cJson 常见用法
Posted fellow_jing
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了cJson 常见用法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
cJson是一个非常轻量级的JSON数据解析和构建的oss。
可以很容易的的在C代码中构建一个JSON格式的字符串。也可以将JSON字符串转成cJson中定义的cJson object.
通常用在,手机浏览器或者app发送一个JSON数据到平台,平台上运行的是C代码,平台需要将JSON字符串转成cJson object,再进行解析JSON中的内容转成C结构体,最终做完处理后,构建JSON字符串返回给手机浏览器和app。
同时,也可以用来搭建简单的JSON RPC机制,在客户端的API中将函数名和参数转换成JSON字符串,在server端去解析JSON字符串做处理。
cJson只包含两个文件cJson.c和cJson.h。我们在使用时可以直接嵌入到代码中,也可以将cJson编译成so再使用。
cJson自带的sample code是cJson用法的比较全面的例子。因此就不自己写sample了。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "cJSON.h"
/* Parse text to JSON, then render back to text, and print! */
void doit(char *text)
{
char *out;cJSON *json;
json=cJSON_Parse(text);//将字符串解析成Json object.
if (!json) {printf("Error before: [%s]\\n",cJSON_GetErrorPtr());}
else
{
out=cJSON_Print(json);
cJSON_Delete(json);
printf("%s\\n",out);
free(out);
}
}
/* Read a file, parse, render back, etc. */
void dofile(char *filename)
{
FILE *f;long len;char *data;
f=fopen(filename,"rb");fseek(f,0,SEEK_END);len=ftell(f);fseek(f,0,SEEK_SET);//计算文件长度。
data=(char*)malloc(len+1);fread(data,1,len,f);fclose(f);
doit(data);
free(data);
}
/* Used by some code below as an example datatype. */
struct record {
const char *precision;
double lat,lon;
const char *address,*city,*state,*zip,*country;
};
/* Create a bunch of objects as demonstration. */
void create_objects()
{
cJSON *root,*fmt,*img,*thm,*fld;char *out;int i; /* declare a few. */
/* Our "days of the week" array: */
const char *strings[7]={"Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"};
/* Our matrix: */
int numbers[3][3]={{0,-1,0},{1,0,0},{0,0,1}};
/* Our "gallery" item: */
int ids[4]={116,943,234,38793};
/* Our array of "records": */
struct record fields[2]={
{"zip",37.7668,-1.223959e+2,"","SAN FRANCISCO","CA","94107","US"},
{"zip",37.371991,-1.22026e+2,"","SUNNYVALE","CA","94085","US"}
};
/* Here we construct some JSON standards, from the JSON site. */
/* Our "Video" datatype: */
//构建的Json数据如下:

root=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "name", cJSON_CreateString("Jack (\\"Bee\\") Nimble"));
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "format", fmt=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fmt,"type", "rect");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fmt,"width", 1920);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fmt,"height", 1080);
cJSON_AddFalseToObject (fmt,"interlace");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fmt,"frame rate", 24);
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\\n",out); free(out); /* Print to text, Delete the cJSON, print it, release the string. */
/* Our "days of the week" array: */
//构建的Json数据如下:

root=cJSON_CreateStringArray(strings,7);
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\\n",out); free(out);
/* Our matrix: */
//构建的Json数据如下:
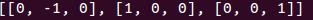
root=cJSON_CreateArray();
for (i=0;i<3;i++) cJSON_AddItemToArray(root,cJSON_CreateIntArray(numbers[i],3));
/* cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(root,1,cJSON_CreateString("Replacement")); */
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\\n",out); free(out);
/* Our "gallery" item: */
//构建的Json数据如下:
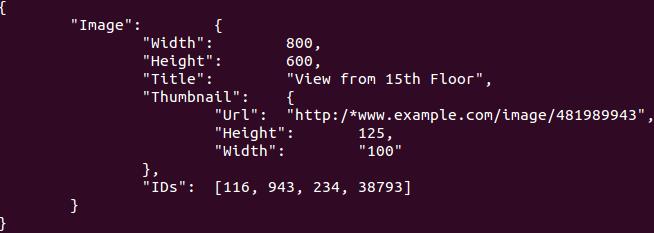
root=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "Image", img=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(img,"Width",800);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(img,"Height",600);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(img,"Title","View from 15th Floor");
cJSON_AddItemToObject(img, "Thumbnail", thm=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddStringToObject(thm, "Url", "http:/*www.example.com/image/481989943");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(thm,"Height",125);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(thm,"Width","100");
cJSON_AddItemToObject(img,"IDs", cJSON_CreateIntArray(ids,4));
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\\n",out); free(out);
/* Our array of "records": */
//构建的Json数据如下:
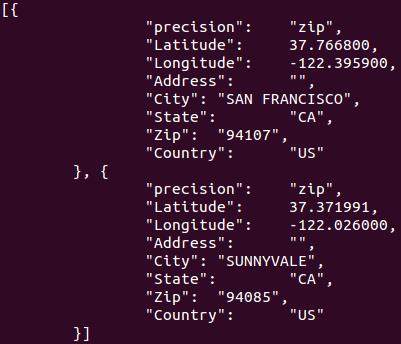
root=cJSON_CreateArray();
for (i=0;i<2;i++)
{
cJSON_AddItemToArray(root,fld=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "precision", fields[i].precision);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fld, "Latitude", fields[i].lat);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fld, "Longitude", fields[i].lon);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "Address", fields[i].address);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "City", fields[i].city);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "State", fields[i].state);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "Zip", fields[i].zip);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "Country", fields[i].country);
}
/* cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON_GetArrayItem(root,1),"City",cJSON_CreateIntArray(ids,4)); */
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\\n",out); free(out);
}
int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {
/* a bunch of json: */
char text1[]="{\\n\\"name\\": \\"Jack (\\\\\\"Bee\\\\\\") Nimble\\", \\n\\"format\\": {\\"type\\": \\"rect\\", \\n\\"width\\": 1920, \\n\\"height\\": 1080, \\n\\"interlace\\": false,\\"frame rate\\": 24\\n}\\n}";
char text2[]="[\\"Sunday\\", \\"Monday\\", \\"Tuesday\\", \\"Wednesday\\", \\"Thursday\\", \\"Friday\\", \\"Saturday\\"]";
char text3[]="[\\n [0, -1, 0],\\n [1, 0, 0],\\n [0, 0, 1]\\n ]\\n";
char text4[]="{\\n \\"Image\\": {\\n \\"Width\\": 800,\\n \\"Height\\": 600,\\n \\"Title\\": \\"View from 15th Floor\\",\\n \\"Thumbnail\\": {\\n \\"Url\\": \\"http:/*www.example.com/image/481989943\\",\\n \\"Height\\": 125,\\n \\"Width\\": \\"100\\"\\n },\\n \\"IDs\\": [116, 943, 234, 38793]\\n }\\n }";
char text5[]="[\\n {\\n \\"precision\\": \\"zip\\",\\n \\"Latitude\\": 37.7668,\\n \\"Longitude\\": -122.3959,\\n \\"Address\\": \\"\\",\\n \\"City\\": \\"SAN FRANCISCO\\",\\n \\"State\\": \\"CA\\",\\n \\"Zip\\": \\"94107\\",\\n \\"Country\\": \\"US\\"\\n },\\n {\\n \\"precision\\": \\"zip\\",\\n \\"Latitude\\": 37.371991,\\n \\"Longitude\\": -122.026020,\\n \\"Address\\": \\"\\",\\n \\"City\\": \\"SUNNYVALE\\",\\n \\"State\\": \\"CA\\",\\n \\"Zip\\": \\"94085\\",\\n \\"Country\\": \\"US\\"\\n }\\n ]";
/* Process each json textblock by parsing, then rebuilding: */
doit(text1);
doit(text2);
doit(text3);
doit(text4);
doit(text5);
/* Parse standard testfiles: */
/* dofile("../../tests/test1"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test2"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test3"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test4"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test5"); */
/* Now some samplecode for building objects concisely: */
create_objects();
return 0;
}
上面的sample大都是字符串构建cJson object的过程。下面我们看看如何解析cJson object中的item。
int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {
/* a bunch of json: */
char text1[]="{\\n\\"name\\": \\"Jack (\\\\\\"Bee\\\\\\") Nimble\\", \\n\\"format\\": {\\"type\\": \\"rect\\", \\n\\"width\\": 1920, \\n\\"height\\": 1080, \\n\\"interlace\\": false,\\"frame rate\\": 24\\n}\\n}";
char *out;cJSON *json;
json=cJSON_Parse(text1);
if (!json) {printf("Error before: [%s]\\n",cJSON_GetErrorPtr());}
else
{
out=cJSON_Print(json);
cJSON *name = NULL;
name = cJSON_GetObjectItem(json, "name");
printf("name:%s\\n", name->valuestring);
cJSON *fmt = cJSON_GetObjectItem(json, "format");
printf("fmt:type:%s\\n", cJSON_GetObjectItem(fmt, "type")->valuestring);
printf("fmt:width:%d\\n",cJSON_GetObjectItem(fmt, "width")->valueint);
printf("fmt:height:%d\\n",cJSON_GetObjectItem(fmt, "height")->valueint);
printf("fmt:interlacetype:%d\\n", cJSON_GetObjectItem(fmt, "interlace")->type);
if (cJSON_GetObjectItem(fmt, "interlace")->type == (int) cJSON_False)
printf("fmt:interlace:false\\n");
else if (cJSON_GetObjectItem(fmt, "interlace")->type == (int)cJSON_True)
printf("fmt:interlace:true\\n");
printf("fmt:frame rate:%d\\n",cJSON_GetObjectItem(fmt, "frame rate")->valueint);
cJSON_Delete(json);
printf("%s\\n",out);
free(out);
}
return 0;
}
输出结果如下:

以上是关于cJson 常见用法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章