关于 JavaScript 中的 reduce() 方法
Posted Leophen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于 JavaScript 中的 reduce() 方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、什么是 reduce() ?
reduce() 方法对数组中的每个元素执行一个升序执行的 reducer 函数,并将结果汇总为单个返回值
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue; // 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 console.log(array1.reduce(reducer)); // 输出: 10 // 5 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 console.log(array1.reduce(reducer, 5)); // 输出: 15
二、数组中 reduce 方法的参数
1、第一个参数:reducer 函数
其中,reducer 函数又有四个参数:
- Accumulator (acc) (累计器)
- Current Value (cur) (当前值)
- Current Index (idx) (当前索引)
- Source Array (src) (源数组)
2、第二个参数(可选):initialValue
代表传递给函数的初始值
// 不传第二个参数的情况 var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4] function myFunction(item) { let result = numbers.reduce(function (total, currentValue, currentIndex, arr) { console.log(total, currentValue, currentIndex, arr) return total + currentValue }) return result } myFunction(numbers)
输出:
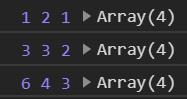
可以看到如果不传第二个参数 initialValue,则函数的第一次执行会将数组中的第一个元素作为 total 参数返回。一共执行3次
下面是传递第二个参数的情况:
// 不传第二个参数的情况 var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4] function myFunction(item) { let result = numbers.reduce(function (total, currentValue, currentIndex, arr) { console.log(total, currentValue, currentIndex, arr) return total + currentValue }, 10) return result } myFunction(numbers)
输出: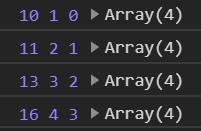
如果传了第二个参数 initialValue,那么第一次执行的时候 total 的值就是传递的参数值,然后再依次遍历数组中的元素。执行4次
总结:如果不传第二参数 initialValue,那么相当于函数从数组第二个值开始,并且将第一个值最为第一次执行的返回值,如果传了第二个参数 initialValue,那么函数从数组的第一个值开始,并且将参数 initialValue 作为函数第一次执行的返回值
三、应用场景
1、数组里所有值的和
var sum = [0, 1, 2, 3].reduce(function (accumulator, currentValue) { return accumulator + currentValue; }, 0); // 和为 6
2、累加对象数组里的值
var initialValue = 0; var sum = [{x: 1}, {x:2}, {x:3}].reduce(function (accumulator, currentValue) { return accumulator + currentValue.x; },initialValue) console.log(sum) // logs 6
3、将二维数组转化为一维
var flattened = [[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]].reduce( function(a, b) { return a.concat(b); }, [] ); // flattened is [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
4、计算数组中每个元素出现的次数
var names = [\'Alice\', \'Bob\', \'Tiff\', \'Bruce\', \'Alice\']; var countedNames = names.reduce(function (allNames, name) { if (name in allNames) { allNames[name]++; } else { allNames[name] = 1; } return allNames; }, {}); // countedNames is: // { \'Alice\': 2, \'Bob\': 1, \'Tiff\': 1, \'Bruce\': 1 }
5、数组去重
var myArray = [\'a\', \'b\', \'a\', \'b\', \'c\', \'e\', \'e\', \'c\', \'d\', \'d\', \'d\', \'d\']; var myOrderedArray = myArray.reduce(function (accumulator, currentValue) { if (accumulator.indexOf(currentValue) === -1) { accumulator.push(currentValue); } return accumulator }, []) console.log(myOrderedArray);
let arr = [1,2,1,2,3,5,4,5,3,4,4,4,4]; let result = arr.sort().reduce((init, current) => { if(init.length === 0 || init[init.length-1] !== current) { init.push(current); } return init; }, []); console.log(result); //[1,2,3,4,5]
以上是关于关于 JavaScript 中的 reduce() 方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章