论文阅读2022年最新迁移学习综述笔注(Transferability in Deep Learning: A Survey)
Posted 囚生CY
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了论文阅读2022年最新迁移学习综述笔注(Transferability in Deep Learning: A Survey)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- 英文标题:Transferability in Deep Learning: A Survey
- 中文标题:深度学习中的可迁移性综述
- 论文下载链接:arxiv@2201.05867
序言
这篇综述整体来说还是比较详实的,迁移学习本身在人工智能中的应用是非常广泛的,因此很容易与其他方法相结合,原文第三大节关于适应性的部分是非常关键的,也是本笔注的重点内容,理论性极强,其他两部分相对要水一些,很多老生常谈的东西就不作记录了。个人感觉是比较适合有一定机器学习基础,然后希望巩固迁移学习相关知识的人进行阅读理解。
摘要
The success of deep learning algorithms generally depends on large-scale data, while humans appear to have inherent ability of knowledge transfer, by recognizing and applying relevant knowledge from previous learning experiences when encountering and solving unseen tasks. Such an ability to acquire and reuse knowledge is known as transferability in deep learning. It has formed the long-term quest towards making deep learning as data-efficient as human learning, and has been motivating fruitful design of more powerful deep learning algorithms. We present this survey to connect different isolated areas in deep learning with their relation to transferability, and to provide a unified and complete view to investigating transferability through the whole lifecycle of deep learning. The survey elaborates the fundamental goals and challenges in parallel with the core principles and methods, covering recent cornerstones in deep architectures, pre-training, task adaptation and domain adaptation. This highlights unanswered questions on the appropriate objectives for learning transferable knowledge and for adapting the knowledge to new tasks and domains, avoiding catastrophic forgetting and negative transfer. Finally, we implement a benchmark and an open-source library, enabling a fair evaluation of deep learning methods in terms of transferability.
文章目录
- 序言
1 导论 Introduction
-
预训练本身就是一种迁移学习。
-
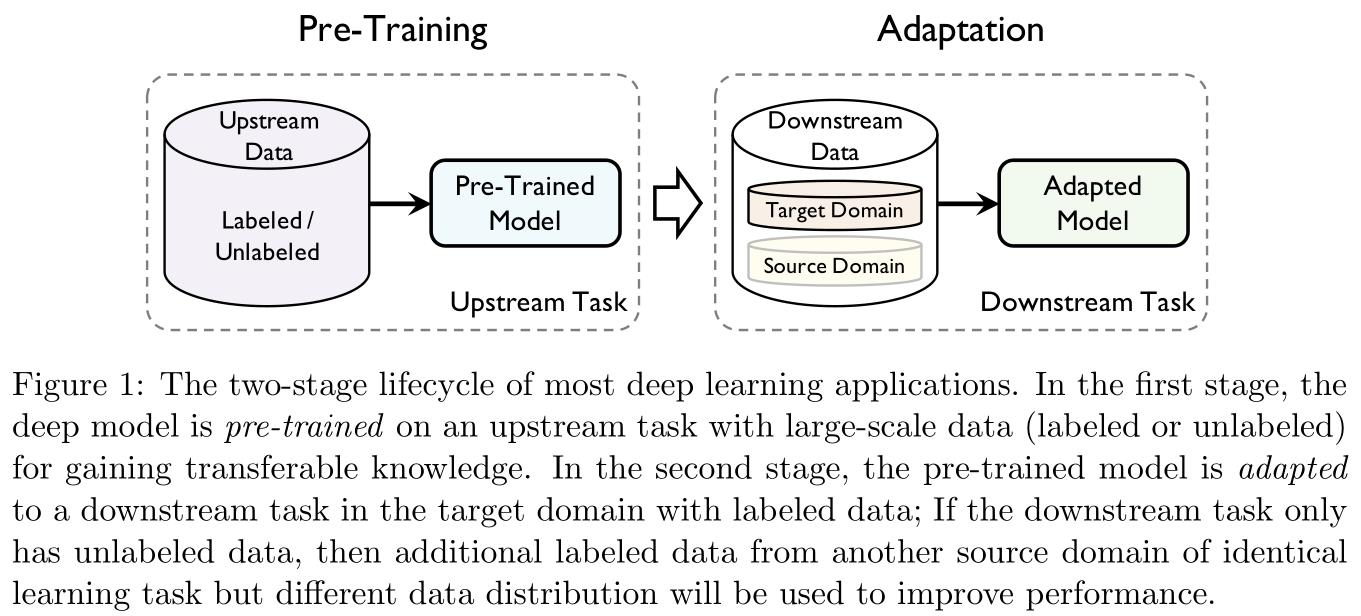
迁移学习分为两阶段:预训练(pre-training)与适应(adaptation)。前者关注一般的可迁移性(generic transferability),后者关注具体的可迁移性(specific transferability)。
1.1 术语 Terminology
| 数学标记 | 具体含义 |
|---|---|
| X \\mathcal X X | 输入空间 |
| Y \\mathcal Y Y | 输出空间 |
| f f f | f : X → Y f:\\mathcal X\\rightarrow \\mathcal Y f:X→Y是需要学习的标注函数 |
| l l l | l : Y × Y → R + l:\\mathcalY\\times \\mathcalY\\rightarrow \\R_+ l:Y×Y→R+是给定的损失函数 |
| D \\mathcal D D | X \\mathcal X X上的某个未知分布 |
| D ^ \\mathcal\\hat D D^ | 独立同分布采样自 D \\mathcal D D的样本 x 1 , . . . , x n \\\\bf x_1,...,\\bf x_n\\ x1,...,xn |
| P ( ⋅ ) P(\\cdot) P(⋅) | 定义在 X \\mathcal X X上的事件概率 |
| E ( ⋅ ) \\mathbb E(\\cdot) E(⋅) | 随机变量数学期望 |
| U \\mathcal U U | 上游数据 |
| S \\mathcal S S | 下游数据的源领域 |
| T \\mathcal T T | 下游数据的目标领域 |
| t ∗ t_* t∗ | ∗ * ∗领域的任务, ∗ * ∗可以取 T , S , U \\mathcalT,S,U T,S,U |
| H \\mathcal H H | 假设空间(可以理解为模型集合) |
| h h h | 假设空间中的一个假设(下文中如不作特殊说明,假设和模型含义相同) |
| ψ \\psi ψ | 特征生成器 |
| θ \\theta θ | 假设参数 |
| x \\bf x x | 模型输入 |
| y \\bf y y | 模型输出 |
| z \\bf z z | 隐层特征激活生成结果 |
| D D D | 用于区分不同分布的辨识器 |
定义 1 1 1(可迁移性):
给定源领域 S \\mathcalS S的学习任务 t S t_\\mathcalS tS以及目标领域 T \\mathcal T T的学习任务 t T t_\\mathcalT tT,可迁移性(transferability)指从 t S t_\\mathcal S tS中获取可迁移的知识,将获取到的知识在 t T t_\\mathcal T tT中进行重用并能够使得 t T t_\\mathcal T tT的泛化误差降低,其中 S ≠ T \\mathcal S\\neq \\mathcal T S=T或 t S ≠ t T t_\\mathcal S\\neq t_\\mathcal T tS=tT。
1.2 概述 Overview
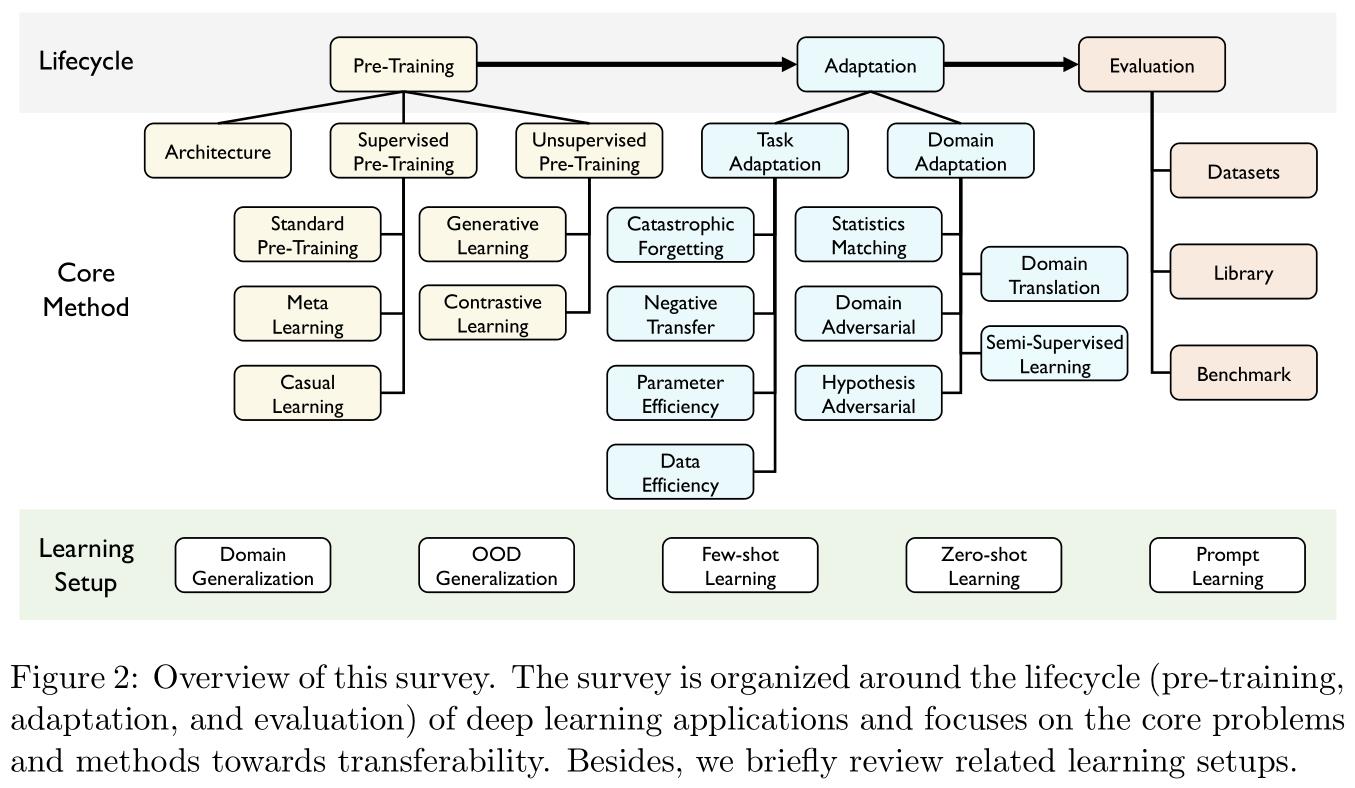
本文分三部分展开:
- 预训练(Pre-training):关于一些重要的迁移模型架构,有监督的预训练与无监督的预训练方法综述。这部分相对浅显,只对重点内容进行摘要记录。
- 适应性(Adaptation):重点在任务适应性(task adaptation)与领域适应性(domain adaptation),这部分理论性极强,尤其是领域适应性部分汇总了大量的定理与统计结果,感觉就不是同一个人写的。
- 评估(Evaluation):本文提出一个开源包用于迁移学习的通用算法以及评估,项目地址在GitHub@TLlib
2 预训练 Pre-Training
2.1 预训练模型 Pre-Training Model
-
一般来说,预训练任务学习的好坏直接影响预训练模型在下游任务中的应用性能。
-
一般来说,预训练会在非常大量的数据集上进行,因此如RNN和CNN这种做了局部连接假设的模型架构通常不会被作为预训练模型架构(因为数据足够多,不需要简化模型架构),目前主流的基本伤都是基于Transformer的大规模预训练模型。相较于RNN和CNN,Transformer对输入数据的结构几乎不作任何假定,即可以用于处理更广泛的数据类型。
-
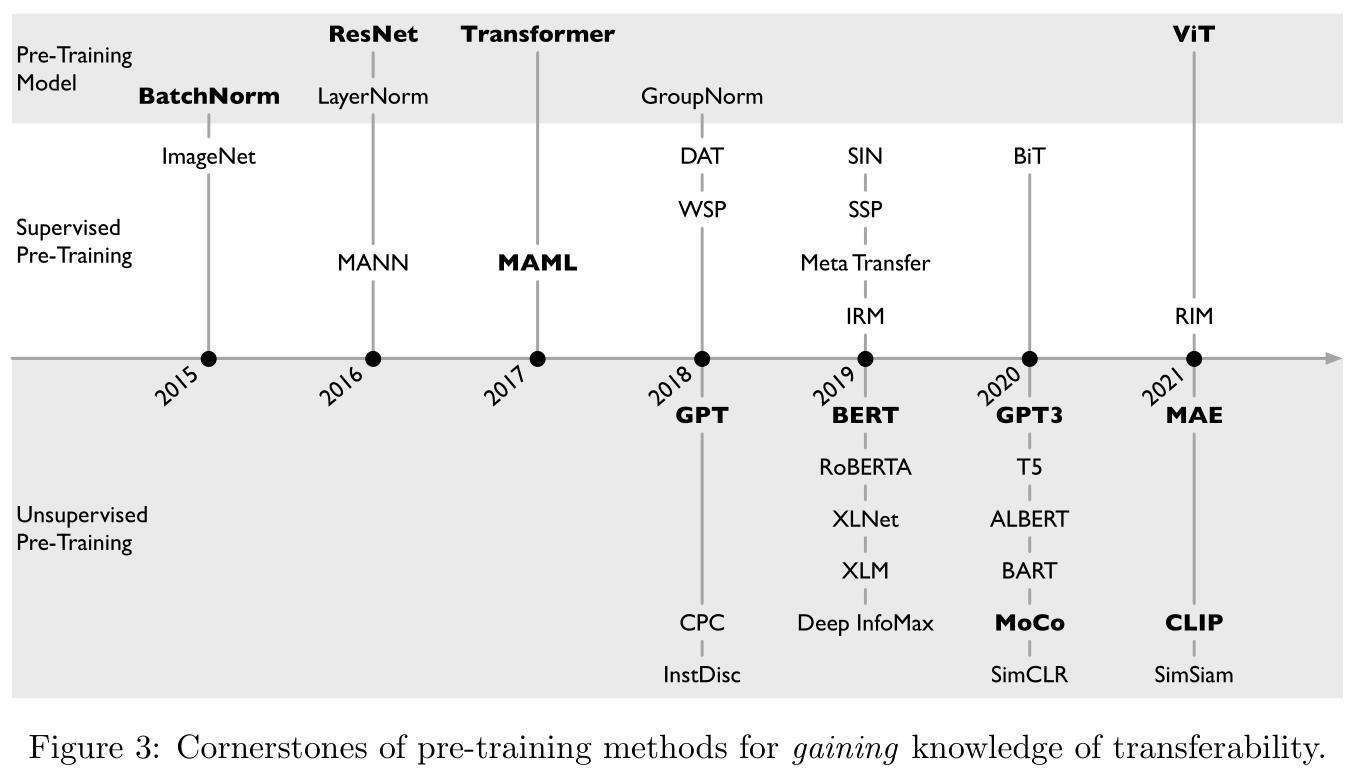
预训练模型在迁移学习中的发展历程(如Figure 3所示):
-
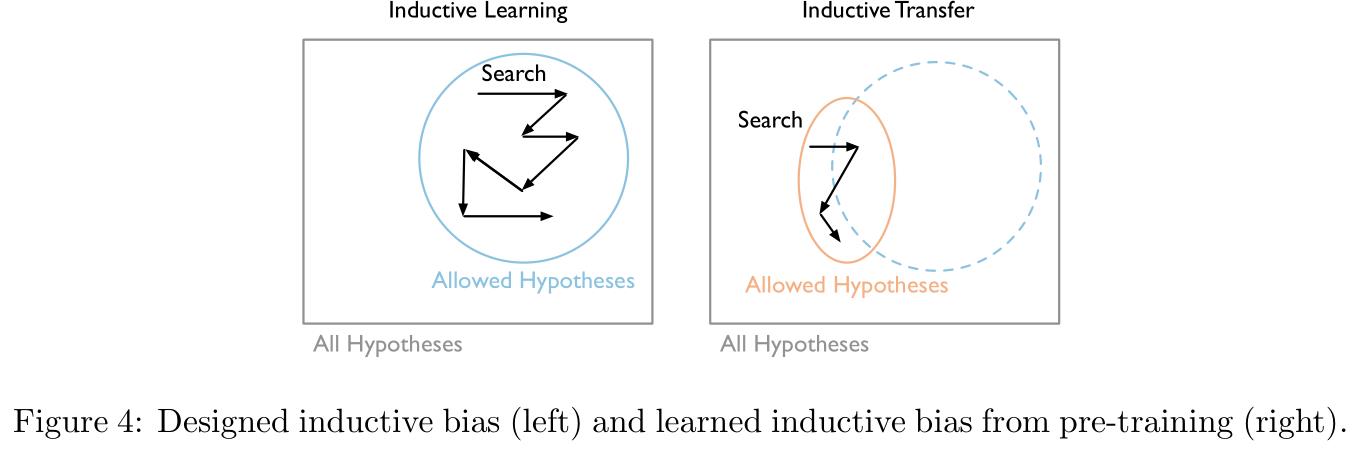
Figure 4中左图是直接训练时模型参数搜索的过程,右图是预训练迁移后的模型参数搜索过程,意思是说预训练的本质是缩小了模型参数的搜索范围(不过似乎也可以理解为是找到了一个更好的初始点):
2.2 有监督的预训练模型 Supervised Pre-training Model
-
有监督的预训练目的是在大规模标注数据上训练获得预训练模型,然后再迁移以增强下游任务(如Figure 5所示)。
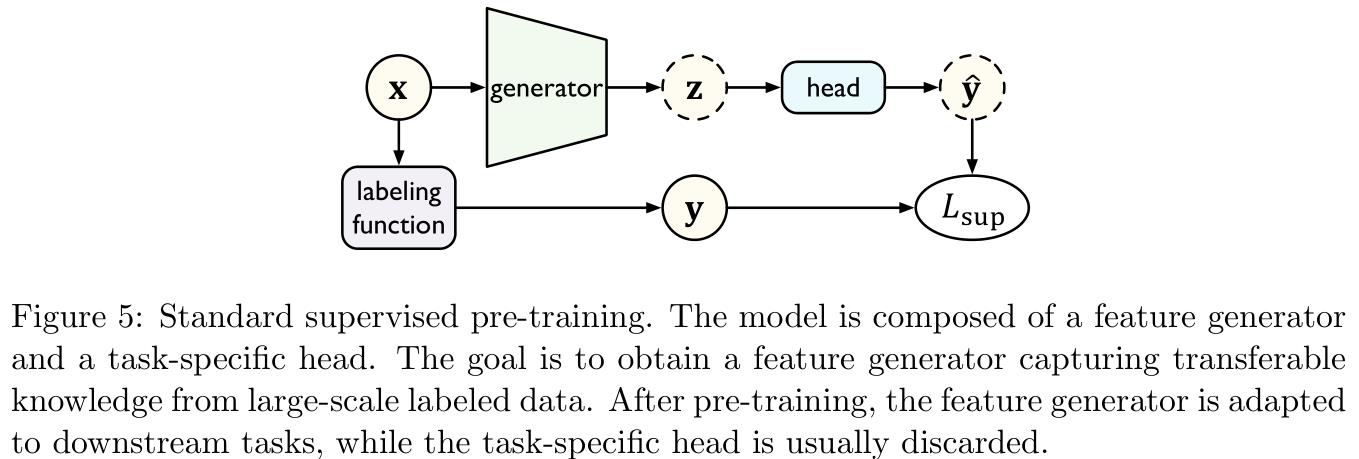
-
标准的有监督的预训练在标注数据量重组的情况下是非常有用的,但是它有时候对于对立样本(adversarial examples)的存在是极其敏感的,这可能会影响迁移的鲁棒性。因此本部分将会着重介绍另外两种有监督的预训练方法。
2.2.1 元学习 Meta Learning
-
所谓元学习(meta-learning),通俗而言即学习如何学习,以提升迁移的效率。其核心在于将元知识(meta knowledge) ϕ \\phi ϕ与模型融合,元知识 ϕ \\phi ϕ可以捕获不同学习任务的本质属性(intrinsic properties),又称为元训练(meta-training)。当需要解决一个新任务时,学习到的元知识救可以帮助目标模型参数 θ \\theta θ快速适应到新任务中,这个过程称为元测试(meta-testing)。
-
如Figure 6所示,左图是为了模拟元测试过程中的快速适应条件,将元训练数据构造成一个由 n n n个学习任务组成的集合,每个任务分别对应一个学习任务 i ∈ [ n ] i\\in[n] i∈[n],包含用于适应此任务的训练集 D i t r \\mathcalD_i^\\rm tr Ditr和用于评估的测试集 D i t s \\mathcalD_i^\\rm ts Dits,右图则是说明元训练的目标函数是一个二级优化问题:
ϕ ∗ = argmax ϕ ∑ i = 1 n log P ( θ i ( ϕ ) ∣ D i t s ) , where θ i ( ϕ ) = argmax θ log P ( θ ∣ D i t r , ϕ ) (1) \\phi^*=\\textargmax_\\phi\\sum_i=1^n\\log P(\\theta_i(\\phi)|\\mathcalD_i^\\rm ts),\\quad\\textwhere \\theta_i(\\phi)=\\textargmax_\\theta\\log P(\\theta|\\mathcalD_i^\\rm tr,\\phi)\\tag1 ϕ∗=argmaxϕi=1∑nlogP(θi(ϕ)∣Dits),where θi(ϕ)=argmaxθlogP(θ∣Ditr,ϕ)(1)
这里内层优化用于更新模型参数 θ \\theta θ,外层优化用于寻找更好的元知识用于迁移,元学习的关键就在于如何构建元知识的形式。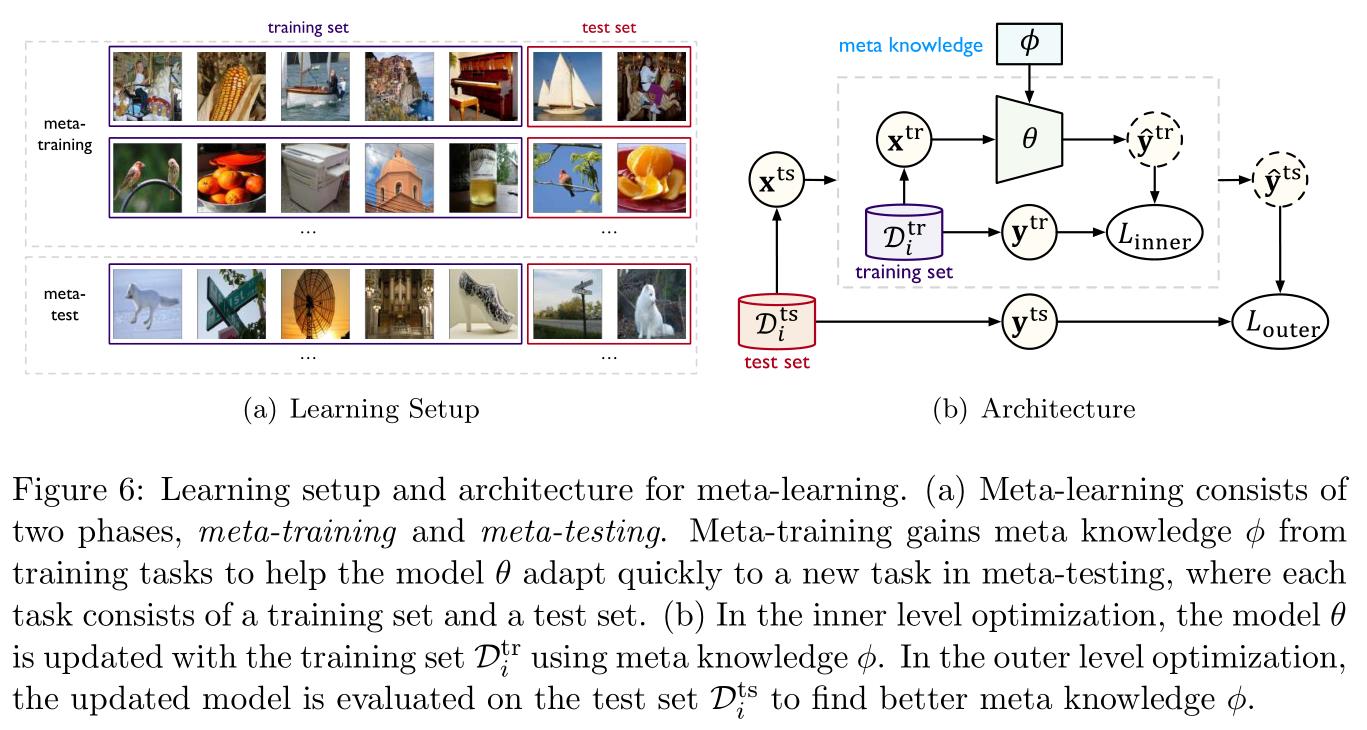
-
基于内存的元学习(memory-based meta-learning):
控制器将从训练数据 D i t r \\mathcalD_i^\\rm tr Ditr中挖掘得到的知识写入内存,并从内存中读取知识以使用基础学习器 θ \\theta θ在测试数据 D i t r \\mathcalD_i^\\rm tr Ditr上进行预测,控制器的参数将不断更新。感觉上这个并不是什么很新奇的方法,本质上你在做项目时预先存好的一些预处理数据都可以视为是基于内存的元学习。
如参考文献 [ 150 ] [150] [150]提出的内存增强神经网络(memory-augmented neural networks,MANN)将绑定样本表示类信息(bound sample representation-class label information)存储在外部内存中,以用于检索作为特征来进行预测。参考文献 [ 121 ] [121] [121]则是提出另一种内存机制,基础学习器用于提供关于当前任务的状态,元学习器则与外部内存交互以生成用于基础学习器的模型参数,以快速学习新任务。
基于内存的元学习对于如少射分类(few-shot classification)以及强化学习的下游任务是比较有优势的,但是需要设计黑盒架构来合并内存机制,往往我们并不知道到底存储了什么东西,以及为什么存储的东西是有益于模型迁移的。
-
基于优
以上是关于论文阅读2022年最新迁移学习综述笔注(Transferability in Deep Learning: A Survey)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章