3d激光雷达开发(旋转和位移)
Posted 费晓行
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了3d激光雷达开发(旋转和位移)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【 声明:版权所有,欢迎转载,请勿用于商业用途。 联系信箱:feixiaoxing @163.com】
对于点云数据来说,旋转和位移的计算是十分必要的。比如数据匹配、识别、定位,如果需要查看获得的旋转矩阵对不对,那么就可以将原来的数据和旋转矩阵做一个乘积,这样就可以立刻看到对应的效果了。
1、准备transform.cpp文件
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/common/transforms.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
// This function displays the help
void
showHelp(char * program_name)
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "Usage: " << program_name << " cloud_filename.[pcd|ply]" << std::endl;
std::cout << "-h: Show this help." << std::endl;
// This is the main function
int
main (int argc, char** argv)
// Show help
if (pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "-h") || pcl::console::find_switch (argc, argv, "--help"))
showHelp (argv[0]);
return 0;
// Fetch point cloud filename in arguments | Works with PCD and PLY files
std::vector<int> filenames;
bool file_is_pcd = false;
filenames = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".ply");
if (filenames.size () != 1)
filenames = pcl::console::parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".pcd");
if (filenames.size () != 1)
showHelp (argv[0]);
return -1;
else
file_is_pcd = true;
// Load file | Works with PCD and PLY files
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr source_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
if (file_is_pcd)
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[filenames[0]], *source_cloud) < 0)
std::cout << "Error loading point cloud " << argv[filenames[0]] << std::endl << std::endl;
showHelp (argv[0]);
return -1;
else
if (pcl::io::loadPLYFile (argv[filenames[0]], *source_cloud) < 0)
std::cout << "Error loading point cloud " << argv[filenames[0]] << std::endl << std::endl;
showHelp (argv[0]);
return -1;
/* Reminder: how transformation matrices work :
|-------> This column is the translation
| 1 0 0 x | \\
| 0 1 0 y | -> The identity 3x3 matrix (no rotation) on the left
| 0 0 1 z | /
| 0 0 0 1 | -> We do not use this line (and it has to stay 0,0,0,1)
METHOD #1: Using a Matrix4f
This is the "manual" method, perfect to understand but error prone !
*/
Eigen::Matrix4f transform_1 = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
// Define a rotation matrix (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotation_matrix)
float theta = M_PI/4; // The angle of rotation in radians
transform_1 (0,0) = std::cos (theta);
transform_1 (0,1) = -sin(theta);
transform_1 (1,0) = sin (theta);
transform_1 (1,1) = std::cos (theta);
// (row, column)
// Define a translation of 2.5 meters on the x axis.
transform_1 (0,3) = 2.5;
// Print the transformation
printf ("Method #1: using a Matrix4f\\n");
std::cout << transform_1 << std::endl;
/* METHOD #2: Using a Affine3f
This method is easier and less error prone
*/
Eigen::Affine3f transform_2 = Eigen::Affine3f::Identity();
// Define a translation of 2.5 meters on the x axis.
transform_2.translation() << 2.5, 0.0, 0.0;
// The same rotation matrix as before; theta radians around Z axis
transform_2.rotate (Eigen::AngleAxisf (theta, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ()));
// Print the transformation
printf ("\\nMethod #2: using an Affine3f\\n");
std::cout << transform_2.matrix() << std::endl;
// Executing the transformation
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr transformed_cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
// You can either apply transform_1 or transform_2; they are the same
pcl::transformPointCloud (*source_cloud, *transformed_cloud, transform_2);
// Visualization
printf( "\\nPoint cloud colors : white = original point cloud\\n"
" red = transformed point cloud\\n");
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer ("Matrix transformation example");
// Define R,G,B colors for the point cloud
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> source_cloud_color_handler (source_cloud, 255, 255, 255);
// We add the point cloud to the viewer and pass the color handler
viewer.addPointCloud (source_cloud, source_cloud_color_handler, "original_cloud");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> transformed_cloud_color_handler (transformed_cloud, 230, 20, 20); // Red
viewer.addPointCloud (transformed_cloud, transformed_cloud_color_handler, "transformed_cloud");
viewer.addCoordinateSystem (1.0, "cloud", 0);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 0); // Setting background to a dark grey
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "original_cloud");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "transformed_cloud");
//viewer.setPosition(800, 400); // Setting visualiser window position
while (!viewer.wasStopped ()) // Display the visualiser until 'q' key is pressed
viewer.spinOnce ();
return 0;
2、代码说明
代码里面主要说明了两种构建旋转矩阵的方法。不管是哪一种,本质上都是要把yaw、pitch、roll、x、y、z通过计算映射到矩阵里面。
3、准备CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8 FATAL_ERROR)
project(transform)
find_package(PCL 1.2 REQUIRED)
include_directories($PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS)
link_directories($PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS)
add_definitions($PCL_DEFINITIONS)
add_executable (transform transform.cpp)
target_link_libraries (transform $PCL_LIBRARIES)4、开始生成sln工程,准备编译,
5、执行transform.exe
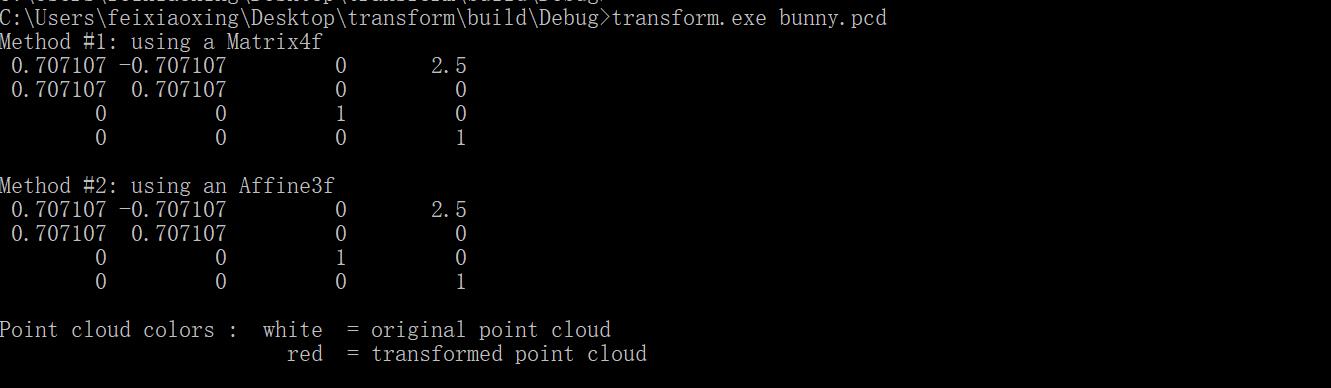
执行过程中,注意输入参数,即transform.exe bunny.pcd。
另外,代码中应该是对点云数据x轴偏移2.5米,z轴旋转theta角度,工作台的打印如下,
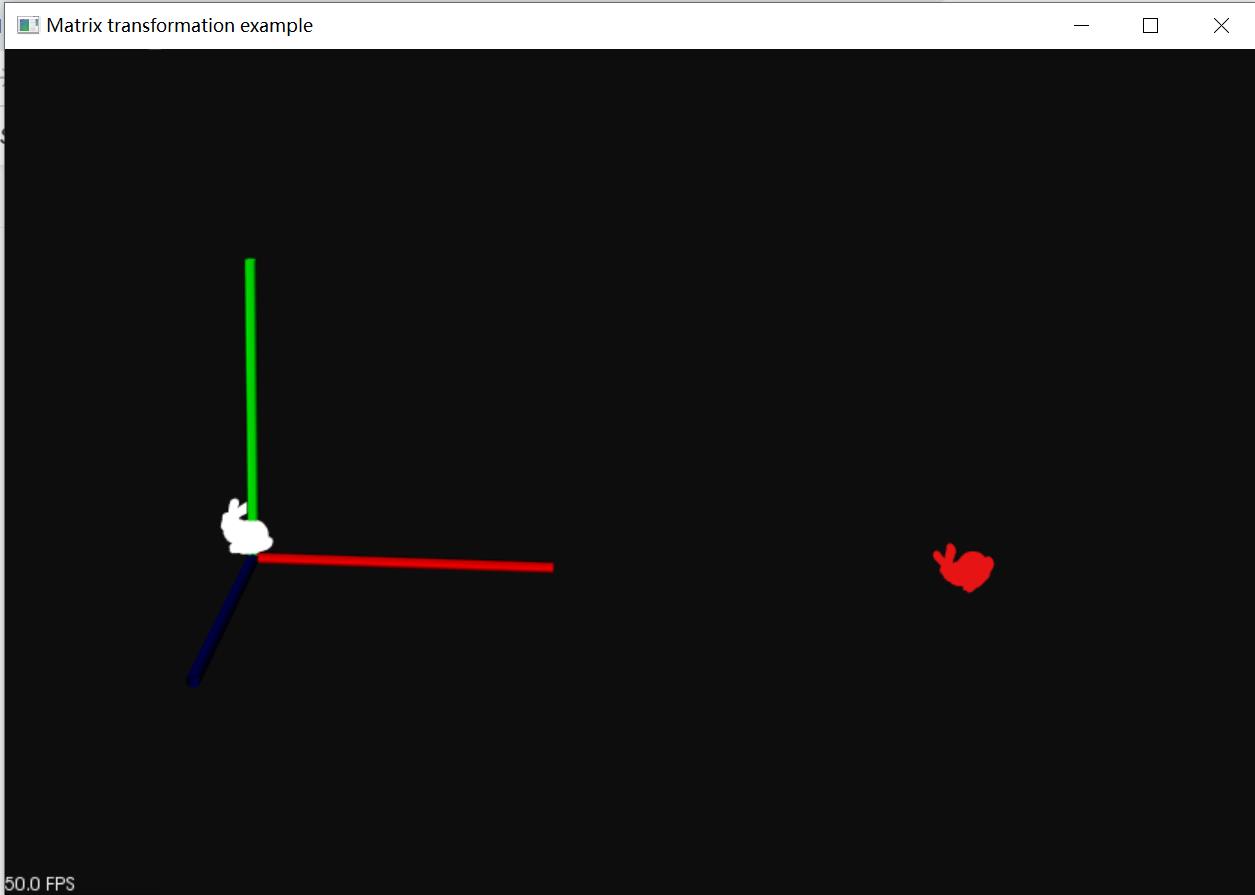
实际效果如下,
以上是关于3d激光雷达开发(旋转和位移)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章