Netty网络编程第二卷
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Netty网络编程第二卷相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Netty网络编程第二卷
- 二. Netty 入门
二. Netty 入门
1. 概述
1.1 Netty 是什么?
Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework
for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients.
Netty 是一个异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架,用于快速开发可维护、高性能的网络服务器和客户端
1.2 Netty 的作者

他还是另一个著名网络应用框架 Mina 的重要贡献者
1.3 Netty 的地位
Netty 在 Java 网络应用框架中的地位就好比:Spring 框架在 JavaEE 开发中的地位
以下的框架都使用了 Netty,因为它们有网络通信需求!
- Cassandra - nosql 数据库
- Spark - 大数据分布式计算框架
- Hadoop - 大数据分布式存储框架
- RocketMQ - ali 开源的消息队列
- ElasticSearch - 搜索引擎
- gRPC - rpc 框架
- Dubbo - rpc 框架
- Spring 5.x - flux api 完全抛弃了 tomcat ,使用 netty 作为服务器端
- Zookeeper - 分布式协调框架
1.4 Netty 的优势
- Netty vs NIO,工作量大,bug 多
- 需要自己构建协议
- 解决 TCP 传输问题,如粘包、半包
- epoll 空轮询导致 CPU 100%
- 对 API 进行增强,使之更易用,如 FastThreadLocal => ThreadLocal,ByteBuf => ByteBuffer
- Netty vs 其它网络应用框架
- Mina 由 apache 维护,将来 3.x 版本可能会有较大重构,破坏 API 向下兼容性,Netty 的开发迭代更迅速,API 更简洁、文档更优秀
- 久经考验,16年,Netty 版本
- 2.x 2004
- 3.x 2008
- 4.x 2013
- 5.x 已废弃(没有明显的性能提升,维护成本高)
2. Hello World
2.1 目标
开发一个简单的服务器端和客户端
- 客户端向服务器端发送 hello, world
- 服务器仅接收,不返回
加入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.39.Final</version>
</dependency>
日志依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0-alpha4</version>
</dependency>
2.2 服务器端
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/1/17 22:52
*/
public class Server
public static void main(String[] args)
//1.启动器,负责组装netty组件,启动服务器
new ServerBootstrap()
//2.BootStrapEventLoop(负责接收客户端连接),WorkerEventLoop(selector,thread)
//每一个Worker对应一个selector,并且都是一个独立的线程,负责处理注册到当前worker上的客户端的读写事件
//group:组
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
//3.选择服务器的ServerSocketChannel的实现,注意OIO指的就是BIO
.channel(NioserverSocketChannel.class)
//4.boss 负责处理连接 worker(child)负责处理读写
//,决定了worker(child)能执行哪些操作(handler)
.childHandler(
//5.channel代表和客户端进行数据读写的通道,Initializer初始化,负责添加别的handler
new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>()
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception
//6.添加具体的handler
//将ByteBuf转换成字符串
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
//自定义handler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter()
@Override//监听读事件
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception
//打印上一步转换好的字符串
System.out.println(msg);
);
)
//4.绑定监听的端口
.bind(8080);
代码解读
-
1 处,创建 NioEventLoopGroup,可以简单理解为
线程池 + Selector后面会详细展开 -
2 处,选择服务 Scoket 实现类,其中 NioServerSocketChannel 表示基于 NIO 的服务器端实现,其它实现还有
-
3 处,为啥方法叫 childHandler,是接下来添加的处理器都是给 SocketChannel 用的,而不是给 ServerSocketChannel。ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次),它的作用是待客户端 SocketChannel 建立连接后,执行 initChannel 以便添加更多的处理器
-
4 处,ServerSocketChannel 绑定的监听端口
-
5 处,SocketChannel 的处理器,解码 ByteBuf => String
-
6 处,SocketChannel 的业务处理器,使用上一个处理器的处理结果
2.3 客户端
public class Client
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
//1.启动类
new Bootstrap()
//2.添加EventLoop
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
//3. 选择客户端channle实现
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//4.添加处理器
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>()
@Override//9.在连接建立后被调用
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception
//编码
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
)
//5.连接服务器
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost",18080))
//6.阻塞直到连接建立
.sync()
//7.返回通道
.channel()
//8.向服务器发送数据
.writeAndFlush("hello world");
代码解读
-
1 处,创建 NioEventLoopGroup,同 Server
-
2 处,选择客户 Socket 实现类,NioSocketChannel 表示基于 NIO 的客户端实现,其它实现还有
-
3 处,添加 SocketChannel 的处理器,ChannelInitializer 处理器(仅执行一次),它的作用是待客户端 SocketChannel 建立连接后,执行 initChannel 以便添加更多的处理器
-
4 处,指定要连接的服务器和端口
-
5 处,Netty 中很多方法都是异步的,如 connect,这时需要使用 sync 方法等待 connect 建立连接完毕
-
6 处,获取 channel 对象,它即为通道抽象,可以进行数据读写操作
-
7 处,写入消息并清空缓冲区
-
8 处,消息会经过通道 handler 处理,这里是将 String => ByteBuf 发出
-
数据经过网络传输,到达服务器端,服务器端 5 和 6 处的 handler 先后被触发,走完一个流程
2.4 流程梳理
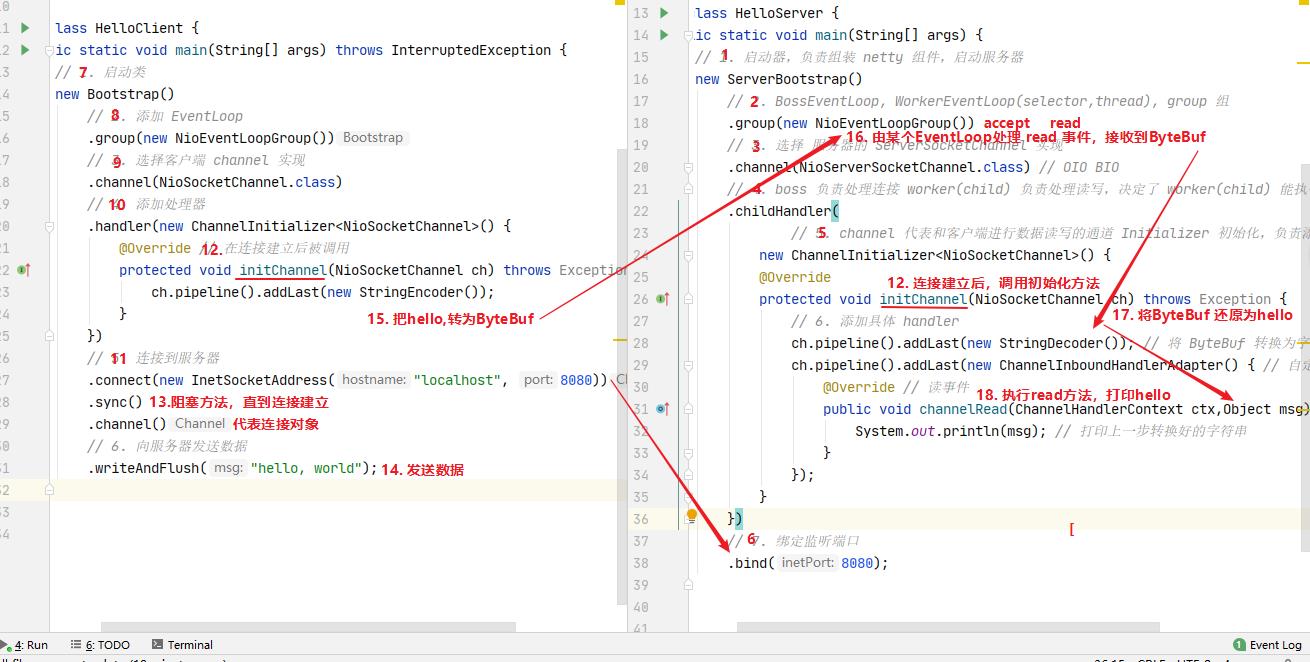
💡 提示
一开始需要树立正确的观念
- 把 channel 理解为数据的通道
- 把 msg 理解为流动的数据,最开始输入是 ByteBuf,但经过 pipeline 的加工,会变成其它类型对象,最后输出又变成 ByteBuf
- 把 handler 理解为数据的处理工序
- 工序有多道,合在一起就是 pipeline,pipeline 负责发布事件(读、读取完成…)传播给每个 handler, handler 对自己感兴趣的事件进行处理(重写了相应事件处理方法)
- handler 分 Inbound 和 Outbound 两类
- 把 eventLoop 理解为处理数据的工人
- 工人可以管理多个 channel 的 io 操作,并且一旦工人负责了某个 channel,就要负责到底(绑定)
- 工人既可以执行 io 操作,也可以进行任务处理,每位工人有任务队列,队列里可以堆放多个 channel 的待处理任务,任务分为普通任务、定时任务
- 工人按照 pipeline 顺序,依次按照 handler 的规划(代码)处理数据,可以为每道工序指定不同的工人
3. 组件
3.1 EventLoop
事件循环对象
EventLoop 本质是一个单线程执行器(同时维护了一个 Selector),里面有 run 方法处理 Channel 上源源不断的 io 事件。
它的继承关系比较复杂
- 一条线是继承自 j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService 因此包含了线程池中所有的方法
- 另一条线是继承自 netty 自己的 OrderedEventExecutor,
- 提供了 boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) 方法判断一个线程是否属于此 EventLoop
- 提供了 parent 方法来看看自己属于哪个 EventLoopGroup
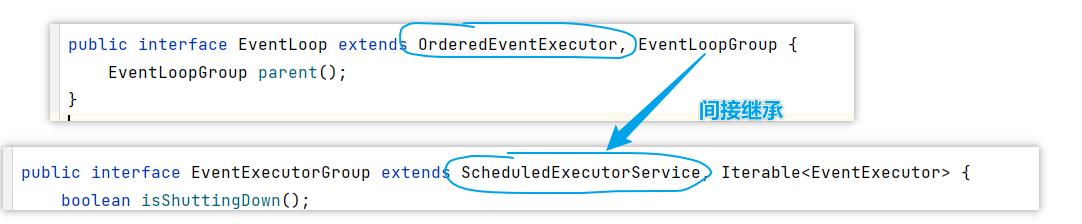

事件循环组
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop,Channel 一般会调用 EventLoopGroup 的 register 方法来绑定其中一个 EventLoop,后续这个 Channel 上的 io 事件都由此 EventLoop 来处理(保证了 io 事件处理时的线程安全)
- 继承自 netty 自己的 EventExecutorGroup
- 实现了 Iterable 接口提供遍历 EventLoop 的能力
- 另有 next 方法获取集合中下一个 EventLoop
以一个简单的实现为例:
// 内部创建了两个 EventLoop, 每个 EventLoop 维护一个线程
DefaultEventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup(2);//只能处理普通任务和定时任务
//EventLoopGroup group=new NioEventLoopGroup();//可以处理IO事件,普通任务和定时任务
System.out.println(group.next());
System.out.println(group.next());
System.out.println(group.next());

输出
io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@60f82f98
io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@35f983a6
io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@60f82f98
也可以使用 for 循环
DefaultEventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup(2);
for (EventExecutor eventLoop : group)
System.out.println(eventLoop);
输出
io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@60f82f98
io.netty.channel.DefaultEventLoop@35f983a6

之所以能直接,遍历,是因为实现了迭代器的接口
普通任务和定时任务
@Slf4j
public class Main
public static void main(String[] args)
// 内部创建了两个 EventLoop, 每个 EventLoop 维护一个线程
DefaultEventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup(2);
//提交普通任务
group.next().submit(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
sleep(1000);
log.debug("2 game over...");
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
);
//提交定时任务
//参数一: 任务 参数二: 开始时推迟多长时间执行 参数三: 每隔多长时间执行一次 参数四:单位
group.next().scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
System.out.println("我执行了一次");
,1000,1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
输出
14:33:19.761 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory - Using SLF4J as the default logging framework
14:33:19.766 [main] DEBUG io.netty.channel.MultithreadEventLoopGroup - -Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: 24
14:33:19.784 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap - -Dio.netty.threadLocalMap.stringBuilder.initialSize: 1024
14:33:19.784 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap - -Dio.netty.threadLocalMap.stringBuilder.maxSize: 4096
我执行了一次
14:33:20.809 [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG dhy.com.Main - 2 game over...
我执行了一次
我执行了一次
我执行了一次
我执行了一次
我执行了一次
线程池默认大小
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2
默认大小是cpu核心数*2
💡 优雅关闭
优雅关闭 shutdownGracefully 方法。该方法会首先切换 EventLoopGroup 到关闭状态从而拒绝新的任务的加入,然后在任务队列的任务都处理完成后,停止线程的运行。从而确保整体应用是在正常有序的状态下退出的
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/1/18 13:57
*/
@Slf4j
public class Main
public static void main(String[] args)
// 内部创建了两个 EventLoop, 每个 EventLoop 维护一个线程
DefaultEventLoopGroup group = new DefaultEventLoopGroup(2);
group.next().submit(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
sleep(1000);
log.debug("2 game over...");
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
);
group.next().submit(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
try
sleep(3000);
log.debug("1 game over...");
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
);
group.shutdownGracefully();
log.debug("优雅关闭程序了");
14:19:02.910 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory - Using SLF4J as the default logging framework
14:19:02.914 [main] DEBUG io.netty.channel.MultithreadEventLoopGroup - -Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: 24
14:19:02.931 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap - -Dio.netty.threadLocalMap.stringBuilder.initialSize: 1024
14:19:02.931 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap - -Dio.netty.threadLocalMap.stringBuilder.maxSize: 4096
14:19:02.940 [main] DEBUG dhy.com.Main - 优雅关闭程序了
14:19:03.941 [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG dhy.com.Main - 2 game over...
14:19:05.952 [defaultEventLoopGroup-2-2] DEBUG dhy.com.Main - 1 game over...
演示 NioEventLoop 处理 io 事件
客户端:
public class DhyClient
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
//1.启动类
Channel channel = new Bootstrap()
//2.添加EventLoop
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
//3. 选择客户端channle实现
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//4.添加处理器
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>()
@Override//在连接建立后被调用
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception
//编码
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
)
.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 18080))
.sync()
.channel();
System.out.println(channel);
System.out.println("");
服务器端两个 nio worker 工人
@Slf4j
public class DhyServer
public static void main(String[] args)
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>()
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel nioSocketChannel) throws Exception
nioSocketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter()
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, 以上是关于Netty网络编程第二卷的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章