一:Ribbon是什么?
Ribbon是Netflix发布的开源项目,主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法,将Netflix的中间层服务连接在一起。Ribbon客户端组件提供一系列完善的配置项如连接超时,重试等。简单的说,就是在配置文件中列出Load Balancer(简称LB)后面所有的机器,Ribbon会自动的帮助你基于某种规则(如简单轮询,随即连接等)去连接这些机器。我们也很容易使用Ribbon实现自定义的负载均衡算法。
二:LB方案分类
目前主流的LB方案可分成两类:一种是集中式LB, 即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施(可以是硬件,如F5, 也可以是软件,如nginx), 由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方;另一种是进程内LB,将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选择出一个合适的服务器。Ribbon就属于后者,它只是一个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址。
三:Ribbon的主要组件与工作流程
Ribbon的核心组件(均为接口类型)有以下几个:
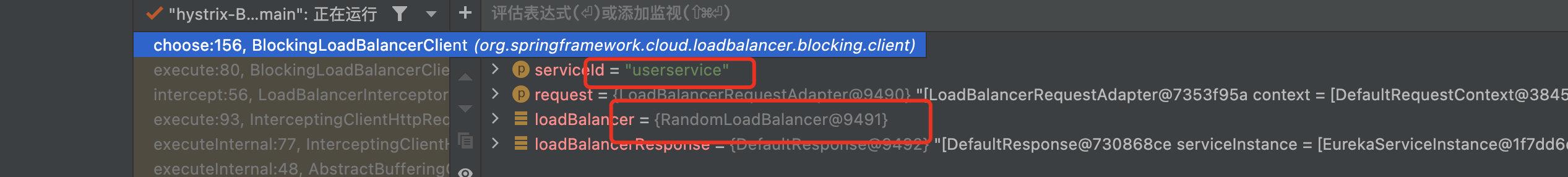
ServerList:用于获取地址列表。它既可以是静态的(提供一组固定的地址),也可以是动态的(从注册中心中定期查询地址列表)。
ServerListFilter:仅当使用动态ServerList时使用,用于在原始的服务列表中使用一定策略过虑掉一部分地址。
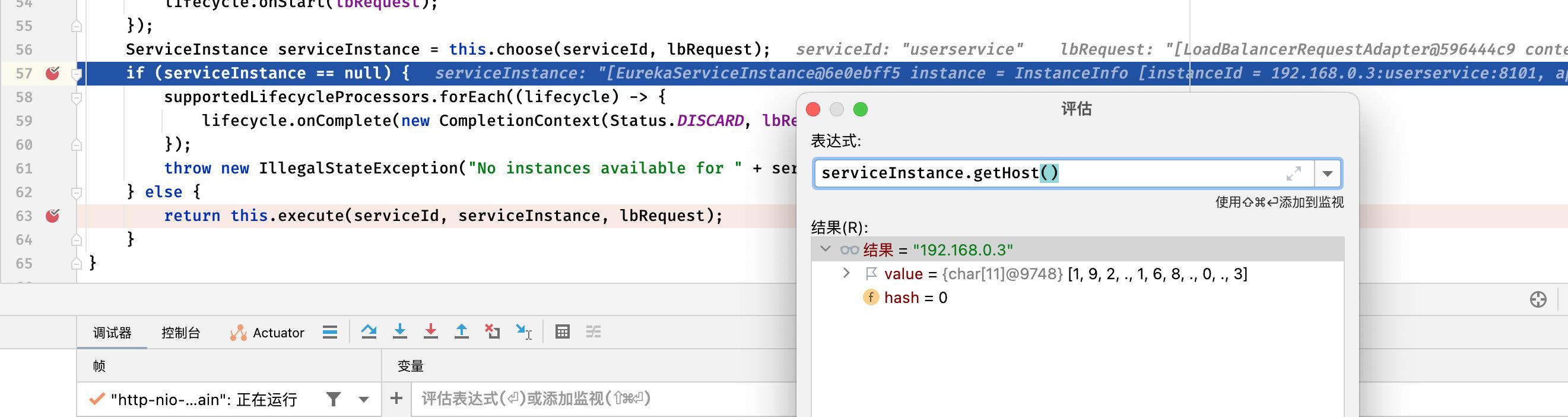
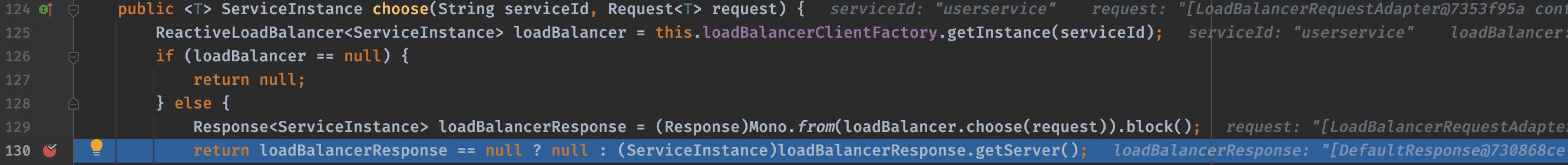
IRule:选择一个最终的服务地址作为LB结果。选择策略有轮询、根据响应时间加权、断路器(当Hystrix可用时)等。
Ribbon在工作时首选会通过ServerList来获取所有可用的服务列表,然后通过ServerListFilter过虑掉一部分地址,最后在剩下的地址中通过IRule选择出一台服务器作为最终结果。
四:Ribbon提供的主要负载均衡策略介绍
1:简单轮询负载均衡(RoundRobin):以轮询的方式依次将请求调度不同的服务器,即每次调度执行i = (i + 1) mod n,并选出第i台服务器。
2:随机负载均衡 (Random): 随机选择状态为UP的Server
3:加权响应时间负载均衡 (WeightedResponseTime):根据相应时间分配一个weight,相应时间越长,weight越小,被选中的可能性越低。
4:区域感知轮询负载均衡(ZoneAvoidanceRule):复合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择server
Ribbon自带负载均衡策略比较
五:Ribbon单独使用
创建一个maven工程,名称是ribbon_client,pom的内容如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.netflix.ribbon</groupId>
<artifactId>ribbon-core</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.netflix.ribbon</groupId>
<artifactId>ribbon-httpclient</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
sample-client.properties配置文件
# Max number of retries sample-client.ribbon.MaxAutoRetries=1 # Max number of next servers to retry (excluding the first server) sample-client.ribbon.MaxAutoRetriesNextServer=1 # Whether all operations can be retried for this client sample-client.ribbon.OkToRetryOnAllOperations=true # Interval to refresh the server list from the source sample-client.ribbon.ServerListRefreshInterval=2000 # Connect timeout used by Apache HttpClient sample-client.ribbon.ConnectTimeout=3000 # Read timeout used by Apache HttpClient sample-client.ribbon.ReadTimeout=3000 # Initial list of servers, can be changed via Archaius dynamic property at runtime sample-client.ribbon.listOfServers=www.sohu.com:80,www.163.com:80,www.sina.com.cn:80 sample-client.ribbon.EnablePrimeConnections=true
RibbonMain代码
import java.net.URI; import com.netflix.client.ClientFactory; import com.netflix.client.http.HttpRequest; import com.netflix.client.http.HttpResponse; import com.netflix.config.ConfigurationManager; import com.netflix.loadbalancer.ZoneAwareLoadBalancer; import com.netflix.niws.client.http.RestClient; public class RibbonMain { public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception { ConfigurationManager.loadPropertiesFromResources("sample-client.properties"); System.out.println(ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().getProperty("sample-client.ribbon.listOfServers")); RestClient client = (RestClient)ClientFactory.getNamedClient("sample-client"); HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder().uri(new URI("/")).build(); for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) { HttpResponse response = client.executeWithLoadBalancer(request); System.out.println("Status for URI:" + response.getRequestedURI() + " is :" + response.getStatus()); } ZoneAwareLoadBalancer lb = (ZoneAwareLoadBalancer) client.getLoadBalancer(); System.out.println(lb.getLoadBalancerStats()); ConfigurationManager.getConfigInstance().setProperty("sample-client.ribbon.listOfServers", "ccblog.cn:80,www.linkedin.com:80"); System.out.println("changing servers ..."); Thread.sleep(3000); for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++) { HttpResponse response = client.executeWithLoadBalancer(request); System.out.println("Status for URI:" + response.getRequestedURI() + " is :" + response.getStatus()); } System.out.println(lb.getLoadBalancerStats()); } }
代码解析
使用 Archaius ConfigurationManager 加载属性;
使用 ClientFactory 创建客户端和负载均衡器;
使用 builder 构建 http 请求。注意我们只支持 URI 的 "/" 部分的路径,一旦服务器被负载均衡器选中,会由客户端计算出完整的 URI;
调用 API client.executeWithLoadBalancer(),不是 exeucte() API;
动态修正配置中的服务器池;
等待服务器列表刷新(配置文件中定义的刷新间隔是为 3 秒钟);
打印出负载均衡器记录的服务器统计信息。
六:Ribbon结合eureka使用
创建maven工程 eureka_ribbon_client 该工程启动和相关配置依赖:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Brixton.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
在应用主类中,通过@EnableDiscoveryClient注解来添加发现服务能力。创建RestTemplate实例,并通过@LoadBalanced注解开启均衡负载能力。
@SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient public class RibbonApplication { @Bean @LoadBalanced RestTemplate restTemplate() { return new RestTemplate(); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(RibbonApplication.class, args); } }
创建ConsumerController来消费service01的getuser服务。通过直接RestTemplate来调用服务
@RestController public class ConsumerController { @Autowired RestTemplate restTemplate; @RequestMapping(value = "/getuserinfo", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String add() { return restTemplate.getForEntity("http://biz-service-0/getuser", String.class).getBody(); } }
Ribbon其实就是一个软负载均衡的客户端组件,他可以和其他所需请求的客户端结合使用,和eureka结合只是其中的一个实例。