JS实现最短路径之弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法
Posted 追风逐月
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JS实现最短路径之弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
弗洛伊德算法是实现最小生成树的一个很精妙的算法,也是求所有顶点至所有顶点的最短路径问题的不二之选。时间复杂度为O(n3),n为顶点数。
精妙之处在于:一个二重初始化,加一个三重循环权值修正,完成了所有顶点至所有顶点的的最短路径计算,代码及其简洁
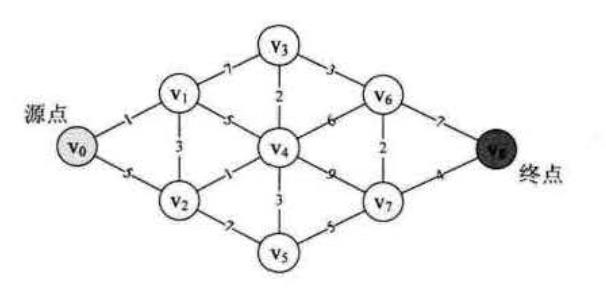
JS实现:
//定义邻接矩阵 let Arr2 = [ [0, 1, 5, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535], [1, 0, 3, 7, 5, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535], [5, 3, 0, 65535, 1, 7, 65535, 65535, 65535], [65535, 7, 65535, 0, 2, 65535, 3, 65535, 65535], [65535, 5, 1, 2, 0, 3, 6, 9, 65535], [65535, 65535, 7, 65535, 3, 0, 65535, 5, 65535], [65535, 65535, 65535, 3, 6, 65535, 0, 2, 7], [65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 9, 5, 2, 0, 4], [65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 7, 4, 0], ] let numVertexes = 9, //定义顶点数 numEdges = 15; //定义边数 // 定义图结构 function MGraph() { this.vexs = []; //顶点表 this.arc = []; // 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 this.numVertexes = null; //图中当前的顶点数 this.numEdges = null; //图中当前的边数 } let G = new MGraph(); //创建图使用 //创建图 function createMGraph() { G.numVertexes = numVertexes; //设置顶点数 G.numEdges = numEdges; //设置边数 //录入顶点信息 for (let i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { G.vexs[i] = \'V\' + i; //scanf(\'%s\'); //ascii码转字符 //String.fromCharCode(i + 65); } console.log(G.vexs) //打印顶点 //邻接矩阵初始化 for (let i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { G.arc[i] = []; for (j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++) { G.arc[i][j] = Arr2[i][j]; //INFINITY; } } console.log(G.arc); //打印邻接矩阵 } let Pathmatirx = []; //二维数组 表示顶点到顶点的最短路径权值和的矩阵 let ShortPathTable = []; //二维数组 表示对应顶点的最小路径的前驱矩阵 function Floyd() { let w, k; for (let v = 0; v < G.numVertexes; ++v) { //初始化 Pathmatirx ShortPathTable Pathmatirx[v] = []; ShortPathTable[v] = []; for (let w = 0; w < G.numVertexes; ++w) { ShortPathTable[v][w] = G.arc[v][w]; Pathmatirx[v][w] = w; } } for (let k = 0; k < G.numVertexes; ++k) { for (let v = 0; v < G.numVertexes; ++v) { for (let w = 0; w < G.numVertexes; ++w) { if (ShortPathTable[v][w] > (ShortPathTable[v][k] + ShortPathTable[k][w])) { //如果经过下标为k顶点路径比原两点间路径更短,当前两点间权值设为更小的一个 ShortPathTable[v][w] = ShortPathTable[v][k] + ShortPathTable[k][w]; Pathmatirx[v][w] = Pathmatirx[v][k]; //路径设置经过下标为k的顶点 } } } } } function PrintAll() { for (let v = 0; v < G.numVertexes; ++v) { for (let w = v + 1; w < G.numVertexes; w++) { console.log(\'V%d-V%d weight: %d\', v, w, ShortPathTable[v][w]); k = Pathmatirx[v][w]; console.log(\' Path: %d\', v); while (k != w) { console.log(\' -> %d\', k); k = Pathmatirx[k][w]; } console.log(\' -> %d\', w); } } } createMGraph(); Floyd(); PrintAll();
运行结果:(结果太长只截取不分)
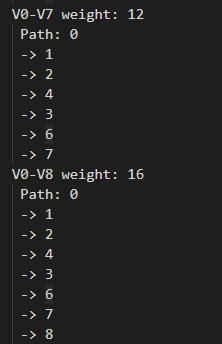
求最短路径的两个算法(迪杰斯特拉算法和弗洛伊德算法),对有向图依然有效,因为二者的差异仅仅是邻接矩阵是否对称而已
参考文献: 程杰 《大话设计模式》
以上是关于JS实现最短路径之弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章