基于 Docker 的 ELK 高可用集群架构
Posted 云计算-Security
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于 Docker 的 ELK 高可用集群架构相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、规划
1.1 主机规划
| Service | Version | 角色 |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.56.133 - 2C/2G 30G - es-1 | 6.8.23 | ES集群 |
| 192.168.56.134 - 2C/2G 30G - es-2 | - | - |
| 192.168.56.135 - 2C/2G 30G - es-3 | - | - |
| 192.168.56.137 - 2C/2G 30G - kafka-1 zookeeper-1 | 3.7.1 | 消息队列 |
| 192.168.56.138 - 2C/2G 30G - kafka-2 zookeeper-2 | - | - |
| 192.168.56.139 - 2C/2G 30G - kafka-3 zookeeper-3 | - | - |
| 192.168.56.140 - 1C/2G 30G - logstash-1 | 6.8.23 | logstash分流 |
| 192.168.56.141 - 1C/2G 30G - logstash-2 | - | - |
| 192.168.56.136 - 2C/2G 30G - kabana - head - nginx | 6.8.23 | web前端展示 |
| 192.168.56.136 - 2C/2G 30G - kabana | - | - |
整体思路:
1、三台服务器做 ES 集群;
2、三台服务器做 Kafka 集群;
3、两台或多台服务器做 Logstash 分流;
4、两台 Kibana 做负载均衡。
1.2 整体架构
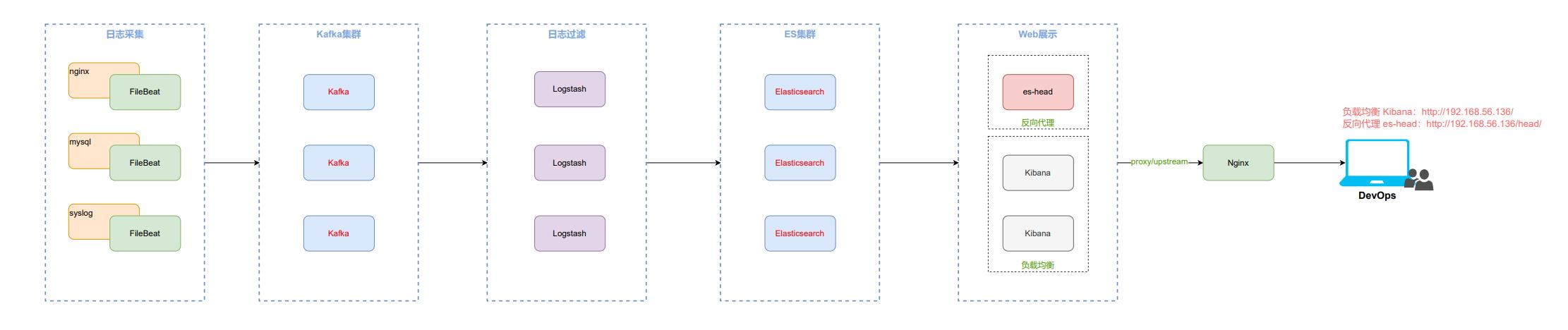
应用场景:适用于高并发场景。
二、部署
2.1 ES 集群
1、安装docker
执行安装脚本,有需要安装脚本的朋友可私我。
2、创建 ES 相关目录
mkdir -p /data/elasticsearch/data
mkdir -p /data/elasticsearch/logs
mkdir -p /data/elasticsearch/plugins
mkdir -p /data/elasticsearch/config/
3、任意一个 ES 节点运行一个es临时容器,拷贝配置文件
docker run -itd \\
--name=tmp \\
-e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx512m" \\
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \\
elasticsearch:6.8.20
docker cp tmp:/usr/share/elasticsearch /data/
# 直接复制ES的工作目录到本地进行持久化,后面运行容器时就使用该目录来做映射。
4、修改 ES 配置文件
-
es-1
elasticsearch.yml
# cluster.name 三者需相同 cluster.name: es-cluster # node.name 节点名,设置与主机名一致即可 node.name: es-1 # node.master 符合成为主节点的条件 node.master: true # node.data 符合成为数据节点的条件 node.data: true # path.data 数据存储路径(下面会进行创建) path.data: /data/elasticsearch/data # path.logs 日志存储路径(下面会进行创建) path.logs: /data/elasticsearch/logs # bootstrap.memory_lock 锁住内存,即只使用内存,不使用交换分区 bootstrap.memory_lock: true # network.host 允许所有IP访问 network.host: 0.0.0.0 # network.publish_host 集群节点交互IP(docker方式的部署填写公网IP) # docker 方式部署的需指定 network.publish_host,否则无法访问集群 network.publish_host: 192.168.56.133 # http.port web访问端口 http.port: 9200 # discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts 关闭单播 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.56.133", "192.168.56.134", "192.168.56.135"] # discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes 指定master备选数(N/2+1)取整,N为集群节点数 discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # discovery.zen.ping_timeout 节点在发现过程中的等待超时时间 #discovery.zen.ping_timeout: 120s # discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries 节点发现重试次数 #discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 10 # client.transport.ping_timeout ping命令的响应超时时间 #client.transport.ping_timeout: 60s # 解决跨域问题 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"jvm.options(这里主要配置一下 JVM 堆大小)
## JVM configuration ################################################################ ## IMPORTANT: JVM heap size ################################################################ ## ## You should always set the min and max JVM heap ## size to the same value. For example, to set ## the heap to 4 GB, set: ## ## -Xms4g ## -Xmx4g ## ## See https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/heap-size.html ## for more information ## ################################################################ # Xms represents the initial size of total heap space # Xmx represents the maximum size of total heap space -Xms512m -Xmx512m ################################################################ ## Expert settings ################################################################ ## ## All settings below this section are considered ## expert settings. Don't tamper with them unless ## you understand what you are doing ## ################################################################ ## GC configuration 8-13:-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC 8-13:-XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=75 8-13:-XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly ## G1GC Configuration # NOTE: G1 GC is only supported on JDK version 10 or later # to use G1GC, uncomment the next two lines and update the version on the # following three lines to your version of the JDK # 10-13:-XX:-UseConcMarkSweepGC # 10-13:-XX:-UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly 14-:-XX:+UseG1GC 14-:-XX:G1ReservePercent=25 14-:-XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent=30 ## DNS cache policy # cache ttl in seconds for positive DNS lookups noting that this overrides the # JDK security property networkaddress.cache.ttl; set to -1 to cache forever -Des.networkaddress.cache.ttl=60 # cache ttl in seconds for negative DNS lookups noting that this overrides the # JDK security property networkaddress.cache.negative ttl; set to -1 to cache # forever -Des.networkaddress.cache.negative.ttl=10 ## optimizations # pre-touch memory pages used by the JVM during initialization -XX:+AlwaysPreTouch ## basic # explicitly set the stack size -Xss1m # set to headless, just in case -Djava.awt.headless=true # ensure UTF-8 encoding by default (e.g. filenames) -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 # use our provided JNA always versus the system one -Djna.nosys=true # turn off a JDK optimization that throws away stack traces for common # exceptions because stack traces are important for debugging -XX:-OmitStackTraceInFastThrow # enable helpful NullPointerExceptions (https://openjdk.java.net/jeps/358), if # they are supported 14-:-XX:+ShowCodeDetailsInExceptionMessages # flags to configure Netty -Dio.netty.noUnsafe=true -Dio.netty.noKeySetOptimization=true -Dio.netty.recycler.maxCapacityPerThread=0 # log4j 2 -Dlog4j.shutdownHookEnabled=false -Dlog4j2.disable.jmx=true -Dlog4j2.formatMsgNoLookups=true -Djava.io.tmpdir=$ES_TMPDIR ## heap dumps # generate a heap dump when an allocation from the Java heap fails # heap dumps are created in the working directory of the JVM -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError # specify an alternative path for heap dumps; ensure the directory exists and # has sufficient space -XX:HeapDumpPath=data # specify an alternative path for JVM fatal error logs -XX:ErrorFile=logs/hs_err_pid%p.log ## JDK 8 GC logging 8:-XX:+PrintGCDetails 8:-XX:+PrintGCDateStamps 8:-XX:+PrintTenuringDistribution 8:-XX:+PrintGCApplicationStoppedTime 8:-Xloggc:logs/gc.log 8:-XX:+UseGCLogFileRotation 8:-XX:NumberOfGCLogFiles=32 8:-XX:GCLogFileSize=64m # JDK 9+ GC logging 9-:-Xlog:gc*,gc+age=trace,safepoint:file=logs/gc.log:utctime,pid,tags:filecount=32,filesize=64m # due to internationalization enhancements in JDK 9 Elasticsearch need to set the provider to COMPAT otherwise # time/date parsing will break in an incompatible way for some date patterns and locals 9-:-Djava.locale.providers=COMPAT # temporary workaround for C2 bug with JDK 10 on hardware with AVX-512 10-:-XX:UseAVX=2 -
es-2
同es-1,唯一不同的是 node.name 和 network.publish_host node.name: es-2 network.publish_host: 192.168.56.134 -
es-3
同es-1,唯一不同的是 node.name 和 network.publish_host node.name: es-3 network.publish_host: 192.168.56.135
5、运行容器
-
es-1
docker run -it \\ --name=es-1 \\ --privileged=true \\ --restart=always \\ --net=host \\ -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\ -v /data/elasticsearch:/usr/share/elasticsearch \\ -d elasticsearch:6.8.23 -
es-2
docker run -it \\ --name=es-2 \\ --privileged=true \\ --restart=always \\ --net=host \\ -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\ -v /data/elasticsearch:/usr/share/elasticsearch \\ -d elasticsearch:6.8.23 -
es-3
docker run -it \\ --name=es-3 \\ --privileged=true \\ --restart=always \\ --net=host \\ -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\ -v /data/elasticsearch:/usr/share/elasticsearch \\ -d elasticsearch:6.8.23
es-head 插件安装看 2.8 小节
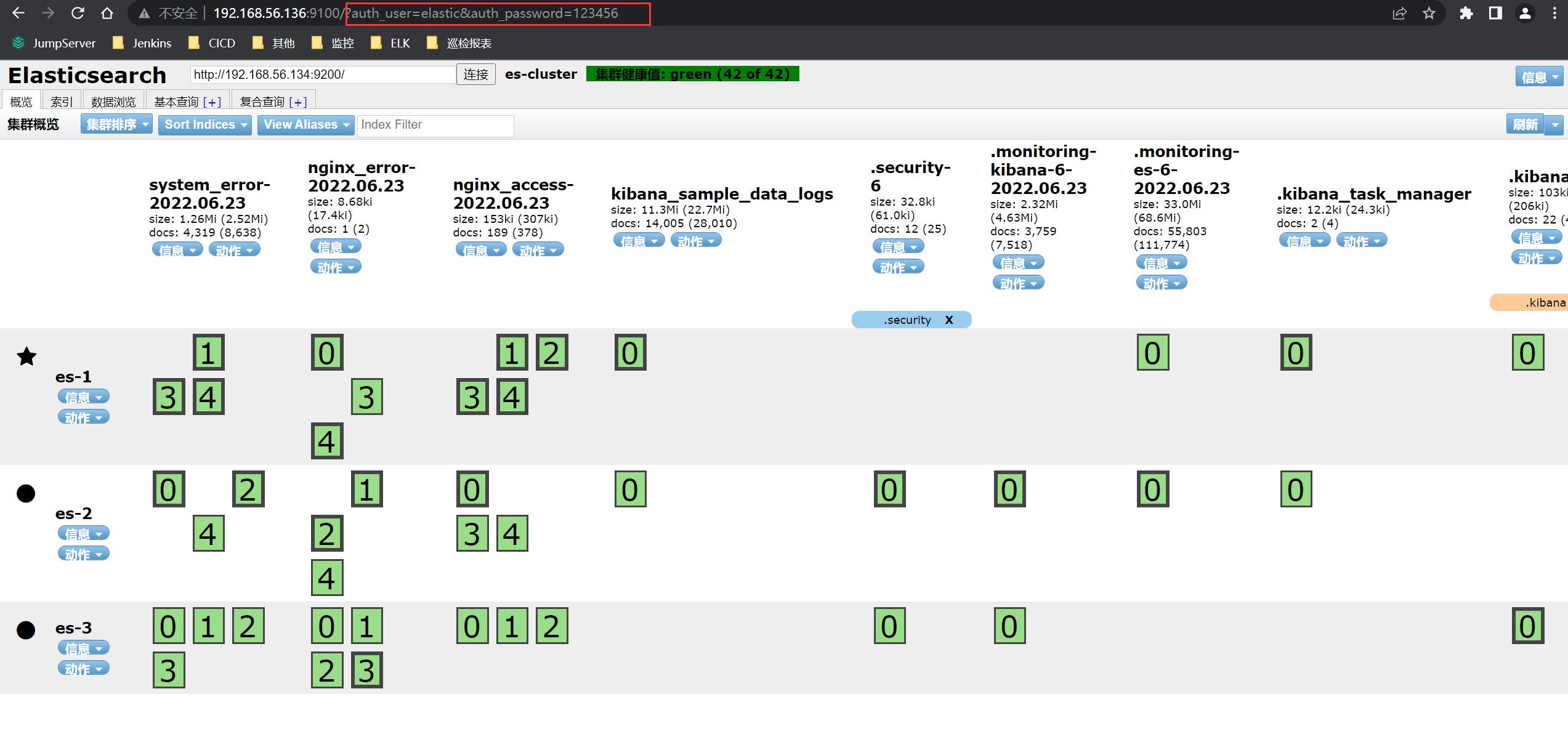
通过 head 插件查看集群状态:

通过 URL 查看集群状态:
浏览器输入 URL 查看集群状态:http://192.168.56.133:9200/_cat/nodes?pretty
标 * 的代表 master(下图与上图不一致,是因为这张图是在我做模拟故障转移时截的)

6、配置 ES 集群证书
先保证在没有使用证书的情况下,ES 集群是正常运行的,然后再配置 ES 集群证书;
在任意 ES 集群节点上生成集群证书(本次我在 es-1 节点);
证书生成完毕之后,再将对应证书 copy 到其他节点的 config 目录下;
重启 ES 集群,此时保证集群正常运行,如果此时集群正常,说明集群间已经通过密钥方式通信;
然后创建 ES 集群的用户名/密码(在任意 ES 集群节点上执行即可,因为集群会同步状态);
启用 ES 集群证书的目:数据安全、防止其他 ES 节点恶意并入集群。
docker exec -it es-1 bash
./bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca
# 会在当前目录生产elastic-stack-ca.p12证书文件
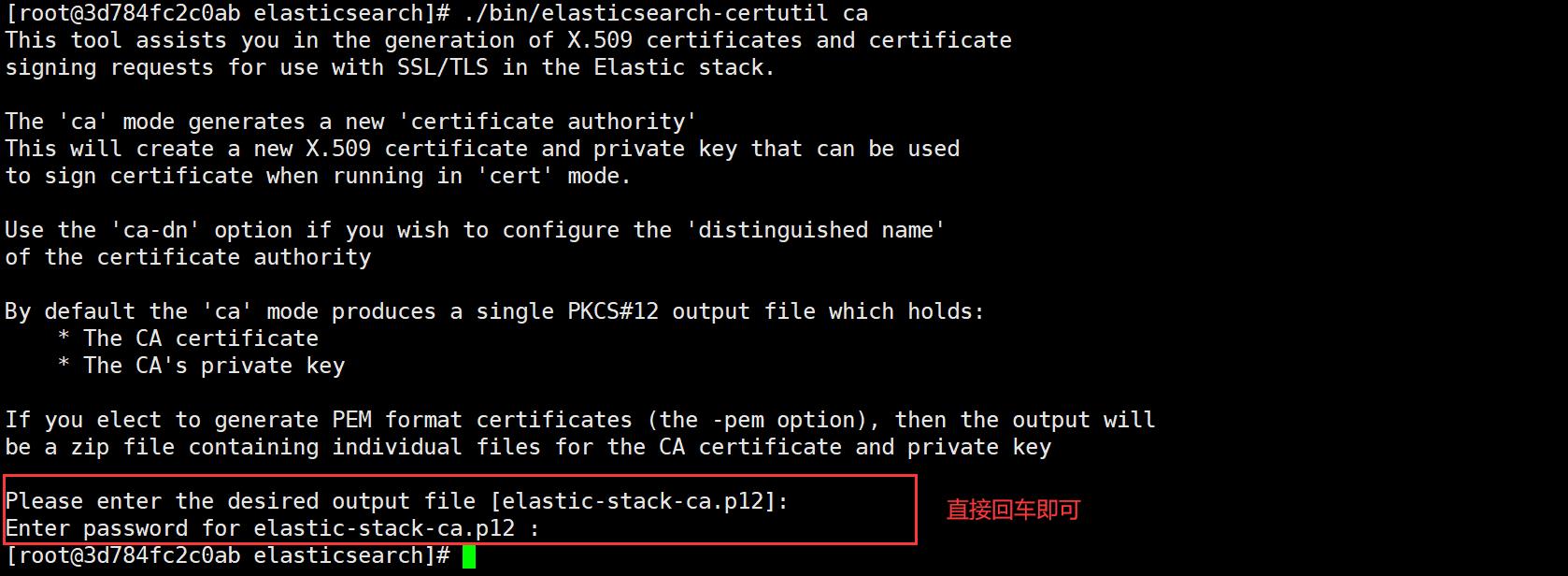
为集群中的每个节点生成证书和私钥:
./bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12

复制证书文件到其他节点:
scp elastic-* es-2:/data/elasticsearch/config/
scp elastic-* es-3:/data/elasticsearch/config/
接着修改 ES 集群配置文件:
# cluster.name 三者需相同
cluster.name: es-cluster
# node.name 节点名,设置与主机名一致即可
node.name: es-1
# node.master 符合成为主节点的条件
node.master: true
# node.data 符合成为数据节点的条件
node.data: true
# path.data 数据存储路径(下面会进行创建)
path.data: /data/elasticsearch/data
# path.logs 日志存储路径(下面会进行创建)
path.logs: /data/elasticsearch/logs
# bootstrap.memory_lock 锁住内存,即只使用内存,不使用交换分区
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
# network.host 允许所有IP访问
network.host: 0.0.0.0
# network.publish_host 集群节点交互IP(docker方式的部署填写公网IP)
# docker 方式部署的需指定 network.publish_host,否则无法访问集群
network.publish_host: 192.168.56.133
# http.port web访问端口
http.port: 9200
# discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts 关闭单播
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.56.133", "192.168.56.134", "192.168.56.135"]
# discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes 指定master备选数(N/2+1)取整,N为集群节点数
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2
# discovery.zen.ping_timeout 节点在发现过程中的等待超时时间
#discovery.zen.ping_timeout: 120s
# discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries 节点发现重试次数
#discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 10
# client.transport.ping_timeout ping命令的响应超时时间
#client.transport.ping_timeout: 60s
# 解决跨域问题
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
# Auth
xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true
xpack.security.enabled: true
xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate
xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.path: elastic-certificates.p12
xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.path: elastic-certificates.p12
重启 ES 集群:
docker restart es-1
docker restart es-2
docker restart es-3
新增用户名、密码:
任意一台 ES 集群节点上执行即可,执行结果会同步到整个 ES 集群
./bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive
# 我的密码为123456

Changed password for user [apm_system]
Changed password for user [kibana]
Changed password for user [logstash_system]
Changed password for user [beats_system]
Changed password for user [remote_monitoring_user]
Changed password for user [elastic]
上面的用户名密码在任意一台 ES 集群服务器上执行就行,密码会被更新到集群中,就算你在其他节点设置密码也是会报错的,而且会提示你,强一致性密码已经更新至集群,如下所示:

2.2 Logstash 分流
Logstash 作为插件,二进制安装即可,因为容器运行,每次在数据采集的时候都要删除容器,在运行容器,很麻烦。
1、下载镜像
docker pull logstash:6.8.23
2、运行临时容器,并拷贝配置文件
docker run -d --name=tmp ogstash:6.8.23
docker cp tmp:/usr/share/logstash /data/
3、创建配置文件并授权
mkdir /data/logstash/config/conf.d
chmod 777 -R /data/logstash
4、启动容器
docker run -d \\
--name=logstash \\
--privileged=true \\
--restart=always \\
-p 5044:5044 \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
-v /data/logstash:/usr/share/logstash \\
-v /data/nginx/logs/access.log:/data/nginx/logs/access.log \\
logstash:6.8.23
二进制安装
1、JDK 环境
上面有安装步骤
2、解压
tar xzf logstash-6.8.23.tar.gz -C /data/
mv /data/logstash-6.8.23/ /data/logstash
3、创建配置文件目录
mkdir /data/logstash/config/conf.d
4、编写配置文件
vim /data/logstash/config/conf.d/all.conf
input
file
path => ["/data/nginx/logs/access.log"]
type => "nginx_access"
start_position => "beginning"
input
file
path => ["/var/log/messages"]
type => "system_error"
start_position => "beginning"
output
if [type] == "nginx_access"
elasticsearch
hosts => ["192.168.56.133:9200","192.168.56.134:9200","192.168.56.135:9200"]
index => ["%type-%+YYYY.MM.dd"]
if [type] == "system_error"
elasticsearch
hosts => ["192.168.56.133:9200","192.168.56.134:9200","192.168.56.135:9200"]
index => ["%type-%+YYYY.MM.dd"]
# 前台启动
/data/logstash/bin/logstash -f /data/logstash/config/conf.d/ --config.reload.automatic
# 后台启动
nohup /data/logstash/bin/logstash -f /data/logstash/config/conf.d/ --config.reload.automatic &
# --config.reload.automatic:可以加载conf.d 目录下的所有.conf文件
# 想要单独加载的话,则去掉--config.reload.automatic参数,并指定具体的 .conf 文件
5、集群验证

2.3 Kibana 前端展示
1、安装 es-head 插件
docker run -d \\
--name=es-head \\
--privileged=true \\
--restart=always \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
-p 9100:9100 \\
docker.io/mobz/elasticsearch-head:5-alpine
2、安装 Kibana
# 运行临时容器
docker run -itd --name=tmp kibana:6.8.23
# 拷贝相关目录
docker cp tmp:/usr/share/kibana /data/
# 授权
chmod 777 -R /data/kibana/*
3、修改配置文件
# Default Kibana configuration for docker target
server.name: kibana
server.host: "0"
elasticsearch.hosts: [ "http://192.168.56.133:9200","http://192.168.56.134:9200","http://192.168.56.135:9200" ]
xpack.monitoring.ui.container.elasticsearch.enabled: true
#kibana.index: ".kibana"
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
elasticsearch.username: "kibana"
elasticsearch.password: "123456"
#xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: "a_random_string"
#xpack.security.encryptionKey: "something_at_least_32_characters"
4、启动新容器
docker run -d \\
--restart=always \\
--privileged=true \\
--name=kibana \\
-p 5601:5601 \\
-v "/data/kibana:/usr/share/kibana" \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
kibana:6.8.23
5、访问验证
http://192.168.56.136:5601/
输入账号密码:
然后就会进入登录页面。
上图是我之前截的图,当时没有设置 ES 集群密码强一致性验证,设置之后你会发现管理菜单下会多出一个安全性,用户/角色

2.4 Nginx 反向代理
1、安装 Nginx
# 看6.2.4
docker run -itd \\
--name=nginx \\
--privileged=true \\
--restart=always \\
--net=host \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
-v /data/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \\
-v /data/nginx/conf/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d \\
-v /data/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html \\
-v /data/nginx/logs:/var/log/nginx nginx:1.20.2
2、反向代理
server
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.56.136;
# kibana前端展示
location /
root html;
proxy_pass http://192.168.56.136:5601/;
# es-head插件
location /head/
proxy_pass http://192.168.56.136:9100/;
# Kafka-Manager可视化管理
location /manager/
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://192.168.56.136:9000/;
2.5 Zookeeper 集群
1、pull 镜像
docker pull zookeeper:3.7.1
2、创建对应目录
mkdir -p /data/zookeeper/conf
mkdir -p /data/zookeeper/data
mkdir -p /data/zookeeper/datalog
mkdir -p /data/zookeeper/logs
# 配置文件路径:/data/zookeeper/conf
# 数据存储路径:/data/zookeeper/data
# 数据日志存储路径:/data/zookeeper/datalog
# 日志存储路径:/data/zookeeper/logs
3、创建配置文件
三个节点均添加
dataDir=/data
dataLogDir=/datalog
quorumListenOnAllIPs=true
clientPort=2181
tickTime=2000
initLimit=20
syncLimit=10
server.1=192.168.56.137:2888:3888;2181
server.2=192.168.56.138:2888:3888;2181
server.3=192.168.56.139:2888:3888;2181
# 端口说明:
# 2181:对Client端提供服务的端口(可自定义)
# 2888:选举Leader的端口(可自定义)
# 3888:集群内部通信端口(可自定义)
4、启动 ZK 集群
zk-1 部署于 kafka-1 服务器上
zk-2 部署于 kafka-2 服务器上
zk-3 部署于 kafka-3 服务器上
# zk-1
docker run -d \\
--restart=always \\
--name=zk-1 \\
--privileged=true \\
--net=host \\
-e ZOO_MY_ID=1 \\
-v /data/zookeeper/conf/zoo.cfg:/conf/zoo.cfg \\
-v /data/zookeeper/data:/data \\
-v /data/zookeeper/datalog:/datalog \\
-v /data/zookeeper/logs:/logs \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
zookeeper:3.7.1
# zk-2
docker run -d \\
--restart=always \\
--name zk-2 \\
--privileged=true \\
--net=host \\
-e ZOO_MY_ID=2 \\
-v /data/zookeeper/conf/zoo.cfg:/conf/zoo.cfg \\
-v /data/zookeeper/data:/data \\
-v /data/zookeeper/datalog:/datalog \\
-v /data/zookeeper/logs:/logs \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
zookeeper:3.7.1
# zk-3
docker run -d \\
--restart=always \\
--name zk-3 \\
--privileged=true \\
--net=host \\
-e ZOO_MY_ID=3 \\
-v /data/zookeeper/conf/zoo.cfg:/conf/zoo.cfg \\
-v /data/zookeeper/data:/data \\
-v /data/zookeeper/datalog:/datalog \\
-v /data/zookeeper/logs:/logs \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
zookeeper:3.7.1
5、查看集群选举情况
看到 leader 为 zk-2,只要其中某一台服务器挂了,剩余两者会进行 leader 选举。
[root@kafka-1 ~]# docker exec -it zk-1 bash
root@kafka-1:/apache-zookeeper-3.7.1-bin# bin/zkServer.sh status
ZooKeeper JMX enabled by default
Using config: /conf/zoo.cfg
Client port found: 2181. Client address: localhost. Client SSL: false.
Mode: follower
[root@kafka-2 ~]# docker exec -it zk-2 bash
root@kafka-2:/apache-zookeeper-3.7.1-bin# bin/zkServer.sh status
ZooKeeper JMX enabled by default
Using config: /conf/zoo.cfg
Client port found: 2181. Client address: localhost. Client SSL: false.
Mode: leader
[root@kafka-3 ~]# docker exec -it zk-3 bash
root@kafka-3:/apache-zookeeper-3.7.1-bin# bin/zkServer.sh status
ZooKeeper JMX enabled by default
Using config: /conf/zoo.cfg
Client port found: 2181. Client address: localhost. Client SSL: false.
Mode: follower
至此,ZK 集群部署完毕!
2.6 Kafka 集群
1、pull 镜像
docker pull bitnami/kafka:3.1.1
2、运行容器
# kafka-1
docker run -d \\
--name=kafka-1 \\
--restart=always \\
--privileged=true \\
--net=host \\
-e KAFKA_BROKER_ID=1 \\
-e KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT="192.168.56.137:2181,192.168.56.138:2181,192.168.56.139:2181" \\
-e KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://192.168.56.137:9092 \\
-e KAFKA_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092 \\
-e ALLOW_PLAINTEXT_LISTENER=yes \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
-t bitnami/kafka:3.1.1
# kafka-2
docker run -d \\
--name=kafka-2 \\
--restart=always \\
--privileged=true \\
--net=host \\
-e KAFKA_BROKER_ID=2 \\
-e KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT="192.168.56.137:2181,192.168.56.138:2181,192.168.56.139:2181" \\
-e KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://192.168.56.138:9092 \\
-e KAFKA_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092 \\
-e ALLOW_PLAINTEXT_LISTENER=yes \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
-t bitnami/kafka:3.1.1
# kafka-3
docker run -d \\
--name=kafka-3 \\
--restart=always \\
--privileged=true \\
--net=host \\
-e KAFKA_BROKER_ID=3 \\
-e KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT="192.168.56.137:2181,192.168.56.138:2181,192.168.56.139:2181" \\
-e KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://192.168.56.139:9092 \\
-e KAFKA_LISTENERS=PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092 \\
-e ALLOW_PLAINTEXT_LISTENER=yes \\
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime \\
-t bitnami/kafka:3.1.1
3、安装 kafka-manager 管理工具
我们在 kibana 上部署
docker pull sheepkiller/kafka-manager:stable
运行容器
docker run -d \\
--name=kafka-manager \\
--restart=always \\
--privileged=true \\
-p 9000:9000 \\
-e ZK_HOSTS="192.168.56.137:2181,192.168.56.138:2181,192.168.56.139:2181" \\
sheepkiller/kafka-manager:stable
浏览器访问:http://192.168.56.136:9000/
创建 Kafka 集群节点,来查看当前集群状态:
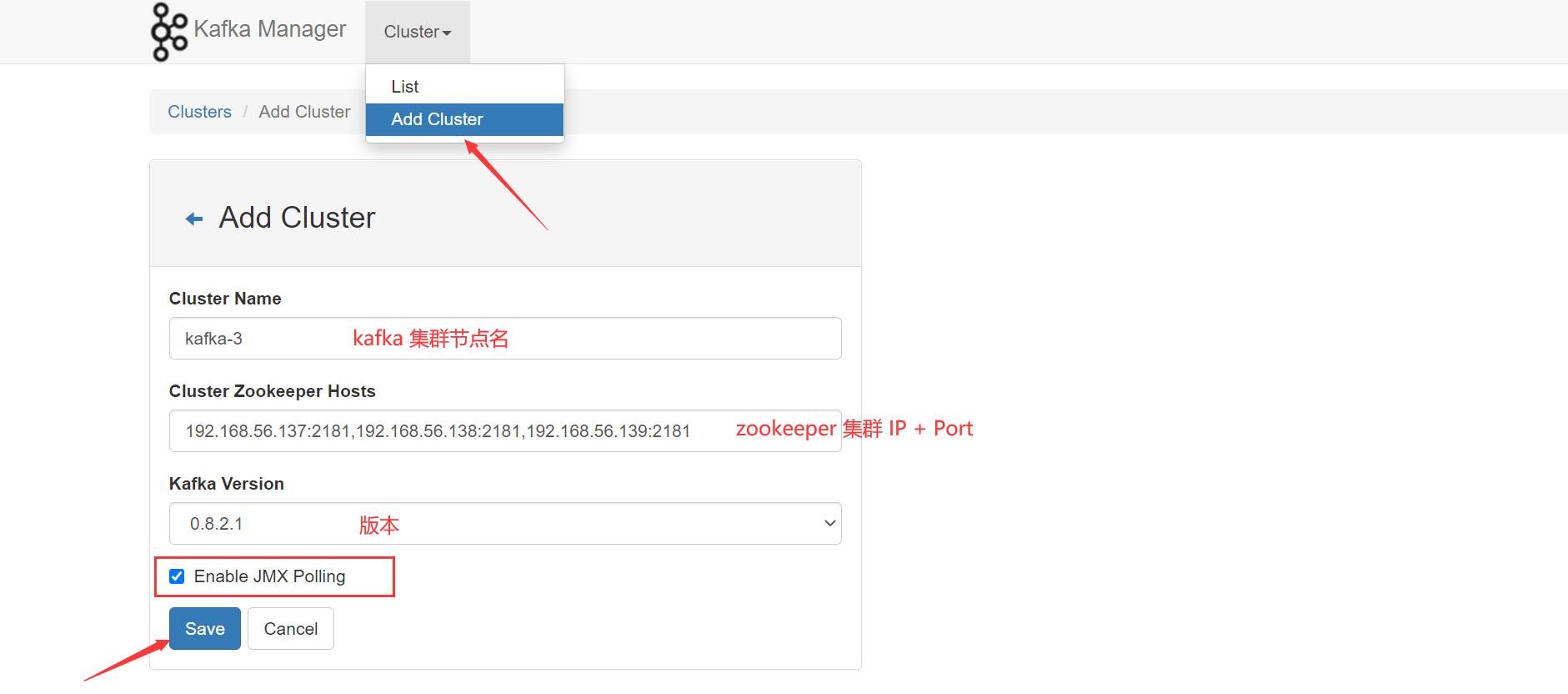
依次建立即可:
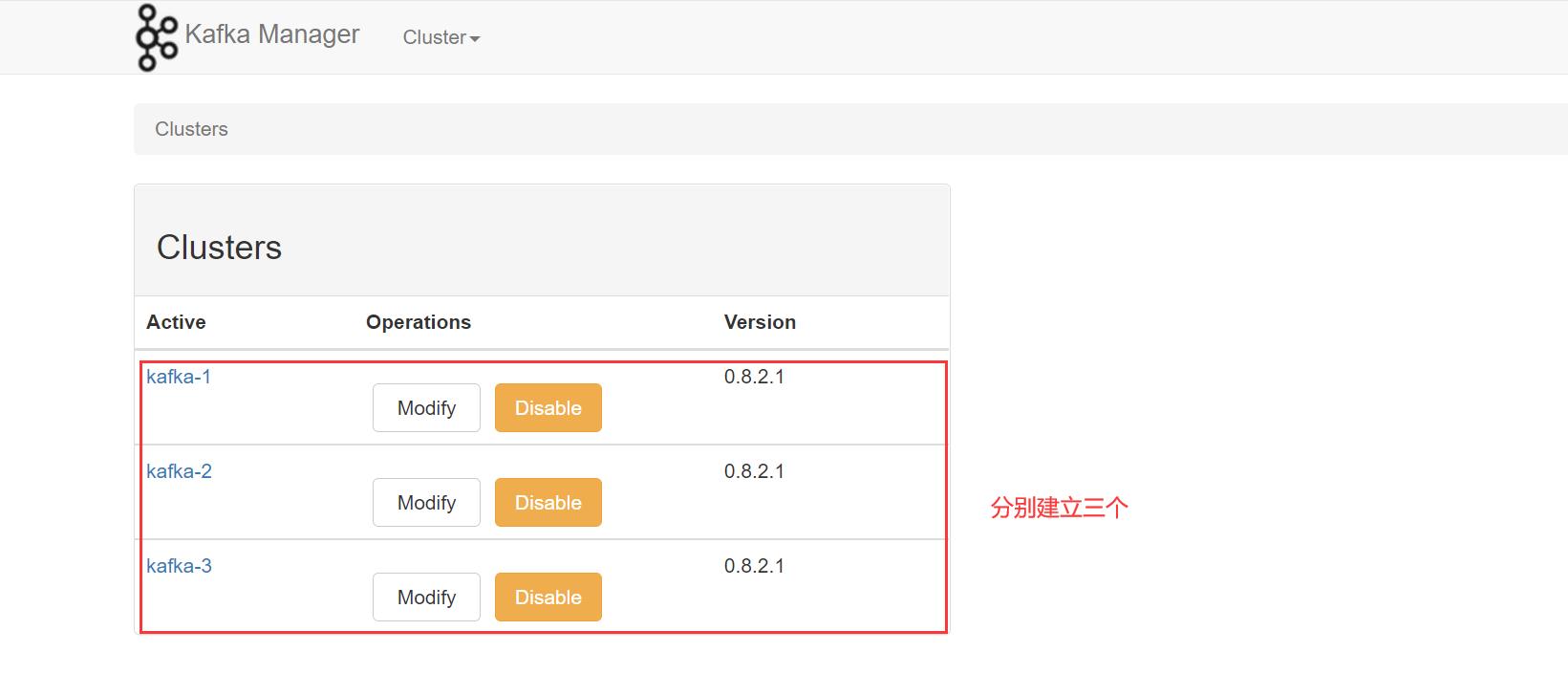
看看集群状态:
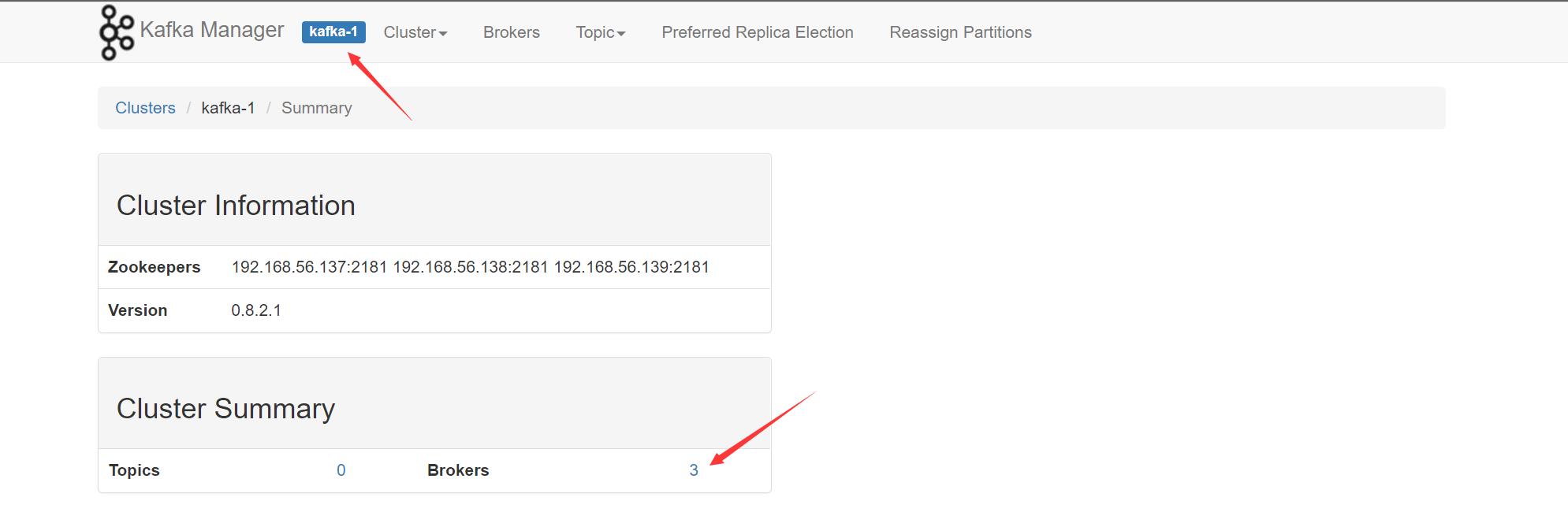
进入 Brokers 查看,每一个 Brokers 代表一个 Kafka 实例,这里显示为 3 ,所以我们的集群实例为三个:
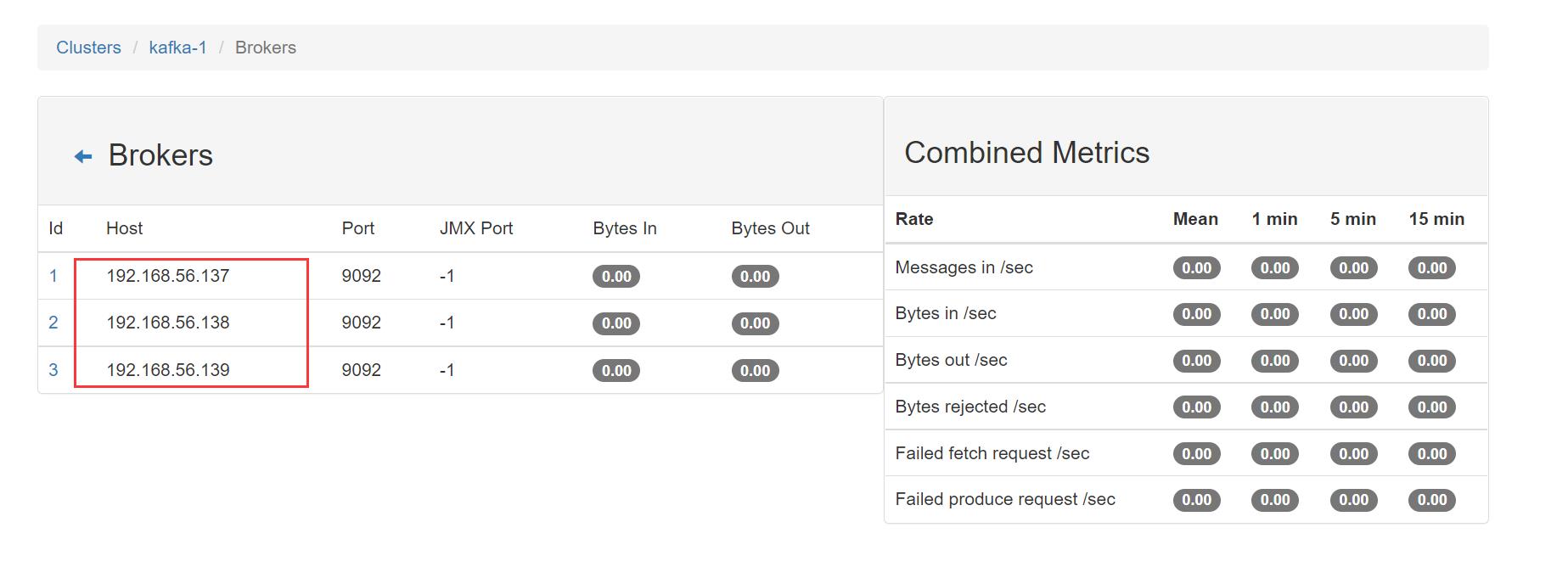
至此,Kafka集群部署完毕!
2.7 Filebeat 轻量级数据收集引擎
2.7.1 架构图
Filebeat 隶属于Beats,一款轻量级的数据收集引擎,那它如何工作于 ELK 集群中呢?
Filebeat 安装在要收集日志的应用服务器中,Filebeat收集到日志之后传输到kafka中,logstash通过kafka拿到日志,在由logstash传给后面的es,es将日志传给后面的kibana,最后通过kibana展示出来。

2.7.2 部署及应用
1、安装
# 在要收集的日志的服务器上部署该插件
tar xzf filebeat-6.8.23-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /data/
mv /data/filebeat-6.8.23-linux-x86_64/ /data/filebeat
2、配置
cd /data/filebeat/
cp filebeat.yml filebeat.yml.bak
cat filebeat.yml
#=========================== Filebeat inputs =============================
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
enabled: true
json.keys_under_root: true
json.add_error_key: true
json.message_key: log
paths:
- /data/nginx/logs/access.log
#============================= Kafka outputs =============================
output.kafka:
enabled: true
hosts: ["192.168.56.137:9092","192.168.56.138:9092","192.168.56.139:9092"]
topic: filebeat_test
运行 filebeat
# 前台启动
/data/filebeat/filebeat -e -c filebeat.yml
# 后台启动
nohup /data/filebeat/filebeat -e -c filebeat.yml &
3、查看 kafka 集群状态
可以看到新增了一个 Topics,说明 filebeat 采集的数据成功输出到了 Kafka 集群中了。
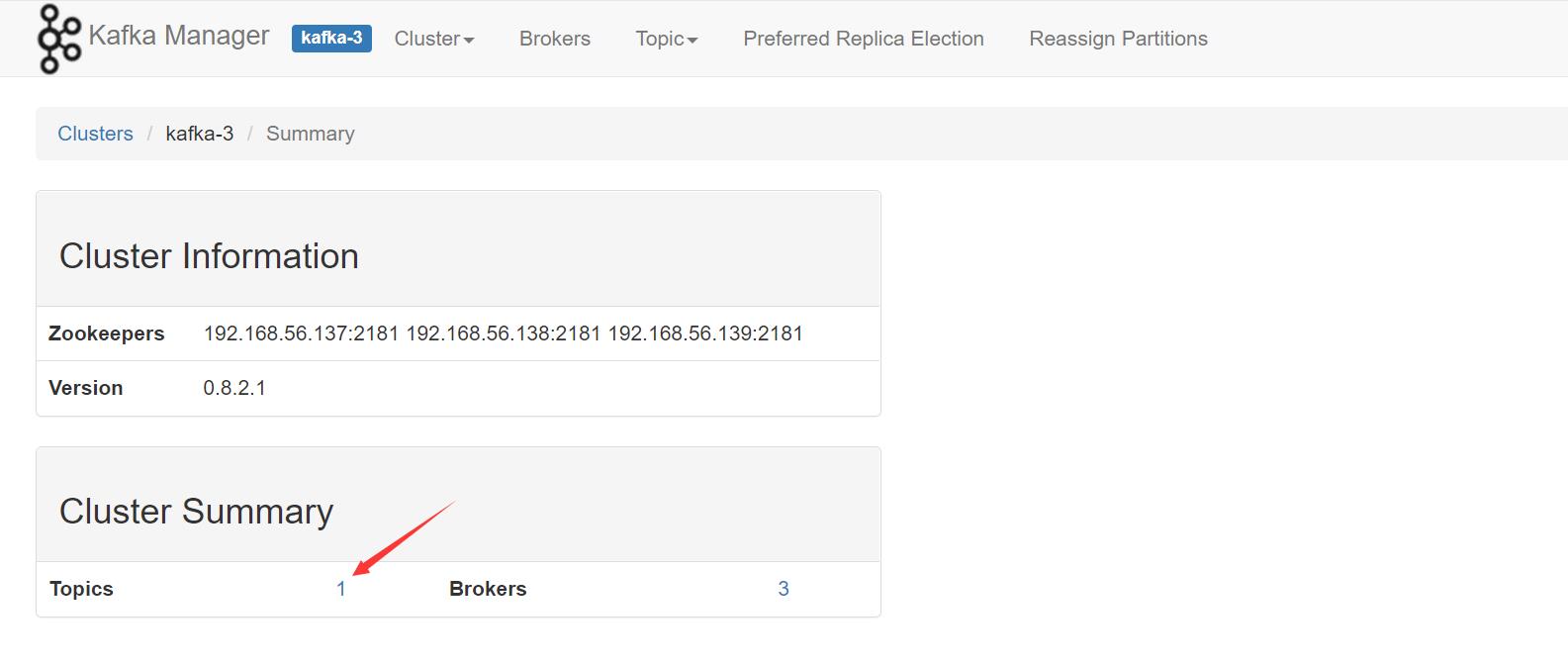
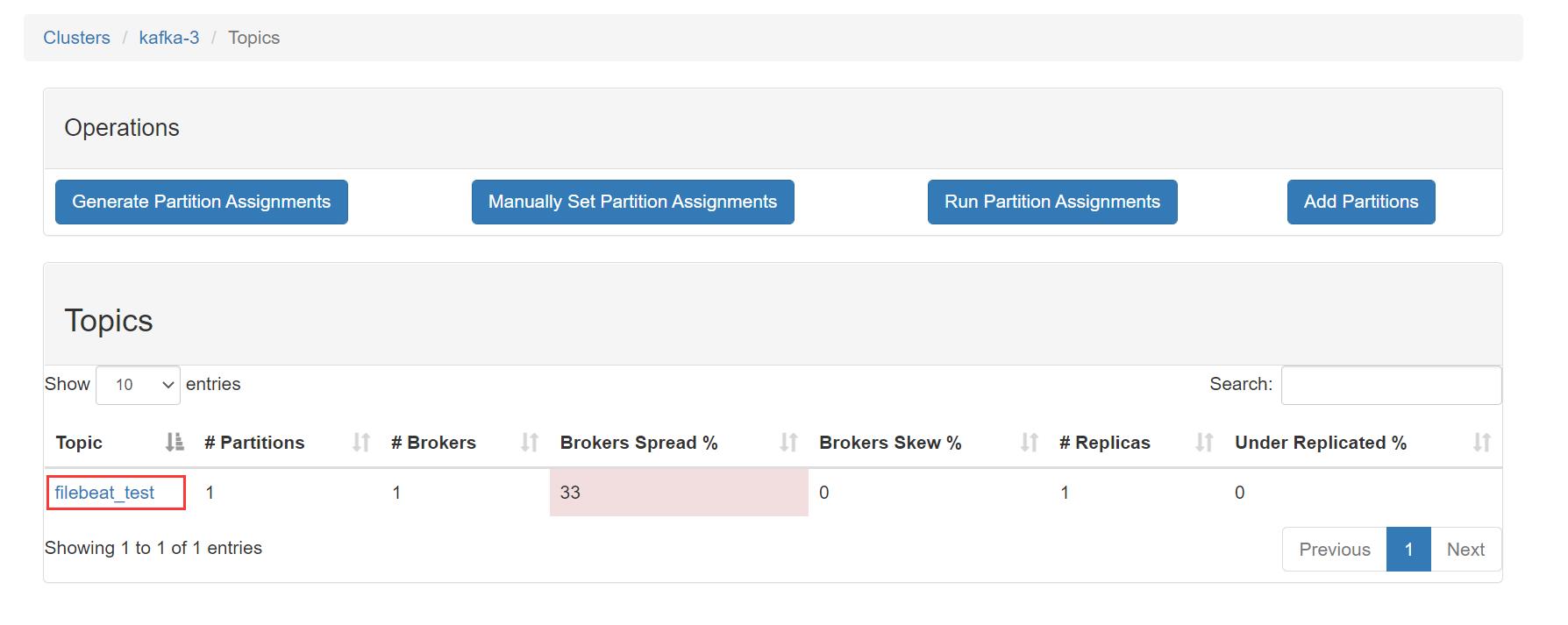
点击进去看看是否是我们上面定义的 Topic: filebeat_test
4、这个时候就需要消费者来消费我这条数据了
从 ELK 集群架构上看,消费者是我们的 ES 集群,那 ES 集群如何消费 Kafka 集群的消息呢?答案是通过 Logstash,为什么这里还要使用 logstash?原因是其具备 input —> filter —> output 的流功能,当然,filebeat 可以将数据直接发送到 ES 集群。
-
配置 logstash
input kafka type => "filebeat_test_log" codec => "json" topics => "filebeat_test" decorate_events => true bootstrap_servers => "192.168.56.137:9092, 192.168.56.138:9092, 192.168.56.139:9092" output elasticsearch hosts => ["192.168.56.133:9200","192.168.56.134:9200","192.168.56.135:9200"] index => ["%type-%+YYYY.MM.dd"] -
运行 logstash
/data/logstash/bin/logstash -f /data/logstash/config/conf.d/filebeat_test.conf -
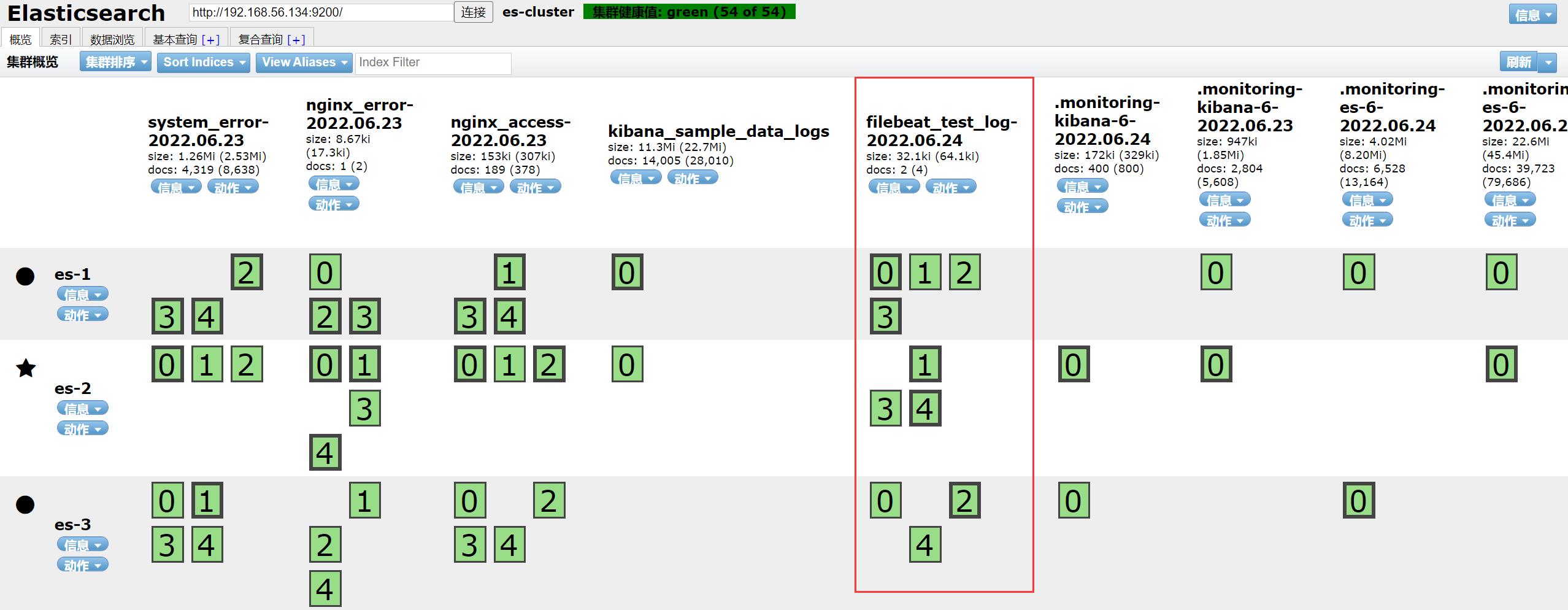
ES 集群查看是否收到了该消息
可看到,ES 集群已经成功消费了 Kafka 集群的消息了。
-
我们再去 Kibana 看看,进行相关检索

三、总结
其实你会发现,ELK 这一套日志解决方案就是一个完整的工程项目,前端 Kibana 展示、后端 ES 集群(做数据存储)、中间件 Kafka 做流量削峰和异步解耦等。整个搭建过程并不难,主要是搞清楚不同架构应用的场景,以及 ELK 的整个工作流程(原理)。至于上图架构中 Kibana 为什么要做负载均衡,主要是考虑到在高并发的情况下(这里的高并发指的是 Client 的高并发),比如公司有上百人同时访问 Kibana,那 Kibana 肯定是存在瓶颈的,可做多个 Kibana 实现负载均衡(其实就类似我们平时项目中前端项目做的负载均衡技术)。
FAQ
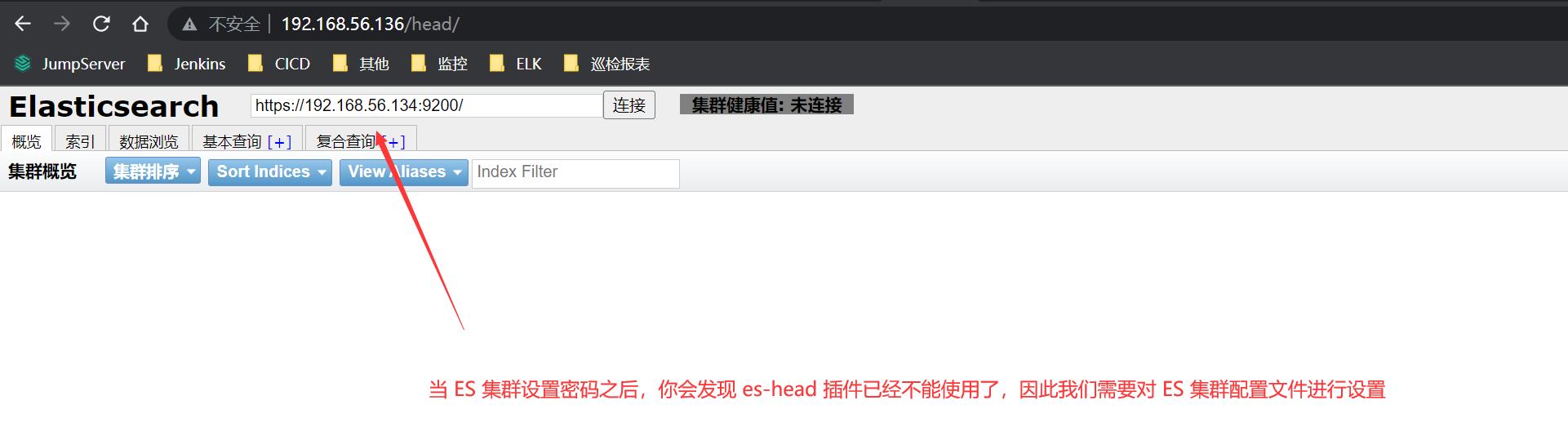
es-head 插件访问不了 ES 集群
1、详情如下图所示:
2、解决方案
修改 ES 集群配置文件:
...
...
# 解决跨域问题
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
# 新增以下内容
http.cors.allow-headers: Authorization,X-Requested-With,Content-Length,Content-Type
...
# 重启 ES 集群
docker restart es-1
docker restart es-2
docker restart es-3
3、es-head 插件访问
http://192.168.56.136:9100/?auth_user=elastic&auth_password=123456
# 说明:
# auth_user:你在ES集群设置的用户名(其实是内置用户)
# auth_password:你当时设置的内置用户名密码
Docker swarm 搭建docker高可用集群
项目名称:基于docker- swarm 搭建docker高可用集群
1、网络拓扑图

网络数据流图

2、项目环境
Docker 20.10.8,CentOS 7.6(7台 1核1G),Nginx 1.19.7,Prometheus2.29.1,Grafana8.1.2,Keepalived,NFS。
3、项目描述
实现一个高可用的负载均衡Web服务器集群,后端采用Swarm管理的Docker集群来提供Web服务,大量使用容器来完成Web服务的扩展性、高可用性,使用Prometheus对整个集群进行监控,保证业务正常进行。
4、项目步骤
1.规划设计整个集群的架构、网络拓扑,安装7台CentOS 7.6的系统,按照规划配置好每台linux的IP,准备好Docker环境,搭建swarm集群
1、创建swarm集群
[root@centos-7 ~]# docker swarm init --advertise-addr 192.168.0.101
Swarm initialized: current node (wxfmm8k75qxwey2fufk204ivv) is now a manager.
To add a worker to this swarm, run the following command:
# 这就是添加节点的方式(要保存初始化后token,因为在节点加入时要使用token作为通讯的密钥
docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-3sqv9hho99m8z686tspko5c5dn3pmk6h02p5zscduh3eq2nkm5-1h1g2xndxeit74aa2vy5304jo 192.168.0.101:2377
To add a manager to this swarm, run 'docker swarm join-token manager' and follow the instructions
2、添加节点主机到Swarm集群(如果想要将其他更多的节点添加到这个swarm集群中,添加方法与其一致)
[root@work_3 ~]# docker swarm join --token SWMTKN-1-3sqv9hho99m8z686tspko5c5dn3pmk6h02p5zscduh3eq2nkm5-1h1g2xndxeit74aa2vy5304jo 192.168.0.101:2377
This node joined a swarm as a worker.
2、使用Volume(挂载目录到NFS服务器下)来提供Web服务,达到所有容器都使用相同的数据;
1、共享文件,编辑/etc/exports文件,写好具体的共享的目录和权限
[root@u-nfs ~]# vim /etc/exports
/web 192.168.0.0/24(rw,all_squash,sync)
2、根据编辑的文件建立web文件
3、刷新输出文件的列表:
exportfs -rv
4、在manage机器上创建服务(注意swarm集群的机器也需要安装nfs服务):
docker service create -d --name nfs-web --mount 'type=volume,source=nfsvolume,target=/usr/share/nginx/html,volume-driver=local,volume-opt=type=nfs,volume-opt=device=:/web,"volume-opt=o=addr=192.168.0.100,rw,nfsvers=4,async"' --replicas 10 -p 8089:80 nginx:latest
3、编译安装Nginx,编写安装脚本,使用Nginx做负载均衡
负载均衡: 将用户的访问请求均衡的分散到后端的真正提供服务的机器上
负载均衡器: 实现负载均衡功能的一个机器
1、编写脚本
#!/bin/bash
#解决软件的依赖关系,需要安装的软件包
yum -y install zlib zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel pcre pcre-devel gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake make psmisc net-tools lsof vim wget
#新建luogan用户和组
id sanchuang || useradd sanchuang -s /sbin/nologin
#下载nginx软件
mkdir /sanchuang99 -p
cd /sanchuang99
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.21.1.tar.gz
#解压软件
tar xf nginx-1.21.1.tar.gz
#进入解压后的文件夹
cd nginx-1.21.1
#编译前的配置
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/scsanchuang99 --user=sanchuang --group=sanchuang --with-http_ssl_module --with-threads --with-http_v2_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-stream
#如果上面的编译前的配置失败,直接退出脚本
if (( $? != 0));then
exit
fi
#编译
make -j 2
#编译安装
make install
#修改PATH变量
echo "PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/scsanchuang99/sbin" >>/root/.bashrc
#执行修改了环境变量的脚本
source /root/.bashrc
#firewalld and selinux
#stop firewall和设置下次开机不启动firewalld
service firewalld stop
systemctl disable firewalld
#临时停止selinux和永久停止selinux
setenforce 0
sed -i '/^SELINUX=/ s/enforcing/disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
#开机启动
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
echo "/usr/local/scsanchuang99/sbin/nginx" >>/etc/rc.local
2、运行安装脚本
[root@load-balancer ~]# bash onekey_install_shediao_nginx_v10.sh
切换用户,加载修改了的PATH变量
[root@load-balancer ~]# su - root
3、配置Nginx的负载均衡功能
cd /usr/local/scsanchuang99/ 进入nginx编译安装指定的目录
[root@load-balancer scsanchuang99]# ls
client_body_temp conf fastcgi_temp html logs proxy_temp sbin scgi_temp uwsgi_temp
cd conf/ 进入配置文件的命令
[root@load-balancer conf]# ls
fastcgi.conf fastcgi_params.default mime.types nginx.conf.default uwsgi_params
fastcgi.conf.default koi-utf mime.types.default scgi_params uwsgi_params.default
fastcgi_params koi-win nginx.conf
scgi_params.default win-utf
nginx.conf 是nginx的配置文件
编辑配置文件:
[root@load-balancer conf]# vim nginx.conf
http{
upstream xuweb { #定义一个负载均衡器名字叫xuweb
server 192.168.0.101:8089;
server 192.168.0.102:8089;
server 192.168.0.97:8089;
}
server {
listen 80; #监听80端口
server_name www.sc.com; #为www.sc.com 域名服务
location / {
proxy_pass http://scweb ; #调用负载均衡器
}
.....省略很多配置
}
nginx -s reload 重新加载配置文件–》相当于重启了nginx服务
4、Keepalived的双vip实现高可用
单点: 整个架构中,只有一台服务器的地方
单点故障: 如果某台服务器down机会导致整个集群出现异常
如何解决单点故障,防止单点故障–》高可用
高可用: 一台出现问题,另外的机器可以顶替,继续保障整个集群的正常运转.
keepalived 是实现高可用的软件
1、安装和配置
在两台安装Nginx的负载k均衡器的基础上安装Keepalived
yum install keepalived -y
2.配置keepalived.conf文件,添加vip和相关信息
cd /etc/keepalived/
vim keepalived.conf
配置文件详细解释:
vrrp_instance VI_1 { 启动一个vrrp的实例 VI_1 实例名,可以自定义
state MASTER --》角色是master
interface ens33 --》在哪个接口上监听vrrp协议,同时绑定vip到那个接口
virtual_router_id 105 --》虚拟路由id(帮派) 0~255范围
priority 120 ---》优先级 0~255
advert_int 1 --》advert interval 宣告消息 时间间隔 1秒
authentication { 认证
auth_type PASS 认证的类型是密码认证 password
auth_pass 11112222 具体的密码,可以自己修改
}
virtual_ipaddress { --》vip的配置,vip可以是多个ip
192.168.200.16
192.168.200.17
192.168.200.18
}
}
cent-nginx-bl的详细配置:
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
acassen@firewall.loc
failover@firewall.loc
sysadmin@firewall.loc
}
notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc
smtp_server 192.168.200.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL
vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr
#vrrp_strict
vrrp_garp_interval 0
vrrp_gna_interval 0
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface ens33
virtual_router_id 108
priority 200
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.0.108
}
}
vrrp_instance VI_2 {
state BACKUP
interface ens33
virtual_router_id 109
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.0.109
}
}
cent-keepalived-bl的详细配置:
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
acassen@firewall.loc
failover@firewall.loc
sysadmin@firewall.loc
}
notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc
smtp_server 192.168.200.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL
vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr
#vrrp_strict
vrrp_garp_interval 0
vrrp_gna_interval 0
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens33
virtual_router_id 108
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.0.108
}
}
vrrp_instance VI_2 {
state MASTER
interface ens33
virtual_router_id 109
priority 200
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.0.109
}
}
5、安装prometheus,在被监控的机器上安装exporter,实现监控功能
1、安装Prometheus
root@prometheus ~]# rz
[root@prometheus ~]# ls
prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@prometheus ~]#
[root@prometheus ~]# mkdir /prometheus
[root@prometheus ~]# mv prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz /prometheus/
#临时添加环境变量
[root@prometheus prometheus]# PATH=$PATH:/prometheus/prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64
[root@prometheus prometheus]# which prometheus
/prometheus/prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64/prometheus
[root@prometheus prometheus]#
永久添加安装路径到PATH环境变量里
[root@prometheus ~]# vim /root/.bashrc
PATH=$PATH:/prometheus/prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64
prometheus 启动程序
prometheus.yml 配置文件
启动prometheus
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]# ./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.yml
level=info ts=2021-08-25T09:23:53.236Z caller=main.go:390 msg="No time or size retention was set so using the default time retention" duration=15d
level=info ts=2021-08-25T09:23:53.237Z caller=main.go:428 msg="Starting Prometheus" version="(version=2.29.1, branch=HEAD, revision=dcb07e8eac34b5ea37cd229545000b857f1c1637)"
level=info ts=2021-08-25T09:23:53.237Z caller=main.go:433 build_context="(go=go1.16.7, user=root@364730518a4e, date=20210811-14:48:27)"
在后台启动prometheus
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]# nohup ./prometheus --config.file=/prometheus/prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64/prometheus.yml &
2、在被监控的服务器上安装exporter
exporter : 是prometheus的客户端程序,需要安装到被监控的服务器上。exporter是一个程序,需要去定制,但是prometheus平台给我们开发了很多通用的或者定制的exporter
exporter会到客户机(被监控的服务器上)收集指定的指标数据,例如:cpu的使用率,内存的使用率,磁盘的使用情况,网络的带宽使用情况等等数据
上传下载的node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz到被监控的服务器
[root@cent7-manage~]# rz
[root@cent7-manage ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg getting-started-master
echo.sh getting-started-master.zip node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz sc-ubuntu2.tar
[root@cent7-manage~]# mkdir /exporter
[root@cent7-manage~]# mv node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz /exporter/
[root@cent7-manage ~]# cd /exporter/
[root@cent7-manage exporter]#
解压软件
[root@cent7-manage exporter]# tar xf node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@cent7-manage exporter]# ls
node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64 node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@cent7-manage exporter]# cd node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# ls
LICENSE node_exporter NOTICE
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]#
执行软件
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# ./node_exporter --help
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# nohup ./node_exporter --web.listen-address="0.0.0.0:9100" &
[1] 96546
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# nohup: 忽略输入并把输出追加到'nohup.out'
查看进程
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# ps aux|grep node
root 96546 0.1 0.2 716440 10996 pts/1 Sl 10:38 0:00 ./node_exporter --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9100
root 96551 0.0 0.0 12348 1144 pts/1 S+ 10:38 0:00 grep --color=auto node
修改PATH环境变量
#临时修改
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# PATH=/exporter/node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64:$PATH
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# which node_exporter
/exporter/node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64/node_exporter
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]#
#永久修改
[root@cent7-manage node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64]# vim /root/.bashrc
PATH=/exporter/node_exporter-1.2.2.linux-amd64:$PATH 在末尾添加
server去访问这个网址获取node上的metrics
http://192.168.0.101:9100/metrics
3.添加被监控服务器到prometheus server里
在server上操作
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]# cd /prometheus/prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]#
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]# vim prometheus.yml
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
#添加需要监控的服务器的信息
- job_name: "swarm-manager"
static_configs:
- targets: ["192.168.0.101:9100"]
重启prometheus服务,因为没有专门的重启脚本,需要手工完成
先杀死原来的进程,然后再启动新的进程,启动新的进程会重启加载配置文件
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]# ps aux|grep prome
root 2160 0.1 6.3 912304 63172 pts/2 Sl 10:06 0:07 ./prometheus --config.file=/prometheus/prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64/prometheus.yml
root 2265 0.0 0.0 112824 980 pts/2 S+ 11:14 0:00 grep --color=auto prome
kill -9 2160 杀死进程
重新启动程序
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]# nohup prometheus --config.file=/prometheus/prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64/ometheus.yml &
[1] 2276
[root@prometheus prometheus-2.29.1.linux-amd64]# nohup: 忽略输入并把输出追加到"nohup.out"
6、添加Grafana,美观、强大的可视化监控指标展示工具
grafana 是一款采用 go
语言编写的开源应用,主要用于大规模指标数据的可视化展现,是网络架构和应用分析中最流行的时序数据展示工具,目前已经支持绝大部分常用的时序数据库。最好的参考资料就是官网(http://docs.grafana.org/)
1、安装
[root@u-nfs yum.repos.d]# vim grafana.repo
[root@u-nfs yum.repos.d]# cat grafana.repo
[grafana]
name=grafana
baseurl=https://packages.grafana.com/enterprise/rpm
repo_gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.grafana.com/gpg.key
sslverify=1
sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
[root@u-nfs yum.repos.d]# yum install grafana -y
启动:
[root@u-nfs yum.repos.d]# systemctl start grafana-server
查看进程
[root@u-nfs yum.repos.d]# ps aux|grep grafana
root 42897 0.0 0.0 169308 756 ? Ss 11:31 0:00 gpg-agent --homedir /var/cache/dnf/grafana-ee12c6ab2813e349/pubring --use-standard-socket --daemon
grafana 43438 3.6 4.3 1229004 80164 ? Ssl 11:34 0:01 /usr/sbin/grafana-server --config=/etc/grafana/grafana.ini--pidfile=/var/run/grafana/grafana-server.pid --packaging=rpm cfg:default.paths.logs=/var/log/grafana cfg:default.paths.data=/var/lib/grafana cfg:default.paths.plugins=/var/lib/grafana/plugins cfg:default.paths.provisioning=/etc/grafana/provisioning
root 43490 0.0 0.0 12324 1060 pts/1 S+ 11:34 0:00 grep --color=auto grafana
查看端口
ss -anplut|grep grafana
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:3000 *:* users:(("grafana-server",pid=43438,fd=8))
到web 浏览器里访问
http://192.168.0.100:3000
web登陆
默认账号和密码都是admin
添加监控项(PromQL里查询的指标)–》grafana帮助我们去出图展示 --》自己去添加监控项遇到:
1.对很多监控项的指标具体对应那个PromQL 语句我们不熟悉
2.如果监控的指标过多,操作笔记复杂
grafana有模板,模板里包含很多的重要的监控项,我们直接导入就可以了 grafana的模板,本质上是一个json格式的文件
5、 项目心得
1.提前规划好整个集群的架构,可以提高项目开展时效率,可以让我们更加清晰;
2.对本地hosts文件进行DNS集群域名解析记录,效果并不明显,考虑在前面加一个负载均衡器,实现论询效果;
3.通过整个项目更加深刻的理解了Docker的相关技术,使用Docker的集群解决方案比传统的集群解决方案更加快捷方便,Docker内部的高可用和负载均衡也非常不错;
4.通过实验锻炼了自己细心和trouble shooting的能力。
以上是关于基于 Docker 的 ELK 高可用集群架构的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章