使用JavaScript写的汉诺塔小游戏
Posted Montai
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用JavaScript写的汉诺塔小游戏相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
汉诺塔有些,是将A柱子上的盘子,借助B柱子,移动到C柱子,移动过程中要求,小盘子,必须放在大盘子上面。
移动过程是采用递归调用的方式。
程序运行界面:如下图:
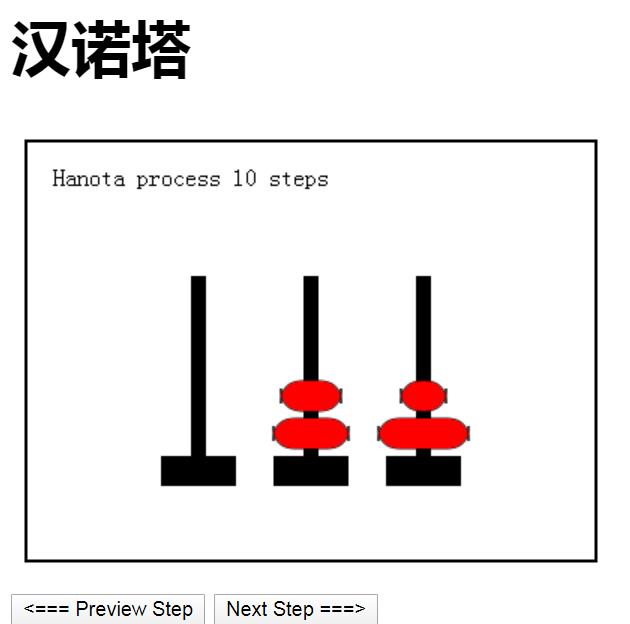
代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>汉诺塔</title> </head> <body> <h1> 汉诺塔 </h1> <canvas id = "canvas" width = 400, height = 300"> </canvas> <div> <button id = "ps" onclick=" pStep()"> <=== Preview Step </button> <button id = "ns" onclick= "nStep()"> Next Step ===> </button> </div> <script> function Stack(name) { this.dataStore = []; this.top = 0; this.name = name; this.push = push; this.pop = pop; this.peek = peek; this.clear = clear; this.length = length; this.get = get; this.drawDish = drawDish; this.myCloneobj= myCloneobj; } function push(ele) { this.dataStore[this.top ++] = ele; } function peek() { return this.dataStore[this.top - 1]; } function pop() { return this.dataStore[-- this.top]; } function clear() { this.top = 0; } function length() { return this.top; } function get(n){ return this.dataStore[n-1]; } function Block(size, location){ this.size = size; this.location = location; this.setLocation = setLocation; this.getSize = getSize; } function setLocation(location) { this.location = location; } function getSize() { return this.size; } function drawDish(){ var canvas = document.getElementById(\'canvas\'); if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas.getContext(\'2d\'); var width, height, layer, pole, xPos, yPos; //x基准点125, y基准点205 //画一个柱子 pole = this.name; n = this.length(); b = new Block(); console.log(" draw pole %d, length %d", pole , n); while (n>0){ b = this.get(n); var size = b.size; width = (size+2)*10; height = 20; layer = n - 1; xPos = 125 + pole * 75 - width/2; yPos = 205 - layer*25 - height/2 ; roundedRect(ctx, xPos, yPos, width, height, 15); ctx.fillStyle = "red"; ctx.fill(); n--; } } } function myCloneobj() { o = new Stack(this.name); console.log("clone pole %d", this.name); n = this.length(); var i=1; while (i <= n) { var bt = this.get(i); var size = bt.size; var location = bt.location; b = new Block(size, location); o.push(b); console.log("insert new b size %d, location %d", size, location); i=i+1; } return o; } //深复制对象方法 function cloneObj(obj) { //1 var newJsonObj = {}; newJsonObj = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)); //2 for (items in obj) { if (typeof obj[items] == "function" || typeof obj[items] == "undefined" || obj[items] instanceof RegExp) { newJsonObj[items] = obj[items]; } } //3 var newObj = new obj.constructor; for (items in newJsonObj) { newObj[items] = newJsonObj[items] } return newObj; } //深复制对象方法 var cloneObj2 = function (obj) { var newObj = {}; if (obj instanceof Array) { newObj = []; } for (var key in obj) { var val = obj[key]; //newObj[key] = typeof val === \'object\' ? arguments.callee(val) : val; //arguments.callee 在哪一个函数中运行,它就代表哪个函数, 一般用在匿名函数中。 newObj[key] = typeof val === \'object\' ? cloneObj2(val): val; } return newObj; }; function roundedRect(ctx, x, y, width, height, radius){ ctx.beginPath(); ctx.moveTo(x, y + radius); ctx.lineTo(x, y + height - radius); ctx.quadraticCurveTo(x, y + height, x + radius, y + height); ctx.lineTo(x + width - radius, y + height); ctx.quadraticCurveTo(x + width, y + height, x + width, y + height - radius); ctx.lineTo(x + width, y + radius); ctx.quadraticCurveTo(x + width, y, x + width - radius, y); ctx.lineTo(x + radius, y); ctx.quadraticCurveTo(x, y, x, y + radius); ctx.stroke(); } function drawRect(){ var canvas = document.getElementById(\'canvas\'); if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas.getContext(\'2d\'); ctx.fillStyle = "black"; //画边框 ctx.strokeRect(10, 10, 380, 280); //画左柱子 ctx.fillRect(120, 100, 10, 120); ctx.fillRect(100, 220, 50, 20); //画中柱子 ctx.fillRect(195, 100, 10, 120); ctx.fillRect(175, 220, 50, 20); //画右柱子 ctx.fillRect(270, 100, 10, 120); ctx.fillRect(250, 220, 50, 20); //ctx.clearRect(125, 25, 10, 200); //ctx.strokeRect(50, 50, 50, 50); } } function drawText(str) { var canvas = document.getElementById(\'canvas\'); if (canvas.getContext){ var ctx = canvas.getContext(\'2d\'); ctx.font = "16px serif"; ctx.fillText(str, 20, 40); } } function clear(){ var canvas = document.getElementById(\'canvas\'); if (canvas.getContext) { var ctx = canvas.getContext(\'2d\'); ctx.clearRect(20,20,360,260); ctx.fillStyle = "black"; } } function moveBlock(s1,s2){ if(s1.length() > 0){ if( (s2.length() == 0) || ((s2.length() > 0) && (s2.peek().size > s1.peek().size))){ b = s1.pop(); b.location = s2.name; s2.push(b); console.log("block %d move form %d to %d", b.size, s1.name, s2.name); //如果是简单变量,会直接创建并复制,如果是类变量,特别是有复杂结构的类变量,只是复制一个地址。 process.push(s1.name); process.push(s2.name); } } } function hanoi(n, a, b, c){ if (n == 1){ moveBlock(a, c); } else{ hanoi(n - 1, a, c, b); moveBlock(a, c); hanoi(n - 1, b, a, c); } } var step = 0; function draw(a, b, c) { var str = " Hanota process "; var s = step + 1; str = str.concat( s.toString(), " steps"); clear(); drawText(str); drawRect(); a.drawDish(); b.drawDish(); c.drawDish(); } var level = 4; var process = []; var leftPole = new Stack(0);//0 - leftPole var middlePole = new Stack(1);//1 - middlePole var rightPole = new Stack(2);//2 - rightPole var i = level; while (i>0){ var block = new Block(i, 0); leftPole.push(block); i--; } var leftPolebk = leftPole.myCloneobj(); var middlePolebk = middlePole.myCloneobj(); var rightPolebk = rightPole.myCloneobj(); draw(leftPolebk, middlePolebk, rightPolebk); hanoi(level, leftPole, middlePole, rightPole); var n = level; var maxStep = 1; while (n>0) { maxStep = maxStep*2; n=n-1; } maxStep = maxStep - 1; function pStep() { step = step - 1;//退回上一个节点 if (step >= 0){ var p1 = process[step*2]; var p2 = process[step*2+1]; console.log(" step %d move from %d to %d ",step, p2, p1); if (p2 == 0) var b = leftPolebk.pop(); else if (p2==1) b = middlePolebk.pop(); else if (p2==2) b = rightPolebk.pop(); else alert("wrong1"); if (p1 == 0) leftPolebk.push(b); else if (p1 == 1) middlePolebk.push(b); else if (p1 == 2) rightPolebk.push(b); else alert("wrong2"); draw(leftPolebk, middlePolebk, rightPolebk); } else { step=0 } } function nStep() { if (step <= maxStep){ var p1 = process[step*2]; var p2 = process[step*2+1]; console.log(" step %d move from %d to %d ",step, p1, p2); if (p1 == 0) var b = leftPolebk.pop(); else if (p1==1) b = middlePolebk.pop(); else if (p1==2) b = rightPolebk.pop(); else return; if (p2 == 0) leftPolebk.push(b); else if (p2 == 1) middlePolebk.push(b); else if (p2 == 2) rightPolebk.push(b); else return; draw(leftPolebk, middlePolebk, rightPolebk); step = step + 1;//指向下一个节点 } } </script> </body> </html>
代码说明:
1. Canvas画布,画塔,盘子和移动说明文字
2. 用Stack类,存放柱子信息,类是用堆栈来实现的, 类的名称属性,表示是哪一根柱子,左,中,还是右?
function Stack(name) {
this.dataStore = [];
this.top = 0;
this.name = name;
3. 用Block类,存放盘子信息,size表示盘子的大小,Location标明盘子在那个柱子上。
function Block(size, location){
this.size = size;
this.location = location;
this.setLocation = setLocation;
this.getSize = getSize;
}
4. 初始化时候,生成了3个盘子,3个柱子,并把3个盘子push到最左边的柱子上。
5. 调用画图函数,画出背景信息,三个柱子信息。
6. 调用递归函数,实现盘子移动
function hanoi(n, a, b, c){ if (n == 1){ moveBlock(a, c); } else{ hanoi(n - 1, a, c, b); moveBlock(a, c); hanoi(n - 1, b, a, c); } }
程序本身没有什么好说的,这里需要说明的是如何将移动的步骤保存下来。
尝试了三种方法:
1、在递归调用过程中,复制对象到一个数组中
2、在递归调用中,将程序停下来
3. 保存移动过程信息,到一个数组中
由于JavaScript对于对象的复制,对于Obj,只复制一个链接。这样导致的结果,复制下来的对象,在数组中都是一样的。
后来采用深度复制的方式,将obj中的obj,全部new来,但是这种方法,对于静态操作有效,在递归迭代过程中,第一层的还能复制,但是第二次以后的,都复制不了了。
在递归调用过程中,尝试alert, promote, sleep方法,暂停程序的执行。但是这种方法,只对异步的操作有效(你给我消息,我相应),但是对于这种代码执行迭代过程,是卡不住的。
最后只好采用一个数组,只记录移动盘子的原和目的地址信息。
7. 移动过程演示
因为递归调用过程,是不能暂停程序的。用了数组将盘子移动的过程录制下来。
在演示过程中,读取录制的移动过程数据,让操作过程再执行一遍。
这里克隆了三个对象,用于操作过程的演示。
var leftPolebk = leftPole.myCloneobj();
var middlePolebk = middlePole.myCloneobj();
var rightPolebk = rightPole.myCloneobj();
8.
以上是关于使用JavaScript写的汉诺塔小游戏的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章