vue 简单版状态机(vuex)
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了vue 简单版状态机(vuex)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A index.jsimport service from '../service.js';
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store(
state:
/**
* 是否需要强制登录
*/
forcedLogin: true,
hasLogin: false,
userName: "",
msg:
,
mutations:
login(state, userName)
state.userName = userName || '新用户';
state.hasLogin = true;
,
logout(state)
state.userName = "";
state.hasLogin = false;
service.removeUser();
,
setmsg(state, msg)
state.msg = msg
)
export default store
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
引入:import
mapState,
mapMutations
from 'vuex'
设置值:
methods:
...mapMutations(['login', 'setmsg']),
let userMsg =
user_grade: data.data.user_grade,
discount_rate: data.data.discount_rate
that.setmsg(userMsg);
获取值:
computed:
...mapState(['forcedLogin', 'hasLogin', 'userName','msg']),
this.msg(就可以出来了)
vue-cli安装以及创建一个简单的项目(vuex使用)
1.vuex的使用
vuex是vue的状态管理中心,vuex来保存我们需要管理的状态值,值一旦被修改,所有引用该值的地方就会自动更新,常用于:
1.多个视图依赖同一状态(l例:菜单导航)
2.来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态(例如评论弹幕)
上篇创建的vue项目目录结构:
在上一节我们已经安装了vuex模块。查看store/index.js内容,如下:
import Vue from \'vue\'; import Vuex from \'vuex\'; Vue.use(Vuex); export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { }, mutations: { }, actions: { }, modules: { }, });
上面引入Vue模块和Vuex模块,并将Vuex安装到Vue中。
下面使用vuex。在Test路由中改变值,在about模块中接收,代码如下:
(1)修改store/index.js
import Vue from \'vue\'; import Vuex from \'vuex\'; Vue.use(Vuex); export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0, }, mutations: { increase() { this.state.count = this.state.count + 1; }, }, actions: { }, modules: { }, });
定义一个状态count,mutations中是修改状态的唯一入口。
(2)修改Test.vue
<template> <div class="test"> 这是Test <button tybe="button" @click="addOne()">点击我</button> </div> </template> <script> import store from \'@/store\'; export default { name: \'Test\', store, methods: { addOne() { console.log(\'add\'); store.commit(\'increase\'); }, }, }; </script>
点击按钮的时候调用方法addOne()。addOne()中调用store.commit("increase") 提交该方法进行修改状态,相当于调用 Vuex.Store 实例的 increase() 方法。
(3)修改About.vue接收状态count
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1>This is an about page</h1>
{{msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import store from \'@/store\';
export default {
name: \'About\',
store,
data() {
return {
msg: store.state.count,
};
},
};
</script>
(4)测试:
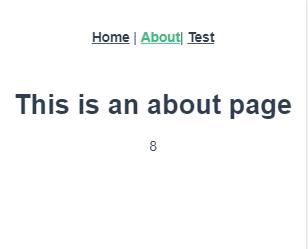
补充:关于vuex调用函数传递参数。比如我们传递一个username参数到vuex中,如:
store/index.js:
import Vue from \'vue\'; import Vuex from \'vuex\'; Vue.use(Vuex); export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { username: \'\' }, mutations: { setLoginUsername(state, username) { state.username = username }, }, actions: { setLoginUsernameFun(context, username) { context.commit("setLoginUsername", username); }, }, modules: { }, });
调用方法如下:(登录成功之后跳转到首页并记录登录的用户)=如下面红色代码
login() { this.isReg = false; var nameLocal = localStorage.getItem("name"); var passwordLocal = localStorage.getItem("name"); if (nameLocal == \'\' || passwordLocal == \'\') { alert("您还没注册!"); return; } if (nameLocal === this.name || passwordLocal === this.password) { store.dispatch("setLoginUsernameFun", nameLocal); this.$router.push(\'/home\') return; } alert("账号或者密码错误"); },
补充:vueX的五个核心属性
(1)state:
state即Vuex中的基本数据!
state就是用来存放数据,若是对数据进行处理输出,比如数据要过滤,一般我们可以写到computed中。
(2)getters(相当于State的计算属性) :
基础用法:
index.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { list: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 20, 30] }, getters: { filteredList: state => { return state.list.filter(item => item > 5) }, listCount: (state, getters) => { return getters.filteredList.length; } } })
vue中:
<template> <div> 过滤后的列表:{{list}} <br> 列表长度:{{listCount}} </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "index.vue", computed: { list() { return this.$store.getters.filteredList; }, listCount() { return this.$store.getters.listCount; } } } </script>
(3)mutation(提交更改数据的方法,同步!必须是同步函数)
使用vuex修改state时,有两种方式:
1)可以直接使用 this.$store.state.变量 = xxx;
2)this.$store.dispatch(actionType, payload)或者 this.$store.commit(commitType, payload)
异同点:
1)共同点: 能够修改state里的变量,并且是响应式的(能触发视图更新)
2)不同点:
若将vue创建 store 的时候传入 strict: true, 开启严格模式,那么任何修改state的操作,只要不经过mutation的函数,
vue就会 throw error : [vuex] Do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers。
(4)action(像一个装饰器,包裹mutations,使之可以异步。)
action的功能和mutation是类似的,都是去变更store里的state,不过action和mutation有两点不同:
1)action主要处理的是异步的操作,mutation必须同步执行,而action就不受这样的限制,也就是说action中我们既可以处理同步,也可以处理异步的操作
2)action改变状态,最后是通过提交mutation。
Action 通过 store.dispatch 方法触发。
(5)modules ( 模块化Vuex):
在Vue中State使用是单一状态树结构,应该的所有的状态都放在state里面,如果项目比较复杂,那state是一个很大的对象,store对象也将对变得非常大,难于管理。
modules:可以让每一个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getters,使得结构非常清晰,方便管理
const moduleA = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... }, getters: { ... } } const moduleB = { state: { ... }, mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... } } const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { a: moduleA, b: moduleB } }) store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态 store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
2. 打包vue项目并制作成app
vue-cli3之后的打包与之前不一样,配置文件在vue.config.js中,并且这个文件需要自己创建置于与package.json同目录。关于其配置项可参考:
如果想打包之后静态页面直接点击运行需要将路由改为hash路由:
(1)修改router/index.js
const router = new VueRouter({ mode: \'hash\', base: process.env.BASE_URL, routes, });
(2)vue.config,js修改打包的默认路径:
module.exports = { publicPath: \'./\', lintOnSave: false }
如果将来我们将页面置于项目中,项目名称为exam,我们将publicPath修改为exam即可。默认是/,./是相对路径。
lintOnSave: false 是关闭eslint验证(这个验证太烦了)
接下来到项目根路径运行打包命令即可得到正常的html、css等文件。如下:
E:\\HBuilderSpace\\vue-demo>npm run build > vue-demo@0.1.0 build E:\\HBuilderSpace\\vue-demo > vue-cli-service build - Building for production... DONE Compiled successfully in 51657ms File Size Gzipped dist\\js\\chunk-vendors.ae7fcf93.js 125.21 KiB 43.38 KiB dist\\js\\app.628ec198.js 7.19 KiB 2.75 KiB dist\\js\\about.672d2588.js 1.32 KiB 0.59 KiB dist\\css\\about.b0b00f5a.css 0.57 KiB 0.31 KiB dist\\css\\app.59544d79.css 0.21 KiB 0.15 KiB
打包后会生成dist目录,并且对文件都进行了压缩,如下:

index.html内容如下:(原本是一行,这是我格式化后的。可以看到路径是相对路由)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=en> <head> <meta charset=utf-8> <meta http-equiv=X-UA-Compatible content="IE=edge"> <meta name=viewport content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1"> <link rel=icon href=favicon.ico> <title>vue-demo</title> <link href=css/about.b0b00f5a.css rel=prefetch> <link href=js/about.672d2588.js rel=prefetch> <link href=css/app.59544d79.css rel=preload as=style> <link href=js/app.628ec198.js rel=preload as=script> <link href=js/chunk-vendors.ae7fcf93.js rel=preload as=script> <link href=css/app.59544d79.css rel=stylesheet> </head> <body> <noscript><strong>We\'re sorry but vue-demo doesn\'t work properly without JavaScript enabled. Please enable it to continue.</strong></noscript> <div id=app></div> <script src=js/chunk-vendors.ae7fcf93.js></script> <script src=js/app.628ec198.js></script> </body> </html>
2.制作一个简单的基于localStorage本地登录的小app
用vue制作一个简单的基于本地登录的app,基于hash的路由。
1.目录结构:

2.附上主要代码:
App.vue:只定义了入口,在router/index.js中设置默认路由
<template> <div id="app"> <router-view/> </div> </template> <style lang="scss"> *{ padding: 0px; text-align: center; } </style>
Main.js
import Vue from \'vue\';
import App from \'./App.vue\';
import router from \'./router\';
import store from \'./store\';
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount(\'#app\');
router/index.js
import Vue from \'vue\';
import VueRouter from \'vue-router\';
import Login from \'../views/Login.vue\';
Vue.use(VueRouter);
const routes = [
{
path: \'/\',
name: \'login\',
component: Login,
},
{
path: \'/home\',
name: \'home\',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ \'../views/Home.vue\'),
redirect: \'/home/user\',
children: [{
path: \'user\',
name: \'user\',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ \'../views/User.vue\')
}, {
path: \'contact\',
name: \'contact\',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ \'../views/Contact.vue\')
}]
},
];
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: \'hash\',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
linkActiveClass: \'active\',
routes,
});
export default router;
定义了默认路由是Login,Login采用一次性加载,其他采用懒加载。登录成功之后的/home重定向到子路由/home/user。
store/index.js
import Vue from \'vue\';
import Vuex from \'vuex\';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
username: \'\'
},
mutations: {
setLoginUsername(state, username) {
state.username = username
},
},
actions: {
setLoginUsernameFun(context, username) {
context.commit("setLoginUsername", username);
},
},
modules: {
},
});
vuex管理组件定义了一个属性与修改属性的方法
vies/Login.vue
<template> <div class="login"> <form v-if="!isReg"> <h1>欢迎来到XXX系统</h1> <br/> <br/> <div>用户名: <input type="text" v-model="name"/> </div> <br/> <div>密 码: <input type="password" v-model="password"/> </div> <div class="rowBtn" @click="login()">登录</div> <div class="rowBtn regBtn" @click="reg()">注册</div> </form> <form v-else> <h1>注册</h1> <br/> <br/> <div>用户名: <input type="text" v-model="name"/> </div> <br/> <div>密 码: <input type="password" v-model="password"/> </div> <br/> <div>确认密码: <input type="password" v-model="passwordRepeat"/> </div> <div class="rowBtn" @click="addUser()">注册</div> <div class="rowBtn regBtn" @click="cancel()">取消</div> </form> </div> </template> <script> import store from \'@/store\'; export default { name: \'login\', store, data() { return { isReg: false, name: \'\', password: \'\', }; }, methods: { login() { this.isReg = false; var nameLocal = localStorage.getItem("name"); var passwordLocal = localStorage.getItem("name"); if (nameLocal == \'\' || passwordLocal == \'\') { alert("您还没注册!"); return; } if (nameLocal === this.name || passwordLocal === this.password) { store.dispatch("setLoginUsernameFun", nameLocal); this.$router.push(\'/home\') return; } alert("账号或者密码错误"); }, reg() { this.isReg = true; }, addUser() { if (this.name == \'\' || this.password == \'\') { alert("必填用户名密码!!!"); return; } if (this.password !== this.passwordRepeat) { alert("两次密码不一致!!!"); return; } localStorage.setItem("name", this.name); localStorage.setItem("password", this.password); this.name = \'\'; this.password = \'\'; alert("注册成功!"); this.isReg = false; }, cancel() { this.isReg = false; } }, }; </script> <style scoped lang="scss"> .rowBtn{ width: 100%; height: 40px; font-size: 20px; text-align: center; line-height: 40px; margin-top: 10px; background: #87CEEB; &.regBtn{ background: #20B2AA; } } </style>
定义了两个表单,登录和注册用的,用isReg属性进行切换。注册成功保存到本地localStorage。
views/Home.vue
<template> <div class="home"> <router-view/> <ul class="footer"> <router-link class="icons" to="/home/user">个人中心</router-link> <router-link class="icons" to="/home/contact">通讯录</router-link> </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: \'home\', }; </script> <style scoped lang="scss"> li{ list-style: none; } .footer{ position: fixed; width: 100%; height: 60px; line-height:60px; left: 0px; bottom: 0px; display: flex; flex-flow: row nowrap; justify-content: space-around; } .icons{ font-size: 16px; flex: 1; text-align:center; border-top: 1px solid #42b983; } a { color: #42b983; &.active{ color: #fff