 叉树的层序遍历相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
310. 最小高度树
2022.4.6 每日一题
题目描述
树是一个无向图,其中任何两个顶点只通过一条路径连接。 换句话说,一个任何没有简单环路的连通图都是一棵树。
给你一棵包含 n 个节点的树,标记为 0 到 n - 1 。给定数字 n 和一个有 n - 1 条无向边的 edges 列表(每一个边都是一对标签),其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条无向边。
可选择树中任何一个节点作为根。当选择节点 x 作为根节点时,设结果树的高度为 h 。在所有可能的树中,具有最小高度的树(即,min(h))被称为 最小高度树 。
请你找到所有的 最小高度树 并按 任意顺序 返回它们的根节点标签列表。
树的 高度 是指根节点和叶子节点之间最长向下路径上边的数量。
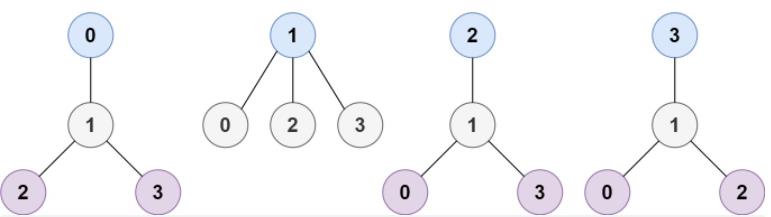
示例 1:
输入:n = 4, edges = [[1,0],[1,2],[1,3]]
输出:[1]
解释:如图所示,当根是标签为 1 的节点时,树的高度是 1 ,这是唯一的最小高度树。
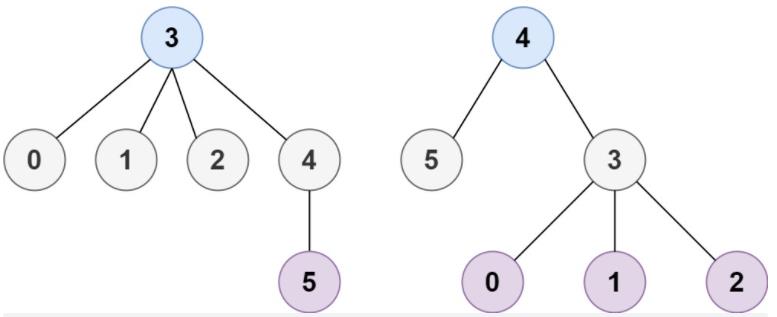
示例 2:
输入:n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]]
输出:[3,4]
提示:
1 <= n <= 2 * 10^4
edges.length == n - 1
0 <= ai, bi < n
ai != bi
所有 (ai, bi) 互不相同
给定的输入 保证 是一棵树,并且 不会有重复的边
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-height-trees
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
明知超时,但是还是写了一遍用广度优先的,思路也很简单,差五个例子
class Solution
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges)
//其中一个简单的思路就是每个点为起点广度优先,然后看哪一个遍历层数最少
//一个剪枝就是如果层数超过最小,那么跳过
//这样估计会超时
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int[] e : edges)
Set<Integer> set0 = map.getOrDefault(e[0], new HashSet<>());
Set<Integer> set1 = map.getOrDefault(e[1], new HashSet<>());
set0.add(e[1]);
set1.add(e[0]);
map.put(e[0], set0);
map.put(e[1], set1);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int min = n + 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(i);
boolean[] used = new boolean[n];
used[i] = true;
int idx = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty() && idx <= min)
int s = queue.size();
idx++;
while(s-- > 0)
int top = queue.poll();
Set<Integer> set = map.getOrDefault(top, new HashSet<>());
for(int t : set)
if(used[t])
continue;
used[t] = true;
queue.offer(t);
//System.out.println(idx);
if(idx < min)
min = idx;
list.clear();
list.add(i);
else if(idx == min)
list.add(i);
return list;
考虑一根绳子,怎么样折叠才能使长度最短,那么肯定是从中间折叠
一样的道理,找到最长的路径,然后从中间折叠就行了
现在的问题就变成了怎么找最长的路径了
看了题解,找最短路径的方法:
- 先从任一个节点,找相距最远的节点x
- 然后从x出发,找相距最远的节点y
- x到y就是最长的路径
class Solution
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map;
int n;
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges)
//其中一个简单的思路就是每个点为起点广度优先,然后看哪一个遍历层数最少
//一个剪枝就是如果层数超过最小,那么跳过
//这样估计会超时
//然后在写的时候发现,中间节点为根组成的树,肯定是高度最小的,
//所以去除掉边界节点,把所有中间节点加入到集合中就是答案,
//而中间节点就是可以连接多个点的节点
//不对,应该是找到最长的链,然后最长链的中间节点就是最小的根,
//就相当于一根绳子拎起来,两头最短只能是拎中间
//那么怎么找到这个最长的链条呢,相当于给定一棵树,找这颗树中最长的链
//好像也做过,但是突然不会了
//看了题解, 很巧妙
//先从任一个节点出发找到最远的节点x
//再从x出发,找到最远的结点y
//x到y就是最长路径
map = new HashMap<>();
this.n = n;
for(int[] e : edges)
Set<Integer> set0 = map.getOrDefault(e[0], new HashSet<>());
Set<Integer> set1 = map.getOrDefault(e[1], new HashSet<>());
set0.add(e[1]);
set1.add(e[0]);
map.put(e[0], set0);
map.put(e[1], set1);
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(n == 1)
res.add(0);
return res;
//在遍历中记录当前结点的父节点,方便最后找路径
int[] parents = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(parents, -1);
int x = helper(0, parents); //其实x不用记录路径
int y = helper(x, parents);
parents[x] = -1; //这里将x的父节点设为-1,这样两条路径不会混乱
//到这里,记录了x的父节点与y的父节点
//需要找到x到y的路径,怎么搞呢
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
while(y != -1)
path.add(y);
y = parents[y];
if(path.size() % 2 == 0)
int mid = path.size() / 2;
res.add(path.get(mid - 1));
res.add(path.get(mid));
else
int mid = path.size() / 2;
res.add(path.get(mid));
return res;
//广度优先找最长路径
public int helper(int t, int[] parents)
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(t);
boolean[] used = new boolean[n];
used[t] = true;
int ans = -1;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
//直接返回队列中最后一个节点
int top = queue.poll();
ans = top;
Set<Integer> set = map.get(top);
for(int node : set)
if(used[node])
continue;
used[node] = true;
queue.offer(node);
parents[node] = top;
return ans;
或者层层剥削,就是说先找到最外圈的节点,删除以后又得到了新的一层外圈节点
然后层层删除,删除到最后肯定还剩最长链的中间节点,这两个或者一个节点就是答案
class Solution
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges)
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (n == 1)
ans.add(0);
return ans;
int[] degree = new int[n];
List<Integer>[] adj = new List[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int[] edge : edges)
adj[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);
adj[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);
degree[edge[0]]++;
degree[edge[1]]++;
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (degree[i] == 1)
queue.offer(i);
int remainNodes = n;
while (remainNodes > 2)
int sz = queue.size();
remainNodes -= sz;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
int curr = queue.poll();
for (int v : adj[curr])
degree[v]--;
if (degree[v] == 1)
queue.offer(v);
while (!queue.isEmpty())
ans.add(queue.poll());
return ans;
796. 旋转字符串
2022.4.7 每日一题
题目描述
给定两个字符串, s 和 goal。如果在若干次旋转操作之后,s 能变成 goal ,那么返回 true 。
s 的 旋转操作 就是将 s 最左边的字符移动到最右边。
- 例如, 若 s = ‘abcde’,在旋转一次之后结果就是’bcdea’ 。
示例 1:
输入: s = “abcde”, goal = “cdeab”
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: s = “abcde”, goal = “abced”
输出: false
提示:
1 <= s.length, goal.length <= 100
s 和 goal 由小写英文字母组成
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-string
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
class Solution
public boolean rotateString(String s, String goal)
int l = s.length();
for(int i = 1; i <= l; i++)
String s1 = s.substring(0, i);
String s2 = s.substring(i, l);
if(goal.equals(s2 + s1))
return true;
return false;
class Solution:
def rotateString(self, s: str, goal: str) -> bool:
m, n = len(s), len(goal)
for i in range(1, m + 1):
if (s[i: ] + s[0 : i]) == goal:
return True
return False
直接拼接两个字符串,看是否包含目标字符串
class Solution:
def rotateString(self, s: str, goal: str) -> bool:
return len(s) == len(goal) and goal in (s + s)
429. N 叉树的层序遍历
2022.4.8 每日一题
题目描述
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
树的序列化输入是用层序遍历,每组子节点都由 null 值分隔(参见示例)。
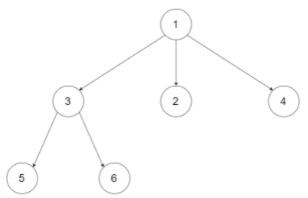
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
输出:[[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
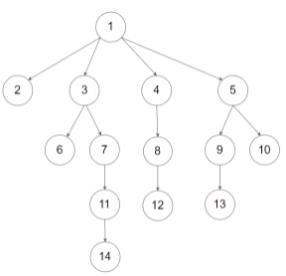
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
输出:[[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
提示:
树的高度不会超过 1000
树的节点总数在 [0, 10^4] 之间
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
就是简单的层序遍历
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node()
public Node(int _val)
val = _val;
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children)
val = _val;
children = _children;
;
*/
class Solution
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root)
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return list;
List<Integer> first = new ArrayList<>();
first.add(root.val);
list.add(first);
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
int sz = queue.size();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
while(sz-- > 0)
Node top = queue.poll();
List<Node> child = top.children;
if(child.isEmpty())
continue;
for(Node n : child)
temp.add(n.val);
queue.offer(n)以上是关于LeetCode 310. 最小高度树(找树中的最长路径) / 796. 旋转字符串 / 429. N 叉树的层序遍历的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章