前端学习笔记(14)-Vue3组件传参
Posted 吃花椒的恩酱
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了前端学习笔记(14)-Vue3组件传参相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.props(父组件传递给子组件)
1.1 实现
如果你没有使用 <script setup>,props 必须以 props 选项的方式声明,props 对象会作为 setup() 函数的第一个参数被传入:
在子组件中:
export default
props:
title: String,
age: Number
setup(props)
console.log(props.title)
在父组件中:
<p-child title="james" :age="12"></p-child>一个组件可以有任意多的 props,默认情况下,所有 prop 都接受任意类型的值。
这种情况下,我们可以使用 v-for 来渲染它们:
<p-child
v-for="item in items"
:key="item.id"
:title="item.title"
/>使用 v-bind (简写':')来传递动态 prop 值
1.2 单项数据流
所有的 prop 都使得其父子 prop 之间形成了一个单向下行绑定:父级 prop 的更新会向下流动到子组件中,但是反过来则不行。这样会防止从子组件意外变更父级组件的状态,从而导致你的应用的数据流向难以理解。
另外,每次父级组件发生变更时,子组件中所有的 prop 都将会刷新为最新的值。这意味着你不应该在一个子组件内部改变 prop。如果你这样做了,Vue 会在浏览器的控制台中发出警告。
2.emit(子组件传递给父组件)
在子组件中,通过 emit() 来触发事件,通知父组件处理
在父组件中,监听子组件事件
实例子组件:
<template>
<div>
<a-button @click="clickHandle">组件传参</a-button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default
name: 'test',
emits: ['changeMsg'],
setup (props, emit )
function clickHandle ()
emit('changeMsg', '我是子组件值')
return
clickHandle
;
</script>
父组件:
<template>
<h3>description</h3>
<HelloWorld @changeMsg="childEvent"></HelloWorld>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import HelloWorld from '../components/HelloWorld.vue'
import ref, defineComponent from 'vue'
export default defineComponent(
name: 'Home',
components: HelloWorld ,
setup()
const description = ref('Default message')
const childEvent = (msg: string): void =>
description.value = msg
return
description,
childEvent,
,
)
</script>
组件实例提供了一个自定义事件系统。父组件可以通过 v-on 或 @ 来选择性地监听子组件上抛的事件,就像监听原生 DOM 事件那样。
官方文档实例
子组件:
子组件可以通过调用内置的 $emit 方法,通过传入事件名称来抛出一个事件:
<template>
<div class="blog-post">
<h4> title </h4>
<button @click="$emit('enlarge-text')">Enlarge text</button>
</div>
</template>
父组件:
<BlogPost
...
@enlarge-text="postFontSize += 0.1"
/>3.双向绑定v-model
2的例子v-on改为v-model
4.依赖注入
使用Prop有时会遇到逐级透传的问题。如下图所示:
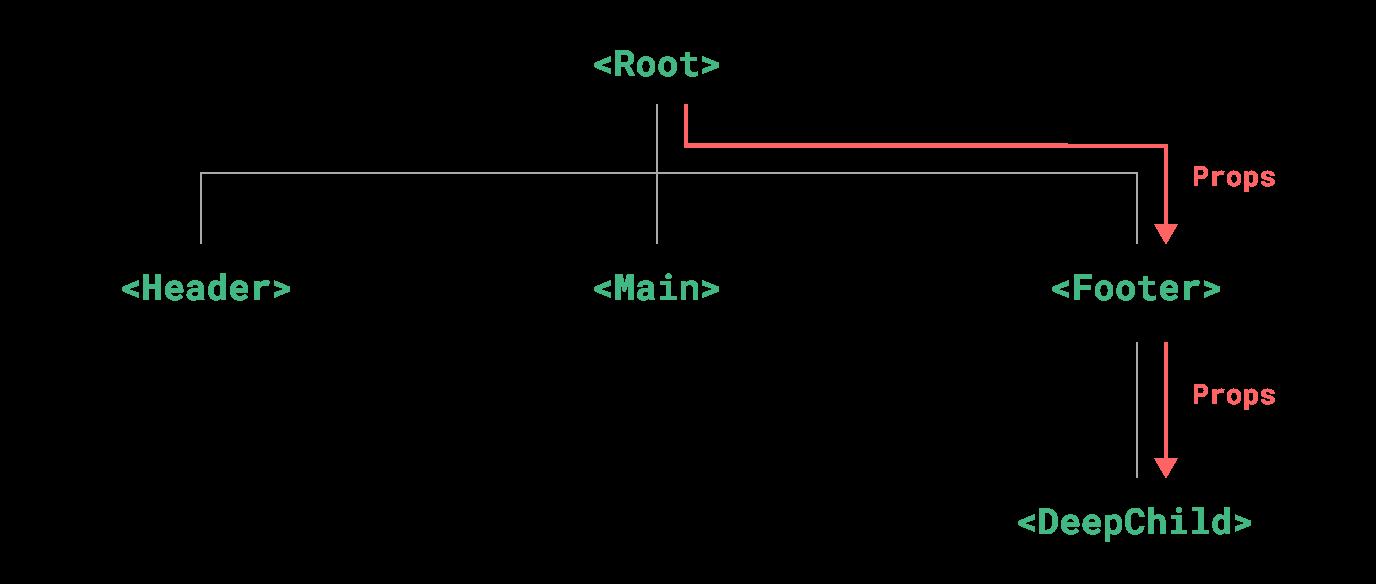
通常情况下,当我们需要从父组件向子组件传递数据时,会使用 props。想象一下这样的结构:有一些多层级嵌套的组件,形成了一颗巨大的组件树,而某个深层的子组件需要一个较远的祖先组件中的部分数据。在这种情况下,如果仅使用 props 则必须将其沿着组件链逐级传递下去,这会非常麻烦。
虽然这里的 <Footer> 组件可能根本不关心这些 props,但为了使 <DeepChild> 能访问到它们,仍然需要定义并向下传递。如果组件链路非常长,可能会影响到更多这条路上的组件。这一问题被称为“prop 逐级透传”,显然是我们希望尽量避免的情况。
provide 和 inject 可以帮助我们解决这一问题。 一个父组件相对于其所有的后代组件,会作为依赖提供者。任何后代的组件树,无论层级有多深,都可以注入由父组件提供给整条链路的依赖。
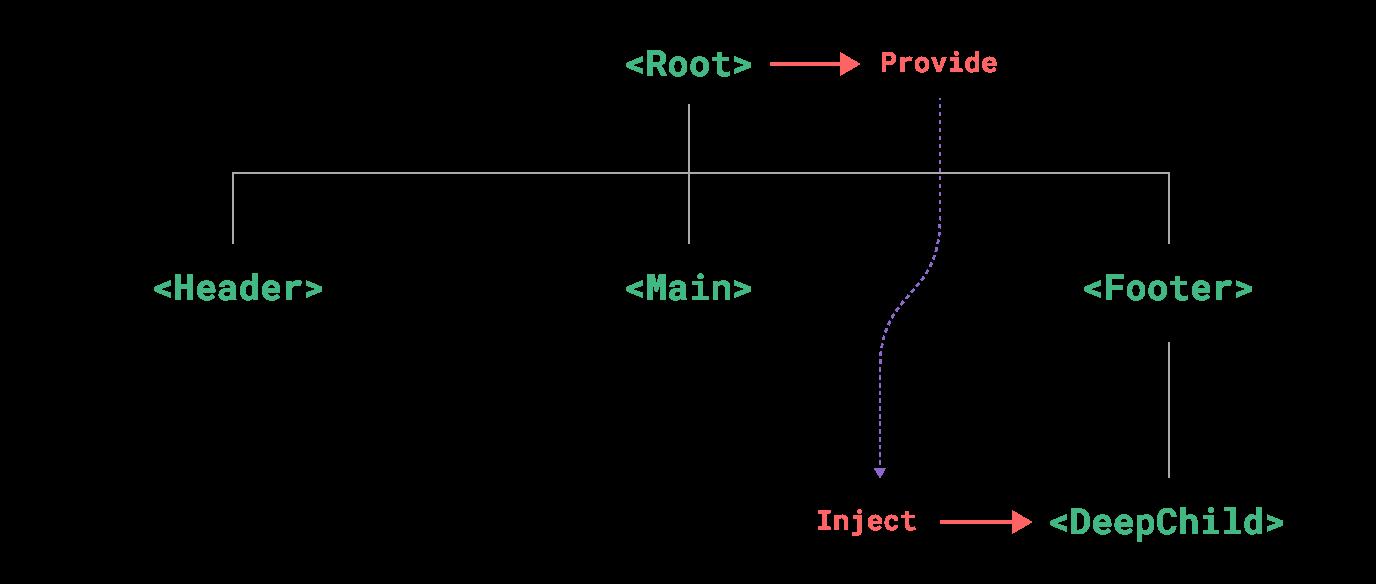
4.1 Provide (提供)
要为组件后代提供数据,需要使用到 provide() 函数:
import provide from 'vue'
export default
setup()
provide(/* 注入名 */ 'message', /* 值 */ 'hello!')
provide() 函数接收两个参数。第一个参数被称为注入名,可以是一个字符串或是一个 Symbol。后代组件会用注入名来查找期望注入的值。一个组件可以多次调用 provide(),使用不同的注入名,注入不同的依赖值。
第二个参数是提供的值,值可以是任意类型,包括响应式的状态,比如一个 ref:
import ref, provide from 'vue'
const count = ref(0)
provide('key', count)提供的响应式状态使后代组件可以由此和提供者建立响应式的联系。
4.2 Inject (注入)
要注入上层组件提供的数据,需使用 inject() 函数:
<!-- 在供给方组件内 -->
<script setup>
import provide, ref from 'vue'
const location = ref('North Pole')
function updateLocation()
location.value = 'South Pole'
provide('location',
location,
updateLocation
)
</script><!-- 在注入方组件 -->
<script setup>
import inject from 'vue'
const location, updateLocation = inject('location')
</script>
<template>
<button @click="updateLocation"> location </button>
</template>注意:provide / inject 类似于消息的订阅和发布,遵循 vue 当中的单项数据流,什么意思呢?就是数据在哪,修改只能在哪,不能在数据传递处修改数据,容易造成状态不可预测。
在订阅组件内修改值的时候,可以被正常修改,如果其他组件也使用该值的时候,状态容易造成混乱,所以需要在源头上规避问题。
5.ref 实现组件的子传父、父传子
5.1 组件上的 ref
组件上的ref获得的值是组件实例:
<child ref="child"></child>ref被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息。引用信息将会注册在父组件的$refs对象上
fatherMethod() this.$refs.child.childMethods();通过this.$refs.child找到的是子组件
多个组件实例可以结合$使用
<div
v-for="item in items"
:key="item.id">
<p-child
:types="item.id"
:ref="`$item.idRef`"
></p-child>
</div>5.2 子组件传递给父组件写法:
子组件:
export default
data()
return
name: '测试'
;
,
methods:
childMethods()
console.log(this.name);
;父组件:
fatherMethod() this.$refs.child.name声明 ref 并调用可以获取子组件 data 中 数据:
5.3 使用ref实现父组件传递给子组件:
childData:
title: String,
age: Number
,
init: (Data: any) =>
let data = ...Data ;
childData =
title: data.title,
age: data.age,
;子组件定义好需要接受的数据,并写好接收方法。
注:vue3 的setup中是没有办法直接使用this的写法:
const child = ref(null);
(child.value as any).(Data)前端vue 跨组件传参,cokies,axion
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
this.$router.push(‘/course‘);this.$router.push({name: course});this.$router.go(-1);this.$router.go(1);<router-link to="/course">课程页</router-link><router-link :to="{name: ‘course‘}">课程页</router-link> |
第一种
router.js
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
routes: [ // ... { path: ‘/course/:id/detail‘, name: ‘course-detail‘, component: CourseDetail },] |
跳转.vue
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<template> <!-- 标签跳转 --> <router-link :to="`/course/${course.id}/detail`">{{ course.name }}</router-link></template><script> // ... goDetail() { // 逻辑跳转 this.$router.push(`/course/${this.course.id}/detail`); }</script> |
接收.vue
|
1
2
3
|
created() { let id = this.$route.params.id;} |
第二种
router.js
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
routes: [ // ... { path: ‘/course/detail‘, name: ‘course-detail‘, component: CourseDetail },] |
跳转.vue
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
<template> <!-- 标签跳转 --> <router-link :to="{ name: ‘course-detail‘, query: {id: course.id} }">{{ course.name }}</router-link></template><script> // ... goDetail() { // 逻辑跳转 this.$router.push({ name: ‘course-detail‘, query: { id: this.course.id } }); }</script> |
接收.vue
|
1
2
3
|
created() { let id = this.$route.query.id;} |
可以完成跨组件传参的四种方式
|
1
2
3
4
|
// 1) localStorage:永久存储数据// 2) sessionStorage:临时存储数据(刷新页面数据不重置,关闭再重新开启标签页数据重置)// 3) cookie:临时或永久存储数据(由过期时间决定)// 4) vuex的仓库(store.js):临时存储数据(刷新页面数据重置) |
vuex仓库插件
store.js配置文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { title: ‘默认值‘ }, mutations: { // mutations 为 state 中的属性提供setter方法 // setter方法名随意,但是参数列表固定两个:state, newValue setTitle(state, newValue) { state.title = newValue; } }, actions: {}}) |
在任意组件中给仓库变量赋值
|
1
2
|
this.$store.state.title = ‘newTitle‘this.$store.commit(‘setTitle‘, ‘newTitle‘) |
在任意组件中取仓库变量的值
|
1
|
console.log(this.$store.state.title) |
vue-cookie插件
安装
|
1
|
>: cnpm install vue-cookies |
main.js 配置
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// 第一种import cookies from ‘vue-cookies‘ // 导入插件Vue.use(cookies); // 加载插件new Vue({ // ... cookies, // 配置使用插件原型 $cookies}).$mount(‘#app‘);?// 第二种import cookies from ‘vue-cookies‘ // 导入插件Vue.prototype.$cookies = cookies; // 直接配置插件原型 $cookies |
使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// 增(改): key,value,exp(过期时间)// 1 = ‘1s‘ | ‘1m‘ | ‘1h‘ | ‘1d‘this.$cookies.set(‘token‘, token, ‘1y‘);?// 查:keythis.token = this.$cookies.get(‘token‘);?// 删:keythis.$cookies.remove(‘token‘); |
注:cookie一般都是用来存储token的
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
// 1) 什么是token:安全认证的字符串// 2) 谁产生的:后台产生// 3) 谁来存储:后台存储(session表、文件、内存缓存),前台存储(cookie)// 4) 如何使用:服务器先生成反馈给前台(登陆认证过程),前台提交给后台完成认证(需要登录后的请求)// 5) 前后台分离项目:后台生成token,返回给前台 => 前台自己存储,发送携带token请求 => 后台完成token校验 => 后台得到登陆用户 |
axios插件
安装
|
1
|
>: cnpm install axios |
main.js配置
|
1
2
|
import axios from ‘axios‘ // 导入插件Vue.prototype.$axios = axios; // 直接配置插件原型 $axios |
使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
this.axios({ url: ‘请求接口‘, method: ‘get|post请求‘, data: {post等提交的数据}, params: {get提交的数据}}).then(请求成功的回调函数).catch(请求失败的回调函数) |
案例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
// get请求this.$axios({ url: ‘http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/ajax/‘, method: ‘get‘, params: { username: this.username }}).then(function (response) { console.log(response)}).catch(function (error) { console.log(error)});?// post请求this.$axios({ url: ‘http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/ajax/‘, method: ‘post‘, data: { username: this.username }}).then(function (response) { console.log(response)}).catch(function (error) { console.log(error)}); |
跨域问题(同源策略)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
// 后台接收到前台的请求,可以接收前台数据与请求信息,发现请求的信息不是自身服务器发来的请求,拒绝响应数据,这种情况称之为 - 跨域问题(同源策略 CORS)?// 导致跨域情况有三种// 1) 端口不一致// 2) IP不一致// 3) 协议不一致?// Django如何解决 - django-cors-headers模块// 1) 安装:pip3 install django-cors-headers// 2) 注册:INSTALLED_APPS = [ ... ‘corsheaders‘]// 3) 设置中间件:MIDDLEWARE = [ ... ‘corsheaders.middleware.CorsMiddleware‘]// 4) 设置跨域:CORS_ORIGIN_ALLOW_ALL = True |
element-ui插件
安装
|
1
|
>: cnpm i element-ui -S |
main.js配置
|
1
2
3
|
import ElementUI from ‘element-ui‘;import ‘element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css‘;Vue.use(ElementUI); |
使用
|
1
|
依照官网 https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/installation api |
以上是关于前端学习笔记(14)-Vue3组件传参的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章