室友竟只在2021的最后一天就学会了哈希表
Posted TZC⑥
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了室友竟只在2021的最后一天就学会了哈希表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
哈希表
哈希概念
通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素
哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构称为哈希表(Hash Table)(或者称散列表)
映射方式
①直接定址法
用数组与数据的相对映射或绝对位置建立索引关系,此时增删查改时间复杂度O(1)
缺陷:
1.如果数据范围很大,直接定制法会浪费大量的空间
2.不能处理字符串,浮点数等数据,无法被拿来作为数组的索引
适用于:整数,并且数据集中的情况

②除留余数法
解决数据范围很大的问题
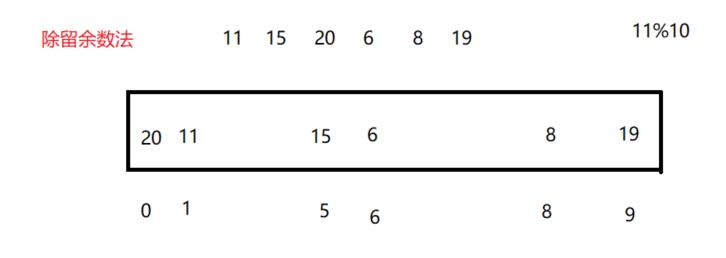
但是除留余数法存在哈希冲突(不同关键字通过相同哈希哈数计算出相同的哈希地址,该种现象称为哈希冲突或哈希碰撞)
解决哈希冲突
1.闭散列(开放定址法)
①线性探测
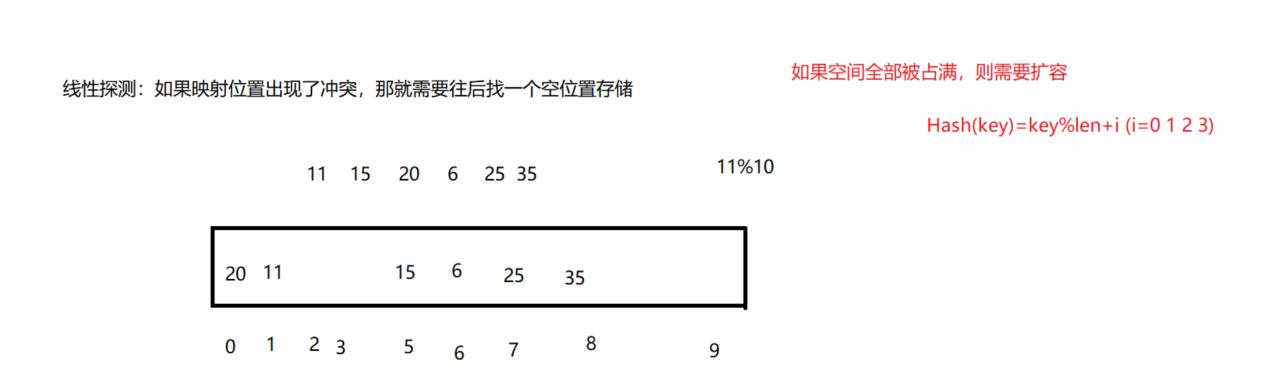
线性探测会导致踩踏效应(连续的位置出现冲突)
②二次探测

二次探测相对线性探测数据更分散,能有效缓解踩踏效应
负载因子(载荷因子)=存储的有效数据个数/空间大小
负载因子越大,冲突的概率越高,增删查改的效率就会越低,空间利用率越高
负载因子越小,冲突的概率越低,增删查改的效率就会越高,空间利用率越低
所以哈希表一个重要的问题就是控制负载因子的大小
③结点的设计
为了判断数组的某一个位置是否为空,我们用State来标识数组中数据的状态
//枚举出数据的三种状态
enum State
EMPTY,//空
EXITS,//存在
DELETE,//被删除 删除时只需要将状态修改为DELETE,这样实现"假"删除
;
template<class K,class V>
struct HashData
//每一个数据结点 存于vector
//kv结构
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = EMPTY;
;
④查找操作
当查找为空时就没找到,我们控制负载因子大小小于0.8,所以一定会存在空位置
HashData<K,V>* Find(const K& key)
//判断是否为空
if (_table.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
HashFunc hf;
size_t start = hf(key) % _table.size();
size_t index = start;
size_t i = 1;
while (_table[index].state != EMPTY)
//找到了
if (_table[index]._state==EXITS && _table[index]._kv.first == key)
return &_table[index];
//往后查找
//线性探测 二次探测只需改为 index=start+i*i;
index =start+ i;
index %= _table.size();
++i;
return nullptr;
⑤插入操作
插入操作需要注意增容问题,增容后,数据必须重新映射
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
//判断是否存在
HashData<K,V>* ret = Find(kv.first);
if (ret)
return false;
//size==0
if (_table.size() == 0)
_table.resize(10);
//计算负载因子
else if ((double)_n/(double)_table.size()>0.8)
//增容后所有数据必须重新映射进新数组
//重新创建HashTable对象 复用其insert函数
HashTable<K, V,HashFunc> newHashTable;
newHashTable.resize(2 * _table.size());
//遍历原Table的数据
for (auto& e : _table)
if (e._state == EXITS)
//复用Insert
newHashTable.Insert(e._kv);
_table.swap(newHashTable._table);
HashFunc hf;
//如果访问大于size<capacity 的数据
size_t start = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();
size_t index = start;
size_t i = 1;
//线性探测或者二次探测
while (_table[index]._state == EXITS)
index += start+i;
index %= _table.size();
++i;
_table[index]._kv = kv;
_table[index]._state = EXITS;
++_n;
⑥删除操作
找到后只需修改状态即可
bool Erase(const K& key)
//查找
HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret == nullptr)
return false;
else
//修改结点状态
ret->_state = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
完整代码
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//closeHash
namespace tzc
enum State
EMPTY,
EXITS,
DELETE,
;
template<class K,class V>
struct HashData
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = EMPTY;
;
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
int operator()(int i)
return i;
;
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
size_t operator()(const string& s)
//return s[0];
size_t value = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
value += ch;
value *= 131;
return value;
;
struct pairHashFunc
size_t operator()(const pair<string, string>& kv)
size_t value = 0;
//以KEY作为标准
for (auto& ch : kv.first)
value += ch;
value *= 131;
return value;
;
template<class K, class V,class HashFunc>
class HashTable
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
//判断是否存在
HashData<K,V>* ret = Find(kv.first);
if (ret)
return false;
//size==0
if (_table.size() == 0)
_table.resize(10);
//计算负载因子
else if ((double)_n/(double)_table.size()>0.8)
//增容后所有数据必须重新映射进新数组
//重新创建HashTable对象 复用其insert函数
HashTable<K, V,HashFunc> newHashTable;
newHashTable.resize(2 * _table.size());
for (auto& e : _table)
if (e._state == EXITS)
//复用插入
newHashTable.Insert(e._kv);
_table.swap(newHashTable._table);
HashFunc hf;
size_t start = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();//table[]
size_t index = start;
size_t i = 1;
//线性探测或者二次探测
while (_table[index]._state == EXITS)
index += start+i;
index %= _table.size();
++i;
_table[index]._kv = kv;
_table[index]._state = EXITS;
++_n;
HashData<K,V>* Find(const K& key)
//判断是否为空
if (_table.size() == 0)
return nullptr;
HashFunc hf;
size_t start = hf(key) % _table.size();
size_t index = start;
size_t i = 1;
while (_table[index].state != EMPTY)
//找到了
if (_table[index]._state==EXITS && _table[index]._kv.first == key)
return &_table[index];
//往后查找
//线性探测 二次探测只需改为 index=start+i*i;
index =start+ i;
index %= _table.size();
++i;
return nullptr;
bool Erase(const K& key)
HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret == nullptr)
return false;
else
ret->_state = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
private:
vector<HashData<K,V>> _table;
size_t _n;//数组中存的数据的个数
;
哈希存在的问题
对于下列语句:
size_t start = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();
当key存储的是string,自定义类型等数据时,不能转换成为映射关系存储在哈希表中
这时就需要自己实现对应的仿函数来转换key取模
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
int operator()(int i)
return i;
;
//模板特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
size_t operator()(const string& s)
//return s[0];
size_t value = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
value += ch;
value *= 131;
return value;
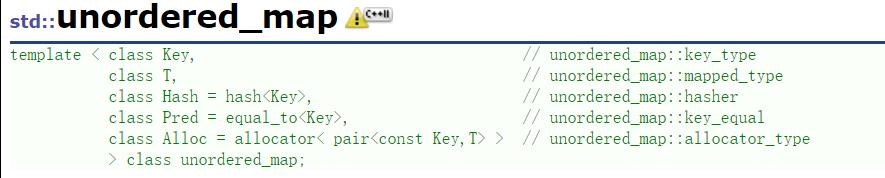
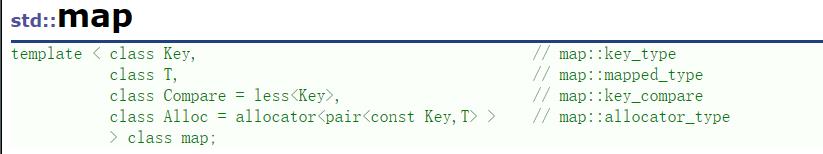
可以看出如果一个类型去做map/set的key需要能支持比较大小
去做unordered_map/unordered_set的key需要能转换成整形(支持取模)以及能比较相等
2.开散列
开散列–哈希桶/拉链法
数组中存储结构体的单链表指针
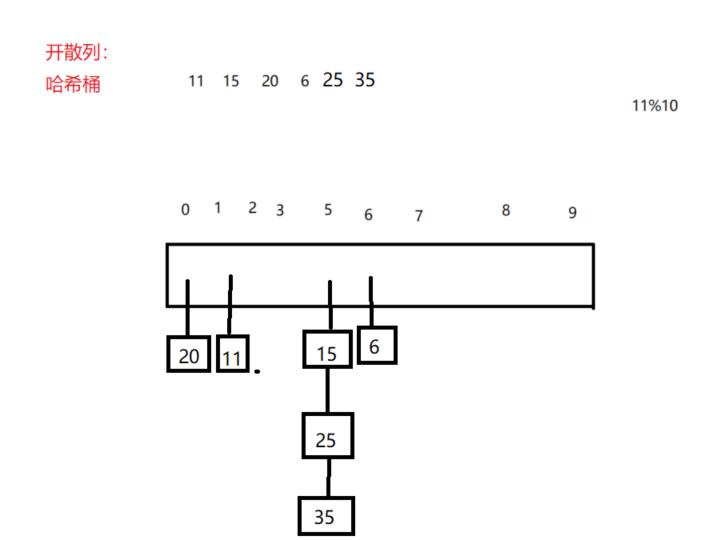
①结点设计
vector存储的结点
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _kv;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_next(__nullptr)
,_kv(kv)
;
HashTable所包含的私有成员
vector<Node*> _table;
size_t _n = 0;//有效数据个数
②插入操作
增容:约定当负载因子等于1时,需要增容重整,遍历旧表中的结点插入到新表中
哈希表重整方法一:巧妙地复用了insert的方法
bool Insert(const pair<K.V>& kv)
if (Find(kv.first))
return false;
if (_n == _table.size())
//开辟新的vector
vector<Node*> newtable;
size_t newSize = _table.size() == 0 ? 11: _table.size() * 2;
newtable.resize(GetNextPrime(_table.size()), nullptr);
//遍历旧的表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); ++i)
if (_table[i])
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t index = cur->_kv.first % newtable.size();
//头插法
cur->_next = _table[index];
_table[index] = cur;
cur = next;
_table[i] = nullptr;
//旧的与新的交换
_table.swap(newtable);
HashFunc fc;
size_t index = fc(kv.first) % _table.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
//头插
newnode->_next = _table[index];
_table[index] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
哈希表重整方法二:通过不断地将旧桶结点的头结点插入到新的对应的vector,来实现了重整
bool Insert(const pair<K.V>& kv)
if (Find(kv.first))
return false;
if (_n == _table.size())
vector<Node*> newtable(sizeof(_table.size()),(Node*)0);
//遍历旧结点
for(size_t i=0;i<_table.size();i++)
Node* cur=_table[i];
while(cur)
//找出结点在哪个桶
HashFunc fc;
size_t cur_bucket= fc(cur.first) % _table.size();
//四步微妙的操作
//1.将cur的下一个结点拿到该桶的头部
_table[i]=cur->next;
//2,3:将cur结点用头插法插入新的vector中
cur->next=newtable[cur_bucket];
newtable[cur_bucket]=cur;
//4.cur重新成为旧桶的头部
cur=_table[i];
_table.swap(newtable);
HashFunc fc;
size_t index = fc(kv.first) % _table.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
//头插
newnode->_next = _table[index];
_table[index] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
③查找操作
Node* Find(const K& key)
if (_table.size() == 0)
return false;
HashFunc fc;
size_t index = fc(key) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[index];
while(cur)
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
return cur;
else
cur = cur->_next;
return nullptr;
④删除操作
bool Erase(const K& key)
HashFunc fc;
size_t i以上是关于室友竟只在2021的最后一天就学会了哈希表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章