状态模式
一个对象有状态变化
每次状态变化都会触发一个逻辑
不能总是用 if...else 来控制
示例:交通信号灯的不同颜色变化
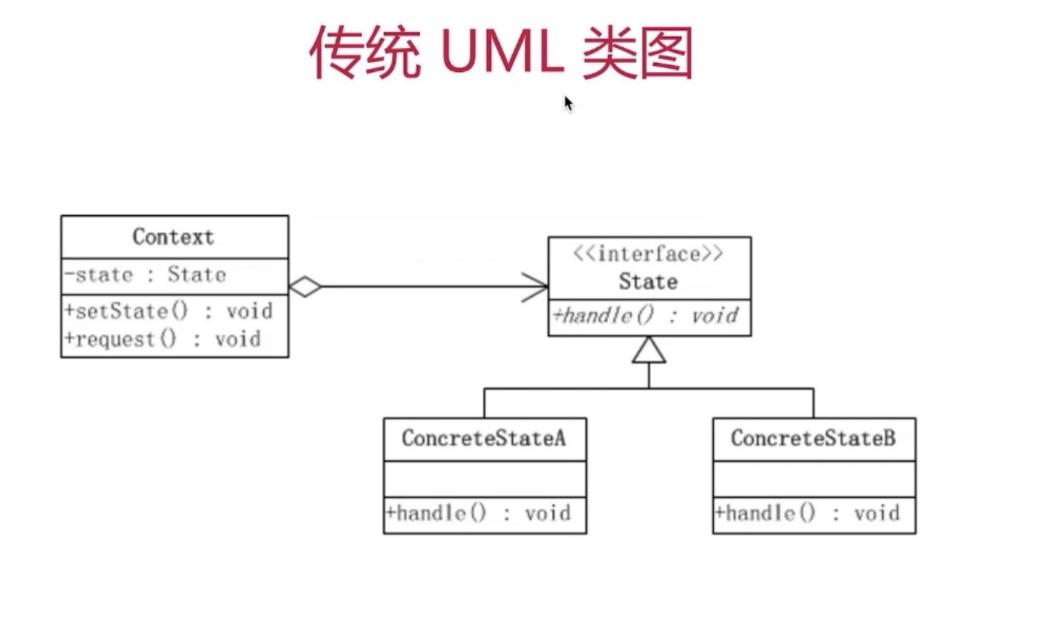
传统的 UML 类图
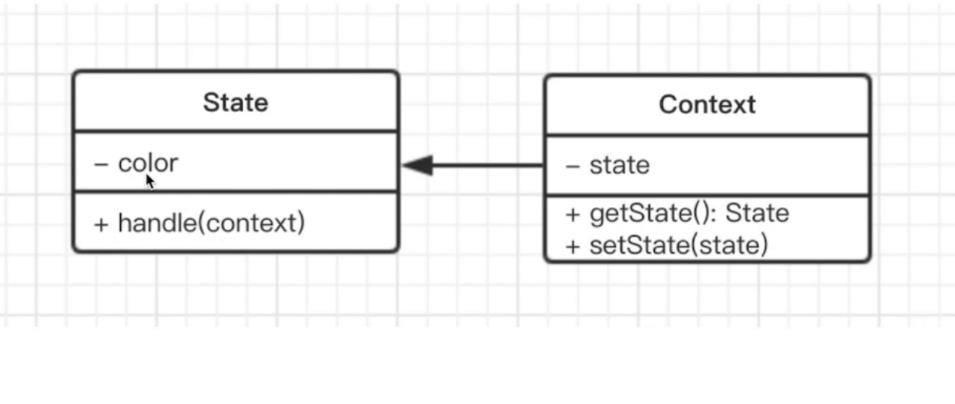
javascript 中的 UML 类图
class State {
constructor(color) {
this.color = color;
}
handle(context) {
console.log(`turn to ${this.color} light`);
context.setState(this);
}
}
class Context {
constructor() {
this.state = null;
}
setState(state) {
this.state = state;
}
getState() {
return this.state;
}
}
// 测试代码
let context = new Context();
let greed = new State("greed");
let yellow = new State("yellow");
let red = new State("red");
// 绿灯亮了
greed.handle(context);
console.log(context.getState());
// 黄灯亮了
yellow.handle(context);
console.log(context.getState());
// 红灯亮了
red.handle(context);
console.log(context.getState());
应用场景
有限状态机
- 有限个状态,以及在这些状态之间的变化
- 交通信号灯
- 利用开源的 lib:JavaScript-state-machine
- javascript-state-machine
- 运行
npm install javascript-state-machine --save
有限状态机的收藏与取消
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>有限状态机</p>
<button id="btn"></button>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="./03-javascript-state-machine.js"></script>
<script>
// 状态机模型
var fsm = new StateMachine({
init: "收藏", // 初始状态,待收藏
transitions: [
{
name: "doStore",
from: "收藏",
to: "取消收藏"
},
{
name: "deleteStore",
from: "取消收藏",
to: "收藏"
}
],
methods: {
// 执行收藏
onDoStore: function() {
alert("收藏成功");
updateText();
},
// 取消收藏
onDeleteStore: function() {
alert("已取消收藏");
updateText();
}
}
});
var $btn = $("#btn");
// 点击事件
$btn.click(function() {
if (fsm.is("收藏")) {
fsm.doStore(1);
} else {
fsm.deleteStore();
}
});
// 更新文案
function updateText() {
$btn.text(fsm.state);
}
// 初始化文案
updateText();
</script>
</body>
</html>
写一个简单的 promise
- promise 就是一个有限自动机
- promise 三种状态:pending fullfilled rejected
- pending -> fullfilled 或者 pending -> rejected
- 不能逆向变化
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="./03-javascript-state-machine.js"></script>
<script>
// 模型
var fsm = new StateMachine({
init: "pending",
transitions: [
{
name: "resolve",
from: "pending",
to: "fullfilled"
},
{
name: "reject",
from: "pending",
to: "rejected"
}
],
methods: {
// 成功
onResolve: function(state, data) {
// 参数:state - 当前状态示例; data - fsm.resolve(xxx) 执行时传递过来的参数
data.successList.forEach(fn => fn());
},
// 失败
onReject: function(state, data) {
// 参数:state - 当前状态示例; data - fsm.reject(xxx) 执行时传递过来的参数
data.failList.forEach(fn => fn());
}
}
});
// 定义 Promise
class MyPromise {
constructor(fn) {
this.successList = [];
this.failList = [];
fn(
() => {
// resolve 函数
fsm.resolve(this);
},
() => {
// reject 函数
fsm.reject(this);
}
);
}
then(successFn, failFn) {
this.successList.push(successFn);
this.failList.push(failFn);
}
}
// 测试代码
function loadImg(src) {
const promise = new MyPromise(function(resolve, reject) {
var img = document.createElement("img");
img.onload = function() {
resolve(img);
};
img.onerror = function() {
reject();
};
img.src = src;
});
return promise;
}
var src = "https://blog-static.cnblogs.com/files/ygjzs/images.gif";
var result = loadImg(src);
console.log(result);
result.then(
function(img) {
console.log("success 1");
},
function() {
console.log("failed 1");
}
);
result.then(
function(img) {
console.log("success 2");
},
function() {
console.log("failed 2");
}
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
设计原则验证
- 将状态对象和主题对象分离,状态的变化逻辑单独处理
- 符合开放封闭原则