Android App实战项目之虚拟现实(VR)的全景相册(附源码和演示视频 可用于学习和大作业)
Posted showswoller
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android App实战项目之虚拟现实(VR)的全景相册(附源码和演示视频 可用于学习和大作业)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
需要源码请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言私信~~~
不管是绘画还是摄影,都是把三维的物体投影到平面上,其实仍旧呈现二维的模拟画面。 随着科技的发展,传统的成像手段越来越凸显出局限性,缘由在于人们需要一种更逼真更接近现实的技术,从而更好地显示三维世界的环境信息,这便催生了增强现实AR和虚拟现实VR。 传统的摄影只能拍摄90度左右的风景,而新型的全景相机能够拍摄360度乃至720度(连同头顶和脚底在内)的场景,这种360/720度的相片即为全景照片。
一、需求描述
传统的照片只是某个视角观测到的平面截图,无法看到视角以外的场景。 现在有了VR技术,只要把全景相机拍摄的全景照片发到手机上,无论在哪里都能及时通过手机浏览全景照片,从而方便掌握最新的现场情况。 全景照片看似一张矩形图片,其实前后左右上下的景色全都囊括在内,但用户每次只能观看某个角度的截图。要想观看其它方向上的图画,就得想办法让全景照片转起来。
二、功能分析
全景照片之于观察者,便是将全景图贴在球体内侧,由此可见,二者的不同之处在于人是在球外还是球内
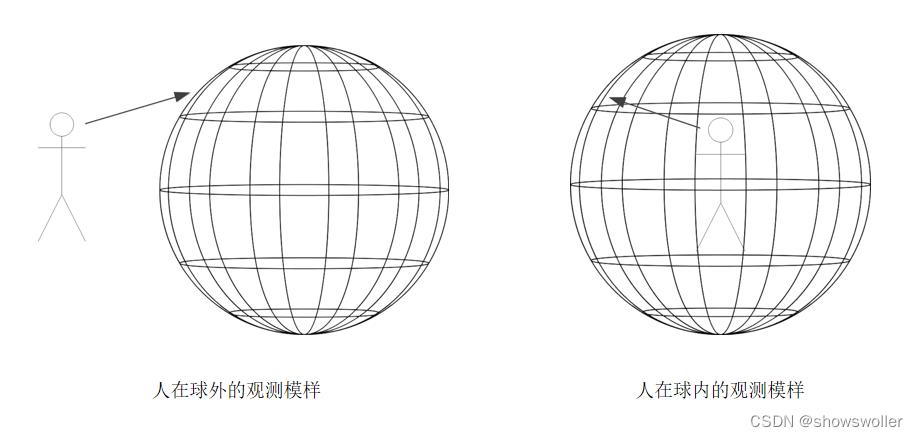
浏览全景照片用到的技术
(1)通过手势的触摸与滑动,把全景照片相应地挪动观测角度。
(2)利用OpenGL ES 库,把平面的全景照片转换为曲面的实景快照。
(3)根据手势滑动在水平方向和垂直方向分别产生的角度变化,实时调整全景图的快照范围。
下面介绍主要代码模块之间的关系
(1)PanoramaActivity.java:这是全景相册的浏览器页面。
(2)PanoramaView.java:这是自定义全景视图的实现代码。
(3)PanoramaRender.java:这是全景图形的三维渲染器代码。
(4)PanoramaUtil.java:这是全景图片的顶点坐标工具类,用于计算全景图片的顶点列表,以及全景图片的纹理列表。
具体到编码过程,主要有以下三项处理
1:实现全景照片的渲染器
2:计算手势触摸引发的角度变更
3:在活动页面加载全景照片的渲染器
三、效果展示
演示视频如下 可以在下拉框中选择不同的相册进行展示,可以放缩或旋转 真正实现了身临其境的感觉
虚拟现实的全景相册
效果图如下


四、代码
部分代码如下 全部源码请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言~
package com.example.threed;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Spinner;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.example.threed.panorama.PanoramaView;
public class PanoramaActivity extends AppCompatActivity
private final static String TAG = "PanoramaActivity";
private PanoramaView pv_content; // 声明一个全景视图对象
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_panorama);
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON); // 保持屏幕常亮
pv_content = findViewById(R.id.pv_content);
pv_content.initRender(resArray[0]); // 设置全景视图的全景图片
initExampleSpinner(); // 初始化样例下拉框
// 初始化样例下拉框
private void initExampleSpinner()
ArrayAdapter<String> exampleAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this,
R.layout.item_select, exampleArray);
Spinner sp_example = findViewById(R.id.sp_example);
sp_example.setPrompt("请选择全景照片例子");
sp_example.setAdapter(exampleAdapter);
sp_example.setOnItemSelectedListener(new ExampleSelectedListener());
sp_example.setSelection(0);
private String[] exampleArray = "现代客厅", "中式客厅", "故宫风光", "城市街景",
"鸟瞰城市", "俯拍高校", "私人会所", "酒店大堂";
private int[] resArray = R.drawable.panorama01, R.drawable.panorama02, R.drawable.panorama03, R.drawable.panorama04,
R.drawable.panorama05, R.drawable.panorama06, R.drawable.panorama07, R.drawable.panorama08;
class ExampleSelectedListener implements AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, final int arg2, long arg3)
pv_content.setDrawableId(resArray[arg2]); // 传入全景图片的资源编号
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> arg0)
util类
package com.example.threed.util;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PanoramaUtil
// 获取全景图片的顶点列表
public static List<Float> getPanoramaVertexList(int perVertex, double perRadius)
List<Float> vertexList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < perVertex; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < perVertex; j++)
float x1 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos(j * perRadius));
float z1 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin(j * perRadius));
float y1 = (float) Math.cos(i * perRadius / 2);
float x2 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos(j * perRadius));
float z2 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin(j * perRadius));
float y2 = (float) Math.cos((i + 1) * perRadius / 2);
float x3 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos((j + 1) * perRadius));
float z3 = (float) (Math.sin((i + 1) * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin((j + 1) * perRadius));
float y3 = (float) Math.cos((i + 1) * perRadius / 2);
float x4 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.cos((j + 1) * perRadius));
float z4 = (float) (Math.sin(i * perRadius / 2) * Math.sin((j + 1) * perRadius));
float y4 = (float) Math.cos(i * perRadius / 2);
vertexList.add(x1);
vertexList.add(y1);
vertexList.add(z1);
vertexList.add(x2);
vertexList.add(y2);
vertexList.add(z2);
vertexList.add(x3);
vertexList.add(y3);
vertexList.add(z3);
vertexList.add(x3);
vertexList.add(y3);
vertexList.add(z3);
vertexList.add(x4);
vertexList.add(y4);
vertexList.add(z4);
vertexList.add(x1);
vertexList.add(y1);
vertexList.add(z1);
return vertexList;
// 获取全景图片的纹理列表
public static List<Float> getPanoramaTextureList(int perVertex)
List<Float> textureList = new ArrayList<>();
double perW = 1 / (float) perVertex;
double perH = 1 / (float) (perVertex);
for (int i = 0; i < perVertex; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < perVertex; j++)
float w1 = (float) (i * perH);
float h1 = (float) (j * perW);
float w2 = (float) ((i + 1) * perH);
float h2 = (float) (j * perW);
float w3 = (float) ((i + 1) * perH);
float h3 = (float) ((j + 1) * perW);
float w4 = (float) (i * perH);
float h4 = (float) ((j + 1) * perW);
textureList.add(h1);
textureList.add(w1);
textureList.add(h2);
textureList.add(w2);
textureList.add(h3);
textureList.add(w3);
textureList.add(h3);
textureList.add(w3);
textureList.add(h4);
textureList.add(w4);
textureList.add(h1);
textureList.add(w1);
return textureList;
XML文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="right"
android:text="全景照片例子:"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="17sp" />
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/sp_example"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:spinnerMode="dialog" />
</LinearLayout>
<com.example.threed.panorama.PanoramaView
android:id="@+id/pv_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>创作不易 觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏~~~
Android开发VR实战三.开发一个寻宝类VR游戏TreasureHunt
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/linglongxin24/article/details/53939303
本文出自【DylanAndroid的博客】
【Android开发VR实战】三.开发一个寻宝类VR游戏TreasureHunt
VR即Virtual Reality虚拟现实。虚拟现实技术是一种可以创建和体验虚拟世界的计算机仿真系统它利用计算机生成一种模拟环境是一种多源信息融合的交互式的三维动态视景和实体行为的系统仿真使用户沉浸到该环境中。
那么,如何在Android中去开发VR功能的APP呢?我们利用谷歌提供的开源SDK去实现一个360°全景游戏的功能。接下来主要是针对谷歌提供的开发VR的SDK中的游戏例子进行翻译。CardBoard:卡纸板,google早期推出的VR 开发集合,封装修改了Activity,GLSurfaceView 以及 Render等标准类的一层API,其中具体细致的实现封在so库中,用户使用CardBoard提供的jar包以及so,按照API的规则使用OPENGL实现特定函数即可开发VR程序
DayDream:白日梦,在CardBoard基础上的专业版,实现了更多的VR特性功能,如3D音效,全景视图,全景视频播放,控制器,封装的API和so也相应的增多,API更加有结构模块化。
TreasureHunt游戏场景包括一个平面接地网格和一个浮动 “宝藏”多维数据集。 当用户观看立方体时,立方体将变成金色。 用户可以直接激活Cardboard触发器在其Cardboard查看器上使用触摸触发器,或使用白日梦基于控制器的触发器仿真。 然后激活触发器,点击寻找宝藏,宝藏消失后随机重新定位立方体。
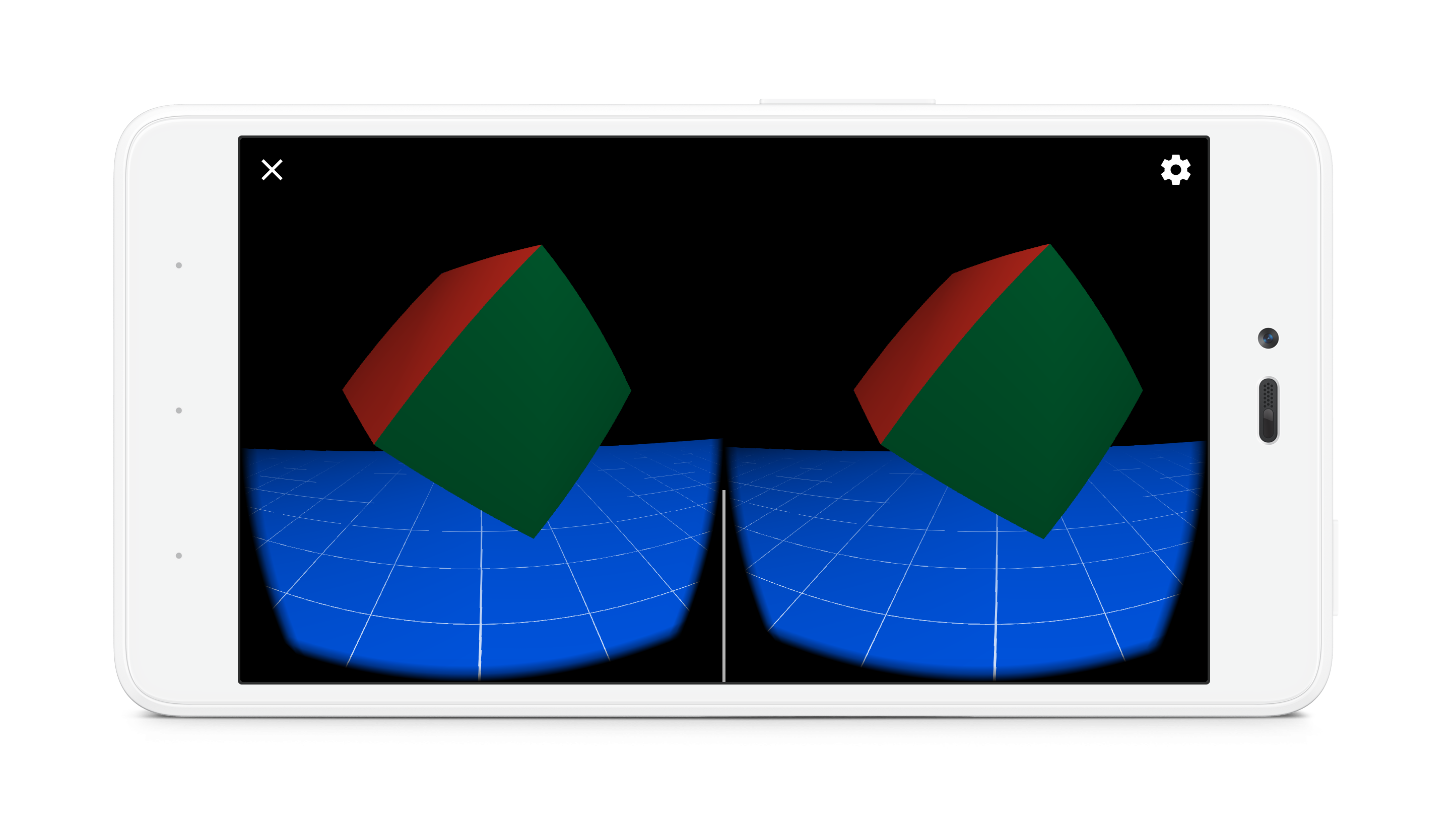
一.在build.gradle中引入谷歌VR的SDK依赖
compile 'com.google.vr:sdk-audio:1.10.0'
compile 'com.google.vr:sdk-base:1.10.0'二.注意支持的最小SDK
minSdkVersion 19
targetSdkVersion 25三.界面布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ui_layout"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<com.google.vr.sdk.base.GvrView
android:id="@+id/gvr_view"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" />
</RelativeLayout>
四.绘制TreasureHunt的VR游戏界面代码
/**
* 将视图设置为我们的GvrView并初始化我们将用于渲染我们的场景的转换矩阵。
*/
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
initializeGvrView();
modelCube = new float[16];
camera = new float[16];
view = new float[16];
modelViewProjection = new float[16];
modelView = new float[16];
modelFloor = new float[16];
tempPosition = new float[4];
// Model first appears directly in front of user.
modelPosition = new float[]0.0f, 0.0f, -MAX_MODEL_DISTANCE / 2.0f;
headRotation = new float[4];
headView = new float[16];
vibrator = (Vibrator) getSystemService(Context.VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
// Initialize 3D audio engine.
gvrAudioEngine = new GvrAudioEngine(this, GvrAudioEngine.RenderingMode.BINAURAL_HIGH_QUALITY);
/**
* 初始化VR显示界面
*/
public void initializeGvrView()
setContentView(R.layout.common_ui);
GvrView gvrView = (GvrView) findViewById(R.id.gvr_view);
gvrView.setEGLConfigChooser(8, 8, 8, 8, 16, 8);
/**设置渲染器**/
gvrView.setRenderer(this);
gvrView.setTransitionViewEnabled(true);
/**使用Daydream耳机启用Cardboard触发反馈。
* 这是一种使用现有Cardboard触发器API支持Daydream控制器输入进行基本交互的简单方法。**/
gvrView.enableCardboardTriggerEmulation();
if (gvrView.setAsyncReprojectionEnabled(true))
/**异步投影,沉浸式,性能模式**/
AndroidCompat.setSustainedPerformanceMode(this, true);
setGvrView(gvrView);
@Override
public void onPause()
gvrAudioEngine.pause();
super.onPause();
@Override
public void onResume()
super.onResume();
gvrAudioEngine.resume();
@Override
public void onRendererShutdown()
Log.i(TAG, "onRendererShutdown");
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(int width, int height)
Log.i(TAG, "onSurfaceChanged");
/**
* 创建用于存储有关3D界面的信息的缓冲区。
* <p>
* <p>OpenGL不使用Java数组,而是需要可以理解的格式的数据。 因此我们使用ByteBuffers。
*
* @param config The EGL configuration used when creating the surface.
*/
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(EGLConfig config)
Log.i(TAG, "onSurfaceCreated");
GLES20.glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 0.5f); // Dark background so text shows up well.
ByteBuffer bbVertices = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COORDS.length * 4);
bbVertices.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeVertices = bbVertices.asFloatBuffer();
cubeVertices.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COORDS);
cubeVertices.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbColors = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COLORS.length * 4);
bbColors.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeColors = bbColors.asFloatBuffer();
cubeColors.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_COLORS);
cubeColors.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbFoundColors =
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_FOUND_COLORS.length * 4);
bbFoundColors.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeFoundColors = bbFoundColors.asFloatBuffer();
cubeFoundColors.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_FOUND_COLORS);
cubeFoundColors.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbNormals = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_NORMALS.length * 4);
bbNormals.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
cubeNormals = bbNormals.asFloatBuffer();
cubeNormals.put(WorldLayoutData.CUBE_NORMALS);
cubeNormals.position(0);
// make a floor
ByteBuffer bbFloorVertices = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COORDS.length * 4);
bbFloorVertices.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
floorVertices = bbFloorVertices.asFloatBuffer();
floorVertices.put(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COORDS);
floorVertices.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbFloorNormals = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_NORMALS.length * 4);
bbFloorNormals.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
floorNormals = bbFloorNormals.asFloatBuffer();
floorNormals.put(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_NORMALS);
floorNormals.position(0);
ByteBuffer bbFloorColors = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COLORS.length * 4);
bbFloorColors.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
floorColors = bbFloorColors.asFloatBuffer();
floorColors.put(WorldLayoutData.FLOOR_COLORS);
floorColors.position(0);
int vertexShader = loadGLShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, R.raw.light_vertex);
int gridShader = loadGLShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, R.raw.grid_fragment);
int passthroughShader = loadGLShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, R.raw.passthrough_fragment);
cubeProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(cubeProgram, vertexShader);
GLES20.glAttachShader(cubeProgram, passthroughShader);
GLES20.glLinkProgram(cubeProgram);
GLES20.glUseProgram(cubeProgram);
checkGLError("Cube program");
cubePositionParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(cubeProgram, "a_Position");
cubeNormalParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(cubeProgram, "a_Normal");
cubeColorParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(cubeProgram, "a_Color");
cubeModelParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_Model");
cubeModelViewParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_MVMatrix");
cubeModelViewProjectionParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_MVP");
cubeLightPosParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(cubeProgram, "u_LightPos");
checkGLError("Cube program params");
floorProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram();
GLES20.glAttachShader(floorProgram, vertexShader);
GLES20.glAttachShader(floorProgram, gridShader);
GLES20.glLinkProgram(floorProgram);
GLES20.glUseProgram(floorProgram);
checkGLError("Floor program");
floorModelParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_Model");
floorModelViewParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_MVMatrix");
floorModelViewProjectionParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_MVP");
floorLightPosParam = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(floorProgram, "u_LightPos");
floorPositionParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(floorProgram, "a_Position");
floorNormalParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(floorProgram, "a_Normal");
floorColorParam = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(floorProgram, "a_Color");
checkGLError("Floor program params");
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelFloor, 0);
Matrix.translateM(modelFloor, 0, 0, -floorDepth, 0); // Floor appears below user.
// Avoid any delays during start-up due to decoding of sound files.
new Thread(
new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
// Start spatial audio playback of OBJECT_SOUND_FILE at the model position. The
// returned sourceId handle is stored and allows for repositioning the sound object
// whenever the cube position changes.
gvrAudioEngine.preloadSoundFile(OBJECT_SOUND_FILE);
sourceId = gvrAudioEngine.createSoundObject(OBJECT_SOUND_FILE);
gvrAudioEngine.setSoundObjectPosition(
sourceId, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
gvrAudioEngine.playSound(sourceId, true /* looped playback */);
// Preload an unspatialized sound to be played on a successful trigger on the cube.
gvrAudioEngine.preloadSoundFile(SUCCESS_SOUND_FILE);
)
.start();
updateModelPosition();
checkGLError("onSurfaceCreated");
/**
* 将保存为资源的原始文本文件转换为OpenGL ES着色器。
*
* @param type The type of shader we will be creating.
* @param resId The resource ID of the raw text file about to be turned into a shader.
* @return The shader object handler.
*/
private int loadGLShader(int type, int resId)
String code = readRawTextFile(resId);
int shader = GLES20.glCreateShader(type);
GLES20.glShaderSource(shader, code);
GLES20.glCompileShader(shader);
// Get the compilation status.
final int[] compileStatus = new int[1];
GLES20.glGetShaderiv(shader, GLES20.GL_COMPILE_STATUS, compileStatus, 0);
// If the compilation failed, delete the shader.
if (compileStatus[0] == 0)
Log.e(TAG, "Error compiling shader: " + GLES20.glGetShaderInfoLog(shader));
GLES20.glDeleteShader(shader);
shader = 0;
if (shader == 0)
throw new RuntimeException("Error creating shader.");
return shader;
/**
* 检查我们在OpenGL ES中是否有错误,如果有错误查看错误。
*
* @param label Label to report in case of error.
*/
private static void checkGLError(String label)
int error;
while ((error = GLES20.glGetError()) != GLES20.GL_NO_ERROR)
Log.e(TAG, label + ": glError " + error);
throw new RuntimeException(label + ": glError " + error);
/**
* 更新立方体的位置。
*/
protected void updateModelPosition()
Matrix.setIdentityM(modelCube, 0);
Matrix.translateM(modelCube, 0, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
// Update the sound location to match it with the new cube position.
if (sourceId != GvrAudioEngine.INVALID_ID)
gvrAudioEngine.setSoundObjectPosition(
sourceId, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
checkGLError("updateCubePosition");
/**
* 将原始文本文件转换为字符串。
*
* @param resId 要转换为着色器的原始文本文件的资源ID。
* @return 文本文件的上下文,或者在出现错误的情况下为null。
*/
private String readRawTextFile(int resId)
InputStream inputStream = getResources().openRawResource(resId);
try
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null)
sb.append(line).append("\\n");
reader.close();
return sb.toString();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
/**
* 在绘制视图之前准备OpenGL ES。
*
* @param headTransform 新帧中的头变换。
*/
@Override
public void onNewFrame(HeadTransform headTransform)
setCubeRotation();
// Build the camera matrix and apply it to the ModelView.
Matrix.setLookAtM(camera, 0, 0.0f, 0.0f, CAMERA_Z, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
headTransform.getHeadView(headView, 0);
// Update the 3d audio engine with the most recent head rotation.
headTransform.getQuaternion(headRotation, 0);
gvrAudioEngine.setHeadRotation(
headRotation[0], headRotation[1], headRotation[2], headRotation[3]);
// Regular update call to GVR audio engine.
gvrAudioEngine.update();
checkGLError("onReadyToDraw");
/**
* 设置立方体旋转矩阵
*/
protected void setCubeRotation()
Matrix.rotateM(modelCube, 0, TIME_DELTA, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f);
/**
* 为我们的视野画每一帧图。
*
* @param eye 视图呈现。 包括所有必需的转换。
*/
@Override
public void onDrawEye(Eye eye)
GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST);
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
checkGLError("colorParam");
// Apply the eye transformation to the camera.
Matrix.multiplyMM(view, 0, eye.getEyeView(), 0, camera, 0);
// Set the position of the light
Matrix.multiplyMV(lightPosInEyeSpace, 0, view, 0, LIGHT_POS_IN_WORLD_SPACE, 0);
// Build the ModelView and ModelViewProjection matrices
// for calculating cube position and light.
float[] perspective = eye.getPerspective(Z_NEAR, Z_FAR);
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelView, 0, view, 0, modelCube, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelViewProjection, 0, perspective, 0, modelView, 0);
drawCube();
// Set modelView for the floor, so we draw floor in the correct location
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelView, 0, view, 0, modelFloor, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelViewProjection, 0, perspective, 0, modelView, 0);
drawFloor();
@Override
public void onFinishFrame(Viewport viewport)
/**
* 绘制立方体。
* <p>
* <p>设置了所有的转换矩阵。简单地将它们传递给着色器。
*/
public void drawCube()
GLES20.glUseProgram(cubeProgram);
GLES20.glUniform3fv(cubeLightPosParam, 1, lightPosInEyeSpace, 0);
// Set the Model in the shader, used to calculate lighting
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(cubeModelParam, 1, false, modelCube, 0);
// Set the ModelView in the shader, used to calculate lighting
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(cubeModelViewParam, 1, false, modelView, 0);
// Set the position of the cube
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
cubePositionParam, COORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, cubeVertices);
// Set the ModelViewProjection matrix in the shader.
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(cubeModelViewProjectionParam, 1, false, modelViewProjection, 0);
// Set the normal positions of the cube, again for shading
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(cubeNormalParam, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, cubeNormals);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(cubeColorParam, 4, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0,
isLookingAtObject() ? cubeFoundColors : cubeColors);
// Enable vertex arrays
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(cubePositionParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(cubeNormalParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(cubeColorParam);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
// Disable vertex arrays
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(cubePositionParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(cubeNormalParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(cubeColorParam);
checkGLError("Drawing cube");
/**
* 画地板。
* <p>
* <p>这将底层的数据馈入着色器。 注意,这不会输入关于灯的位置的数据,因此,如果我们重写我们的代码来绘制地板,照明可能
* 看起来很奇怪。
*/
public void drawFloor()
GLES20.glUseProgram(floorProgram);
// Set ModelView, MVP, position, normals, and color.
GLES20.glUniform3fv(floorLightPosParam, 1, lightPosInEyeSpace, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(floorModelParam, 1, false, modelFloor, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(floorModelViewParam, 1, false, modelView, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(floorModelViewProjectionParam, 1, false, modelViewProjection, 0);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(
floorPositionParam, COORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, floorVertices);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(floorNormalParam, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, floorNormals);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(floorColorParam, 4, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 0, floorColors);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(floorPositionParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(floorNormalParam);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(floorColorParam);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 24);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(floorPositionParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(floorNormalParam);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(floorColorParam);
checkGLError("drawing floor");
/**
* 当点击或拉动Cardboard触发器时调用。
*/
@Override
public void onCardboardTrigger()
Log.i(TAG, "onCardboardTrigger");
if (isLookingAtObject())
successSourceId = gvrAudioEngine.createStereoSound(SUCCESS_SOUND_FILE);
gvrAudioEngine.playSound(successSourceId, false /* looping disabled */);
hideObject();
// Always give user feedback.
vibrator.vibrate(50);
/**
* 方法作用:隐藏物体即为对象找到一个新的随机位置。
* <p>
* 方法说明:我们将围绕Y轴旋转它,使它看不见,然后向上或向下一点点。
*/
protected void hideObject()
float[] rotationMatrix = new float[16];
float[] posVec = new float[4];
// First rotate in XZ plane, between 90 and 270 deg away, and scale so that we vary
// the object's distance from the user.
float angleXZ = (float) Math.random() * 180 + 90;
Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, angleXZ, 0f, 1f, 0f);
float oldObjectDistance = objectDistance;
objectDistance =
(float) Math.random() * (MAX_MODEL_DISTANCE - MIN_MODEL_DISTANCE) + MIN_MODEL_DISTANCE;
float objectScalingFactor = objectDistance / oldObjectDistance;
Matrix.scaleM(rotationMatrix, 0, objectScalingFactor, objectScalingFactor, objectScalingFactor);
Matrix.multiplyMV(posVec, 0, rotationMatrix, 0, modelCube, 12);
float angleY = (float) Math.random() * 80 - 40; // Angle in Y plane, between -40 and 40.
angleY = (float) Math.toRadians(angleY);
float newY = (float) Math.tan(angleY) * objectDistance;
modelPosition[0] = posVec[0];
modelPosition[1] = newY;
modelPosition[2] = posVec[2];
updateModelPosition();
/**
* 通过计算对象在眼睛空间中的位置来检查用户是否正在查看对象。
*
* @return 如果用户正在查看对象,则为true。
*/
private boolean isLookingAtObject()
// Convert object space to camera space. Use the headView from onNewFrame.
Matrix.multiplyMM(modelView, 0, headView, 0, modelCube, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMV(tempPosition, 0, modelView, 0, POS_MATRIX_MULTIPLY_VEC, 0);
float pitch = (float) Math.atan2(tempPosition[1], -tempPosition[2]);
float yaw = (float) Math.atan2(tempPosition[0], -tempPosition[2]);
return Math.abs(pitch) < PITCH_LIMIT && Math.abs(yaw) < YAW_LIMIT;
五.GitHub
以上是关于Android App实战项目之虚拟现实(VR)的全景相册(附源码和演示视频 可用于学习和大作业)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章