数据包回放工具-tomahawk
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据包回放工具-tomahawk相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 在离线情况下利用数据包回放模拟一个真实的网络环境是一种常用方法,因而寻找一种方法对网络数据包进行可靠地回放变得尤为重要。如何在离线的实验室环境下,将捕获的网络数据包按照实验人员的意愿回放到离线网络环境中,从而进行离线评估和流量测试。常用的回放工具有tomahawk和tcpreplay。
tomahawk
tomahawk是一款用于测试入侵防御系统(IPS)的工具,工作在OSI模型的第二层,只能测试网桥型网络设备。它通过分析截获的网络数据包文件(需要有一个完整的TCP连接,包括三次握手包和四次分手包),分辨出其中的Client和Server端,再通过指定的两个网卡发送出去。
tomahawk使用格式
tomahawk [ -i interface1 ] [ -j interface1] [ -h ] [ -Z ] [ -q ] [ -d ] [ -W ] [ -R rate ] [ -m window ] [ -w lookahead ][ -a startIpAddr ] [ -s startId ] [ -e endId ] [ -L logFile ] [ -N maxActive ][ -A (0|1) ] [ -t timeout ] [ -r maxRetrans ] [ -n maxActive ] [ -l loops ] [-f file ]
• -i interface1 从interface1网口发送client到server方向的包
• -j interface2 从interface2 网口发送 server到client方向的包
• -R rate 限制tomahawk发送测试网络速率, MB/秒, 这个数可以是浮动数, 比如100Kbps的流量,可以使用-R 0.1表示
• -a startIpAddress 当重写IP地址时, 可以从startIpAddress开始分配IP地址
• -A (0|1) 是否需要修改包中的IP地址标记,0为不修改。
• -d随机最低2 byte的IP address (使用仅仅当在pcap有2 IPs)
• -t timeout 等待一个数据包到达目的端网卡的最小时间值
• -n maxActive 在网线中同时的流拷贝最大连接数
• -l loops 循环回放文件的次数
• -f file 要回放的数据包文件
[Nsos6.3 SSG]# tomahawk -l 1 -A 0 -i eth0 -j eth1 -f license-kehuchaxun.pcap
Beginning test
Completed 1 loop of trace license-kehuchaxun.pcap (hid: 1)
Finished 1 loops of trace license-kehuchaxun.pcap Completed: 1, Timed out: 0
Retrans: 0
Sent: 8
Recv: 8
流量回放工具之GoReplay input_file 源码分析
前言
GoReplay 对数据流的抽象出了两个概念,即用 输入(input ) 和 输出(output ) 来表示数据来源与去向,统称为 plugin,用介于输入和输出模块之间的中间件实现拓展机制。
input_file.go:实现文件读取的输入插件, 实现 io.Reader 接口,最后根据配置注册到 Plugin.inputs 队列里。
主要参数
-input-file value //从一个文件中读取请求
Read requests from file:
gor --input-file ./requests.gor --output-http staging.com
-input-file-dry-run //模拟从数据源读取数据而不重新回放它
Simulate reading from the data source without replaying it. You will get information about expected replay time, number of found records etc.
-input-file-loop //循环读取文件
Loop input files, useful for performance testing.
-input-file-max-wait duration //设置请求之间的最大时间间隔
Set the maximum time between requests. Can help in situations when you have too long periods between request, and you want to skip them. Example: --input-raw-max-wait 1s
-input-file-read-depth int //尝试提前读取和缓存多个记录。与此同时,如果请求没有按顺序出现,它还可以对请求进行排序。因为它需要在内存中保存这个缓冲区,较大的值会导致更差的性能(默认为100)
GoReplay tries to read and cache multiple records, in advance. In parallel it also perform sorting of requests, if they came out of order. Since it needs hold this buffer in memory, bigger values can cause worse performance (default 100)
变速回放
使用说明
GoReplay 实现压力测试的核心特性就是满足流量变速回放功能。支持将录制的生产实际请求流量减少或者放大回放以用于压力测试
比如运行以下命令,将流量从文件回放到 237 服务器,并放大两倍:
[root@vm-1 ~]./gor --input-file "requests.gor|200%" --output-http="http://172.16.106.237:8082"
2021/08/17 15:03:58 [PPID 12356 and PID 18187] Version:1.3.0
[DEBUG][elapsed 1.361742ms]: [INPUT-FILE] FileInput: end of file 'requests.gor'
- requests.gor|1:最大不超过1QPS;
- requests.gor|100%:超过原流量的100%。
源码解析
gor.go 为 main 方法,初始化所有插件,启动 emiter(核心处理器) 监听
初始化插件:
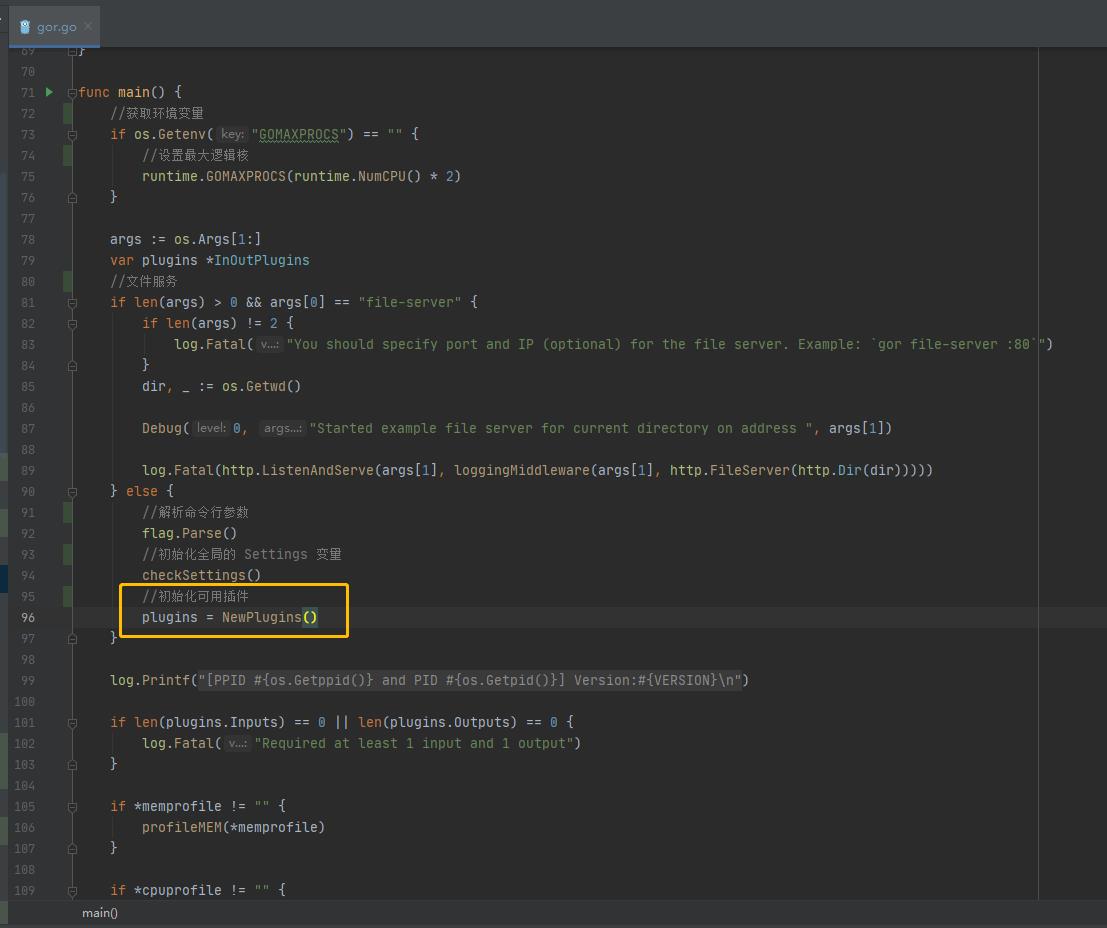
启动 emitter:

原始代码如下:
func main()
//获取环境变量
if os.Getenv("GOMAXPROCS") == ""
//设置最大逻辑核
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(runtime.NumCPU() * 2)
args := os.Args[1:]
var plugins *InOutPlugins
//文件服务
if len(args) > 0 && args[0] == "file-server"
if len(args) != 2
log.Fatal("You should specify port and IP (optional) for the file server. Example: `gor file-server :80`")
dir, _ := os.Getwd()
Debug(0, "Started example file server for current directory on address ", args[1])
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(args[1], loggingMiddleware(args[1], http.FileServer(http.Dir(dir)))))
else
//解析命令行参数
flag.Parse()
//初始化全局的 Settings 变量
checkSettings()
//初始化可用插件
plugins = NewPlugins()
log.Printf("[PPID %d and PID %d] Version:%s\\n", os.Getppid(), os.Getpid(), VERSION)
if len(plugins.Inputs) == 0 || len(plugins.Outputs) == 0
log.Fatal("Required at least 1 input and 1 output")
if *memprofile != ""
profileMEM(*memprofile)
if *cpuprofile != ""
profileCPU(*cpuprofile)
if Settings.Pprof != ""
go func()
log.Println(http.ListenAndServe(Settings.Pprof, nil))
()
closeCh := make(chan int)
//程序核心事件处理
emitter := NewEmitter()
//调用 Start 函数,启动 emitter
go emitter.Start(plugins, Settings.Middleware)
if Settings.ExitAfter > 0
log.Printf("Running gor for a duration of %s\\n", Settings.ExitAfter)
time.AfterFunc(Settings.ExitAfter, func()
log.Printf("gor run timeout %s\\n", Settings.ExitAfter)
close(closeCh)
)
c := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(c, os.Interrupt, syscall.SIGTERM)
exit := 0
select
case <-c:
exit = 1
case <-closeCh:
exit = 0
//关闭所有协程
emitter.Close()
os.Exit(exit)
plugins.go 类中,通过 limiter 类执行各种变速操作:
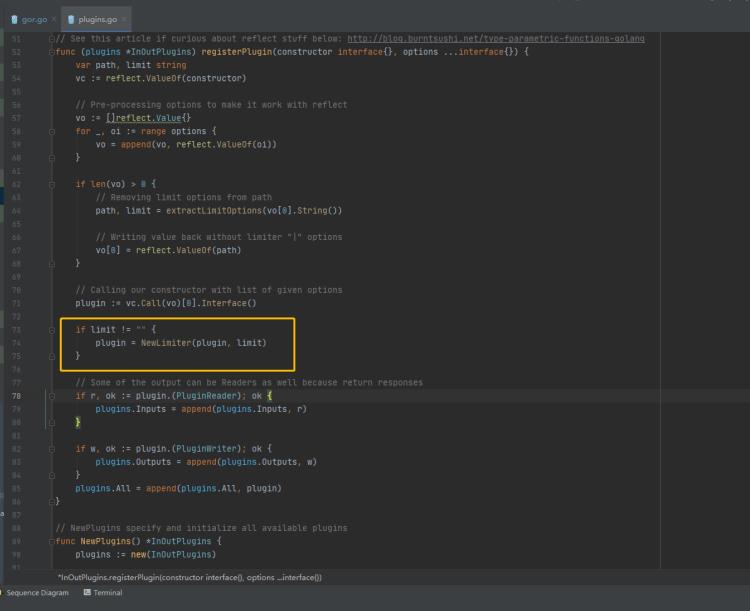
源代码如下:
// Automatically detects type of plugin and initialize it
//
// See this article if curious about reflect stuff below: http://blog.burntsushi.net/type-parametric-functions-golang
func (plugins *InOutPlugins) registerPlugin(constructor interface, options ...interface)
var path, limit string
vc := reflect.ValueOf(constructor)
// Pre-processing options to make it work with reflect
vo := []reflect.Value
for _, oi := range options
vo = append(vo, reflect.ValueOf(oi))
if len(vo) > 0
// Removing limit options from path
path, limit = extractLimitOptions(vo[0].String())
// Writing value back without limiter "|" options
vo[0] = reflect.ValueOf(path)
// Calling our constructor with list of given options
plugin := vc.Call(vo)[0].Interface()
if limit != ""
plugin = NewLimiter(plugin, limit)
// Some of the output can be Readers as well because return responses
if r, ok := plugin.(PluginReader); ok
plugins.Inputs = append(plugins.Inputs, r)
if w, ok := plugin.(PluginWriter); ok
plugins.Outputs = append(plugins.Outputs, w)
plugins.All = append(plugins.All, plugin)
plugins.go 类中,对类似 ‘request.gor|100%’ 的参数进行解析:
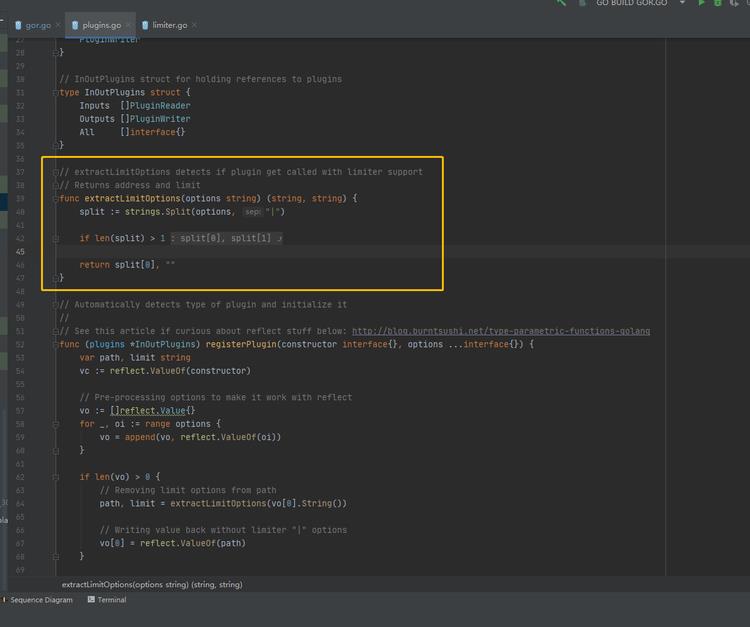
源代码如下:
// extractLimitOptions detects if plugin get called with limiter support
// Returns address and limit
func extractLimitOptions(options string) (string, string)
split := strings.Split(options, "|")
if len(split) > 1
return split[0], split[1]
return split[0], ""
主要执行方法在 limiter.go 类,源代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"math/rand"
"strconv"
"strings"
"time"
)
// Limiter is a wrapper for input or output plugin which adds rate limiting
type Limiter struct
plugin interface
limit int
isPercent bool
currentRPS int
currentTime int64
func parseLimitOptions(options string) (limit int, isPercent bool)
if n := strings.Index(options, "%"); n > 0
limit, _ = strconv.Atoi(options[:n])
isPercent = true
else
limit, _ = strconv.Atoi(options)
isPercent = false
return
// NewLimiter constructor for Limiter, accepts plugin and options
// `options` allow to sprcify relatve or absolute limiting
func NewLimiter(plugin interface, options string) PluginReadWriter
l := new(Limiter)
l.limit, l.isPercent = parseLimitOptions(options)
l.plugin = plugin
l.currentTime = time.Now().UnixNano()
// FileInput have its own rate limiting. Unlike other inputs we not just dropping requests, we can slow down or speed up request emittion.
if fi, ok := l.plugin.(*FileInput); ok && l.isPercent
fi.speedFactor = float64(l.limit) / float64(100)
return l
func (l *Limiter) isLimited() bool
// File input have its own limiting algorithm
if _, ok := l.plugin.(*FileInput); ok && l.isPercent
return false
if l.isPercent
return l.limit <= rand.Intn(100)
if (time.Now().UnixNano() - l.currentTime) > time.Second.Nanoseconds()
l.currentTime = time.Now().UnixNano()
l.currentRPS = 0
if l.currentRPS >= l.limit
return true
l.currentRPS++
return false
// PluginWrite writes message to this plugin
func (l *Limiter) PluginWrite(msg *Message) (n int, err error)
if l.isLimited()
return 0, nil
if w, ok := l.plugin.(PluginWriter); ok
return w.PluginWrite(msg)
// avoid further writing
return 0, io.ErrClosedPipe
// PluginRead reads message from this plugin
func (l *Limiter) PluginRead() (msg *Message, err error)
if r, ok := l.plugin.(PluginReader); ok
msg, err = r.PluginRead()
else
// avoid further reading
return nil, io.ErrClosedPipe
if l.isLimited()
return nil, nil
return
func (l *Limiter) String() string
return fmt.Sprintf("Limiting %s to: %d (isPercent: %v)", l.plugin, l.limit, l.isPercent)
// Close closes the resources.
func (l *Limiter) Close() error
if fi, ok := l.plugin.(io.Closer); ok
fi.Close()
return nil
limiter.go 类同样实现文件限速功能:

input_file.go 类调用了文件限速功能:
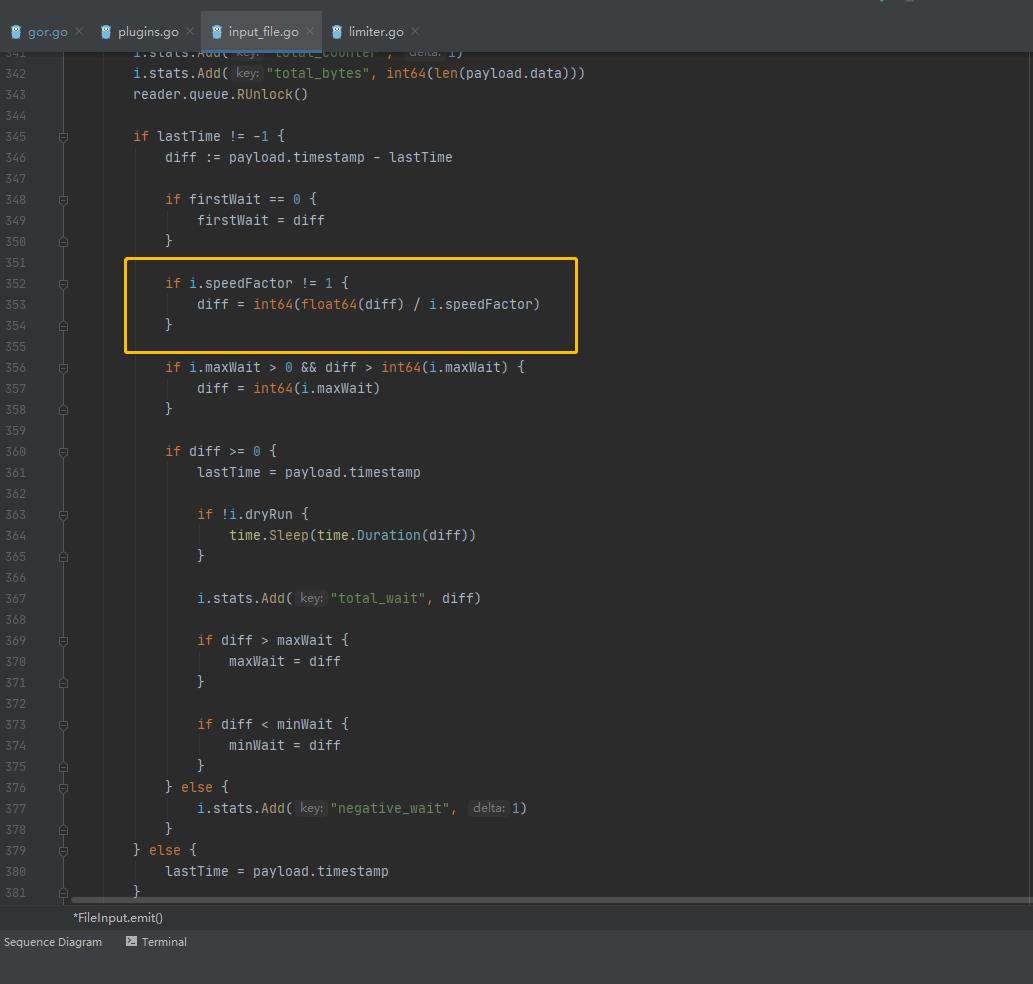
文件循环读取
主要参数为:–input-file-loop
比如:
$ sudo ./gor --input-file 'request.gor|10000%' --input-file-loop --output-http 'http://10.96.136.36:8201'
在 plufins.go 类中应用文件循环使用:
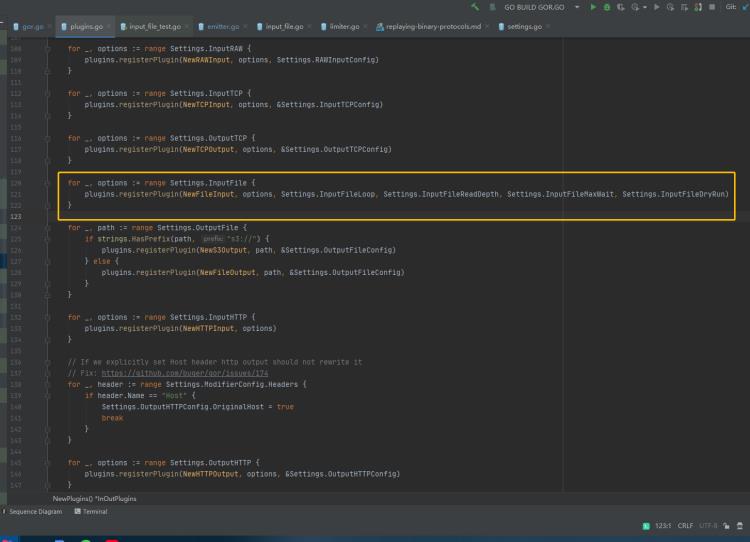
源代码:
for _, options := range Settings.InputFile
plugins.registerPlugin(NewFileInput, options, Settings.InputFileLoop, Settings.InputFileReadDepth, Settings.InputFileMaxWait, Settings.InputFileDryRun)
input_file.go 类中实现文件读取功能:
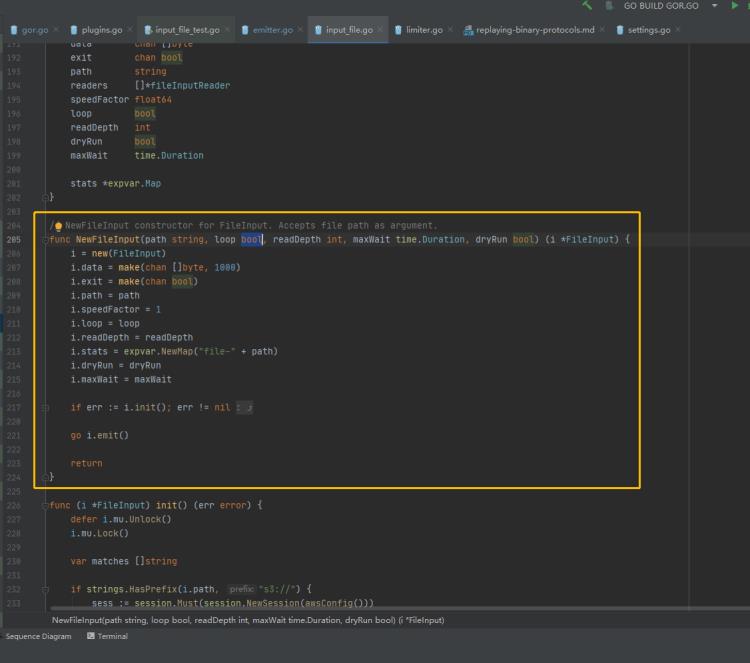
源代码如下:
// NewFileInput constructor for FileInput. Accepts file path as argument.
func NewFileInput(path string, loop bool, readDepth int, maxWait time.Duration, dryRun bool) (i *FileInput)
i = new(FileInput)
i.data = make(chan []byte, 1000)
i.exit = make(chan bool)
i.path = path
i.speedFactor = 1
i.loop = loop
i.readDepth = readDepth
i.stats = expvar.NewMap("file-" + path)
i.dryRun = dryRun
i.maxWait = maxWait
if err := i.init(); err != nil
return
go i.emit()
return
FileInput的构造函数,传入文件路径等参数。
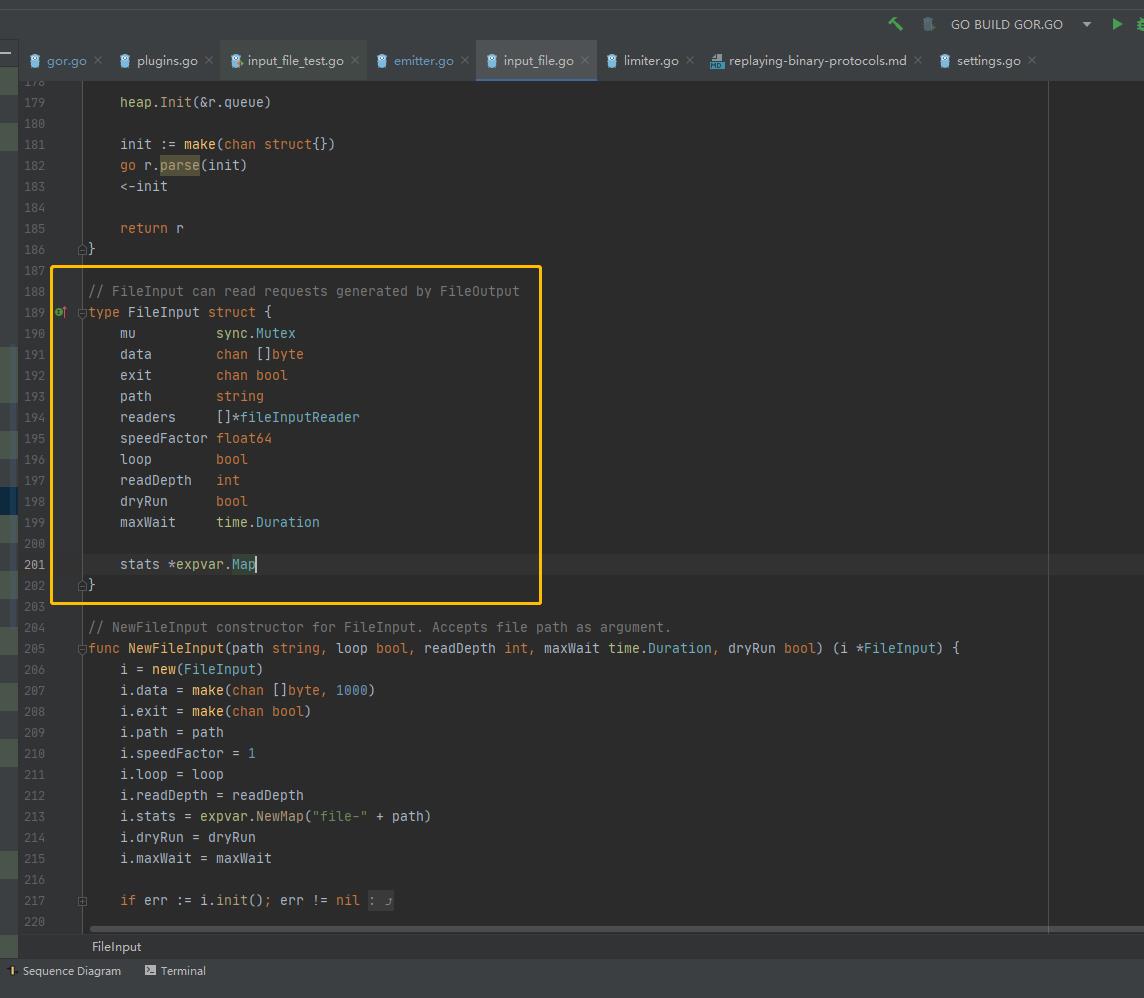
源代码如下:
// FileInput can read requests generated by FileOutput
type FileInput struct
mu sync.Mutex
data chan []byte
exit chan bool
path string
readers []*fileInputReader
speedFactor float64
loop bool
readDepth int
dryRun bool
maxWait time.Duration
stats *expvar.Map
判断是否循环读取:
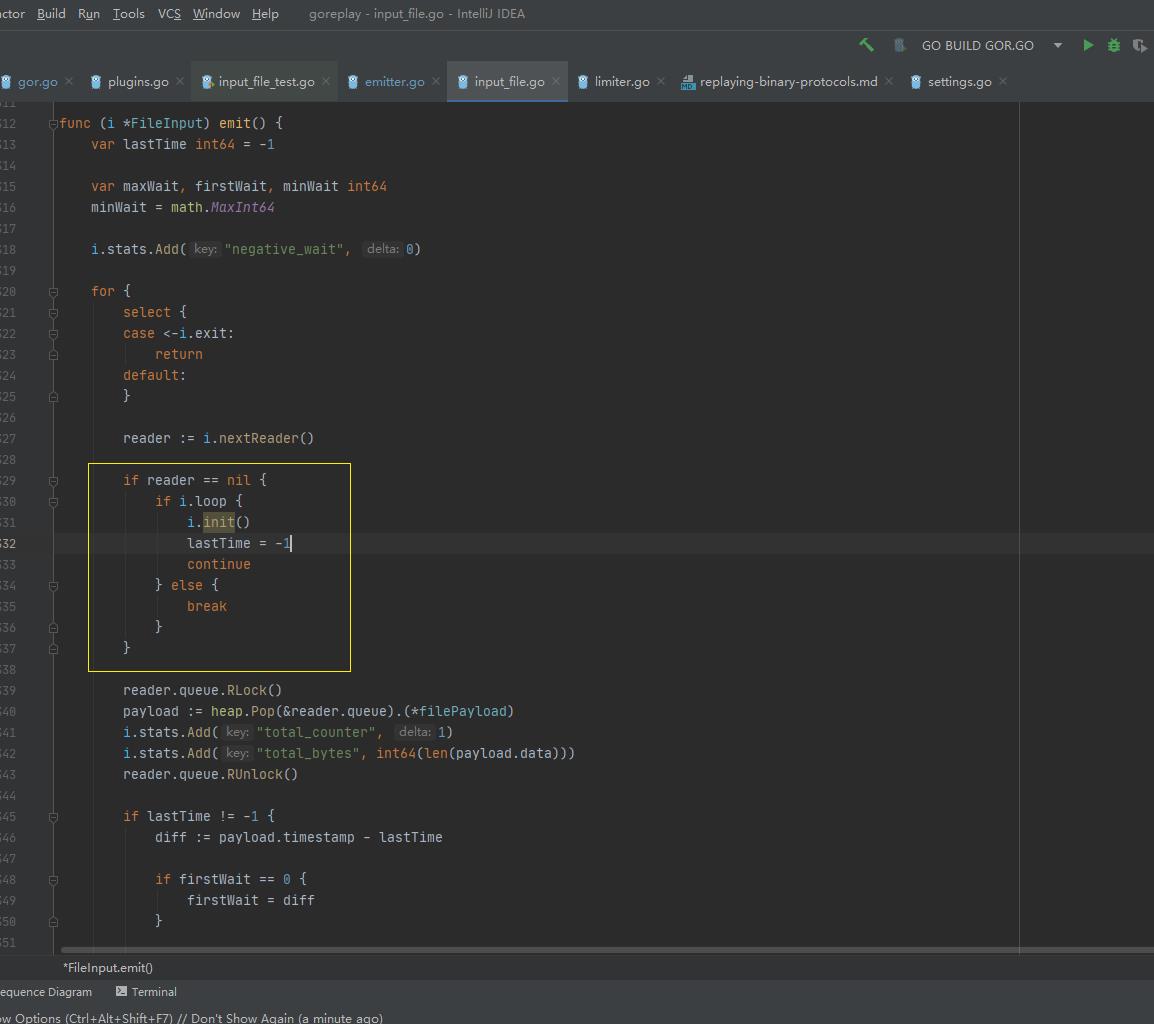
源代码如下:
if reader == nil
if i.loop
i.init()
lastTime = -1
continue
else
break
核心代码逻辑调用

以上是关于数据包回放工具-tomahawk的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章