ElastiSearch默认分词器
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ElastiSearch默认分词器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 在Elasticsearch中的数据可以分为两类: 精确值(exact values)以及全文(full text) 。
精确值 :例如日期类型date,若date其有两个值:2014-09-15与2014,那么这两个值不相等。又例如字符串类型foo与Foo不相等。
全文 :通常是人类语言写的文本,例如一段tweet信息、email的内容等。
精确值很容易被索引 :一个值要么相当要么不等。 索引全文值就需要很多功夫。例如我们不仅要想:这个文档符合我们的查询吗?还要想:这个文档有多符合我们的查询?换句话说就是:这个文档跟我们的查询关联大吗?我们很少精确的去匹配整个全文,我们最想要的是去匹配全文文本的内部信息。除此,我们还希望搜索能够理解我们的意图:例如
如果你搜索UK,我们需要包含United Kingdom的文本也会被匹配。 如果你搜索jump,那么包含jumped,jumps,jumping,更甚者leap的文本会被匹配。
为了更方便的进行全文索引,Elasticsearch首先要先分析文本,然后使用分析过的文本去创建倒序索引。
Elasticsearch全文检索默认分词器为standard analyzer。standard analyzer中,character Filter什么也没有做,Token Filters只是把英文大写转化为小写,因此Elasticsearch默认对大小写不敏感,下面主要介绍Tokenizer。
token分隔符把text分隔为token(term)。数据写入的时候会使用standard analyzer处理,text会被处理为token列表。搜索的text也会执行相同的处理,最后使用处理后的token和源text处理后的token匹配。
除了“a-z、A-Z、0-9、_”以外,但不包括“.;,”这三个字符,其他情况都是token分隔符。
“.”链接number和char时,作为token分隔符,其它情况不是分隔符
1)“number.number”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number.number]
例如“123.123s”,搜索“123”是搜索不到的,搜索“123.123s”是可以匹配的
2)“char.char”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[char.char]
例如“test.test”,搜索“test”是搜索不到的,搜索“test.test”是可以匹配的
3)“number.char或者char.number”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number、char]
例如“test1.s1”,token列表为[test1、s1],搜索“test1”是可以匹配的
“;”链接number和number时,不作为token分隔符,其它情况都是分隔符
1)“number;number”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number;number]
例如“123;123”,搜索“123”是搜索不到的,搜索“123;123”是可以匹配的
2)“number;char或者char;number”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number、char]
例如“test1;s1”,搜索“test1”是可以匹配的
3)“char;char”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[char、char]
例如“test1;ss1”,搜索“test1s”可以匹配的
“,”链接number和number时,不作为token分隔符,其它情况都是分隔符
1)“number,number”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number,number]
例如“123,123”,搜索“123”是搜索不到的,搜索“123,123”是可以匹配的
2)“number,char或者char,number”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number、char]
例如“test1,s1”,搜索“test1”是可以匹配的
3)“char,char”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[char、char]
例如“test;s1”,搜索“test”是可以匹配的
在最前面和最后面都是token分隔符
1)“[,.;]char [,.;]”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[char]
例如“,.test…”,搜索“test”可以匹配
2)“[,.;]number [,.;]”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number]
例如“,.123…”,搜索“123”可以匹配
3)“_[token分隔符]number或者”经过standard analyzer处理后,token列表[number]
存储字符串:“123 test1:a_b a.b”,分词后的token为:[123、test1、a_b、a.b]
1)使用关键字term搜索 123、test1、a_b或a.b可以匹配
2)使用关键字term搜索“test1##a_b”也可以匹配,在这儿“#”只是起了个分隔符的作用,没有实际意义,和搜索“test1:a_b”的意义一样,搜索字符串分隔为两个token[test1和a_b]去匹配。
3)使用关键字term搜索“test1?.,“也可以匹配,相当于使用token”test1“去搜索
4)搜索“a“,就没有匹配结果,源字符串分隔后的token中没有“a”
存储字符串:“123;456 test”,分词后的term为:[123;456、test]
1) 查询“123”是没有返回结果的
2) 查询“123:456”是没有返回结果的
3) 查询“123;456”是有结果
4) 查询“.123;456#”是有结果
参考: http://unicode.org/reports/tr29/
除了汉字外的所有字符都是分隔符,每个字都会作为一个term。因此在搜索中,存在除了汉字以为的字符都不起任何作用,不会作为匹配字符.
Elastisearch 简介 使用 Query DSL 映射 分词 Elasticsearch-Rest-Client
1、简介
Elasticsearch是一个开源的分布式、RESTful 风格的搜索和数据分析引擎。在大数据检索的效率下,比mysql等传统数据库效率高几十倍。淘宝,京东,首页分类检索底层都是用至少Elasticsearch级别数据搜索框架。
2、基本概念


2.1 索引(Index) 就像mysql的数据库
Elastic 会索引所有字段,经过处理后写入一个反向索引(Inverted Index)。查找数据的时候,直接查找该索引。
所以,Elastic 数据管理的顶层单位就叫做 Index(索引)。它是单个数据库的同义词。每个 Index (即数据库)的名字必须是小写。
- 索引做动词,相当于mysql的insert
- 索引做名词,相当于mysql的database
2.2 Type(类型)
在 Index(索引)中,可以定义一个或多个类型。
类似于 MySQL 的 Table,每一种类 型的数据存放在一起。
但是:在Elasticsearch6.0之后,Type 类型被移除。
ElasticSearch7-去掉type概念:
关系型数据库中两个数据表示是独立的,即使他们里面有相同名称的列也不影响使用,但ES中不是这样的。elasticsearch是基于Lucene开发的搜索引擎,而ES中不同type下名称相同的filed最终在Lucene中的处理方式是一样的。
- 两个不同type下的两个user_name,在ES同一个索引下其实被认为是同一个filed,你必须在两个不同的type中定义相同的filed映射。否则,不同type中的相同字段名称就会在处理中出现冲突的情况,导致Lucene处理效率下降。
- 去掉type就是为了提高ES处理数据的效率。
- Elasticsearch 7.x URL中的type参数为可选。比如,索引一个文档不再要求提供文档类型。
- Elasticsearch 8.x 不再支持URL中的type参数。
解决办法:
将索引从多类型迁移到单类型,每种类型文档一个独立索引
将已存在的索引下的类型数据,全部迁移到指定位置即可。详见数据迁移
2.3 Document(文档)
保存在某个 Index(索引)下,某种 Type(类型)的一个数据,Document(文档)是JSON格式的,Document 就像是 MySQL 中某个 Table 里面每一行的数据,字段就是Document里的属性。
2.4 字段(Fields)
每个Document都类似一个JSON结构,它包含了许多字段,每个字段都有其对应的值,多个字段组成了一个 Document,可以类比关系型数据库数据表中的字段。
在 Elasticsearch 中,文档(Document)归属于一种类型(Type),而这些类型存在于索引(Index)中,下图展示了Elasticsearch与传统关系型数据库的类比:

3、Elasticsearch-基本使用
3.1 安装并运行Elasticsearch
网上找教程吧,还是挺麻烦的。
启动成功后,Elasticsearch运行在本地的9200端口,在浏览器中输入网址“http://localhost:9200/”,如果看到以下信息就说明你的电脑已成功安装Elasticsearch:
{
"name" : "YTK8L4q",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "hB2CZPlvSJavhJxx85fUqQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "6.5.4",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "d2ef93d",
"build_date" : "2018-12-17T21:17:40.758843Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "7.5.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}3.2 _cat 查看节点
(1) /_cat/nodes:查看所有节点
接口: GET http://192.168.163.131:9200/_cat/nodes
用PostMan 来模拟,访问该接口
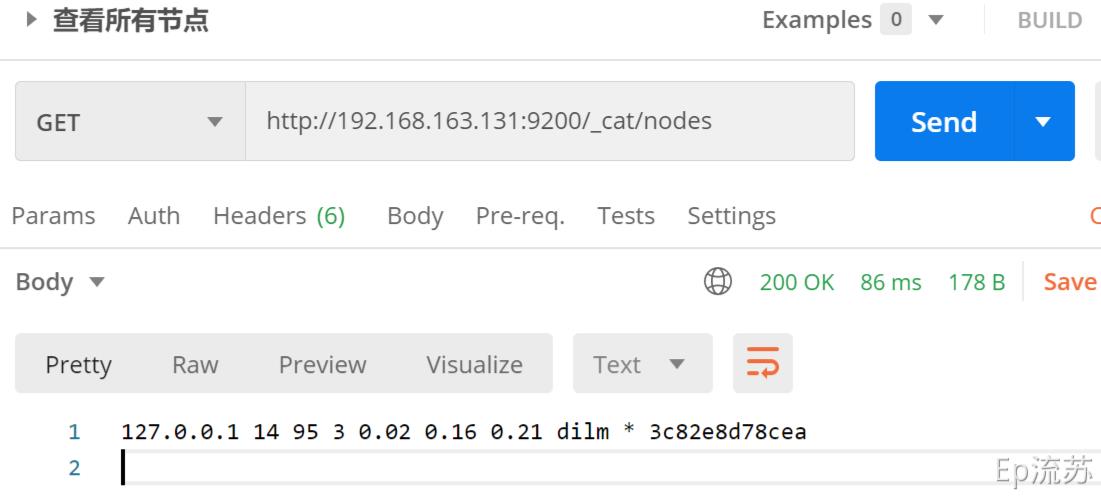
(2)/_cat/health:查看ES健康状况
接口:GET http://192.168.163.131:9200/_cat/health
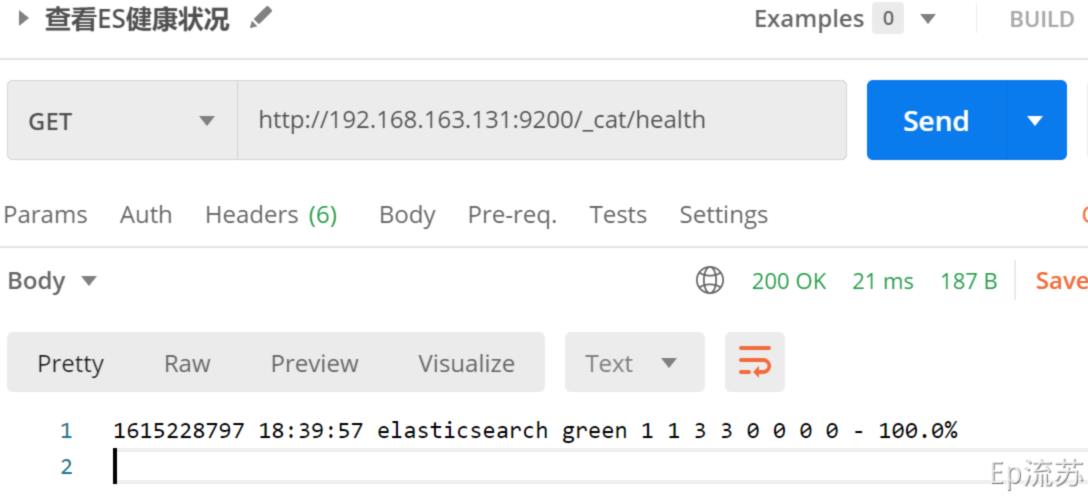
(3)/_cat/master:查看主节点信息
接口:GET http://192.168.163.131:9200/_cat/master
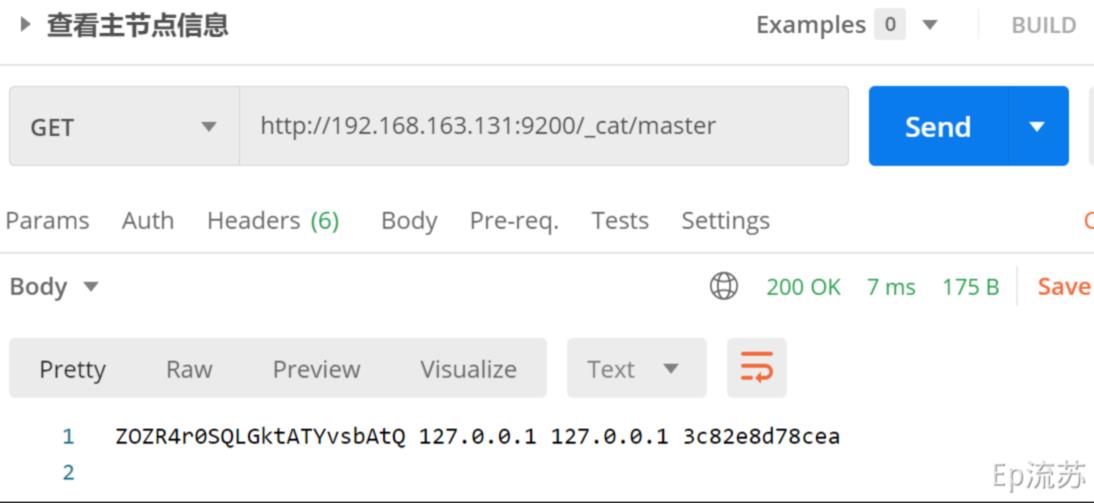
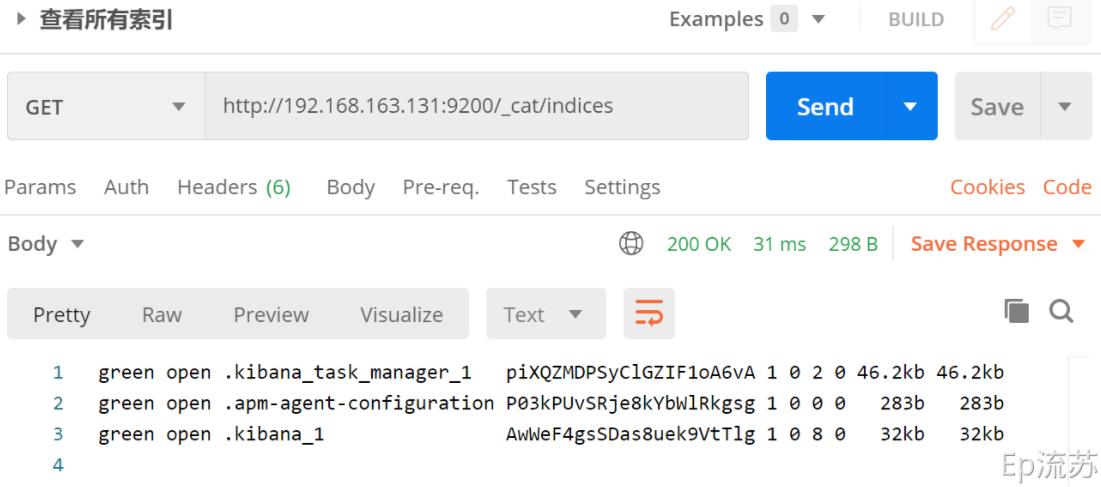
(4) /_cat/indicies:查看所有索引
等价于 mysql 数据库的 show databases;
接口:GET http://192.168.163.131:9200/_cat/indices
3.3 索引一个文档(新增)
即保存一条数据,保存在哪个索引的哪个类型下,指定用哪个唯一标识。
(1)PUT 请求
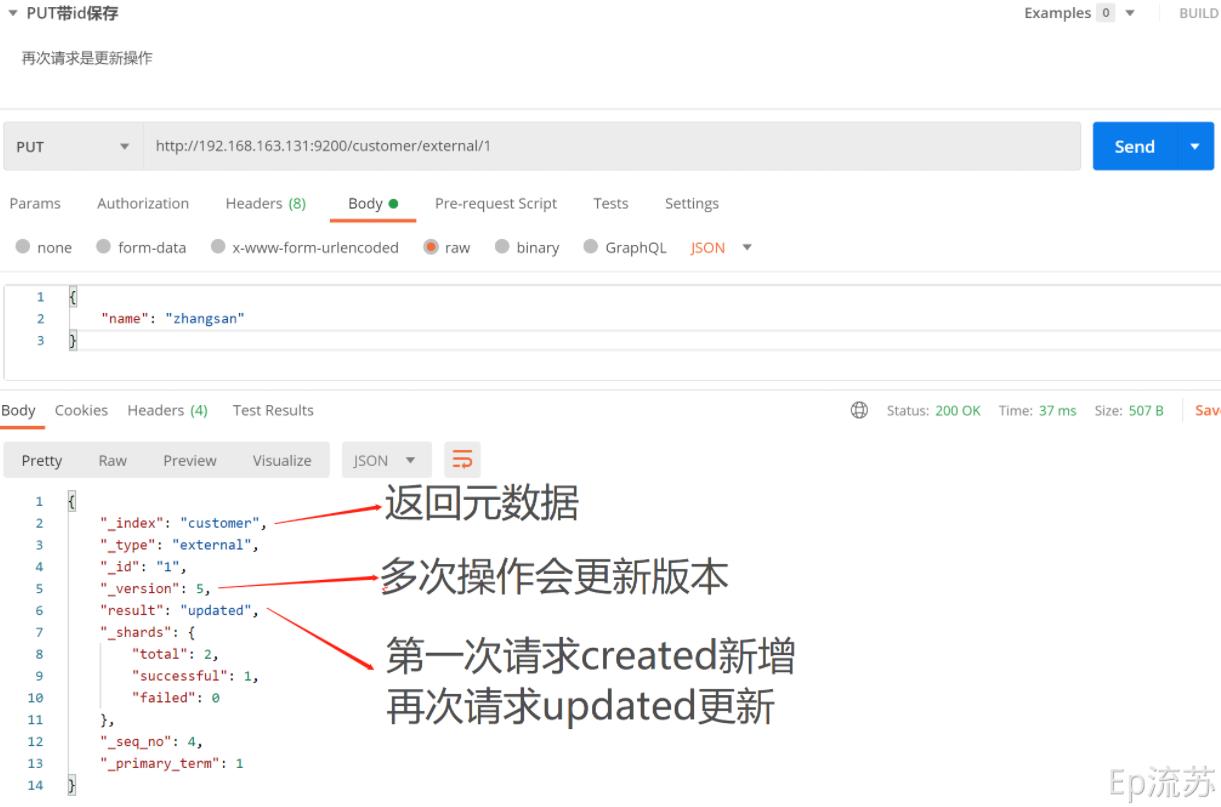
接口:PUT http://192.168.163.131:9200/customer(索引)/external(type)/1(id)
(2)POST请求
接口:POST http://192.168.163.131:9200/customer/external/
案例就没带id,但是自动生成了id

(3)小结
PUT和POST:
- POST新增,如果不指定id,会自动生成id。指定id就会修改这个数据,并新增版本号;
- PUT可以新增也可以修改。PUT必须指定id;由于PUT需要指定id,我们一般用来做修改操作,不指定id会报错。
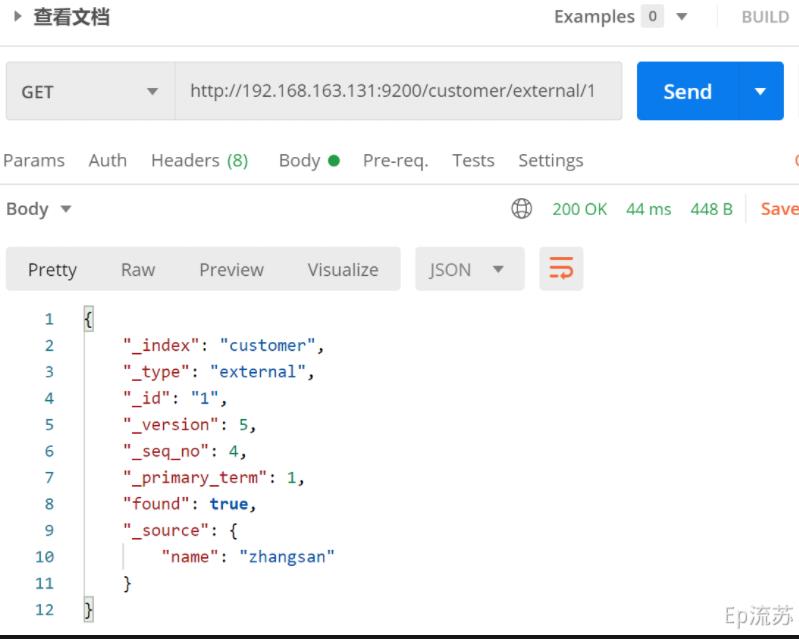
3.4 查看文档
/index/type/id
接口:GET http://192.168.163.131:9200/customer(索引)/external(type)/1(id)
解释:
{
"_index": "customer", # 在哪个索引(库)
"_type": "external", # 在哪个类型(表)
"_id": "1", # 文档id(记录)
"_version": 5, # 版本号
"_seq_no": 4, # 并发控制字段,每次更新都会+1,用来做乐观锁
"_primary_term": 1, # 同上,主分片重新分配,如重启,就会变化
"found": true,
"_source": { # 数据
"name": "zhangsan"
}
}
# 乐观锁更新时携带 ?_seq_no=0&_primary_term=1 当携带数据与实际值不匹配时更新失败3.5 更新文档 /index/type/id/_update
接口:POST http://192.168.163.131:9200/customer/external/1/_update

几种更新文档的区别
在上面索引文档即保存文档的时候介绍,还有两种更新文档的方式:
- 当PUT请求带id,且有该id数据存在时,会更新文档;
- 当POST请求带id,与PUT相同,该id数据已经存在时,会更新文档;
这两种请求类似,即带id,且数据存在,就会执行更新操作。
类比:
- 请求体的报文格式不同,_update方式要修改的数据要包裹在 doc 键下
- _update方式不会重复更新,数据已存在不会更新,版本号不会改变,另两种方式会重复更新(覆盖原来数据),版本号会改变
- 这几种方式在更新时都可以增加属性,PUT请求带id更新和POST请求带id更新,会直接覆盖原来的数据,不会在原来的属性里面新增属性
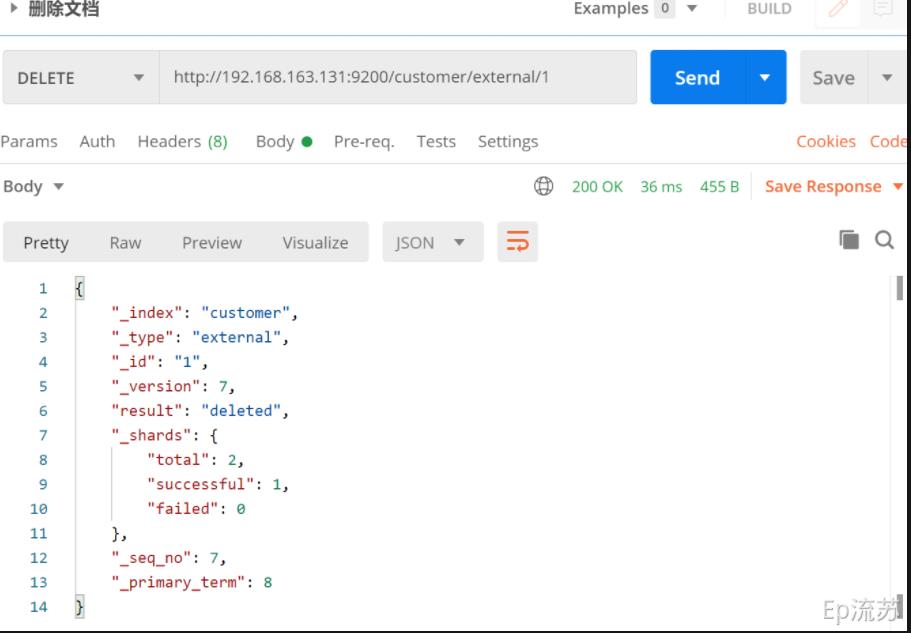
3.6 删除文档&索引
(1)删除文档
接口:DELETE http://192.168.163.131:9200/customer/external/1
(2)删除索引
接口:DELETE http://192.168.163.131:9200/customer

4、 bulk-批量操作数据
语法格式:
{action:{metadata}}\\n // 例如index保存记录,update更新
{request body }\\n //文档的内容了
{action:{metadata}}\\n
{request body }\\n4.1 指定索引和类型的批量操作
接口:POST /customer/external/_bulk
参数:
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name":"John Doe"}
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name":"John Doe"}在Kibana中使用dev-tools测试批量:

4.2 对所有索引执行批量操作
接口:POST /_bulk
参数:
{"delete":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"create":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"title":"my first blog post"}
{"index":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog"}}
{"title":"my second blog post"}
{"update":{"_index":"website","_type":"blog","_id":"123"}}
{"doc":{"title":"my updated blog post"}}
- 这里的批量操作,当发生某一条执行发生失败时,其他的数据仍然能够接着执行,也就是说彼此之间是独立的。
- bulk api以此按顺序执行所有的action(动作)。如果一个单个的动作因任何原因失败,它将继续处理它后面剩余的动作。
- 当bulk api返回时,它将提供每个动作的状态(与发送的顺序相同),所以您可以检查是否一个指定的动作是否失败了。
5、检索案例
本节参考 官方文档 检索示例
(1)5.1 导入样本测试数据
准备一份顾客银行账户信息的虚构的JSON文档样本。每个文档都有下列的 schema(模式)。
{
"account_number": 1,
"balance": 39225,
"firstname": "Amber",
"lastname": "Duke",
"age": 32,
"gender": "M",
"address": "880 Holmes Lane",
"employer": "Pyrami",
"email": "amberduke@pyrami.com",
"city": "Brogan",
"state": "IL"
}指令: POST并且没带id,就是新增如图数据
POST bank/account/_bulk
(2) 请求方式
下面的请求都是在Kibana dev-tools 操作
ES支持两种基本方式检索;
- 通过REST request uri 发送搜索参数 (uri +检索参数);
- 通过REST request body 来发送它们(uri+请求体);
GET bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc
# q=* 查询所有
# sort=account_number:asc 按照account_number进行升序排列
_search: 搜索bank索引中的所有文档
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"account_number": "asc"
}
]
}
# query 查询条件
# sort 排序条件(3)请求后收到的响应数据
{
"took" : 7, #took – how long it took Elasticsearch to run the query, in milliseconds
"timed_out" : false,# whether or not the search request timed out
"_shards" : { #how many shards were searched and a breakdown of how many shards succeeded, failed, or were skipped.
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : { #how many matching documents were found
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null, #the score of the most relevant document found
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "0",
"_score" : null, #the document’s relevance score (not applicable when using match_all)
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 0,
"balance" : 16623,
"firstname" : "Bradshaw",
"lastname" : "Mckenzie",
"age" : 29,
"gender" : "F",
"address" : "244 Columbus Place",
"employer" : "Euron",
"email" : "bradshawmckenzie@euron.com",
"city" : "Hobucken",
"state" : "CO"
},
"sort" : [ #the document’s sort position (when not sorting by relevance score)
0
]
},
...
]
}
}响应结果说明:
Elasticsearch 默认会分页返回10条数据,不会一下返回所有数据。
6、Query DSL
本小节参考官方文档:Query DSL
Elasticsearch提供了一个可以执行查询的Json风格的DSL。这个被称为Query DSL,该查询语言非常全面。
6.1 基本语法格式
- 查询语句典型结构:
QUERY_NAME:{
ARGUMENT:VALUE,
ARGUMENT:VALUE,...
}- 如果针对于某个字段,那么它的结构如下:
{
QUERY_NAME:{
FIELD_NAME:{
ARGUMENT:VALUE,
ARGUMENT:VALUE,...
}
}
}- exp
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 5,
"sort": [
{
"account_number": {
"order": "desc"
},
"balance": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}
# match_all 查询类型【代表查询所有的所有】,es中可以在query中组合非常多的查询类型完成复杂查询;
# from+size 限定,完成分页功能;从第几条数据开始,每页有多少数据
# sort 排序,多字段排序,会在前序字段相等时后续字段内部排序,否则以前序为准;6.2 基础示例
(1)请求
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 5,
"sort": [
{
"account_number": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"_source": ["balance","firstname"]
}
# _source 指定返回结果中包含的字段名(2)返回结果
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "bank",
"_type" : "account",
"_id" : "999",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"firstname" : "Dorothy",
"balance" : 6087
},
"sort" : [
999
]
},
...
]
}
}6.3 match-匹配查询
(1)精确查询-基本数据类型(非文本)
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"account_number": 20
}
}
}
# 查找匹配 account_number 为 20 的数据 非文本推荐使用 term(2)模糊查询-文本字符串
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "mill lane"
}
}
}
# 查找匹配 address 包含 mill 或 lane 的数据match即全文检索,对检索字段进行分词匹配,会按照响应的评分 _score 排序,原理是倒排索引。
(3)精确匹配-文本字符串(注意和上面的模糊查询对比)
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address.keyword": "288 Mill Street"
}
}
}
# 查找 address 为 288 Mill Street 的数据。
# 这里的查找是精确查找,只有完全匹配时才会查找出存在的记录,
# 如果想模糊查询应该使用match_phrase 短语匹配(4)match_phrase-短语匹配
将需要匹配的值当成一整个单词(不分词)进行检索
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "mill lane"
}
}
}
# 这里会检索 address 匹配包含短语 mill lane 的数据(5)multi_math-多字段匹配
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "mill",
"fields": [
"city",
"address"
]
}
}
}
# 检索 city 或 address 匹配包含 mill 的数据,会对查询条件分词6.4 bool - 复合查询
复合语句可以合并,任何其他查询语句,包括复合语句。这也就意味着,复合语句之间
可以互相嵌套,可以表达非常复杂的逻辑。
- must:必须达到must所列举的所有条件
- must_not,必须不匹配must_not所列举的所有条件。
- should,应该满足should所列举的条件。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"gender": "M"
}
},
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
]
}
}
}
# 查询 gender 为 M 且 address 包含 mill 的数据说明:
在boolean查询中,must, should 和must_not 元素都被称为查询子句 。 文档是否符合每个“must”或“should”子句中的标准,决定了文档的“相关性得分”。 得分越高,文档越符合您的搜索条件。 默认情况下,Elasticsearch 返回根据这些相关性得分排序的文档。 (must得分会高于should)
“must_not”子句中的条件被视为“过滤器”。 它影响文档是否包含在结果中,但不影响文档的评分方式。还可以显式地指定任意过滤器来包含或排除基于结构化数据的文档。
6.5 filter-结果过滤
并不是所有的查询都需要产生分数,特别是哪些仅用于filtering过滤的文档。为了不计算分数,elasticsearch会自动检查场景并且优化查询的执行。
filter 对结果进行过滤,且不计算相关性得分。
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"address": "mill"
}
}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"balance": {
"gte": "10000",
"lte": "20000"
}
}
}
}
}
}
# 这里先是查询所有匹配 address 包含 mill 的文档,
# 然后再根据 10000<=balance<=20000 进行过滤查询结果6.6 term-精确检索(一般用于非文本类型)
在上文(3)精确匹配-文本字符串中有介绍对于非文本字段的精确查询,Elasticsearch 官方对于这种非文本字段,使用 term来精确检索是一个推荐的选择。
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.11/query-dsl-term-query.html
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"age": "28"
}
}
}
# 查找 age 为 28 的数据注意:避免使用 term 查询文本字段,文本字段使用(3)精确匹配-文本字符串 来查询
6.7 Aggregation-执行聚合
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.11/search-aggregations.html
- 聚合语法:
GET /my-index-000001/_search
{
"aggs":{
"aggs_name":{ # 这次聚合的名字,方便展示在结果集中
"AGG_TYPE":{ # 聚合的类型(avg,term,terms)
}
}
}
}(1)搜索address中包含mill的所有人的年龄分布以及平均余额
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "Mill"
}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 10
}
},
"ageAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
},
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
# "ageAgg": { --- 聚合名为 ageAgg
# "terms": { --- 聚合类型为 term
# "field": "age", --- 聚合字段为 age
# "size": 10 --- 取聚合后前十个数据
# }
# },
# ------------------------
# "ageAvg": { --- 聚合名为 ageAvg
# "avg": { --- 聚合类型为 avg 求平均值
# "field": "age" --- 聚合字段为 age
# }
# },
# ------------------------
# "balanceAvg": { --- 聚合名为 balanceAvg
# "avg": { --- 聚合类型为 avg 求平均值
# "field": "balance" --- 聚合字段为 balance
# }
# }
# ------------------------
# "size": 0 --- 不显示命中结果,只看聚合信息返回结果:
{
"took" : 10,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"ageAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 38,
"doc_count" : 2
},
{
"key" : 28,
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : 32,
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
},
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 34.0
},
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 25208.0
}
}
}(2)按照年龄聚合,并且求这些年龄段的这些人的平均薪资
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": {
"ageAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}返回结果:
{
"took" : 12,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"ageAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 31,
"doc_count" : 61,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 28312.918032786885
}
},
{
"key" : 39,
"doc_count" : 60,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 25269.583333333332
}
},
{
"key" : 26,
"doc_count" : 59,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 23194.813559322032
}
},
{
"key" : 32,
"doc_count" : 52,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 23951.346153846152
}
},
{
"key" : 35,
"doc_count" : 52,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 22136.69230769231
}
},
{
"key" : 36,
"doc_count" : 52,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 22174.71153846154
}
},
{
"key" : 22,
"doc_count" : 51,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 24731.07843137255
}
},
{
"key" : 28,
"doc_count" : 51,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 28273.882352941175
}
},
{
"key" : 33,
"doc_count" : 50,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 25093.94
}
},
{
"key" : 34,
"doc_count" : 49,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 26809.95918367347
}
},
{
"key" : 30,
"doc_count" : 47,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 22841.106382978724
}
},
{
"key" : 21,
"doc_count" : 46,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 26981.434782608696
}
},
{
"key" : 40,
"doc_count" : 45,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27183.17777777778
}
},
{
"key" : 20,
"doc_count" : 44,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27741.227272727272
}
},
{
"key" : 23,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27314.214285714286
}
},
{
"key" : 24,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 28519.04761904762
}
},
{
"key" : 25,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27445.214285714286
}
},
{
"key" : 37,
"doc_count" : 42,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 27022.261904761905
}
},
{
"key" : 27,
"doc_count" : 39,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 21471.871794871793
}
},
{
"key" : 38,
"doc_count" : 39,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 26187.17948717949
}
},
{
"key" : 29,
"doc_count" : 35,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 29483.14285714286
}
}
]
}
}
}(3)查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中M的平均薪资和F的平均薪资以及这个年龄段的总体平均薪资
GET bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 100
},
"aggs": {
"genderAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "gender.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"balanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
},
"ageBalanceAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
# "field": "gender.keyword" gender是txt没法聚合 必须加.keyword精确替代返回结果:
{
"took" : 17,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"ageAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 31,
"doc_count" : 61,
"genderAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "M",
"doc_count" : 35,
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 29565.628571428573
}
},
{
"key" : "F",
"doc_count" : 26,
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 26626.576923076922
}
}
]
},
"ageBalanceAvg" : {
"value" : 28312.918032786885
}
},
{
"key" : 39,
"doc_count" : 60,
"genderAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "F",
"doc_count" : 38,
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 26348.684210526317
}
},
{
"key" : "M",
"doc_count" : 22,
"balanceAvg" : {
"value" : 23405.68181818182
}
}
]
},
"ageBalanceAvg" : {
"value" : 25269.583333333332
}
},
...
]
}
}
}7、Elasticsearch-Mapping(映射)
官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.11/mapping.html
7.1 简介
Maping是用来定义一个文档(document),以及它所包含的属性(字段field)是如何存储和索引的。
比如:使用maping来定义:
- 哪些字符串属性应该被看做全文本属性(full text fields);
- 哪些属性包含数字,日期或地理位置;
- 文档中的所有属性是否都能被索引(all 配置);
- 日期的格式;
- 自定义映射规则来执行动态添加属性;
查看mapping信息
GET bank/_mapping
{
"bank" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"account_number" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"address" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"balance" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"city" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"email" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"employer" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"firstname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"gender" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"lastname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"state" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}7.2 属性类型
比如上文的keyword, 太多了,不用记忆,用的时候自行查官网手册
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.x/mapping-types.html#_core_datatypes
7.3、 映射操作
7.3.1 创建索引映射
创建索引并指定属性的映射规则(相当于新建表并指定字段和字段类型)
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}返回结果:
{
"acknowledged" : true,
"shards_acknowledged" : true,
"index" : "my_index"
}7.3.2 给已有映射增加字段
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.x/explicit-mapping.html#add-field-mapping
PUT /my_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"employee-id": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
}
}
}
# 这里的 "index": false,表明新增的字段不能被检索。默认是true
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.x/mapping-index.html返回结果:
{
"acknowledged" : true
}7.3.3 查看映射
GET /my_index/_mapping
# 查看某一个字段的映射
GET /my_index/_mapping/field/employee-id返回结果:
{
"my_index" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"email" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"employee-id" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"index" : false
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
}
# index false 表示不能被索引找到7.3.4 更新映射 数据迁移
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.x/explicit-mapping.html#update-mapping
对于已经存在的字段映射,我们不能更新。更新必须创建新的索引,进行数据迁移。
7.3.5 数据迁移
(1)无type数据迁移(Elasticsearch7 以后)
POST reindex [固定写法]
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}(2)有type数据迁移
POST reindex [固定写法]
{
"source":{
"index":"twitter",
"twitter":"twitter"
},
"dest":{
"index":"new_twitters"
}
}(3)数据迁移实例
对于我们的测试数据,是包含 type 的索引 bank。
现在我们创建新的索引 newbank 并修改一些字段的类型来演示当需要更新映射时的数据迁移操作。
① 查看索引 bank 当前字段映射类型
GET /bank/_mapping
# 结果
{
"bank" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"account_number" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"address" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"balance" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"city" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"email" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"employer" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"firstname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"gender" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"lastname" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"state" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}② 创建新索引 newbank 并修改字段类型
PUT /newbank
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"account_number": {
"type": "long"
},
"address": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"balance": {
"type": "long"
},
"city": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"employer": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"firstname": {
"type": "text"
},
"gender": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"lastname": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"state": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}③ 数据迁移
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "bank",
"type": "account"
},
"dest": {
"index": "newbank"
}
}返回结果:
#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in reindex requests is deprecated.
{
"took" : 269,
"timed_out" : false,
"total" : 1000,
"updated" : 0,
"created" : 1000,
"deleted" : 0,
"batches" : 1,
"version_conflicts" : 0,
"noops" : 0,
"retries" : {
"bulk" : 0,
"search" : 0
},
"throttled_millis" : 0,
"requests_per_second" : -1.0,
"throttled_until_millis" : 0,
"failures" : [ ]
}④ 查看迁移后的数据
GET /newbank/_search
# 结果: 迁移后 type 统一为 _doc 移除 type
{
"took" : 367,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1000,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "newbank",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"account_number" : 1,
"balance" : 39225,
"firstname" : "Amber",
"lastname" : "Duke",
"age" : 32,
"gender" : "M",
"address" : "880 Holmes Lane",
"employer" : "Pyrami",
"email" : "amberduke@pyrami.com",
"city" : "Brogan",
"state" : "IL"
}
},
...8、Elasticsearch-分词
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.x/analysis.html
8.1 简介
一个tokenizer(分词器)接收一个字符流,将之分割为独立的tokens(词元,通常是独立的单词),然后输出tokens流。
例如:whitespace tokenizer遇到空白字符时分割文本。它会将文本“Quick brown fox!”分割为[Quick,brown,fox!]。
该tokenizer(分词器)还负责记录各个terms(词条)的顺序或position位置(用于phrase短语和word proximity词近邻查询),以及term(词条)所代表的原始word(单词)的start(起始)和end(结束)的character offsets(字符串偏移量)(用于高亮显示搜索的内容)。
elasticsearch提供了很多内置的分词器,可以用来构建custom analyzers(自定义分词器)。
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}默认的分词器一般都是针对于英文,对于中文我们需要安装额外的分词器来进行分词。
8.2 IK分词器
IK分词器是一个非常好用的中文分词器,下载,安装,测试过程就自行百度了。本文不再赘述
8.3 自定义扩展分词库(结合Nginx)
我们在 nginx 中自定义分词文件,通过配置 es 的 ik 配置文件来远程调用 nginx 中的分词文件来实现自定义扩展词库。
注:默认 nginx 请求的是 数据目录的 html 静态目录
(1)step1:在nginx分词文件中(fenci.txt)自定义新的分词内容
nginx 默认请求地址为 ip:port/fenci.txt;本机为:127.0.0.1:80/fenci.txt
如果想要增加新的词语,只需要在该文件追加新的行并保存新的词语即可。
echo "加拿大电鳗" > /mydata/nginx/html/fenci.txt(2)step2 给 es 配置自定义词库
打开并编辑 ik 插件配置文件
vim /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins/ik/config/IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml修改为以下内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties>
<comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 -->
<entry key="ext_dict"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典-->
<entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 -->
<!-- <entry key="remote_ext_dict">words_location</entry> -->
<entry key="remote_ext_dict">http://192.168.163.131/fenci.txt</entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典-->
<!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> -->
</properties>(3)step3:重启 elasticsearch 容器
docker restart elasticsearch(4)step4: 测试自定义词库
GET my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text":"加拿大电鳗"
}返回结果:
{
"tokens": [
{
"token" : "加拿大电鳗",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
}
]
}9、Elasticsearch—Java API(重点)
和Mysql一样,Elasticsearch同样提供了API来让java程序员来快捷的操作Elasticsearch
9.1 Elasticsearch-Rest-Client 客户端
官方RestClient,封装了ES操作,API层次分明,上手简单;
官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/java-rest/current/java-rest-high.html
9.2 使用示例
9.2.1: 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.4.2</version>
</dependency>特别注意有坑:
elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client 有个子依赖 elasticsearch。这个子依赖在springboot项目中被springboot锁定了版本(具体锁定的版本跟springboot版本有关)。springboot比较强势,该子依赖版本elasticsearch会跟着springboot走,而不是跟着elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client走。
比如在springboot 2.1.8中,elasticsearch 版本被锁定为6.8.6 。 现在我们想让elasticsearch版本和elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client 的7.4.2版本匹配。就需要做以下步骤:
(1)继承的springboot (springboot是父pom 即parent) 大多数情况是这种。
只需要添加合适的<properties>元素。浏览spring-boot-dependencies POM可以获取一个全面的属性列表。例如,想要选择一个不同的elasticsearch版本,你可以添加以下内容:
<properties>
<elasticsearch.version>7.4.2</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>(2)传递来的springboot
以上是关于ElastiSearch默认分词器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
ELK---- Elasticsearch 使用ik中文分词器
Elasticsearch7.8.0版本进阶——IK中文分词器