Solidity 基础知识
Posted ”PANDA
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Solidity 基础知识相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Solidity 基础知识
官网:Solidity
版本设置
// SPDX-License-Identifier:MIT 表示身份协议
// ^0.8.7 表示当前代码支持 0.8.7 及以后 solidity 版本
// >=0.8.7 <0.8.12 表示支持该范围的版本
pragma solidity 0.8.7;
基本数据类型
// 基础数据类型:boolean uint(无符号整数) int address bytes
bool sutFlag = true;
// uint 存储空间大小可以设置 最少设置 8(1 bit 占 8 位,以 2 的指数倍设置) 默认是 256 一般都显式定义出来 如果不赋值默认为 0
uint256 public studentNum = 123;
// bytes 一般是 0x 开头接一些随机的数字字母,这里存的字符串 xiao,会自动转成 bytes,最大空间是 32
bytes32 stuName1 = "xiao";
// string 只能用来存字符串
string stuName = "panda";
函数和变量的四种可见标识符
- public
public 外部和内部可见(为存储/状态变量创建一个getter 函数) - private
仅在当前合约中可见 - external
仅在外部可见(仅适用于函数) - 即只能被消息调用(通过this.func) - internal
只在内部可见
不消耗 gas 的两种关键字
- view:标识函数代表只读,不允许在当前函数中修改任何状态
- pure:不允许修改状态,同时不允许读取区块链数据
注意:如果一个要改变区块链状态的函数调用了 view 或者 pure 函数,还是会消耗 gas。
结构体
// 定义
struct People
uint256 num;
string name;
// 使用
People public person = People(myNum: 2, name: "panda");
数组
People[] public persons;
function addPeople(string memory _name, uint256 _num) public
// 两种创建数组的方式
persons.push(People(_num, _name));
People memory person = People(myNum: 2, name: "panda");
persons.push(person);
// 映射
habbitMap[_name] = _num;
映射
mapping(string => uint256) public habbitMap;
EVM 存储
- Stack:栈内存存储
- Memory:变量只存在于临时的,可以再次赋值,且仅用于数组,结构体,映射对象(string 是字节数组)
- Storage:即使在执行的函数外,也存在变量
- Calldata:调用数据,变量只存在于临时的,当变量使用 calldata 定义时,变量不能再次赋值
- Code
- Logs
solidity笔记1(基础部分)
以太坊Solidity是一种面向智能合约的高级语言,其语法与JavaScript类似。solidity是用于生成在EVM上执行的机器级代码的工具。solidity编译器获取高级代码并将其分解为更简单的指令。Solidity代码封装在Contracts中。
因为之前实验课程已经完成了相关内容,所以主要整理一部分个人觉得比较难以理解和重要的部分
1.solidity基础操作整理
1.1.solidity的四种可见度
public:公共函数任何人都可以调用该函数,包括DApp的使用者。
private:只有合约本身可以调用该函数(在另一个函数中)。
internal:只有这份合同以及由此产生的所有合同才能称之为合同。
external:只有外部可以调用该函数,而合约内部不能调用。
1.2.solidity的三种修饰符
view: 可以自由调用,因为它只是“查看”区块链的状态而不改变它(查看)
pure: 也可以自由调用,既不读取也不写入区块链
payable:常常用于将代币发送给合约地址。
2.函数结构
一个solidity的函数应有以下部分组成
function
你的函数名字(类型1 名字,类型2 名字,。。。,类型n 名字) 如果没有就什么都不填即可
可见度/访问权限,即public/private/internal/external 如果不写则系统默认为public并且警告
修饰符,即view/pure/payable 如果需要花费gas则不写
returns(类型1 名字,类型2 名字,。。。,类型n 名字) 如果有的话
pragma solidity ^0.4.0;
contract helloworld
function stringtest(string inputstr) public view returns(string)
return inputstr;
6.函数
1.函数重载是指函数命名相同,但需要满足以下两个条件之一
a.函数传入参数类型不同
b.函数传入参数数量不同
2.如果函数多个参数都匹配,那么会报错
3.address因为实际存储的也是uint160
pragma solidity ^0.4.0;
contract funtest
/*function fun0()
function fun0()
*/
uint public test= 0;
function fun1(uint num1,uint num2)
test = 10;
function fun1(uint num1)
test = 20;
function fun2(uint a)
test = 100;
function fun2(string a)
test = 200;
function fun3(address a)
test=1000;
function fun3(uint160 a)
test=2000;
function fun4(uint8 a)
test=10000;
function fun4(uint16 a)
test=20000;
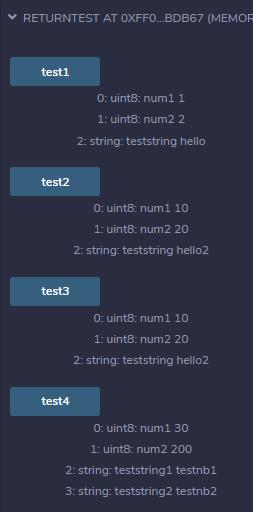
function fun1test() public view returns(uint)
fun1(1,2);
return test;
function fun2test() public view returns(uint)
fun2('asdasd');
return test;
function fun3test() public view returns(uint)
fun3(0x2e805eC48BdFBc458e7446058F94a315896A1cF6);
//仅使用address类型,可以运行并运行address参数的重载函数
return test;
//function fun3test2() public view returns(uint160)
//uint160 如果转化成uint160类型并运行,那么报错
//temp=uint160(0x2e805eC48BdFBc458e7446058F94a315896A1cF6);
//fun3(temp);
//return temp;
//
function fun4test() public view returns(uint)
fun4(256);
return test;
function reset() public
test = 0;
运行结果
3.数据类型
3.1bool、int、uint 、bytes、bytes1-bytes32
//布尔类型 bool 数据操作:逻辑与、逻辑或、逻辑非 ||、 && 、!
int num1=100;
int num2=200;
//整型 int=int256 uint=uint256 数据操作:加减乘除求余、求平方 +-*/%、**
return a**b;
//计算a的b次方
//位运算:按位与、按位或、按位取反、按位异或、左移、右移 &、|、~、^、<<、>>
uint8 a=3; uint8 b=4
return a|b;
//按位或,结果为7
//整型字面量:在solidity里面运算是计算出结果再赋值
uint num=1/2*1000;
return num;
//返回500
//字节(数组)类型:bytes1(byte)、bytes2...bytes32,长度固定且内部数据不可修改
//属性:length 可以进行比较,位运算
bytes9 name=0xe69d8ee79fa5e681a9;
byte num=0x7a;
return num.length;
//返回1
return name[index];
//按照index获得字节数组的值
3.2 动态字节数组:bytes num=new bytes()
bytes public num=new bytes(2);//创建动态字节数组
num[0]=0x12;
num[1]=0x34;
//初始化数组
return num.length;
//获取数组长度
num.length=5;
//修改数组长度
num.push(0x56);
//push方法在数组末尾追加数据
3.3 字符串类型
string name1="方晰雨
3.4 数组
3.4.1 固定数组
//固定数组初始化
uint[5] arr=[1,2,3,4,5];
//获取数组元素并修改
arr[1]=200;
3.4.2 可变数组
// 可变数组初始化
uint[] grade=[1,2,3,4,5];
//获取可变数组元素并修改
grade[0]=100;
grade[1]=200;
4.1 地址 address
address 在存储上和uint160一样,且二者可以互相转换,地址之间也可以进行比较大小
pragma solidity ^0.4.0;
contract whatisaddress
//0x75e453B2039c8A168b8Dab1AA97F4735618559De
address account1;
address account2 = 0x75e453B2039c8A168b8Dab1AA97F4735618559De;
function showaddress1() public view returns(address)
return account1; //可以看到未赋值时,参数为0
function showaddress2() public view returns(uint160)
return uint160(account2);//说明可以转化为uint160类型
function typechange(uint160 num) public view returns(address)
return address(num);//可以互相转换
//0x76E67229eaE13967955cb972658ca33bAa36b696
address account3 = 0x76E67229eaE13967955cb972658ca33bAa36b696;
function largetest() public view returns(bool)
return account3>account1;
4.2.转账操作与余额获取
1.可以通过地址.balance获取某个地址的余额
2.this指的是当前合约的地址,如此处就是paytest合约的地址
3.转账可以通过remix图形界面来进行转账数目的改变
4.对其他账户的转账需要使用账户名称.transfer(msg.value)或者账户名称.transfer(数量 单位,如1 ether)如果在输入value的同时又写的是数量 单位,那么多余的value就自动转账到合约地址里去
5.如果对当前合约使用transfer转账this.transfer(msg.value)则必须需要一个回滚函数。
6…如果函数含有payable而函数里面没有要求给某个账户转账的话,则会默认转账到合约当中
7.send和transfer的区别是,前者是底层函数,返回bool值;后者会直接在调用时报错。具体体现在如果转账金额为0是,send正常运行但是返回false 现在尝试了之后发现即使转账金额0,两者均都不报错,返回的为true,见测试5
contract paytest
function payabletest() payable
function getbalance(address account) public view returns(uint)
return account.balance;
function thistest() public view returns(address)
return this;
function transfertest1() payable public returns(uint)
address account1=0xeb46e45709DE0b10AECa4A9C9D1800beB6a13C6C;//账户随意
account1.transfer(msg.value);
return account1.balance;
function transfertest2() payable public returns(uint)
this.transfer(msg.value);
return this.balance;
function () payable
运行结果
1.先得到this的地址,再讲this的地址复制进去查看,可以知道此时合约的余额为0

2.修改remix界面中的value值然后点击我们payabletest,再调用之后就可以发现余额发生了变化
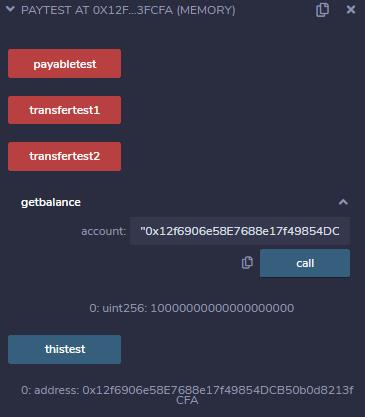
3.原本0xeb46e45709DE0b10AECa4A9C9D1800beB6a13C6C地址的余额是

PS.虽然显示是这个,但实际上是100eth,但这些先不追究
输入2之后点击transfertest1可以看到余额发生变化
4.转账8个,但是只接受4个,剩下的都到合约地址去了
5.value设置为0
调用sendtest,返回值为true
调用transfertest2,正常运行没有报错
5.mapping映射
1.定义映射mapping(类型1 => 类型2) 映射名称
contract mappingtest
mapping(address => uint) ATU;
mapping(uint => string) UTS;
uint sum=0;
function test(string teststring)
address account=msg.sender;
sum++;
ATU[account]= sum;
UTS[sum]= teststring;
function ATUtest() public view returns(uint)
address account=msg.sender;
return ATU[account];
function UTStest() public view returns(string)
return UTS[sum];

6.简单继承
1.合约通过is来继承上一个合约可以继承的函数,参数等
2.合约可以连续继承,即
b is a,b继承了a的元素
c is b,c继承b的元素同时继承了a的元素
3.子合约继承父合约的变量以及函数时,如果子合约定义了同名变量或者函数,那么子合约的变量/函数会覆盖继承过来的
4.合约如果一次性要继承多个合约的话,通过逗号连接,如果有重复的变量名或者函数名以最后一个出现的为准。当然子合约出现的话最终还是以自合约为准
代码
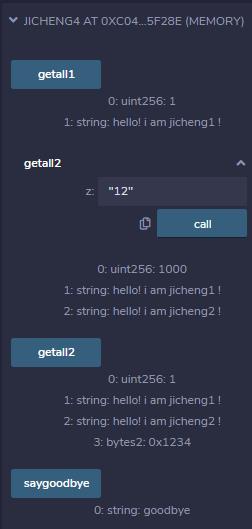
contract jicheng1
uint a=1;
string b='hello! i am jicheng1 !';
function saygoodbye() public view returns(string)
return 'goodbye';
contract jicheng2 is jicheng1
function getall1() public view returns(uint,string )
return (a,b);
string c='hello! i am jicheng2 !';
bytes2 d=0x1234;
contract jicheng3 is jicheng2
function getall2() public view returns(uint,string,string,bytes2)
return (a,b,c,d);
contract jicheng4 is jicheng3
uint a=1000;
function getall2(uint a) public view returns(uint,string,string)
return (a,b,c);
运行结果
6.memory与storage
1.在solidity合约内部
函数外部声明的变量默认储存在storage里
函数内部声明的变量默认储存在memory里

7.结构体
代码示例
pragma solidity ^0.4.0;
contract structtest1
struct stu
uint id;
string name;
mapping(uint=>string) maptest; //mapping即使在结构体内,初始化时也是可以忽略的
function init1() public returns(uint,string)
stu memory student1= stu(1234,'stu1');
return (student1.id,student1.name); //初始化方法一
function init2() public returns(uint,string)
stu memory student2=stu(name:'stu2',id:5678);
return (student2.id,student2.name); //初始化方法二
stu tempstudent1; //只要是函数外面的都是storage
function mappingtest() public returns(uint,string)
stu memory student3=stu(name:'stu3',id:5678);
//student3.maptest[100]='mapstu3';
//直接赋值会报错,因为storage不能转化为memory
tempstudent1=student3;
//此时tempstudent1,student3使用的是统一指针,所以下面对tempstudent1修改就等于修改student3
tempstudent1.maptest[100]='how to map';
return (student3.id,tempstudent1.maptest[100]);
7.2结构体storage转storage
1.要是函数以结构体作为参数,那么函数修饰符必须有private/internal
2.storage可以接受storage的值,并且storage的改动影响其它storage
代码
contract STS //此例temp,student1均为storage
struct stu
uint id;
string name;
stu student1;
function structtest(stu storage temp) internal //传入storage结构体
student1=temp; //赋值
temp.id=2; //即使只是修改并未再次赋值,student1的id也会改变
function tets() public view returns(uint)
structtest(student1);
return (student1.id);
7.3结构体memory转storage
1.要是函数以结构体作为参数,那么函数修饰符必须有private/internal
2.storage可以接受memory的值
3.memory的改动不影响storage
4.storage的改动不影响memory
contract MTS
struct stu
uint id;
string name;
stu student1;
uint memorynum; //记录memory的值是否受storage影响
function structtest1(stu memory temp) internal
student1=temp; //storage可以接受memory的值,但是memory的改动不影响storage
temp.id=2; //改变memory的值,看看storage值是否随之改变
memorynum=temp.id; //如果student1随着temp改变,那么说明storage受memory影响
function structtest2(stu memory temp) internal
student1=temp;
student1.id=3;//改变storage的值,看看memory值是否随之改变
memorynum=temp.id; //如果temp随着student1改变,那么说明memory受storage影响
function test1() public returns(uint,uint)
stu memory temp=stu(1,'a');
structtest1(temp);
return (student1.id,memorynum);
function test2() public returns(uint,uint)
stu memory temp=stu(1,'a');
structtest2(temp);
return (student1.id,memorynum);
7.4.结构体storage转memory
1.要是函数以结构体作为参数,那么函数修饰符必须有private/internal
2.storage可以接受memory的值
3.memory的改动不影响storage
4.storage的改动不影响memory
代码
contract STM
struct stu
uint id;
string name;
stu student1=stu(1,'a');
uint memorynum; //记录memory的值是否受storage影响
function structtest1(stu storage temp) internal
stu memory student2=temp;
student2.id=2;//改变memory的值,看看storage值是否随之改变
memorynum=student2.id;
function structtest2(stu storage temp) internal
stu memory student2=temp;
temp.id=3;//改变storage的值,看看memory值是否随之改变
memorynum=student2.id;
function test1() public view returns(uint,uint)
structtest1(student1);
return (student1.id,memorynum);
function test2() public view returns(uint,uint)
structtest2(student1);
return (student1.id,memorynum);
7.5.结构体memory转memory
1.要是函数以结构体作为参数,那么函数修饰符必须有private/internal
2.在此处中看似不影响,但是solidity自我优化是的传入的memory转化为指针,然后连锁导致后面的也全部变为指针,相当于storage转storage了
代码
以上是关于Solidity 基础知识的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
