Fabric源码分析之Peer链码安装
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Fabric源码分析之Peer链码安装相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A environment:fabric v1.4.2
在Fabric中交易的处理过程,客户端将提案首先发送到背书节点,背书节点检提案的合法性。如果合法的话,背书节点将通过交易所属的链码临时执行一个交易,并执行背书节点在本地持有的状态副本。
Chaincode应该仅仅被安装于chaincode所有者的背书节点上,链码运行在节点上的沙盒(Docker容器)中,并通过gRPC协议与相应的Peer节点进行交互,以使该chaincode逻辑对整个网络的其他成员保密。
请务必在一条channel上每一个要运行你chaincode的背书节点上安装你的chaincode
其他没有chaincode的成员将无权成为chaincode影响下的交易的认证节点(endorser)。也就是说,他们不能执行chaincode。不过,他们仍可以验证交易并提交到账本上。
ChainCode要在区块链网络中运行,需要经过链码安装和链码实例化两个步骤。
链码的安装涉及到3个服务,分别是client,peer背书节点和LSCC容器
主要流程:
以下是在客户端执行 "peer chaincode install ..." 的业务流程图:
客户端执行链码安装命令:
客户端的整个流程切入点为 fabric/peer/main.go 的 main 函数
然后继续找到 peer/chaincode/chaincode.go
继续找到 peer/chaincode/install.go 的 installCmd 函数,可以看出 chaincodeInstall 为主要的入口函数
我们进去看看 InitCmdFactory 做了什么,位置在 peer/chaincode/common.go
返回了 ChaincodeCmdFactory 的结构体,定义为:
找到定义 genChaincodeDeploymentSpec
先看 getChaincodeSpec ,位于 peer/chaincode/common.go
封装返回 ChaincodeSpec 结构体
刚才生成的 ChaincodeSpec 作为 getChaincodeDeploymentSpec 函数的输入参数,返回 ChaincodeDeploymentSpec 结构体
CreateInstallProposalFromCDS 位于 protos/utils/proutils.go
调用 createProposalFromCDS
从结构体 ChaincodeInvocationSpec 可以看到用户链码安装需要调用到系统链码 lscc
通过 CreateProposalFromCIS=>CreateChaincodeProposal=>CreateChaincodeProposalWithTransient
再看 CreateChaincodeProposalWithTxIDNonceAndTransient 函数
最后返回 Proposal 结构体,定义见 protos\peer\proposal.pb.go
到这里 install 调用的 CreateInstallProposalFromCDS 完毕,返回 Proposal 结构体
关系有点复杂,给出一个类图能看得清晰点
回到 install ,看 GetSignedProposal 对刚创建的提案结构进行签名
函数位于 protos/utils/txutils.go
返回 SignedProposal 结构体,定义位于 protos/peer/proposal.pb.go
提案签名完后 install 调用 ProcessProposal 发送提案到peer节点进行处理,参数带了 SignedProposal 结构体
接下来client端就等到peer的 proposalResponse
当client调用了 ProposalResponse 消息就发送到peer背书节点,也就是走peer节点背书提案流程.
要看安装链码前做了什么,直接看 peer节点背书提案流程 就好。
我们从 core/endorser/endorser.go 的 callChaincode=>Execute 函数开始讲
在 core/chaincode/chaincode_support.go 找到 Execute
主要看 Invoke :
根据之前的信息,我们调用的是 lscc 来安装链码,所以在peer启动的时候已经初始化 lscc 链码容器了,所以回直接返回 handler 对象,后面的语句就不说了,在启动链码容器的章节再详细研究。
接着我们看 execute 函数,调用 createCCMessage 创建一个 ChaincodeMessage结构体消息 . Execute 负责把消息发送出去
在 core/chaincode/handler.go 找到 Execute
这里关键是 h.serialSendAsync(msg) 语句,功能是把包装好的信息以grpc协议发送出去,直接就等返回结果了。
至此 Execute 调用的 Invoke 就在等返回结果,结果返回就调用 processChaincodeExecutionResult 对链码结果进行处理
peer发送的信息哪去了呢?
我们定位到 code/chaincode/shim/chaincode.go ,我们看到两个入口函数 Start 和 StartInProc , Start 为用户链码的入口函数,而 StartInProc 是系统链码的入口函数,他们同时都调用了 chatWithPeer ,因为我们调用的是lscc,就看 StartInProc
chatWithPeer就是开启grpc的接收模式在等到节点发来信息,接收到信息后就调用 handleMessage 处理信息。
因为我们信息类型为 ChaincodeMessage_TRANSACTION ,所以我们在 core/chaincode/shim/handler.go 顺着 handleMessage=>handleReady 扎到 handleTransaction
其中关键语句 res := handler.cc.Invoke(stub) ,这语句是调用相应链码的 Invoke 函数,所以我们找到 core/scc/lscc/lscc.go 下的 Invoke 函数
进去 core/scc/lscc/lscc.go 的 Invoke 函数可以看到,这里有 "INSTALL", "DEPLOY", "UPGRADE" 等操作,我们只看 INSTALL 部分。
关键调用函数是 executeInstall
接着看 executeInstall
HandleChaincodeInstall 为处理statedb,而 PutChaincodeToLocalStorage 是把链码文件安装到本地文件目录
链码安装到peer的默认路径 /var/hyperledger/production/chaincodes
到此链码的安装完毕
lscc链码安装完毕后,返回信息给peer节点,peer节点就给提案背书返回给client服务端,至此链码安装完毕。
github
参考:
5-ChainCode生命周期、分类及安装、实例化命令解析
fabric源码解读【peer chaincode】:安装链码
Fabric1.4源码解析:客户端安装链码
实战:区块链hyperledger fabric 初体验 - 3: 链码实例安装实例化调用及代码
本文链码实例为Fabric 官方实例examples/chaincode/go/chaincode_example02,实现简单的转账功能
进入到cli容器里面
1. 链码安装
以在org1, peer0 为例
1.1 设置环境变量
| export CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org2MSP export CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer1.org2.example.com:7051 export CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp export CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer1.org2.example.com/tls/ca.crt |
1.2 安装链码
| # peer chaincode install -n test02 -v 1.0 -p examples/chaincode/go/chaincode_example02 |
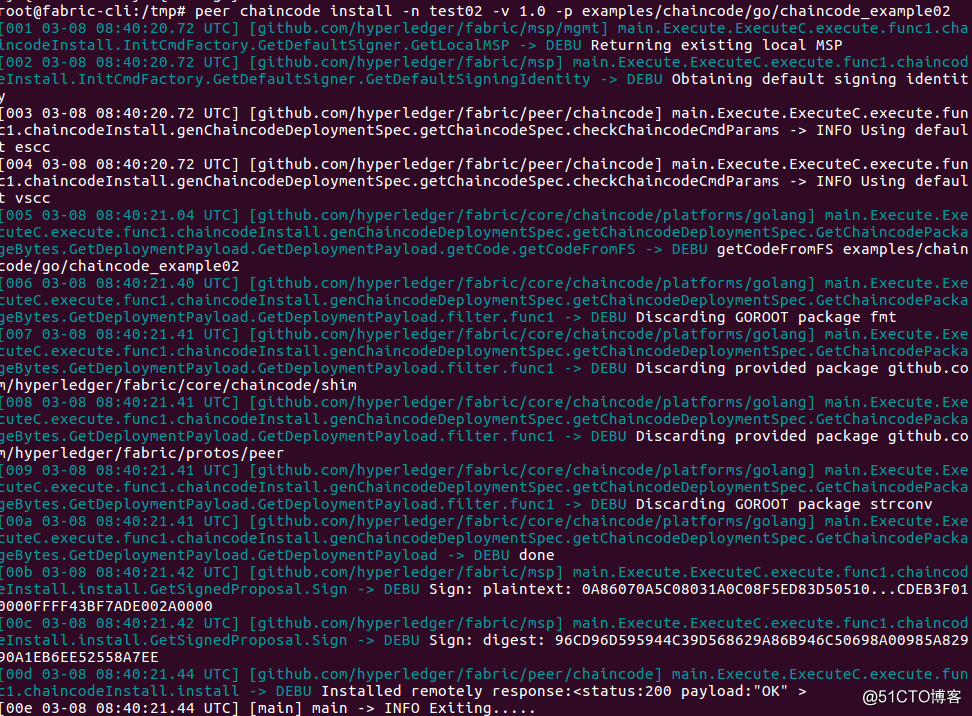
修改相关环境变量和参数,重复步骤1.1 和1.2,在{org1, peer1},{org2, peer0},{org2, peer1}上安装链码
2.链码实例化
以下过程在任意一个节点执行一次就行。
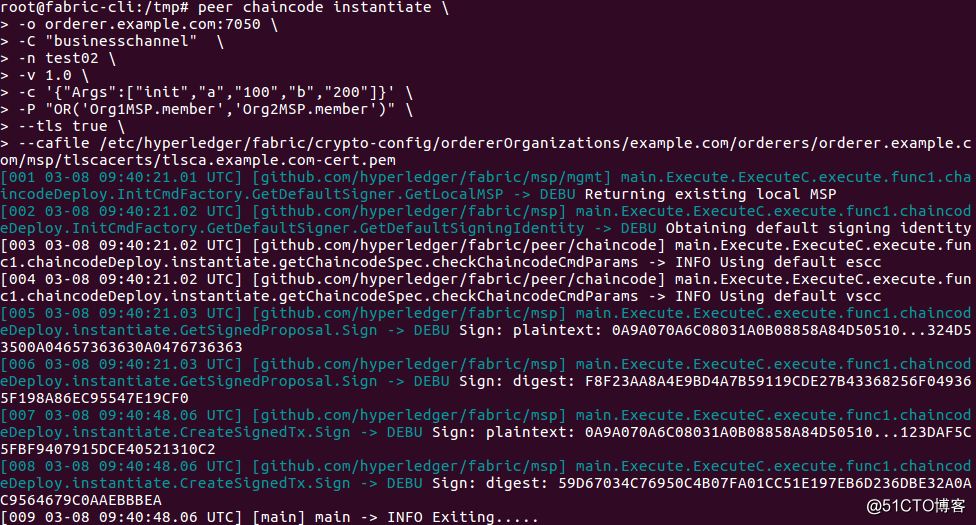
| peer chaincode instantiate \ -o orderer.example.com:7050 \ -C "businesschannel" \ -n test02 \ -v 1.0 \ -c '{"Args":["init","a","100","b","200"]}' \ -P "OR ('Org1MSP.member','Org2MSP.member')" \ --tls true \ --cafile /etc/hyperledger/fabric/crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem |
3.测试链码
3.1 查询初始值
| # peer chaincode query -C "businesschannel" -n "exp02" -c '{"Args":["query","a"]}' |
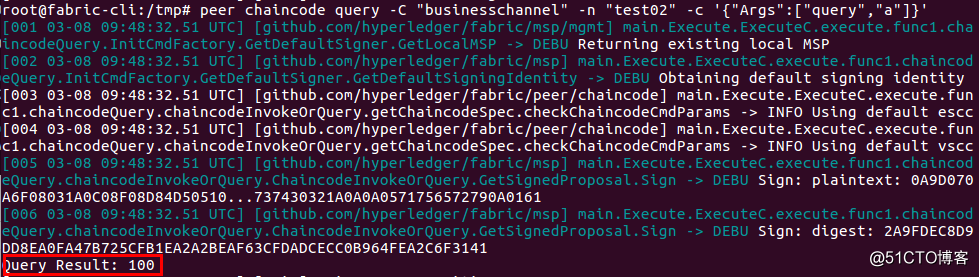
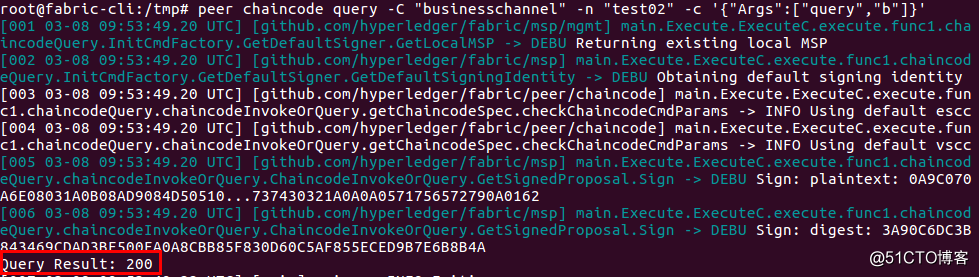
| # peer chaincode query -C "businesschannel" -n "exp02" -c '{"Args":["query","b"]}' |
3.2 转账:从"a" 的账户转账10到"b" 的账户
| peer chaincode invoke \ -o orderer.example.com:7050 \ -C "businesschannel" \ -n "test02" \ -c '{"Args":["invoke","a","b","10"]}' \ --tls true \ --cafile /etc/hyperledger/fabric/crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp/tlscacerts/tlsca.example.com-cert.pem |
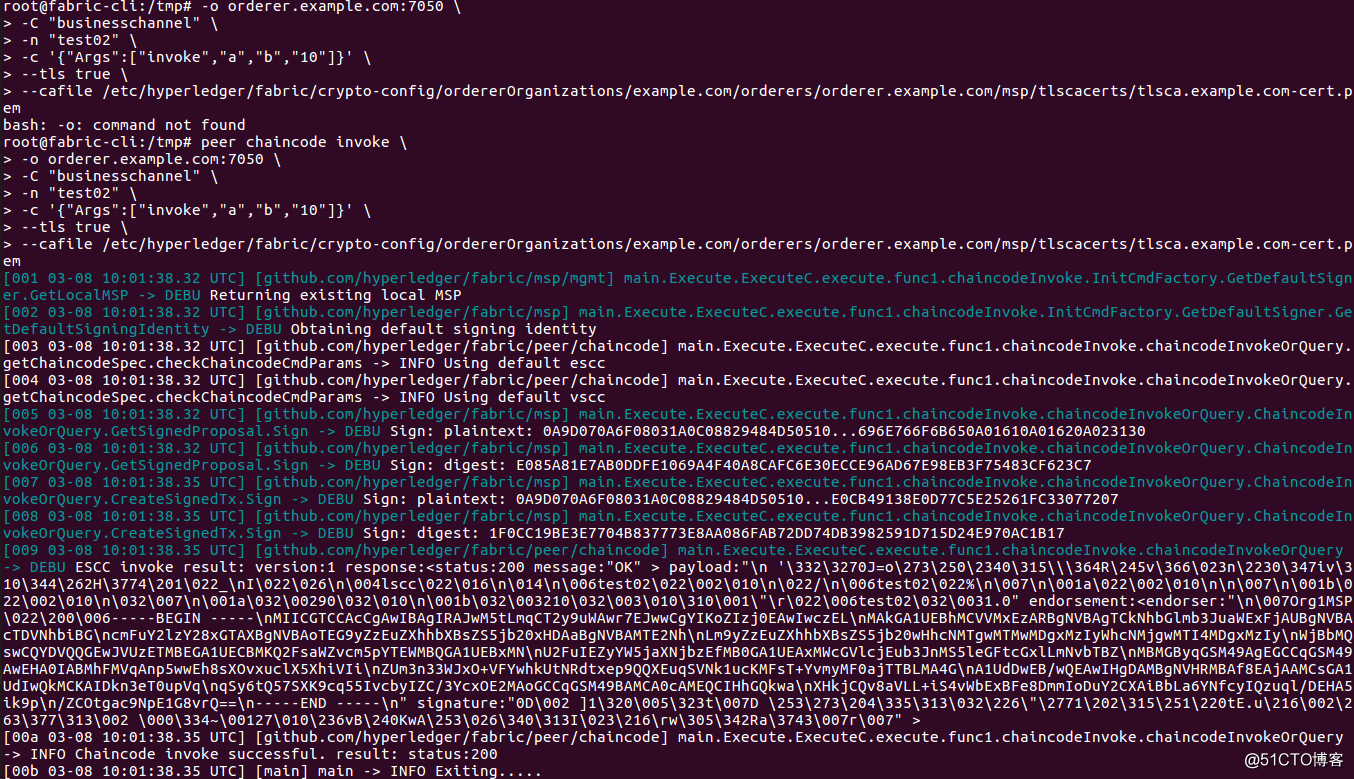
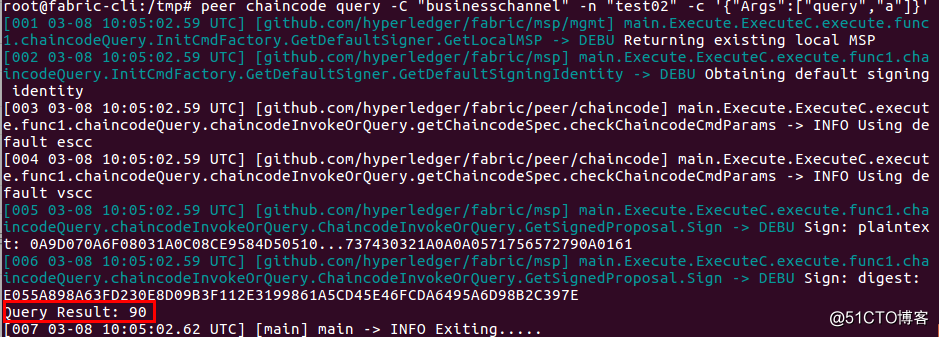
3.3 查询转账结果
| # peer chaincode query -C "businesschannel" -n "test02" -c '{"Args":["query","a"]}' |
查询另一个节点{org2,peer1} 的账本
| export CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org2MSP export CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer1.org2.example.com:7051 export CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/users/[email protected]/msp export CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org2.example.com/peers/peer1.org2.example.com/tls/ca.cr |
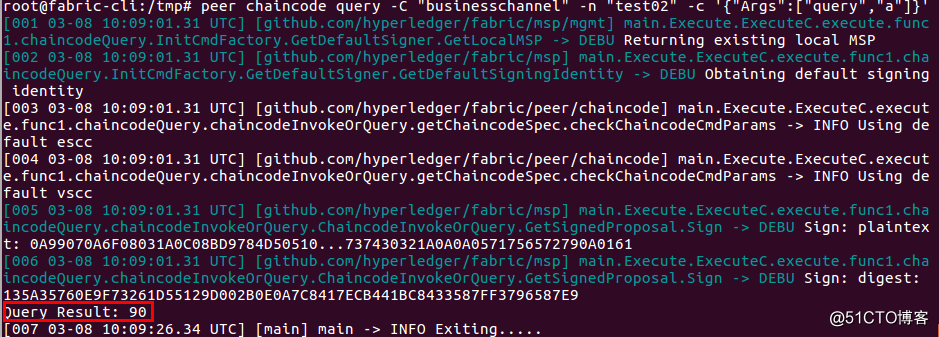
结果一致。
4.代码解析
4.1 引入必要的包
| import ( "fmt" "strconv" "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim" pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer" ) |
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim":shim包提供了链码与账本交互的中间层。
4.2 初始化
| func (t *SimpleChaincode) Init(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response { ...... //提取参数 var A, B string // Entities var Aval, Bval int // Asset holdings ...... // 初始化链码 Aval, err = strconv.Atoi(args[1]) ...... B = args[2] Bval, err = strconv.Atoi(args[3])...... // 把状态写入账本 ...... err = stub.PutState(B, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Bval))) ...... return shim.Success(nil) } |
4.3 Inovke方法
获取function值
| function, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters() |
根据function值不同,执行不同的分支处理逻辑。
| if function == "invoke" { // Make payment of X units from A to B return t.invoke(stub, args) } else if function == "delete" { // Deletes an entity from its state return t.delete(stub, args) } else if function == "query" { // the old "Query" is now implemtned in invoke return t.query(stub, args) } |
query分支
func (t *SimpleChaincode) query(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response { ...... A = args[0] // 从账本获得状态值Avalbytes, err := stub.GetState(A) ...... } |
invoke分支
func (t *SimpleChaincode) invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response { ...... //从账本获取"a"的值 Avalbytes, err := stub.GetState(A) ...... //从账本获取"b"的值 Bvalbytes, err := stub.GetState(B) ...... //执行转账 Aval = Aval - X ...... //结果计入账本 err = stub.PutState(A, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Aval))) ...... err = stub.PutState(B, []byte(strconv.Itoa(Bval))) ......} |
delete分支
func (t *SimpleChaincode) delete(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response { ...... //删除一个实体 err := stub.DelState(A) |
}
以上是关于Fabric源码分析之Peer链码安装的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章