Spring6| Bean的四种获取方式(实例化) Posted 2023-03-30 @每天都要敲代码
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring6| Bean的四种获取方式(实例化)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一:Bean的实例化方式
1. 通过构造方法实例化
2. 通过简单工厂模式实例化
3. 通过factory-bean实例化
4. 通过FactoryBean接口实例化
5. BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别(面试题)
6. 使用FactoryBean注入自定义Date
一:Bean的实例化方式
Spring为Bean提供了多种实例化方式,通常包括4种方式。(也就是说在Spring中为Bean对象的创建准备了多种方案,目的是:更加灵活)
第一种:通过构造方法实例化
第二种:通过简单工厂模式实例化
第三种:通过factory-bean实例化(工厂方法模式)
第四种:通过FactoryBean接口实例化
1. 通过构造方法实例化
我们之前一直使用的就是这种方式!默认情况下,会调用Bean的无参数构造方法,这里在复习一遍!
SpringBean类
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
public class SpringBean
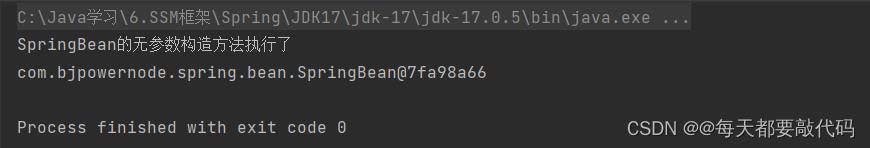
public SpringBean()
System.out.println("SpringBean的无参数构造方法执行了");
spring.xml配置
第一种:在spring配置文件中直接配置类全路径,Spring会自动调用该类的无参数构造方法来实例化Bean!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--Spring提供的实例化方式,第一种-->
<bean id="sb" class="com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.SpringBean"/>
</beans>BeanInstantiationTest测试类
package com.bjpowernode.spring.test;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.SpringBean;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanInstantiationTest
@Test
public void tesInstantiation1()
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
SpringBean sb = applicationContext.getBean("sb", SpringBean.class);
System.out.println(sb);
执行结果:成功调用无参数构造方法实例化对象
2. 通过简单工厂模式实例化
简单工厂模式又叫做静态工厂方法模式,因为工厂类中有一个静态方法!
第一步:定义一个Bean
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
public class Vip
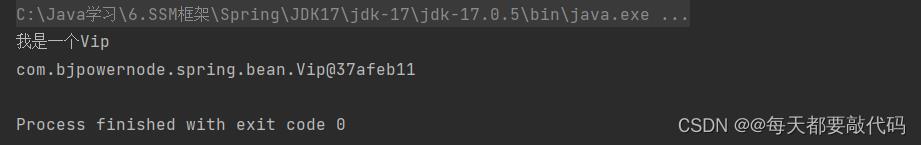
public Vip()
System.out.println("我是一个Vip");
第二步:编写简单工厂模式当中的工厂类
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
public class VipFactory
// 里面有一个静态方法
public static Vip get()
// 实际上对象的创建还是我们程序员 第三步:在Spring配置文件中指定创建该Bean的方法
第二种:通过简单工厂模式。
需要在Spring配置文件中告诉Spring框架,调用哪个类 的哪个方法 获取Bean?
①class属性 指定的是工厂类的全限定类名 !
②factory-method属性 指定的是工厂类当中的静态方法
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--Spring提供的实例化方式,第二种-->
<bean id="vipBean" class="com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.VipFactory" factory-method="get"/>
</beans>
第四步:编写测试程序
package com.bjpowernode.spring.test;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.SpringBean;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.Vip;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.VipFactory;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanInstantiationTest
@Test
public void tesInstantiation2()
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Object vipBean = applicationContext.getBean("vipBean", Vip.class);
System.out.println(vipBean);
执行结果:通过简单工厂模式也能实例化对象
3. 通过factory-bean实例化
本质上是:通过工厂方法模式进行实例化对象!
注:简单工厂模式和工厂方法模式的区别
①简单工厂模式是所有的产品对应一个工厂类,使用的是静态方法!
②工厂方法模式是一个产品对应一个工厂类,使用的是实例方法!
第一步:定义一个Bean
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
// 工厂方法模式当中的:具体产品角色
public class Gun
public Gun()
System.out.println("Gun的无参数构造方法执行");
第二步:定义具体工厂类,工厂类中定义实例方法
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
// 工厂方法模式当中:的具体工厂角色
public class GunFactory
// 实例方法
public Gun get()
// 还是我们自己new的对象
return new Gun();
第三步:在Spring配置文件中指定factory-bean以及factory-method
第三种:通过工厂方法模式。
通过 factory-bean属性 + factory-method属性来共同完成 调用哪个对象 (因为是实例方法需要创建对象)的哪个方法 来获取Bean。
①factory-bean属性 用来告诉Spring调用那个对象 !
②factory-method属性 用来告诉Spring调用该对象的那个方法!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--Spring提供的实例化方式,第三种-->
<bean id="gunBean" class="com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.GunFactory"/>
<bean id="gun" factory-bean="gunBean" factory-method="get"/>
</beans>第四步:编写测试程序
package com.bjpowernode.spring.test;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.Gun;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.SpringBean;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.Vip;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.VipFactory;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanInstantiationTest
@Test
public void tesInstantiation3()
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Gun gun = applicationContext.getBean("gun", Gun.class);
System.out.println(gun);
执行结果:通过工厂方法模式也能实例化对象
4. 通过FactoryBean接口实例化
①在第三种方式中,factory-bean和factory-method都是我们自己定义的。
②在Spring中,当编写的类 直接实现 FactoryBean接口 之后 factory-bean和factory-method就不需要指定了!
第一步:定义一个Bean
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
public class Person
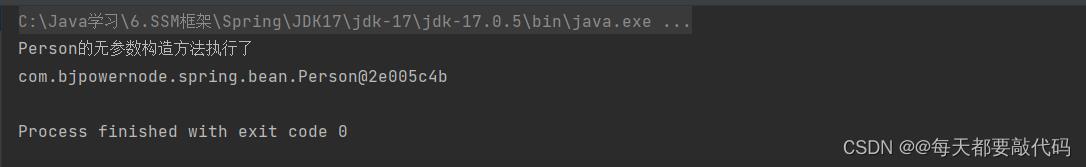
public Person()
System.out.println("Person的无参数构造方法执行了");
第二步:编写一个类实现FactoryBean接口,重写里面的方法
PersonFactory也是一个Bean,只不过这个Bean比较特殊,叫做工厂Bean。通过工厂Bean这个特殊的Bean可以获取一个普通的Bean!
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
public class PersonFactory implements FactoryBean<Person>
@Override
public Person getObject() throws Exception
// 对象的创建也是自己new的
return new Person();
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType()
return null;
@Override
public boolean isSingleton()
// 这个方法是默认存在的,true表示单例,false表示原型
return true;
第三步:在Spring配置文件中配置FactoryBean
第四种:通过FactoryBean接口来实现,这种方式实际上就是第三种方式的简化!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--Spring提供的实例化方式,第四种-->
<bean id="person" class="com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.PersonFactory" />
</beans>第四步:编写测试程序
package com.bjpowernode.spring.test;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanInstantiationTest
@Test
public void tesInstantiation4()
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
执行结果:通过FactoryBean接口实例化
注:FactoryBean在Spring中是一个接口,被称为“工厂Bean”。“工厂Bean”是一种特殊的Bean,所有的“工厂Bean”都是用来协助Spring框架来创建其他Bean对象的!
5. BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别(面试题)
(1)BeanFactory(是一个工厂)
BeanFactory是Spring IoC容器的顶级对象,BeanFactory被翻译为“Bean工厂”,在Spring的IoC容器中,“Bean工厂”负责创建Bean对象!
(2)FactoryBean(是一个Bean)
FactoryBean是一个Bean,是一个能够辅助Spring实例化其它Bean对象的一个Bean!
在Spring中,Bean可以分为两类:
第一类:普通Bean 第二类:工厂Bean(工厂Bean也是一种Bean,只不过这种Bean比较特殊,它可以辅助Spring实例化其它Bean对象)
6. 使用FactoryBean注入自定义Date
①前面我们说过,java.util.Date在Spring中被当做简单类型,简单类型在注入的时候可以直接使用value属性或value标签来完成。
②但是之前我们已经测试过了,对于Date类型来说,采用value属性或value标签赋值的时候,对日期字符串的格式要求非常严格,必须是这种格式的:Mon Oct 10 14:30:26 CST 2022,其他格式是不会被识别的!
③当然我们也可以当成非简单类型处理,使用ref属性来处理,但是却有一个弊端,获取的都是当前的时间,并不能自己指定时间!
注:下面我们就使用FactoryBean来完成这个骚操作!
Student类
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
import java.util.Date;
public class Student
// 每个学生都有出生日期
private Date birth;
@Override
public String toString()
return "Student" +
"birth=" + birth +
'';
public void setBirth(Date birth)
this.birth = birth;
编写DateFactory实现FactoryBean接口
package com.bjpowernode.spring.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateFactory implements FactoryBean<Date>
// 定义一个日期属性,用来处理传过来的日期字符串
private String date;
// 通过构造方法给日期字符串属性赋值
public DateFactory(String date)
this.date = date;
@Override
public Date getObject() throws Exception
// 处理
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
return sdf.parse(this.date);
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType()
return null;
编写spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--通过这个类的构造方法,把字符串转换成Date-->
<bean id="date" class="com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.DateFactory">
<constructor-arg name="date" value="1999-01-14"/>
</bean>
<!--把上面的Date通过上面的类,使用ref属性引进来-->
<bean id="studentBean" class="com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.Student">
<property name="birth" ref="date"/>
</bean>
</beans>编写测试程序
package com.bjpowernode.spring.test;
import com.bjpowernode.spring.bean.*;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanInstantiationTest
@Test
public void testDate()
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
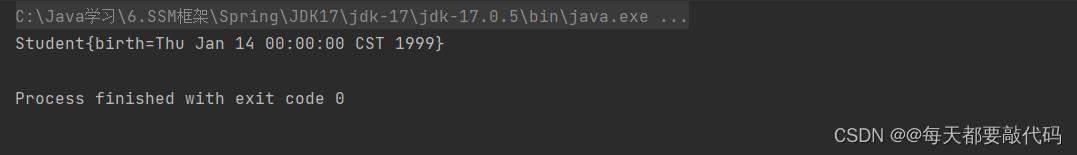
Student studentBean = applicationContext.getBean("studentBean", Student.class);
System.out.println(studentBean);
执行结果
Spring中四种实例化bean的方式
本文主要介绍四种实例化bean的方式(注入方式) 或者叫依赖对象实例化的四种方式。上面的程序,创建bean 对象,用的是什么方法 ,用的是构造函数的方式 (Spring 可以在构造函数私有化的情况下把类对象创建出来)
常用的创建方式有以下四种:
1) setter 方法
2) 构造函数
3) 静态工厂
4) 实例工厂
一、用 setter 方式
public interface IUserDao {
void addUser();
void delUser();
void updateUser();
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
public void addUser() {
System.out.println( "addUser方法被调用了");
}
public void delUser() {
System.out.println( "delUser方法被调用了");
}
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println( "updateUser方法被调用了");
}
}
public class UserAction {
private IUserDao dao; // dao是一个依赖对象,要由springg进行管理,要生成 get set 方法
public void execute(){
dao.addUser();
dao.updateUser();
dao.delUser();
}
}
// 配置文件
<bean name="userAction_name" class ="cat.action.UserAction" >
<property name="dao" ref="userDao_name" /> // 引用的是下面的名称
</bean>
<bean name="userDao_name" class ="cat.dao.UserDaoImpl" />
// 测试
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
UserAction action =(UserAction)ctx.getBean("userAction_name");
action.execute();
二、构造函数
public class UserAction {
// public UserAction(){} 可以保保留一个无参的构造函数
// 这是几个依赖对象,不用生成get set方法了
private UserInfo user;
private String school;
private IUserDao dao;
// 希望Spring 由构造函数注入依赖对象
public UserAction(IUserDao dao,UserInfo user,String school){
this .dao=dao;
this .school=school;
this .user=user;
}
public void execute(){
dao.addUser();
dao.updateUser();
dao.delUser();
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(school);
}
// 配置文件
<bean name="userInfo_name" class ="cat.beans.UserInfo" >
<property name="id" value="1" />
<property name="userName" value="周周" />
<property name="password" value="123" />
<property name="note" value="这是备注" />
</bean>
<bean name="userAction_name" class ="cat.action.UserAction" >
<constructor-arg ref="userDao_name" />
<constructor-arg ref="userInfo_name" />
<constructor-arg value="哈尔滨师范大学" />
</bean>
/*
也可以指定 索引和 type 属性 , 索引和type 都可以不指定
<bean name="userAction_name" class="cat.action.UserAction" >
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="userDao_name" type="cat.dao.IUserDao" /> 如果是接口,就不能指定是实现类的类型
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="userInfo_name" type="cat.beans.UserInfo" />
<constructor-arg index="2" value="哈尔滨师范大学" />
</bean>
*/
<bean name="userDao_name" class ="cat.dao.UserDaoImpl" />
// 测试
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
UserAction action =(UserAction)ctx.getBean("userAction_name");
action.execute();
三、静态工厂方式
// 工厂,用来生成dao的实现类
public class UserDaoFactory {
public static IUserDao createUserDaoInstance(){
return new UserDaoOracleImpl();
}
}
public class UserAction {
private IUserDao dao;// 使用工厂方式注值,也要生成set方法
public void execute(){
dao.addUser();
dao.updateUser();
dao.delUser();
}
public void setDao(IUserDao dao) {
this .dao = dao;
}
}
// 配置文件
<bean name="userAction_name" class ="cat.action.UserAction" >
<property name="dao" ref="userDao_name" />
</bean>
<bean name="userDao_name" class ="cat.dao.UserDaoFactory" factory-method="createUserDaoInstance" />
// 测试
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
UserAction action =(UserAction)ctx.getBean("userAction_name");
action.execute();
四、实例工厂
// 工厂 =>
public class UserDaoFactory {
// 这个方法不是静态的
public IUserDao createUserDaoInstance(){
return new UserDaoOracleImpl();
}
}
// 配置文件
<bean name="userAction_name" class ="cat.action.UserAction" >
<property name="dao" ref="userDao_name" />
</bean>
<bean name="userDaoFactory_name" class ="cat.dao.UserDaoFactory" />
<bean name="userDao_name" factory-bean="userDaoFactory_name" factory-method="createUserDaoInstance" /> 以上是关于Spring6| Bean的四种获取方式(实例化)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
DI(依赖注入)的四种方式
Spring通过构造方法注入的四种方式
spring获取bean的几种方式
[Spring6.0源码解析]简述@Configuration注解
Spring Bean 作用域
单例模式中的四种方式