1.Ajax简介
AJAX 不是新的编程语言,而是一种使用现有标准的新方法。
AJAX 最大的优点是在不重新加载整个页面的情况下,可以与服务器交换数据并更新部分网页内容。(这一特点给用户的感受是在不知不觉中完成请求和响应过程)
AJAX 不需要任何浏览器插件,但需要用户允许javascript在浏览器上执行。
特点:
异步请求,局部刷新
2.局部刷新
如果是from表单提交之后,如果验证失败会自动刷新页面
使用Ajax能保证只刷新局部
示例:
url
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
path(\'admin/\', admin.site.urls),
path(\'login/\', views.login,name=\'login\'),
path(\'home/\', views.home,name=\'home\'),
]
views
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect
# Create your views here.
def login(request):
if request.method == \'GET\':
return render(request,\'login.html\')
else:
uname = request.POST.get(\'username\')
pwd = request.POST.get(\'password\')
if uname == \'zbb\' and pwd == \'123\':
return HttpResponse(\'1\')
else:
return HttpResponse(\'0\')
def home(request):
return render(request,\'home.html\')
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<button id="sub">提交</button>
<span class="error"></span>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(\'#sub\').click(function () {
var uname = $(\'#username\').val();
var pwd = $(\'#password\').val();
$.ajax({
url:\'{% url "login" %}\',
type:\'post\',
data:{username:uname,password:pwd},
success:function (res) {
if (res === \'1\'){
location.href = \'/home/\';
}else{
$(\'.error\').text(\'用户名密码错误!\');
}
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
home.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登陆成功</h1>
</body>
</html>
3.CSRF
详述CSRF(Cross-site request forgery),中文名称:跨站请求伪造,也被称为:one click attack/session riding,缩写为:CSRF/XSRF。攻击者通过HTTP请求江数据传送到服务器,从而盗取回话的cookie。盗取回话cookie之后,攻击者不仅可以获取用户的信息,还可以修改该cookie关联的账户信息。
Django默认会禁止未标识 post请求
login.html
4.from请求设置
中加入 {% csrf_token %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<input type="submit">
</form>
<span class="error"></span>
</body>
</html>
5.Ajax请求设置
第一种方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<button id="sub">提交</button>
<span class="error"></span>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(\'#sub\').click(function () {
var uname = $(\'#username\').val();
var pwd = $(\'#password\').val();
var csrf = \'{{ csrf_token }}\'; //加在这里
$.ajax({
url:\'{% url "login" %}\',
type:\'post\',
data:{username:uname,password:pwd,csrfmiddlewaretoken:csrf},//发送出
success:function (res) {
if (res === \'1\'){
location.href = \'/home/\'; // http://127.0.0.1:8000/home/
}else{
$(\'.error\').text(\'用户名密码错误!\');
}
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
第二种方法
需要引入一个jquery.cookie.js插件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<button id="sub">提交</button>
<span class="error"></span>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery-cookie/1.4.1/jquery.cookie.js"></script>
<script>
$(\'#sub\').click(function () {
var uname = $(\'#username\').val();
var pwd = $(\'#password\').val();
$.ajax({
url:\'{% url "login" %}\',
type:\'post\',
data:{username:uname,password:pwd},
headers:{
"X-CSRFToken":$.cookie(\'csrftoken\'),
},
//其实在ajax里面还有一个参数是headers,自定制请求头,可以将csrf_token加在这里,我们发contenttype类型数据的时候,csrf_token就可以这样加
success:function (res) {
if (res === \'1\'){
location.href = \'/home/\';
}else{
$(\'.error\').text(\'用户名密码错误!\');
}
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
6.网络请求安全解决
常见的网络请求安全解决方法
Cookies Hashing:每一个表单请求中都加入随机的Cookie,由于网站中存在XSS漏洞而被偷窃的危险。
HTTP refer:可以对服务器获得的请求来路进行欺骗以使得他们看起来合法,这种方法不能够有效防止攻击。
验证码:用户提交的每一个表单中使用一个随机验证码,让用户在文本框中填写图片上的随机字符串,并且在提交表单后对其进行检测。
令牌Token:一次性令牌在完成他们的工作后将被销毁,比较安全。
7.文件上传
请求头ContentType
ContentType指的是请求体的编码类型,常见的类型共有3种:
1 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
这应该是最常见的 POST 提交数据的方式了。浏览器的原生 <form> 表单,如果不设置 enctype 属性,那么最终就会以 默认格式application/x-www-form-urlencoded 方式提交数据,ajax默认也是这个。请求类似于下面这样(无关的请求头在本文中都省略掉了):
POST http://www.example.com HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8
user=yuan&age=22 #这就是上面这种contenttype规定的数据格式,后端对应这个格式来解析获取数据,不管是get方法还是post方法,都是这样拼接数据,大家公认的一种数据格式,但是如果你contenttype指定的是urlencoded类型,但是post请求体里面的数据是下面那种json的格式,那么就出错了,服务端没法解开数据。
2.multipart/form-data
这又是一个常见的 POST 数据提交的方式。我们使用表单上传文件时,必须让 <form> 表单的 enctype 等于 multipart/form-data,form表单不支持发json类型的contenttype格式的数据,而ajax什么格式都可以发,也是ajax应用广泛的一个原因
3.application/json
application/json 这个 Content-Type 作为响应头大家肯定不陌生。实际上,现在越来越多的人把它作为请求头,用来告诉服务端消息主体是序列化后的 JSON 字符串。由于 JSON 规范的流行,除了低版本 IE 之外的各大浏览器都原生支持 JSON.stringify,服务端语言也都有处理 JSON 的函数,使用 JSON 不会遇上什么麻烦。
form表单文件上传
url
path(\'upload/\', views.upload,name=\'upload\'),
views
def upload(request):
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request,\'upload.html\')
else:
print(request.POST)
print(request.FILES)
uname = request.POST.get("username")
pwd = request.POST.get(\'password\')
file_obj = request.FILES.get(\'file\')
print(file_obj.name)
with open(file_obj.name,\'wb\') as f:
# for i in file_obj:
# f.write(i)
#文件太大只有一行怎么办?
for chunk in file_obj.chunks():
#默认一次返回大小为经测试为65536B,也就是64KB,最大为2.5M,是一个生成器
f.write(chunk)
return HttpResponse("ok")
upload.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{# 告诉浏览器不要一起发送,要一段一段的发送,指定:ContentType ..指的是请求体的编码类型#}
{% csrf_token %}
用户名: <input type="text" name="username">
密码: <input type="password" name="password">
头像: <input type="file" name="file">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Ajax文件上传
upload.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
用户名: <input type="text" name="username">
密码: <input type="password" name="password">
头像: <input type="file" name="file" multiple>
{# multiple 的意思是可以上传多个#}
<button id =\'sub\'>提交</button>
<span class=\'error\'></span>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery-cookie/1.4.1/jquery.cookie.js"></script>
<script>
$(\'#sub\').click(function () {
var formdata = new FormData();
var uname = $(\'#username\').val();
var pwd = $(\'#password\').val();
var file_obj = $(\'[type=file]\')[0].files[0];
formdata.append(\'username\',uname);
formdata.append(\'password\',pwd);
formdata.append(\'file\',file_obj);
$.ajax({
url:\'{% url "upload" %}\',
type:\'post\',
data:formdata,
processData:false,
contentType:false,
//固定语法 不得对数据加工,直接发送原生数据
headers:{
"X-CSRFToken":$.cookie(\'csrftoken\'),
},
success:function (res) {
$(\'.error\').text(\'完成\');
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
8.json数据交互

json数据类型和python数据类型的对比

JsonResponse对象
JsonResponse是HttpResponse的子类,专门用来生成JSON编码的响应。
from django.http import JsonResponse
response = JsonResponse({\'foo\': \'bar\'})
print(response.content)
b\'{"foo": "bar"}\'
class JsonResponse(data, encoder=DjangoJSONEncoder, safe=True, json_dumps_params=None,**kwargs)
这个类是HttpRespon的子类,它主要和父类的区别在于:
1.它的默认Content-Type 被设置为: application/json
2.第一个参数,data应该是一个字典类型,当 safe 这个参数被设置为:False ,那data可以填入任何能被转换为JSON格式的对象,比如list, tuple, set。 默认的safe 参数是 True. 如果你传入的data数据类型不是字典类型,那么它就会抛出 TypeError的异常。
3.json_dumps_params参数是一个字典,它将调用json.dumps()方法并将字典中的参数传入给该方法。
#如果这样返回,ajax还需要进行json解析
#views.py
return HttpResponse(json.dumps({"msg":"ok!"}))
#index.html
var data=json.parse(data)
console.log(data.msg);
使用HttpResponse对象来响应数据的时候,还可以通过content_type指定格式:
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(data),content_type="application/json")
前端调试窗口就可以看到这个类型
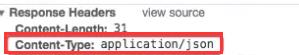
如果不写这个参数是这个类型:长得像json格式的字符串,当然也可以转换成json的

看下面这种,JsonResponse默认就是content_type="application/json"。
#如果这样返回,两边都不需要进行json的序列化与反序列化,ajax接受的直接是一个对象
#views.py
from django.http import JsonResponse
return JsonResponse({"msg":"ok!"})
#index.html
console.log(data.msg);
urls
path(\'jsontest/\', views.jsontest,name=\'jsontest\'),
代码 views
from django.http import JsonResponse
import json
def jsontest(request):
"""
状态码;
1000 : 登录成功
1001 : 登录失败
:param request:
:return:
"""
if request.method == \'GET\':
return render(request,\'jsontest.html\')
else:
username = request.POST.get(\'username\')
pwd = request.POST.get(\'password\')
ret_data = {\'status\':None,\'msg\':None}
print(\'>>>>>\',request.POST)
#<QueryDict: {\'{"username":"123","password":"123"}\'>
if username == \'zbb\' and pwd == \'123\':
ret_data[\'status\'] = 1000 # 状态码
ret_data[\'msg\'] = \'登录成功\'
else:
ret_data[\'status\'] = 1001 # 状态码
ret_data[\'msg\'] = \'登录失败\'
# ret_data_json = json.dumps(ret_data,ensure_ascii=False)
# return HttpResponse(ret_data_json,content_type=\'application/json\')
#ret_data = [\'aa\',22,\'bb\'] /如果是数组
return JsonResponse(ret_data) #safe =Flaser
jsontest.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
用户名: <input type="text" id="username">
密码: <input type="password" id="password">
<button id="sub">提交</button>
<span class="error"></span>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery-cookie/1.4.1/jquery.cookie.js"></script>
<script>
$(\'#sub\').click(function () {
var uname = $(\'#username\').val();
var pwd = $(\'#password\').val();
$.ajax({
url:\'{% url "jsontest" %}\',
type:\'post\',
data:{username:uname,password:pwd},
headers:{
"X-CSRFToken":$.cookie(\'csrftoken\'),
},
success:function (res) {
{#console.log(res,typeof res); // statusmsg {"status": 1001, "msg": "登录失败"}#}
console.log(res,typeof res); //直接就是反序列化之后的了
if (res.status === 1000){
location.href = \'/home/\';
}else{
$(\'.error\').text(res.msg);
}
}
})
})
</script>
</html>
9.补充一个SweetAlert插件
下载地址 百度jq2
https://github.com/lipis/bootstrap-sweetalert
url
path(\'chajian/\', views.chajian)
views
def chajian(request):
return render(request,\'chajian.html\')
html
{% load static %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static \'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap-theme.min.css\' %}">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static \'bootstrap-sweetalert-master/dist/sweetalert.css\' %}">
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button class="btn btn-danger">删除</button>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="{% static \'bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/js/bootstrap.min.js\' %}"></script>
<script src="{% static \'bootstrap-sweetalert-master/dist/sweetalert.js\' %}"></script>
<script>
$(".btn-danger").on("click", function () {
swal({
title: "你确定要删除吗?",
text: "删除可就找不回来了哦!",
type: "warning",
showCancelButton: true,
confirmButtonClass: "btn-danger",
confirmButtonText: "我已经下定决心",
cancelButtonText: "容我三思",
closeOnConfirm: false
},
function () {
var deleteId = $(this).parent().parent().attr("data_id");
$.ajax({
url: "/delete_book/",
type: "post",
data: {"id": deleteId},
success: function (data) {
console.log(data,typeof data);
if (data === \'1\') {
swal("删除成功!", "你可以准备跑路了!", "success");
} else {
swal("删除失败", "你可以再尝试一下!", "error")
}
}
})
});
})
</script>
</html>