HashMap核心代码解析
Posted 水田如雅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HashMap核心代码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1,基本结构图解
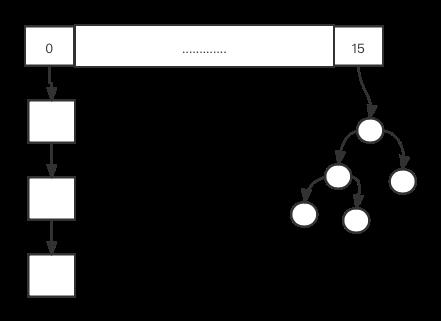
HashMap首先是一个 数组,数组的每个位置,挂的是链表或者红黑树 (jdk 1.8及其以上);在jdk 1.8之前,HashMap的实现仅仅是在数组的每个位置上 挂链表;
只用链表的弊端:可能以为位置上hash冲突过多,造成去定位时候,查找效率比较低,ps,链表的查找时间复杂度为O(n),红黑树查找的复杂度为O(logn);
2,如何去定位在数组中的位置
首先先来看HashMap是如何把数据打散的:
首先先来看HashMap是如何把数据打散的:
static final int hash(Object key)
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
拿到一个key的值,如果是null,直接返回默认0;
如果是其他,拿到key的hashcode,完了把hashcode的高16位和低16位异或。
ps,异或操作是均匀的0和1的位运算,这步操作每一位上取到0和1的概率一样,所以算是均匀的打散;
把key打散之后,直接取模获取数组的index:
i = (n - 1) & hash
这里没有进行除取余,因为位运算效率比较高;另外,n一般取的是2的整数倍;
3,如何放置
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict)
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount)
if ((e = p.next) == null)
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
if (e != null) // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
3.1 初始化hashmap
先来分段解析下:
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
首先,如果还没初始化,table,table也就是那个数组:
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
先去走初始化 数组,初始化这块也在resize里面,先不管别 的,光看初始化相关代码:
else // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
其实就是赋值个初始化的容量,还有一个threshold的值;
3.2 放置,不存在hash冲突的时候
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
当table里面计算出来的index不能在hash冲突的时候,直接new一个结点,放在这个位上。
而且这时候,创建的结点不是树的结点,就只是个链表的普通结点:
// Create a regular (non-tree) node
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next)
return new Node<>(hash, key, value, next);
3.3 放置,存在hash冲突的时候-就是头结点
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
对比头结点的hash和key发现要写入的值就是数组槽里面的头结点,直接把这个头结点赋值给e,这里的e代表我们这次要放入的结点。
3.4放置,存在hash冲突的时候-当前头结点是个红黑树的结点
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
拿到的是树的结点,放树上;
3.5放置,存在hash冲突的时候-当前头结点是是个链表
先来看整段的吧:
else
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount)
if ((e = p.next) == null)
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
if (e != null) // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
先来看binCount:
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
hashmap里面:
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
链表调整为树的临界值是8,当现在链表里面有超过7个元素时候,就先去调整,
if ((e = p.next) == null)
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
此时 p代表的是当前结点 ,如果当前结点没有next,也就是下面没链接着别的结点,直接放在p后面;
注意,与jdk 1.8之前相比,这里是链表的尾插法,因为每次肯定是要去判断链表长度,所以会从链表头结点找到尾部结点,插入 尾部去;
当要插入的key在链表中找到时候:
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
直接跳出循环,不找了;
如果是在链表里面,存在hash值和key相等的,就去把值修改下:
if (e != null) // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
整个写入操作完成之后 ,还要去:
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
modCount:表示被修改过多少次;
另外,如果实际长度 大于所能负载 的个数,去做一个resize的操作。
4, resize如何进行的
在初始化,和每次插入新元素之后,都会去执行resize操作。
4.1 当前数组已经被初始化完成-扩容两倍
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0)
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
首先,如果之前数组的长度大于0,先去判断是否数组长度已经扩容到最大容量:
最大容量为2的30次:
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
当前是最大容量,就不扩容了。
没达到最大容量,新容量扩容两倍,同时,负载容量也扩容两倍。
4.2 使用有参数的构造函数构造的hashmap
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
当自定义了初始容量和负载因子,
先来看:
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap)
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
这个过程就是把cap-1之后,拿到最高位上的1,其实还是为了保证初始容量是你2的几次方;之后 这个初始容量,会保存在 threshold里面;
所以,当我们去resize时候,才会有:
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
如果没定义初始容量啥 的,这里走个默认的:
else // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
然后是对负载容量的一些赋值:
if (newThr == 0)
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
threshold = newThr;
之后就比较粗暴:
4.3 核心调整过程
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes","unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
table就直接变成了一个刚声明的数组;
下面是核心的调整过程:
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j)
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null)
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0)
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
else
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null)
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
if (hiTail != null)
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
还是分段来看吧。
老数组只有一个结点,直接扔到新数组:
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
新数组的下标为:e.hash & (newCap - 1)。这里是不用去计算老的hash值的,因为都在node里面存着;
往下走,如果是树的结点:
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
走个分裂的方法:
spit()
方法的作用是将旧数组转移到新数组
split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit)
方法的四个参数分别是:
当前hashMap对象、新数组、正在遍历的旧数组下标、旧数组的长度
final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V以上是关于HashMap核心代码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章