Bioinformatics Servers
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Bioinformatics Servers相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术ANCBI-Blast: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi
EMBL-Blast: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/sss/ncbiblast/nucleotide.html
Clustal Omega: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/
MAFFT: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/mafft/
Seq2Logo: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?Seq2Logo-2.0
Blast2Logo: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?Blast2logo-1.1
MEGA: https://megasoftware.net
Clustal Omega: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/
BioEdit: https://www.bioedit.com
BioEdit: https://www.bioedit.com
Promoter: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?Promoter-2.0
Softberry: http://linux1.softberry.com
PlantCARE: http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html
Plant: https://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/?action=newplace
TransFac: http://gene-regulation.com/
JASPAR: https://jaspar.genereg.net/
EPD: https://epd.epfl.ch/index.php
NetStart: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetStart-1.0
GSDS: http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn
BGEE: https://bgee.org
NCBI ORF: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/gorf/orfig.cgi
ProtScale: https://web.expasy.org/protscale/
ProtParam: https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ <br />氨基酸数目、分子量(Da 道尔顿)、等电点(酸性:<7,碱性:>7)、不稳定指数(40)、亲水性(正:亲水,负:疏水)
PredictkProtein: https://www.predictprotein.org/
NCBI CDD: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi
SMART: http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de
ProSite: https://prosite.expasy.org/
PFam: http://pfam.xfam.org/search/sequence
HMMER: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/hmmer/
MEME: http://meme-suite.org/
NPSA SOPMA: https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html
PSI Pred: http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred/#
Swiss-Model: https://swissmodel.expasy.org/
Robetta: http://robetta.bakerlab.org/
CPHmodels: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/CPHmodels
Phyre2: http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index
SwissModel: https://swissmodel.expasy.org
MSD: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd-srv/ssm/
NetPhos: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetPhos-3.1
NetNGlyc: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetNGlyc-1.0
YinOYang: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?YinOYang-1.2
SCRATCH: http://www.ics.uci.edu/~baldig/scratch/index.html
ProteinAtlas: http://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000186350-RXRA/cell
GeneCards: https://www.genecards.org
ProteinAtlas: https://www.proteinatlas.org
TargetP: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?TargetP-2.0
PSORT: https://www.genscript.com/psort.html
PSORT: http://psort1.hgc.jp/form.html
Plant: http://wolfpsort.org
NLStradamus: http://www.moseslab.csb.utoronto.ca/NLStradamus/
DeepTMHMM: https://dtu.biolib.com/app/DeepTMHMM/run
TMHMM: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?TMHMM-2.0
TMpred: http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/TMPRED_form.html
SOSUI: http://harrier.nagahama-i-bio.ac.jp/sosui/sosui_submit.html
SignalP: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?SignalP-5.0
StringDB: https://string-db.org
GO: http://geneontology.org
KEGG: https://www.genome.jp/kegg/
KEGG: https://www.kegg.jp
BlastKOALA: https://www.kegg.jp/blastkoala/
GhostKOALA: https://www.kegg.jp/ghostkoala/
KofamKOALA: https://www.genome.jp/tools/kofamkoala/
DAVID: https://david.ncifcrf.gov
KOBAS: http://kobas.cbi.pku.edu.cn
G-Profile: https://biit.cs.ut.ee/gprofiler/gost
Enrichr: https://maayanlab.cloud/Enrichr/
MetaScape: http://metascape.org/gp/index.html#/main/step1
FunRich: http://funrich.org/
GuoLab: http://bioinfo.life.hust.edu.cn/guo_lab#!/
Plant TFDB: http://planttfdb.gao-lab.org/
Animal TFDB: http://bioinfo.life.hust.edu.cn/AnimalTFDB/#!/
Human TFDB: http://bioinfo.life.hust.edu.cn/HumanTFDB#!/
Animal: http://bioinfo.life.hust.edu.cn/AnimalTFDB/#!/tfbs_predict
HOCOMOCO: https://hocomoco11.autosome.ru
JASPAR: https://jaspar.genereg.net
FootPrintDB: http://floresta.eead.csic.es/footprintdb/?search
DRV: https://drv.brc.hu/
TFBSShape: https://tfbsshape.usc.edu
WebLogo: http://weblogo.threeplusone.com
HTFtarget: http://bioinfo.life.hust.edu.cn/hTFtarget#!/
JASPAR: https://jaspar.genereg.net
TRRUST: https://www.grnpedia.org/trrust/
ChipBase: https://rna.sysu.edu.cn/chipbase/index.php
CistromeDB: http://cistrome.org/db/#/
CancerTarget: http://cistrome.org/CistromeCancer/CancerTarget/
TCGAEnhancer: http://cistrome.org/CistromeCancer/TCGA_enhancer/
TransFac: https://new.bio-store.org/#
GenexPlain: https://platform.genexplain.com/bioumlweb/#
HOMER: http://homer.ucsd.edu/homer/motif/
KnockTF: http://www.licpathway.net/KnockTF/index.html
TF DBD: https://transcriptionfactor.org
Promoter: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?Promoter-2.0
GTRD: http://gtrd.biouml.org/#!
SGPPI: 使用GCN在严格条件下对蛋白质相互作用的结构感知预测Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2023

背景简述:
深度学习模型的出现极大地促进了蛋白质互作(PPI)的预测。由于蛋白结构有限,因此多数预测方法依赖于蛋白质序列信息(氨基酸理化性质、进化相似性)和蛋白质互作网络信息,而AlphaFold2的出现极大地增加了原子水平上的蛋白质结构数目,因此深度学习整合蛋白质结构特征有助于提升蛋白质互作预测。
研究目的:
On the other hand, it is therefore interesting to explore how the GCN representation of residue networks could better describe the inter- actions between specific protein pairs and predict specific PPIs.
研究思路:
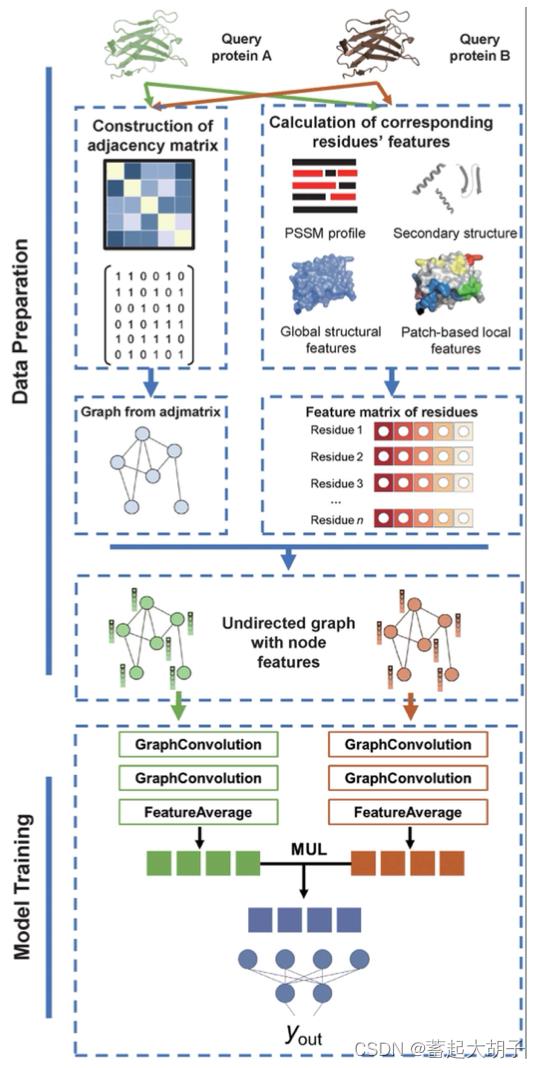
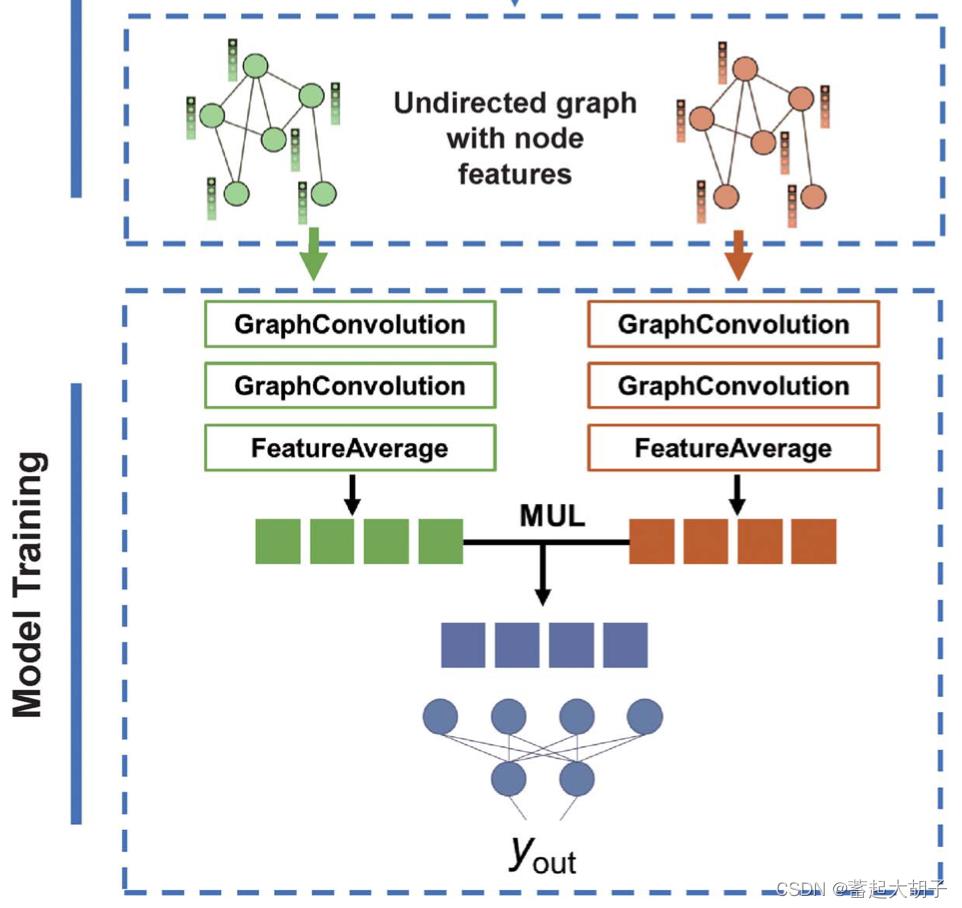
就本文而言,作者开发了一个名为SGPPI的蛋白质互作预测方法。SGPPI利用Siamese network architecture分别对Protein A和Protein B进行特征提取,之后用2层GCN对这两个蛋白分别进行卷积处理得到两组特征矩阵,最后将这两组特征矩阵输入到全连接的前馈神经网络(fully connected feedforward neural network)中并用SoftMax进行处理得到互作预测打分 y_out 。
材料和方法:
数据集构建:
对数据集进行处理的原因:
In other words, a classical PPI prediction model, which was trained on a dataset with many frequently presented similar proteins, is prone to detect interactions as the consequence of over-representation of proteins that are more likely to be involved in PPIs (e.g. hubs in the PPI network) rather than predicting specific PPIs.
对数据集的处理方法:
To limit the influence of sequence similarity of proteins, the sequence redundancy of interacting proteins was removed by setting the sequence identity threshold to 40%.
数据集的处理结果:
三个来源的数据集(Profppikernel dataset、HuRI 和 Pan’s dataset),结果如下:
| 名称 | 物种 | PPI数目 |
|---|---|---|
| Profppikernel dataset | human and yeast | 842 human PPIs and 746 yeast PPIs |
| HuRI human dataset | human | 1706 PPIs |
| Pan’s dataset | human | 1160 PPIs |
正负样本构建:
10-fold cross-validation,上述三个数据集各自分为10组,每组进行随机抽样,使得正样本数目:负样本数目 = 10:1,从而确保每组中的样本在序列上是不相似的。
构建SGPPI框架:
SGPPI used a Siamese network architecture to represent and predict the interacting proteins, where each protein was characterized separately.
整体上是一个Siamese network architecture,可以分为Data Preparation和Model Training两部分。
Data Preparation:
数据准备部分主要是对蛋白的特征进行提取,原始输入是两个蛋白(Protein A和B)的序列和结构,特征提取过程可分为一下几步:(顺序是根据Python源码确定的)
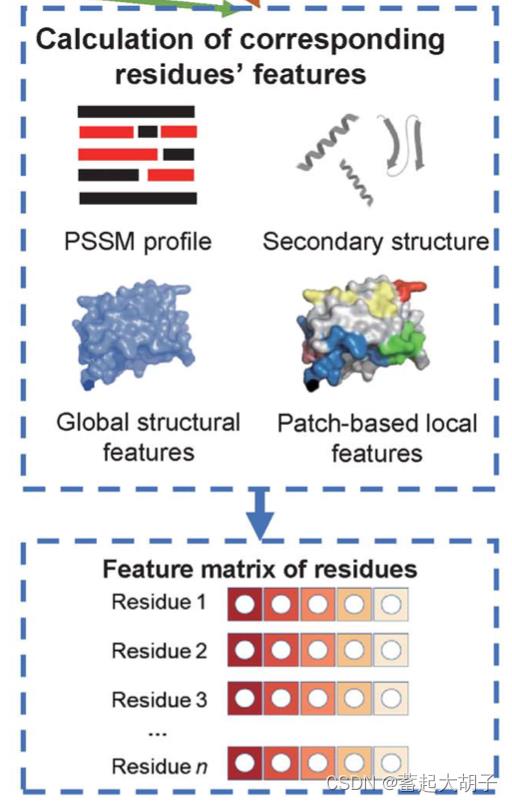
1. 分别获取Protein A和B的氨基酸残基特征(利用feature_extract.py得到.features):
1.1 进化信息(.pssm):
利用 NCBI在线版本的 PSI-Basic Local Alignment Search Tool 比对 NR90 database,迭代三次,e-value设为0.0001,获得.pssm序列进化信息文件(pssm,position-specific scoring matrices)。
1.2 二级结构信息(dssp.txt):
利用DSSP识别二级结构,输出结果有8种状态,然后用 One-hot 对这8种二级结构状态进行编码,得到dssp.txt文件。
1.3 蛋白质结构的局部和全局几何特征(.cv .cvlocal .atomAxs .axs):
用JET2识别蛋白质互作界面,将界面区域分为3部分:seed、extension和outer layer。seed区域是通过计算蛋白质序列中氨基酸的保守性来确定的;之后在seed的基础上,根据残基的进化信息、界面特性以及圆方差(circular variances)对seed区域进行拓展,得到extension区。
根据JET2的结果,首先用0和1表示氨基酸残基是否在互作界面的区域上,并且用JET2计算的结果来反应原子(.atomAxs)和残基(.axs)水平上的可及性。之后用圆方差来衡量3D空间中某一固定点和周围邻居点集合之间的向量分布,得到全局圆方差.cv和局部圆方差.cvlocal,用来分别描述整个蛋白界面的几何特征和局部残基的几何特征。
同时保留JET2识别的潜在互作界面(.clusters)。
关于JET2全局和局部特征获取参数(PMC4686965):
1.4 将上述所有氨基酸特征保存在.features文件中。
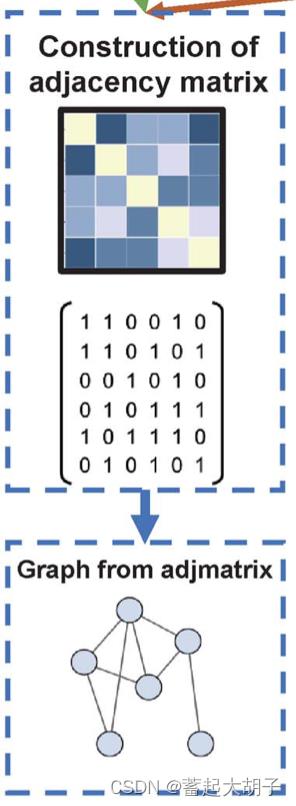
2. 分别构建Protein A和B的邻接矩阵(利用adjmatrix_extract.py得到.adj):
根据蛋白质结构中氨基酸残基的 C_alpha 之间的距离 < 10 埃来生成这些残基的邻接矩阵(.adj)(矩阵的行列一样,都是序列中的氨基酸,数值0或1表示某两个氨基酸之间在空间上的距离是否小于10埃),之后再将邻接矩阵转化为网络图谱。
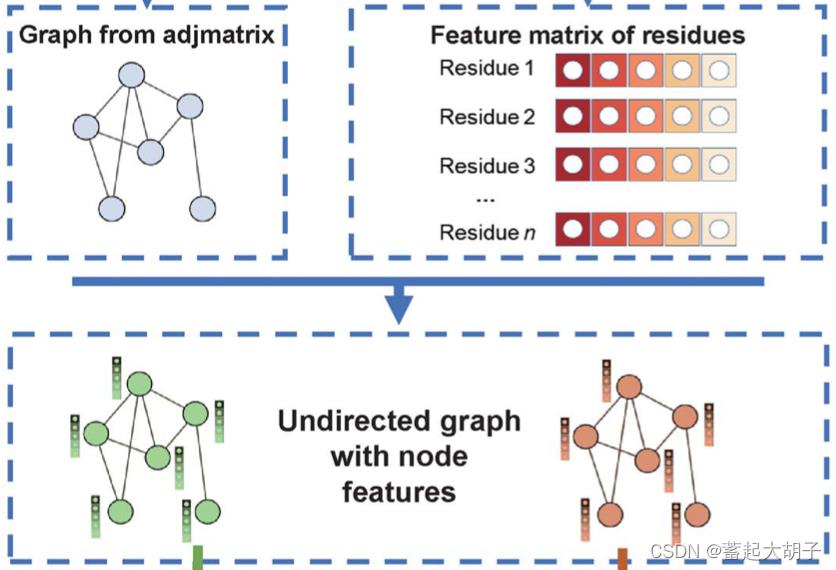
3. 生成带有节点特征的无向图(利用SaveToDict.py得到sample_adj.pkl和sample_fea.pkl):
根据邻接矩阵转化的无向图,将上述1,2得到的氨基酸残基特征和邻接矩阵整合到无向图中,以字典的形式分别存储(sample_adj.pklsample_fea.pkl)。
Model Training:
带有节点特征的无向图 --> 2层GCN --> 节点特征取均值(FeatureAverage)–> Protein A和B的特征作 Hadamard product --> SoftMax获取y_out --> 计算precision、recall等。(train_model.py)
其他:
1. 文中提到的一些现有方法:
| 方法 | 原理 |
|---|---|
| Profppikernel | 基于进化图谱 |
| PIPR | deep residual recurrent CNN |
| SigProd | 3-mers + SVM |
| PIPE2 | 正样本中序列的字序列在蛋白对中出现次数越多,就认为互作(感觉类似于基于motif-domain互作来预测PPI) |
2. 其他的编码方式:
AAC(amino acid composition ):
一条序列中每种氨基酸出现的频率。
CKSAAP(Compositon of k-spaced Amino Acid Pairs):
一条序列中,两个氨基酸组合在所有组合中出现的次数。k表示间隔,因为20种氨基酸可以产生 20x20 种组合,所以会产生一个长度为400的向量。具体参考 http://www.nohup.cc/article/110/ 和 https://bmcstructbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6807-7-25#Sec7。
3. 文中所用RF和SVM的参数设置:
| 方法 | 参数 |
|---|---|
| RF + CKSAAP | n_estimators and max_depth : 300 and 12 |
| RF + AAC | n_estimators and max_depth : 100 and 9 |
| SVM | kernel function : rbf, the optimized C and gamma : 0.1 and 16 |
以上是关于Bioinformatics Servers的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
推荐一本学习Perl书Beginning Perl for Bioinformatics(中文版)
SGPPI: 使用GCN在严格条件下对蛋白质相互作用的结构感知预测Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2023