了解String类
Posted 3 ERROR(s)
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了了解String类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
系列文章目录
文章目录
一、创建字符串
1.创建字符串的三种方法
//方式一
String str1="Hello";
//方式二
String str2 = new String("Hello");
//方式三
char arr[]='a','b','c','d';
String str3=new String(arr);
1.2创建字符串的内存布局
String str1="hello";
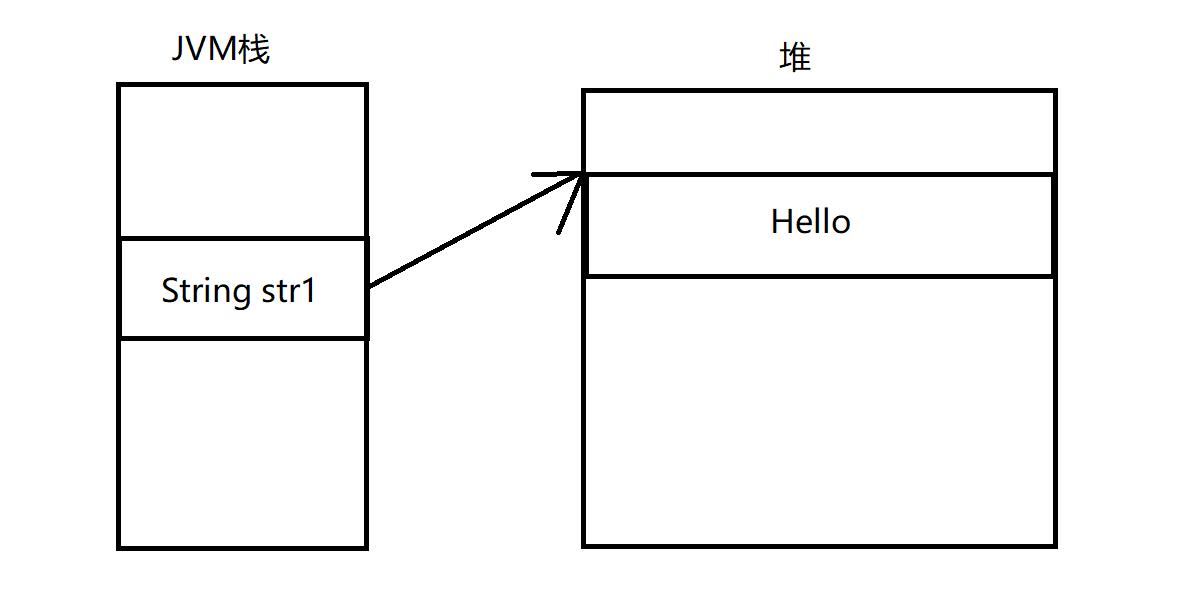
String str1="hello";
String str2="hello";
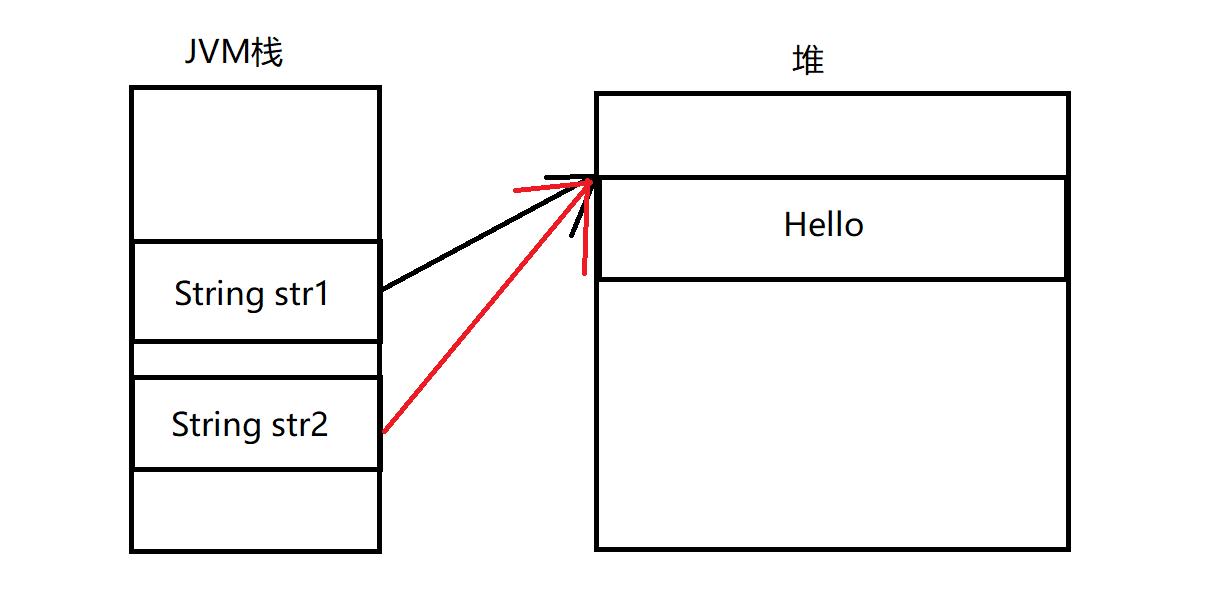
如果我们这时候修改str1的值,那么str2的值会改变吗?
public class Revise
public static void main(String[] args)
String str1="Hello";
String str2="Hello";
str1="world";
System.out.println(str2);
结果如下:
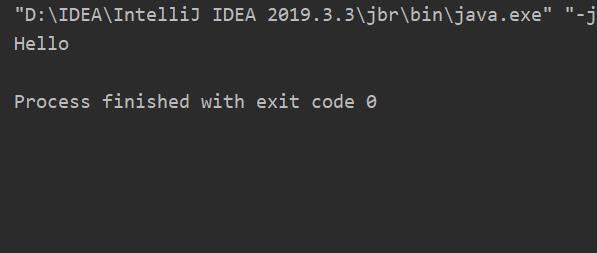
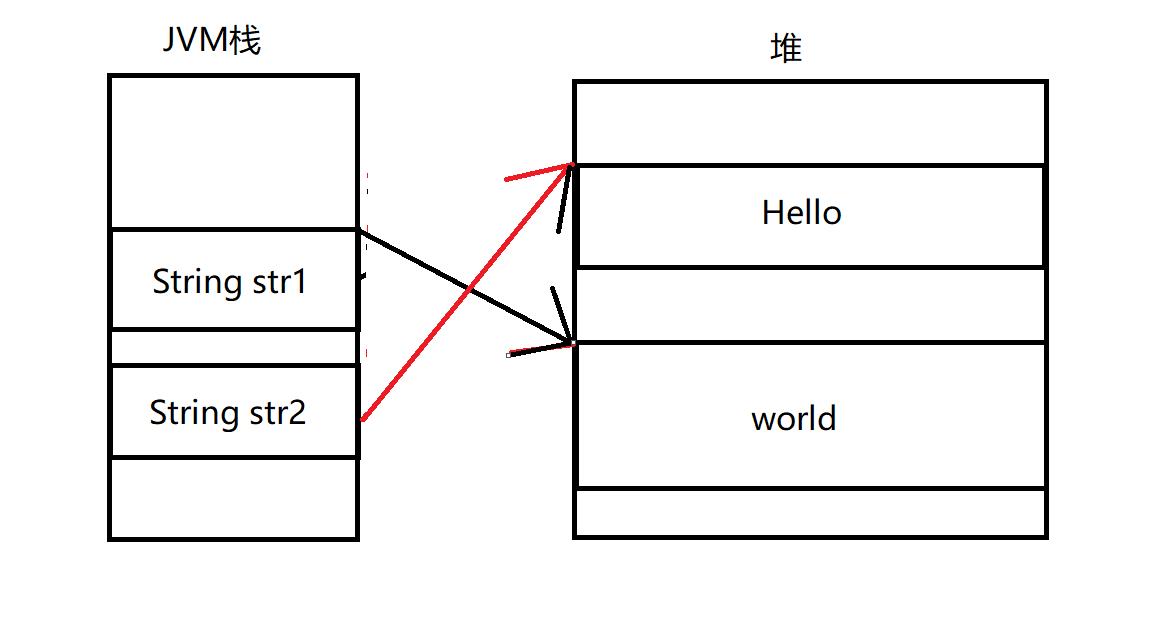
str2的值并没有改变事实上str1="world"只是让str1指向了一个新的String对象。
其内存布局如下图
二、字符串比较
1.方式一创建字符串的比较
public class Compare
public static void main(String[] args)
String str1="Hello";
String str2="Hello";
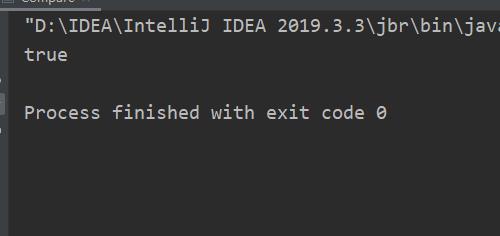
System.out.println(str1==str2);
结果:
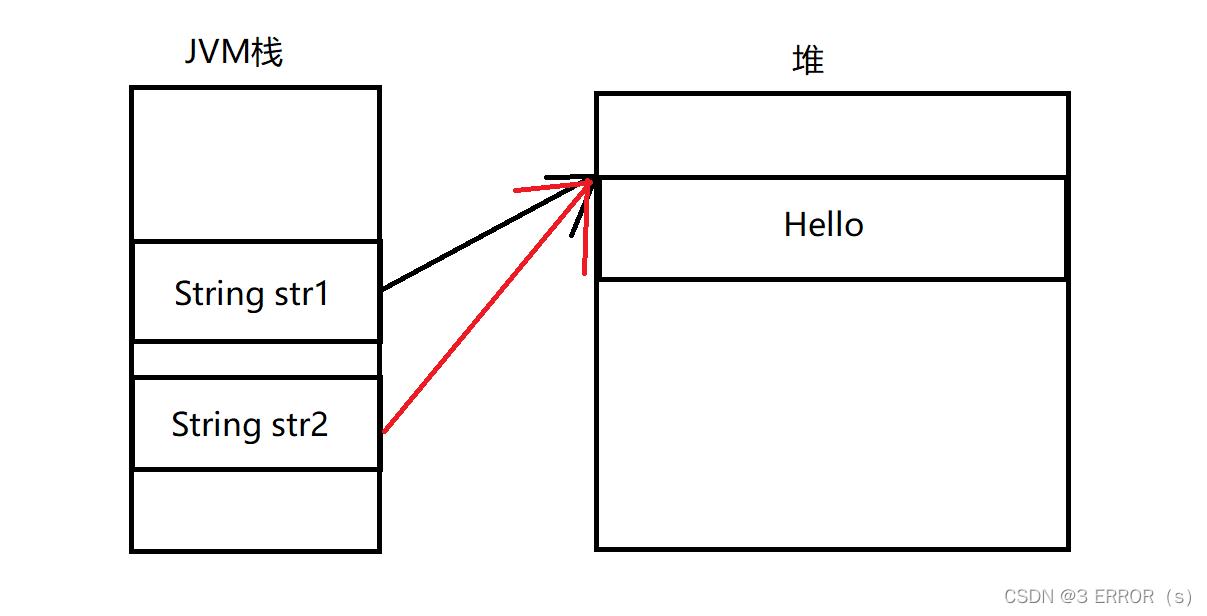
其内存布局如下:
2.方式二创建字符串的比较
public class Compare
public static void main(String[] args)
String str1=new String("World");
String str2=new String("World");
System.out.println(str1==str2);
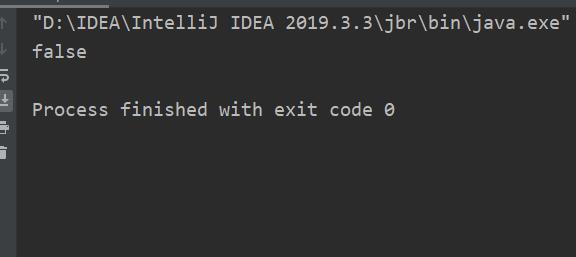
其内存图如下: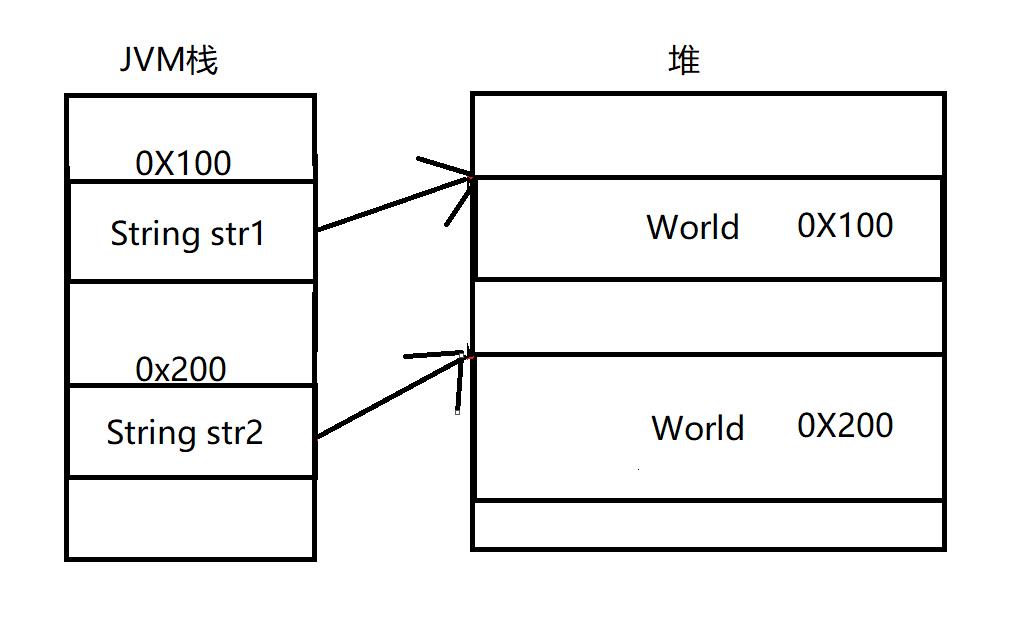 String中使用==比较不是用来比较内容的,而是比较两个引用是否指向同一个对象。
String中使用==比较不是用来比较内容的,而是比较两个引用是否指向同一个对象。
3.比较字符串内容
Java中想要比较字符串内容就要用到equals方法。
public class Compare
public static void main(String[] args)
String str3=new String("World");
String str4=new String("World");
System.out.println(str4.equals(str3));
三、字符串常量池
根据之前的解释我们已经知道了使用方式一的创建字符串方式创建相同的字符串,除第一个创建之外其余的创建并没有开辟新的堆内存空间,为什么呢?
在JVM底层实际上会自动维护一个字符串常量池
- 如果才用直接赋值的方式进行String对象的初始化,那么该实例化对象将自动保存到整个常量池中去。
- 如果下次继续采用直接赋值的模式生命String对象,如果此时常量池中就这个内容,就直接进行引用。
- 如果没有,就会开辟新的空间将他保存起来供下次使用。
String str3=new String("World");
String str4=new String("World");
上述这种才用构造方法实例化字符串的做法有两个缺点:
- 会开辟两块空间,并且创建了str4之后str3就变成了垃圾空间
- 同一个字符串可能被存储多次,浪费空间。
为了解决上述问题我们可以使用 intern 方法来将String对象手动入池。
intern方法用来判定当前字符串是否存在于常量池当中
- 不存在:手动入池。
- 存在:把字符常量的引用赋给当前引用。
String str1=new String("World").intern();
String str2="World";
System.out.println(str1==str2);
四、使用反射修改字符串
字符串是一种不可变对象,他的内容不可变。
反射可以破坏封装,访问一个类内部的private成员
public class Reflex
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException
String str="Hello";
//获取Class对象
Class str1=String.class;
//获取value字段
Field field=str1.getDeclaredField("value");
//将这个字段的访问权限设为true
field.setAccessible(true);
//把str的value属性获取到
char [] val=(char[]) field.get(str);
//修改str的值
val[0]='h';
System.out.println(str);
为什么要String不可变?
- 方便实现字符串常量池
- 不可变对象是线程安全的
- 不可变对象更方便缓存hash code,作为key可以更高效的被保存在Hashmap中。
五、字符串常见操作
1.将字符串转换为字符数组
String str="abcdefg"
char[] data=str.toCharArray();
2.将字符数组转换为字符串
char[]arr='a','b','c';
String str= new String(arr);
3.字符串的比较
- equals 区分大小写的比较
- equalsIgnoreCase 不区分大小写的比较
- compareTo 比较两个字符串大小,返回一个整形 相等返回0;小于返回小于0;大于返回大于0
public class TestDemo
public static void main(String[] args)
String str1="abcd";
String str2="ABCD";
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2));
4.字符串查找
- cantains 判断字符串是否存在
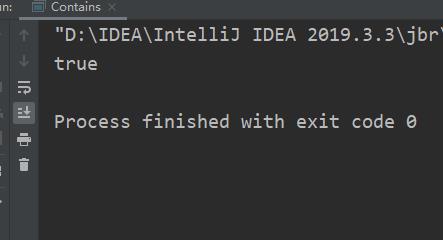
public class Contains
public static void main(String[] args)
String str="hello word";
System.out.println(str.contains("hello"));
- indexOf 从头开始查找字符串的位置,查到了返回索引查不到返回-1
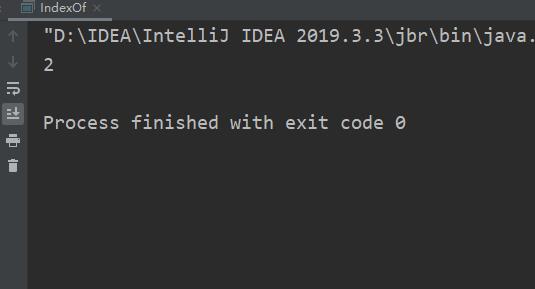
public class IndexOf
public static void main(String[] args)
String str="hello";
System.out.println(str.indexOf('l'));
由结果可得治他只查找到了第一个相同字符的下标
- startsWith 判断是否以制定字符串开头
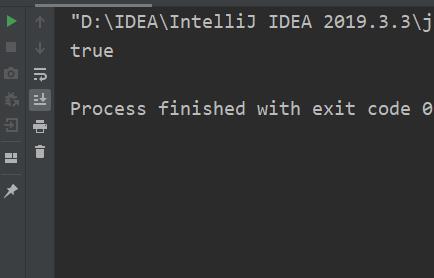
public class StartsWith
public static void main(String[] args)
String str="hello";
System.out.println(str.startsWith("h"));
- endsWith 判断是否以字符串结尾
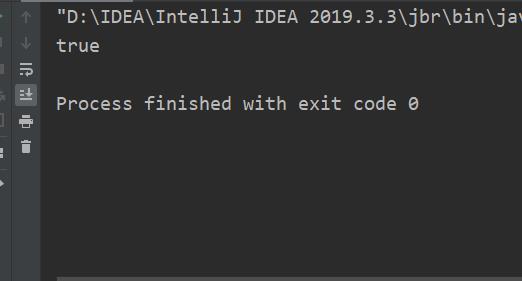
public class EndsWith
public static void main(String[] args)
String str ="helloll";
System.out.println(str.endsWith("oll"));
5.字符串替换
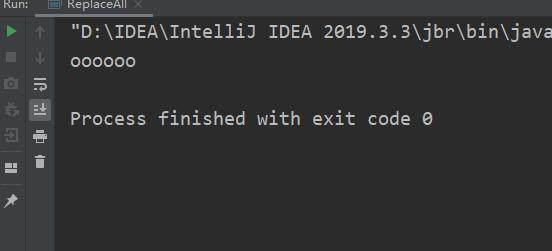
- replaceAll 替换所有的制定内容
public class ReplaceAll
public static void main(String[] args)
String str="wwwwww";
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("w", "o"));
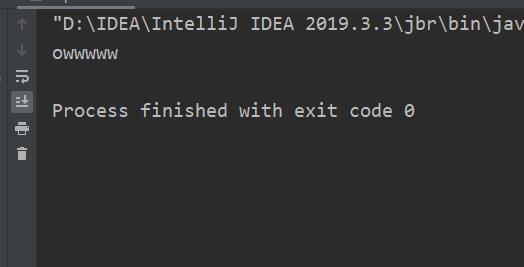
- replaceFirst 替换首个内容
public class ReplaceAll
public static void main(String[] args)
String str="wwwwww";
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("w", "o"));
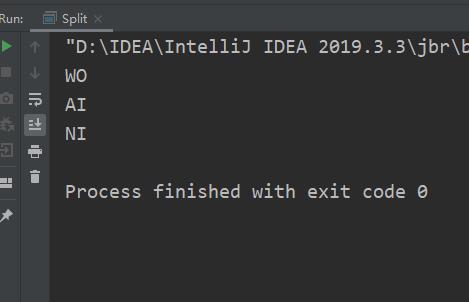
6.字符串拆分
- split 将字符串全部拆分
public class Split
public static void main(String[] args)
String str ="WO AI NI";
String [] ret=str.split(" ");
for (String s:ret)
System.out.println(s);
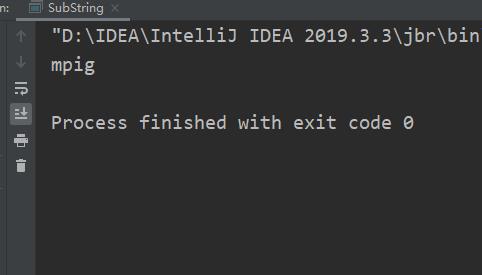
7.字符串截取
- subString 从指定位置开始截取
public class SubString
public static void main(String[] args)
String str="impig";
System.out.println(str.substring(1));
注意如果是(0,5)不包含5
8.其他字符串操作方法
- trim() 去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间的空格
- toUpperCase() 字符串转大写
public class ToUpperCase
public static void main(String[] args)
String str="ddad";
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
- toLowerCase() 字符串转小写
- isEmpty() 判断字符串是否为空,返回值为0
六、StringBuffer和StringBuilder
- StringBuffer是线程安全的
- String拼接会产生大量的临时变量,String拼接会被优化为StringBuilder的append()
- StringBuffer和StringBuilder有逆置方法。reverse();
public static void main(String[] args)
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
sb.append("hello").append("world");
System.out.println(sb);
String和StringBuffer的区别在于:String的内容无法修改,StringBuffer的内容可以修改,需要大量修改字符串则需要用到StringBuffer
以上是关于了解String类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章