Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门
Posted qingshandaiyue
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、组件简介
组件系统是Vue.js其中一个重要的概念,它提供了一种抽象,让我们可以使用独立可复用的小组件来构建大型应用,任意类型的应用界面都可以抽象为一个组件树: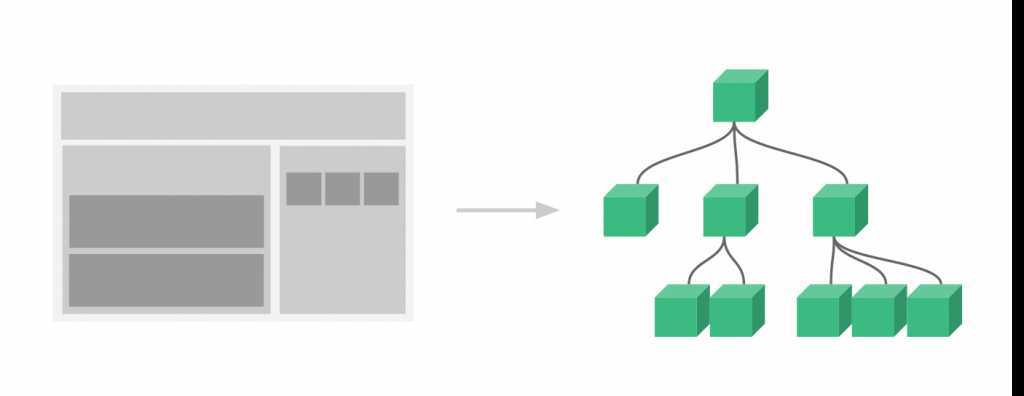
那么什么是组件呢?
组件可以扩展html元素,封装可重用的HTML代码,我们可以将组件看作自定义的HTML元素。
本文的Demo和源代码已放到GitHub,如果您觉得本篇内容不错,请点个赞,或在GitHub上加个星星!
(所有示例都放在GitHub Pages上了,请访问https://github.com/keepfool/vue-tutorials查看示例汇总)
由于组件的篇幅较大,我将会把组件的入门知识分为两篇来讲解,这样也便于各位看官们快速消化。
二、组件的创建和注册
2.1 基本步骤
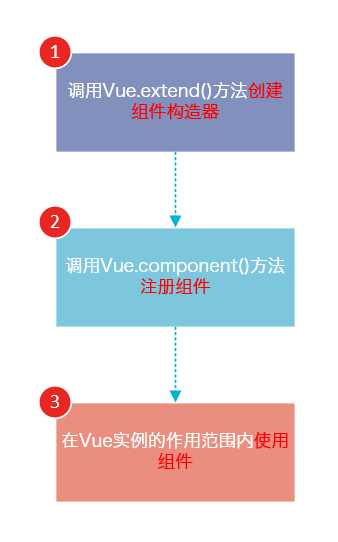
Vue.js的组件的使用有3个步骤:创建组件构造器、注册组件和使用组件。
下面的代码演示了这3个步骤:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- 3. #app是Vue实例挂载的元素,应该在挂载元素范围内使用组件--> <my-component></my-component> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> // 1.创建一个组件构造器 var myComponent = Vue.extend({ template: ‘<div>This is my first component!</div>‘ }) // 2.注册组件,并指定组件的标签,组件的HTML标签为<my-component> Vue.component(‘my-component‘, myComponent) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘ }); </script> </html>
运行结果如下:

可以看到,使用组件和使用普通的HTML元素没什么区别。
2.2 理解组件的创建和注册
我们用以下几个步骤来理解组件的创建和注册:
Vue.extend()是Vue构造器的扩展,调用Vue.extend()创建的是一个组件构造器。2.
Vue.extend()构造器有一个选项对象,选项对象的template属性用于定义组件要渲染的HTML。3. 使用
Vue.component()注册组件时,需要提供2个参数,第1个参数时组件的标签,第2个参数是组件构造器。4. 组件应该挂载到某个Vue实例下,否则它不会生效。
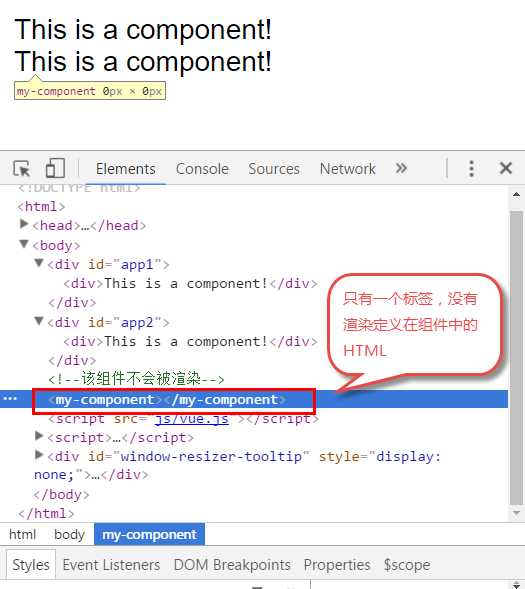
请注意第4点,以下代码在3个地方使用了<my-component>标签,但只有#app1和#app2下的<my-component>标签才起到作用。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <div id="app1"> <my-component></my-component> </div> <div id="app2"> <my-component></my-component> </div> <!--该组件不会被渲染--> <my-component></my-component> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> var myComponent = Vue.extend({ template: ‘<div>This is a component!</div>‘ }) Vue.component(‘my-component‘, myComponent) var app1 = new Vue({ el: ‘#app1‘ }); var app2 = new Vue({ el: ‘#app2‘ }) </script> </html>
2.3 全局注册和局部注册
调用Vue.component()注册组件时,组件的注册是全局的,这意味着该组件可以在任意Vue示例下使用。
如果不需要全局注册,或者是让组件使用在其它组件内,可以用选项对象的components属性实现局部注册。
上面的示例可以改为局部注册的方式:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- 3. my-component只能在#app下使用--> <my-component></my-component> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> // 1.创建一个组件构造器 var myComponent = Vue.extend({ template: ‘<div>This is my first component!</div>‘ }) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, components: { // 2. 将myComponent组件注册到Vue实例下 ‘my-component‘ : myComponent } }); </script> </html>
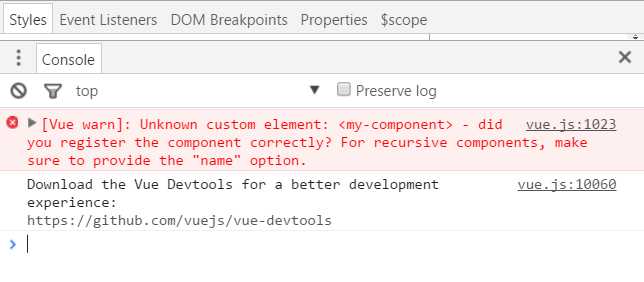
由于my-component组件是注册在#app元素对应的Vue实例下的,所以它不能在其它Vue实例下使用。
<div id="app2"> <!-- 不能使用my-component组件,因为my-component是一个局部组件,它属于#app--> <my-component></my-component> </div> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#app2‘ }); </script>
如果你这样做了,浏览器会提示一个错误:
2.4 父组件和子组件
我们可以在组件中定义并使用其他组件,这就构成了父子组件的关系。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <div id="app"> <parent-component> </parent-component> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> var Child = Vue.extend({ template: ‘<p>This is a child component!</p>‘ }) var Parent = Vue.extend({ // 在Parent组件内使用<child-component>标签 template :‘<p>This is a Parent component</p><child-component></child-component>‘, components: { // 局部注册Child组件,该组件只能在Parent组件内使用 ‘child-component‘: Child } }) // 全局注册Parent组件 Vue.component(‘parent-component‘, Parent) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘ }) </script> </html>
我们分几个步骤来理解这段代码:
var Child = Vue.extend(...)定义一了个Child组件构造器var Parent = Vue.extend(...)定义一个Parent组件构造器components: { ‘child-component‘: Child },将Child组件注册到Parent组件,并将Child组件的标签设置为child-component。template :‘<p>This is a Parent component</p><child-component></child-component>‘,在Parent组件内以标签的形式使用Child组件。Vue.component(‘parent-component‘, Parent)全局注册Parent组件- 在页面中使用<parent-component>标签渲染Parent组件的内容,同时Child组件的内容也被渲染出来
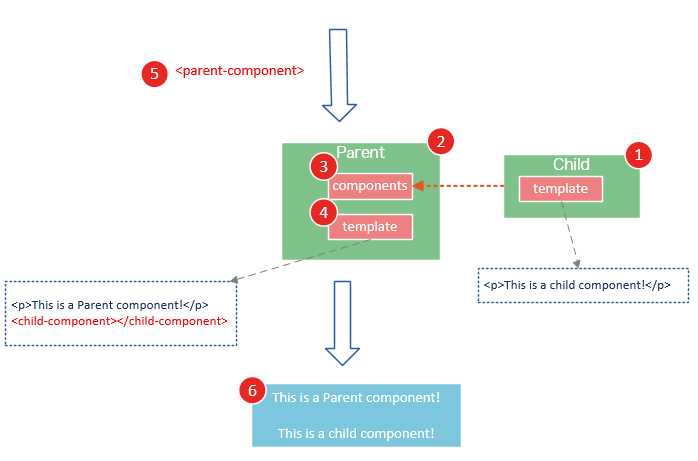
Child组件是在Parent组件中注册的,它只能在Parent组件中使用,确切地说:子组件只能在父组件的template中使用。
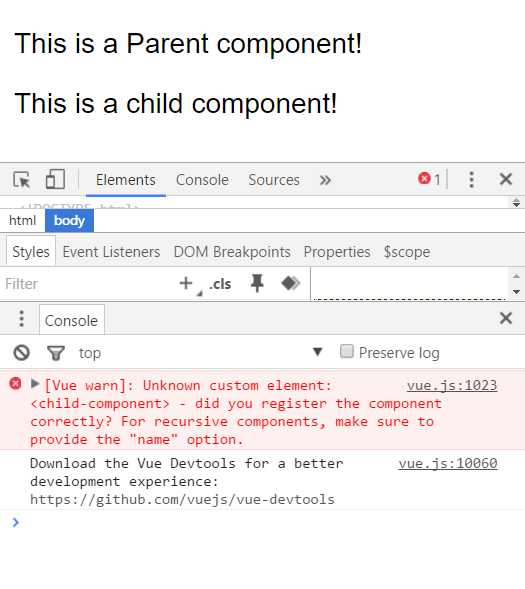
请注意下面两种子组件的使用方式是错误的:
1. 以子标签的形式在父组件中使用
<div id="app"> <parent-component> <child-component></child-component> </parent-component> </div>
2. 在父组件标签外使用子组件
<div id="app"> <parent-component> </parent-component> <child-component> </child-component> </div>
运行这段代码,浏览器会提示以下错误
2.5 组件注册语法糖
以上组件注册的方式有些繁琐,Vue.js为了简化这个过程,提供了注册语法糖。
使用Vue.component()直接创建和注册组件:
// 全局注册,my-component1是标签名称 Vue.component(‘my-component1‘,{ template: ‘<div>This is the first component!</div>‘ }) var vm1 = new Vue({ el: ‘#app1‘ })
Vue.component()的第1个参数是标签名称,第2个参数是一个选项对象,使用选项对象的template属性定义组件模板。
使用这种方式,Vue在背后会自动地调用Vue.extend()。
在选项对象的components属性中实现局部注册:
var vm2 = new Vue({ el: ‘#app2‘, components: { // 局部注册,my-component2是标签名称 ‘my-component2‘: { template: ‘<div>This is the second component!</div>‘ }, // 局部注册,my-component3是标签名称 ‘my-component3‘: { template: ‘<div>This is the third component!</div>‘ } } })
2.6 使用script或template标签
尽管语法糖简化了组件注册,但在template选项中拼接HTML元素比较麻烦,这也导致了HTML和javascript的高耦合性。
庆幸的是,Vue.js提供了两种方式将定义在JavaScript中的HTML模板分离出来。
使用<script>标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <div id="app"> <my-component></my-component> </div> <script type="text/x-template" id="myComponent"> <div>This is a component!</div> </script> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘my-component‘,{ template: ‘#myComponent‘ }) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘ }) </script> </html>
template选项现在不再是HTML元素,而是一个id,Vue.js根据这个id查找对应的元素,然后将这个元素内的HTML作为模板进行编译。

注意:使用<script>标签时,type指定为text/x-template,意在告诉浏览器这不是一段js脚本,浏览器在解析HTML文档时会忽略<script>标签内定义的内容。

使用<template>标签
如果使用<template>标签,则不需要指定type属性。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <my-component></my-component> </div> <template id="myComponent"> <div>This is a component!</div> </template> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘my-component‘,{ template: ‘#myComponent‘ }) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘ }) </script> </html>
在理解了组件的创建和注册过程后,我建议使用<script>或<template>标签来定义组件的HTML模板。
这使得HTML代码和JavaScript代码是分离的,便于阅读和维护。
另外,在Vue.js中,可创建.vue后缀的文件,在.vue文件中定义组件,这个内容我会在后面的文章介绍。
2.7 组件的el和data选项
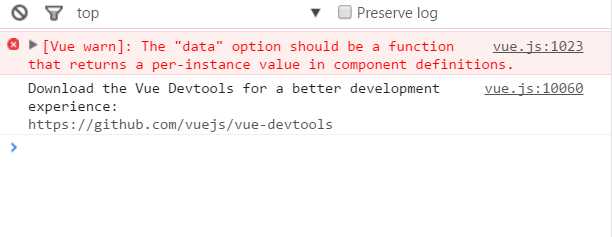
传入Vue构造器的多数选项也可以用在 Vue.extend() 或Vue.component()中,不过有两个特例: data和el。
Vue.js规定:在定义组件的选项时,data和el选项必须使用函数。
下面的代码在执行时,浏览器会提出一个错误
Vue.component(‘my-component‘, {
data: {
a: 1
}
})
另外,如果data选项指向某个对象,这意味着所有的组件实例共用一个data。
我们应当使用一个函数作为 data 选项,让这个函数返回一个新对象:
Vue.component(‘my-component‘, {
data: function(){
return {a : 1}
}
})
三、使用props
组件实例的作用域是孤立的。这意味着不能并且不应该在子组件的模板内直接引用父组件的数据。可以使用 props 把数据传给子组件。
3.1 props基础示例
下面的代码定义了一个子组件my-component,在Vue实例中定义了data选项。
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
name: ‘keepfool‘,
age: 28
},
components: {
‘my-component‘: {
template: ‘#myComponent‘,
props: [‘myName‘, ‘myAge‘]
}
}
})
为了便于理解,你可以将这个Vue实例看作my-component的父组件。
如果我们想使父组件的数据,则必须先在子组件中定义props属性,也就是props: [‘myName‘, ‘myAge‘]这行代码。
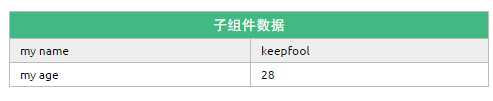
定义子组件的HTML模板:
<template id="myComponent"> <table> <tr> <th colspan="2"> 子组件数据 </th> </tr> <tr> <td>my name</td> <td>{{ myName }}</td> </tr> <tr> <td>my age</td> <td>{{ myAge }}</td> </tr> </table> </template>
将父组件数据通过已定义好的props属性传递给子组件:
<div id="app"> <my-component v-bind:my-name="name" v-bind:my-age="age"></my-component> </div>
注意:在子组件中定义prop时,使用了camelCase命名法。由于HTML特性不区分大小写,camelCase的prop用于特性时,需要转为 kebab-case(短横线隔开)。例如,在prop中定义的myName,在用作特性时需要转换为my-name。
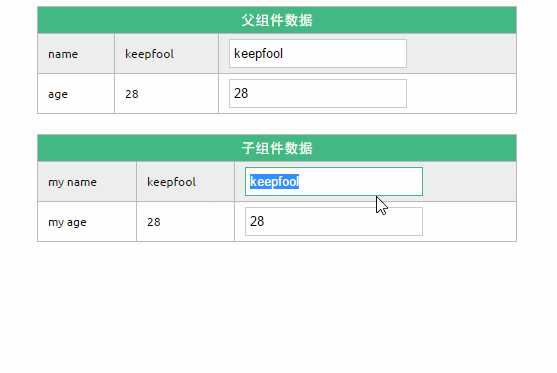
这段程序的运行结果如下:
父组件是如何将数据传给子组件的呢?相信看了下面这图,也许你就能很好地理解了。
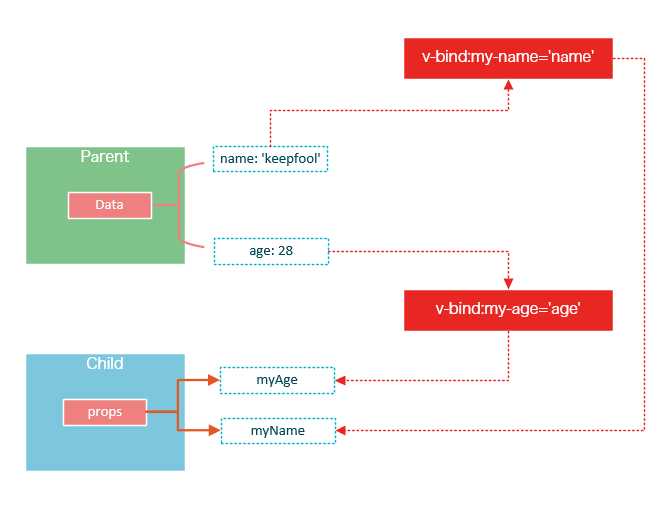
在父组件中使用子组件时,通过以下语法将数据传递给子组件:
<child-component v-bind:子组件prop="父组件数据属性"></child-component>
3.2 prop的绑定类型
单向绑定
既然父组件将数据传递给了子组件,那么如果子组件修改了数据,对父组件是否会有所影响呢?
我们将子组件模板和页面HTML稍作更改:
<div id="app"> <table> <tr> <th colspan="3">父组件数据</td> </tr> <tr> <td>name</td> <td>{{ name }}</td> <td><input type="text" v-model="name" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>age</td> <td>{{ age }}</td> <td><input type="text" v-model="age" /></td> </tr> </table> <my-component v-bind:my-name="name" v-bind:my-age="age"></my-component> </div> <template id="myComponent"> <table> <tr> <th colspan="3">子组件数据</td> </tr> <tr> <td>my name</td> <td>{{ myName }}</td> <td><input type="text" v-model="myName" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>my age</td> <td>{{ myAge }}</td> <td><input type="text" v-model="myAge" /></td> </tr> </table> </template>
运行这个页面,我们做两个小试验:
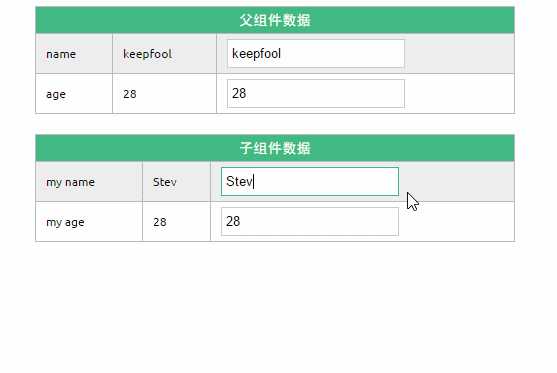
1. 在页面上修改子组件的数据
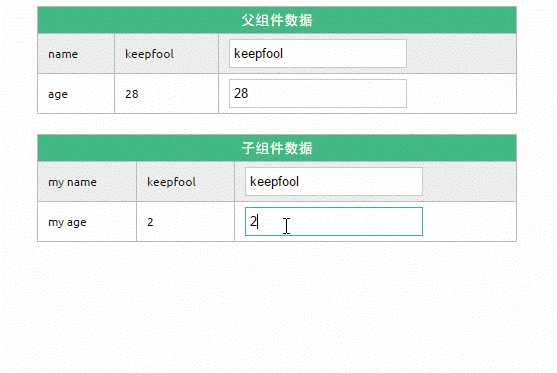
修改了子组件的数据,没有影响父组件的数据。
2. 在页面上修改父组件的数据
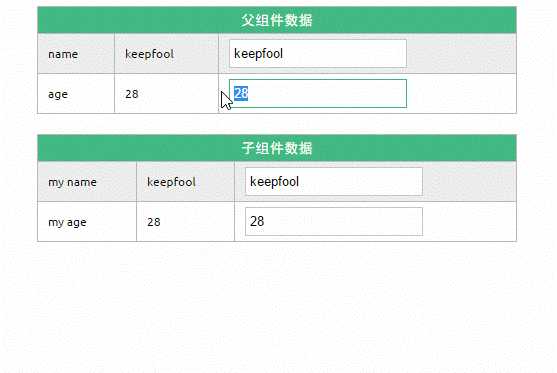
修改了父组件的数据,同时影响了子组件。
双向绑定
可以使用.sync显式地指定双向绑定,这使得子组件的数据修改会回传给父组件。
<my-component v-bind:my-name.sync="name" v-bind:my-age.sync="age"></my-component>
单次绑定
可以使用.once显式地指定单次绑定,单次绑定在建立之后不会同步之后的变化,这意味着即使父组件修改了数据,也不会传导给子组件。
<my-component v-bind:my-name.once="name" v-bind:my-age.once="age"></my-component>
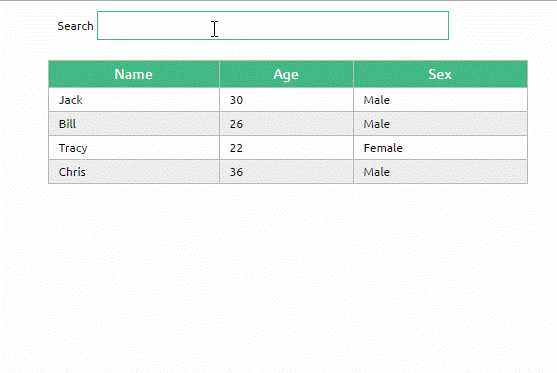
示例
为了尽快消化这些知识,我们来做一个小示例吧。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles/demo.css" /> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div id="searchBar"> Search <input type="text" v-model="searchQuery" /> </div> <simple-grid :data="gridData" :columns="gridColumns" :filter-key="searchQuery"> </simple-grid> </div> <template id="grid-template"> <table> <thead> <tr> <th v-for="col in columns"> {{ col | capitalize}} </th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for="entry in data | filterBy filterKey"> <td v-for="col in columns"> {{entry[col]}} </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </template> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘simple-grid‘, { template: ‘#grid-template‘, props: { data: Array, columns: Array, filterKey: String } }) var demo = new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, data: { searchQuery: ‘‘, gridColumns: [‘name‘, ‘age‘, ‘sex‘], gridData: [{ name: ‘Jack‘, age: 30, sex: ‘Male‘ }, { name: ‘Bill‘, age: 26, sex: ‘Male‘ }, { name: ‘Tracy‘, age: 22, sex: ‘Female‘ }, { name: ‘Chris‘, age: 36, sex: ‘Male‘ }] } }) </script> </html>
除了以上介绍的知识点,这个示例还用到了两个知识点:
1. prop验证
props: {
data: Array,
columns: Array,
filterKey: String
}
这段代码表示:父组件传递过来的data和columns必须是Array类型,filterKey必须是字符串类型。
更多prop验证的介绍,请参考:官方文档prop验证
2. filterBy过滤器
可以根据指定的字符串过滤数据。
使用组件的前提是创建并注册组件,本篇文章详细介绍了组件从创建到使用的步骤,并介绍了几种不同的方式去创建和注册组件;然后介绍了组件的props选项,它用于将父组件的数据传递给子组件,最后我们用一个小的示例演示了这些知识点。我们重点介绍了组件的创建、注册和使用,熟练这几个步骤将有助于深入组件的开发。另外,在子组件中定义props,可以让父组件的数据传递下来,这就好比子组件告诉父组件:“嘿,老哥,我开通了一个驿站,你把东西放到驿站我就可以拿到了。”
今天我们将着重介绍slot和父子组件之间的访问和通信,slot是一个非常有用的东西,它相当于一个内容插槽,它是我们重用组件的基础。Vue的事件系统独立于原生的DOM事件,它用于组件之间的通信。
本文的主要内容如下:
- 组件的编译作用域
- 在组件template中使用<slot>标签作为内容插槽
- 使用$children, $refs, $parent 实现父子组件之间的实例访问
- 在子组件中,使用$dispatch向父组件派发事件;在父组件中,使用$broadcast向子组件传播事件
- 结合这些基础知识,我们一步一步实现一个CURD的示例
注意:以下示例的组件模板都定义在<template>标签中,然而IE不支持<template>标签,这使得在IE中<template>标签中的内容会显示出来。解决办法——隐藏<template>标签
template{
display: none;
}
个浏览器对<template>标签的支持情况,请参见:http://caniuse.com/#feat=template
四、编译作用域
尽管使用组件就像使用一般的HTML元素一样,但它毕竟不是标准的HTML元素,为了让浏览器能够识别它,组件会被解析为标准的HTML片段,然后将组件的标签替换为该HTML片段。
<div id="app"> <my-component> </my-component> </div> <template id="myComponent"> <div> <h2>{{ msg }}</h2> <button v-on:click="showMsg">Show Message</button> </div> </template> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, components: { ‘my-component‘: { template: ‘#myComponent‘, data: function() { return { msg: ‘This is a component!‘ } }, methods: { showMsg: function() { alert(this.msg) } } } } })
这段代码定义了一个my-component组件,<my-component><my-component>不是标准的HTML元素,浏览器是不理解这个元素的。
那么Vue是如何让浏览器理解<my-component><my-component>标签的呢?(下图是我个人的理解)
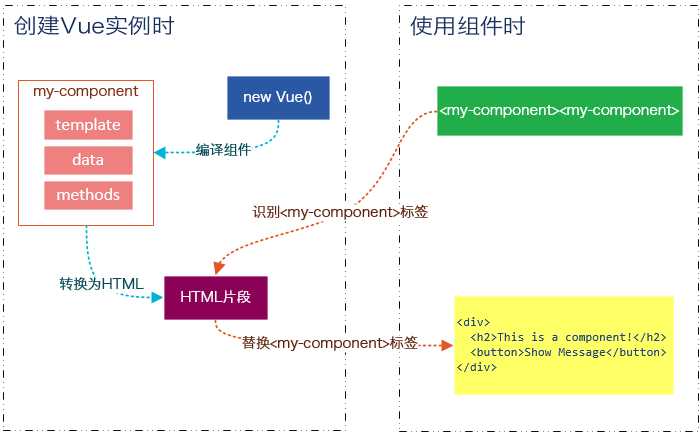
在创建一个Vue实例时,除了将它挂载到某个HTML元素下,还要编译组件,将组件转换为HTML片段。
除此之外,Vue实例还会识别其所挂载的元素下的<my-component>标签,然后将<my-component>标签替换为HTML片段。
实际上浏览器仍然是不理解<my-component>标签的,我们可以通过查看源码了解到这一点。
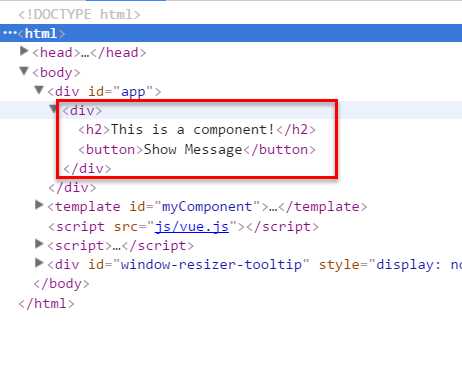
组件在使用前,经过编译已经被转换为HTML片段了,组件是有一个作用域的,那么组件的作用域是什么呢?
你可以将它理解为组件模板包含的HTML片段,组件模板内容之外就不是组件的作用域了。
例如,my-component组件的作用域只是下面这个小片段。
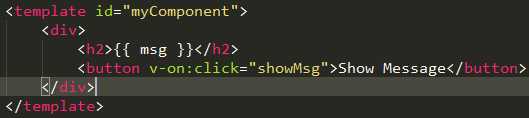
组件的模板是在其作用域内编译的,那么组件选项对象中的数据也应该是在组件模板中使用的。
考虑下面的代码,在Vue实例和组件的data选项中分别追加一个display属性:
new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
display: true
},
components: {
‘my-component‘: {
template: ‘#myComponent‘,
data: function() {
return {
msg: ‘This is a component!‘,
display: false
}
},
methods: {
showMsg: function() {
alert(this.msg)
}
}
}
}
})
然后在my-component标签上使用指令v-show="display",这个display数据是来源于Vue实例,还是my-component组件呢?
<div id="app"> <my-component v-show="display"> </my-component> </div>
答案是Vue实例。
至此,我们应该认识到组件的作用域是独立的:
通俗地讲,在子组件中定义的数据,只能用在子组件的模板。在父组件中定义的数据,只能用在父组件的模板。如果父组件的数据要在子组件中使用,则需要子组件定义props。
五、使用Slot
为了让组件可以组合,我们需要一种方式来混合父组件的内容与子组件自己的模板。这个处理称为内容分发,Vue.js 实现了一个内容分发 API,使用特殊的 <slot> 元素作为原始内容的插槽。
如果不理解这段话,可以先跳过,你只要知道<slot>元素是一个内容插槽。
单个Slot
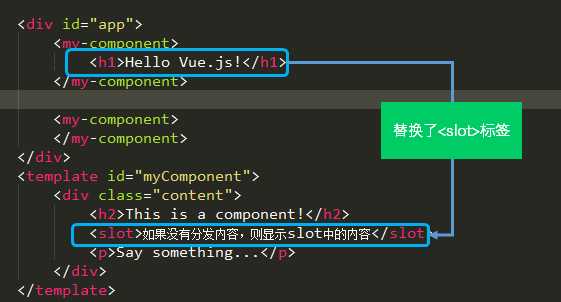
下面的代码在定义my-component组件的模板时,指定了一个<slot></slot>元素。
<div id="app"> <my-component> <h1>Hello Vue.js!</h1> </my-component> <my-component> </my-component> </div> <template id="myComponent"> <div class="content"> <h2>This is a component!</h2> <slot>如果没有分发内容,则显示slot中的内容</slot> <p>Say something...</p> </div> </template> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘my-component‘, { template: ‘#myComponent‘ }) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘ }) </script>
这段代码运行结果如下:
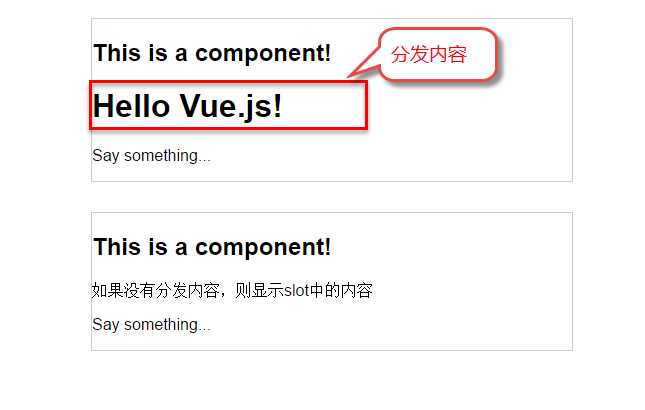
第一个<my-component>标签有一段分发内容<h1>Hello Vue.js!</h1>,渲染组件时显示了这段内容。
第二个<my-component>标签则没有,渲染组件时则显示了slot标签中的内容。
指定名称的slot
上面这个示例是一个匿名slot,它只能表示一个插槽。如果需要多个内容插槽,则可以为slot元素指定name属性。
多个slot一起使用时,会非常有用。例如,对话框是HTML常用的一种交互方式。
在不同的运用场景下,对话框的头部、主体内容、底部可能是不一样的。

这时,使用不同名称的slot就能轻易解决这个问题了。
<template id="dialog-template"> <div class="dialogs"> <div class="dialog" v-bind:class="{ ‘dialog-active‘: show }"> <div class="dialog-content"> <div class="close rotate"> <span class="iconfont icon-close" @click="close"></span> </div> <slot name="header"></slot> <slot name="body"></slot> <slot name="footer"></slot> </div> </div> <div class="dialog-overlay"></div> </div> </template> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘modal-dialog‘, { template: ‘#dialog-template‘, props: [‘show‘], methods: { close: function() { this.show = false } } }) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, data: { show: false }, methods: { openDialog: function() { this.show = true }, closeDialog: function() { this.show = false } } }) </script>
在定义modal-dialog组件的template时,我们使用了3个slot,它们的name特性分别是header、body和footer。
在<modal-dialog>标签下,分别为三个元素指定slot特性:
<div id="app"> <modal-dialog v-bind:show.sync="show"> <header class="dialog-header" slot="header"> <h1 class="dialog-title">提示信息</h1> </header> <div class="dialog-body" slot="body"> <p>你想在对话框中放什么内容都可以!</p> <p>你可以放一段文字,也可以放一些表单,或者是一些图片。</p> </div> <footer class="dialog-footer" slot="footer"> <button class="btn" @click="closeDialog">关闭</button> </footer> </modal-dialog> <button class="btn btn-open" @click="openDialog">打开对话框</button> </div>
对话框的标题内容、主体内容、底部内容,完全由我们自定义,而且这些内容就是一些简单的HTML元素!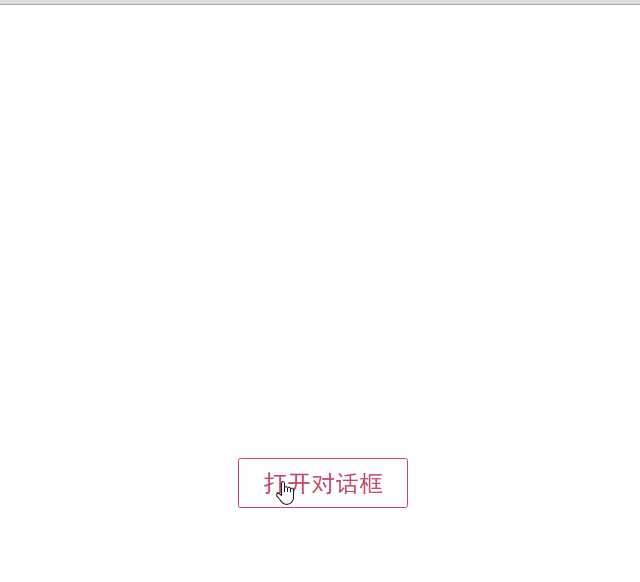
如果需要定制对话框的样式,我们只需要在<modal-dialog>上追加一个v-bind指令,让它绑定一个class。
<modal-dialog v-bind:show.sync="show" v-bind:class="dialogClass">
然后修改一下Vue实例,在data选项中追加一个dialogClass属性,然后修改openDialog()方法:
new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
show: false,
dialogClass: ‘dialog-info‘
},
methods: {
openDialog: function(dialogClass) {
this.show = true
this.dialogClass = dialogClass
},
closeDialog: function() {
this.show = false
}
}
})

虽然我们在modal-dialog组件中定义了3个slot,但是在页面中使用它时,并不用每次都指定这3个slot。
比如,有时候我们可能只需要header和body:
<modal-dialog v-bind:show.sync="show" v-bind:class="dialogClass"> <header class="dialog-header" slot="header"> <h1 class="dialog-title">提示信息</h1> </header> <div class="dialog-body" slot="body"> <p>你想在对话框中放什么内容都可以!</p> <p>你可以放一段文字,也可以放一些表单,或者是一些图片。</p> </div> </modal-dialog>
现在看到的对话框是没有底部的,只有标题和主体内容。
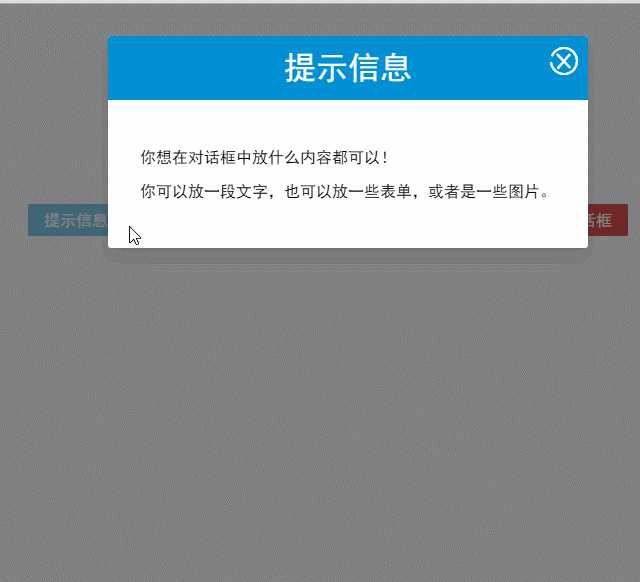
多个slot同时使用的场景还有很多,例如:用户的注册、登录、找回密码等这些表单集合,也可以用一个组件来完成。
父子组件之间的访问
有时候我们需要父组件访问子组件,子组件访问父组件,或者是子组件访问根组件。
针对这几种情况,Vue.js都提供了相应的API:
- 父组件访问子组件:使用
$children或$refs - 子组件访问父组件:使用
$parent - 子组件访问根组件:使用
$root
$children示例
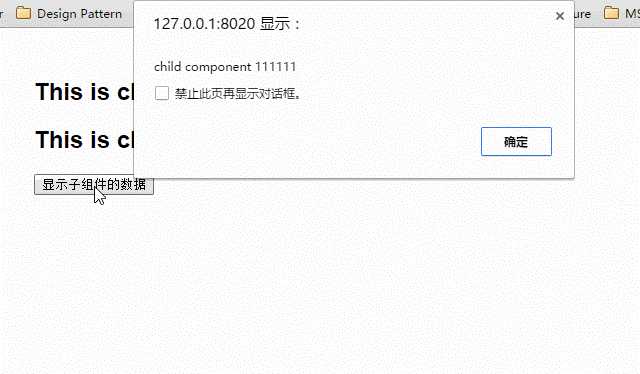
下面这段代码定义了3个组件:父组件parent-component,两个子组件child-component1和child-component2。
在父组件中,通过this.$children可以访问子组件。this.$children是一个数组,它包含所有子组件的实例。
<div id="app"> <parent-component></parent-component> </div> <template id="parent-component"> <child-component1></child-component1> <child-component2></child-component2> <button v-on:click="showChildComponentData">显示子组件的数据</button> </template> <template id="child-component1"> <h2>This is child component 1</h2> </template> <template id="child-component2"> <h2>This is child component 2</h2> </template> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘parent-component‘, { template: ‘#parent-component‘, components: { ‘child-component1‘: { template: ‘#child-component1‘, data: function() { return { msg: ‘child component 111111‘ } } }, ‘child-component2‘: { template: ‘#child-component2‘, data: function() { return { msg: ‘child component 222222‘ } } } }, methods: { showChildComponentData: function() { for (var i = 0; i < this.$children.length; i++) { alert(this.$children[i].msg) } } } }) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘ }) </script>
$refs示例
组件个数较多时,我们难以记住各个组件的顺序和位置,通过序号访问子组件不是很方便。
在子组件上使用v-ref指令,可以给子组件指定一个索引ID:
<template id="parent-component"> <child-component1 v-ref:cc1></child-component1> <child-component2 v-ref:cc2></child-component2> <button v-on:click="showChildComponentData">显示子组件的数据</button> </template>
在父组件中,则通过$refs.索引ID访问子组件的实例:
showChildComponentData: function() {
alert(this.$refs.cc1.msg);
alert(this.$refs.cc2.msg);
}
$parent示例
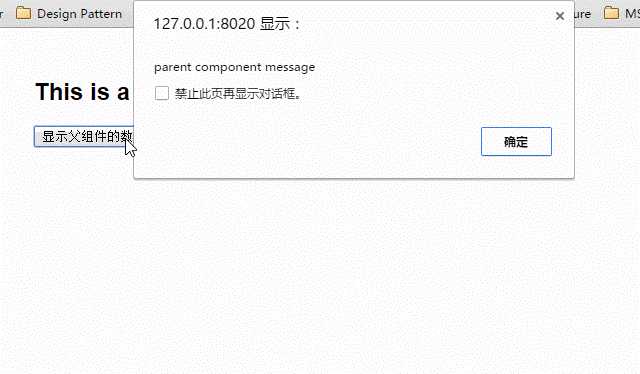
下面这段代码定义了两个组件:child-component和它的父组件parent-component。
在子组件中,通过this.$parent可以访问到父组件的实例。
<div id="app"> <parent-component></parent-component> </div> <template id="parent-component"> <child-component></child-component> </template> <template id="child-component"> <h2>This is a child component</h2> <button v-on:click="showParentComponentData">显示父组件的数据</button> </template> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘parent-component‘, { template: ‘#parent-component‘, components: { ‘child-component‘: { template: ‘#child-component‘, methods: { showParentComponentData: function() { alert(this.$parent.msg) } } } }, data: function() { return { msg: ‘parent component message‘ } } }) new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘ }) </script>
注意:尽管可以访问父链上任意的实例,不过子组件应当避免直接依赖父组件的数据,尽量显式地使用 props 传递数据。另外,在子组件中修改父组件的状态是非常糟糕的做法,因为:
1.这让父组件与子组件紧密地耦合;
2. 只看父组件,很难理解父组件的状态。因为它可能被任意子组件修改!理想情况下,只有组件自己能修改它的状态。
自定义事件
有时候我们希望触发父组件的某个事件时,可以通知到子组件;触发子组件的某个事件时,可以通知到父组件。
Vue 实例实现了一个自定义事件接口,用于在组件树中通信。这个事件系统独立于原生 DOM 事件,用法也不同。
每个 Vue 实例都是一个事件触发器:
- 使用
$on()监听事件; - 使用
$emit()在它上面触发事件; - 使用
$dispatch()派发事件,事件沿着父链冒泡; - 使用
$broadcast()广播事件,事件向下传导给所有的后代。
派发事件
下面这段代码是一个简单的事件派发处理
<div id="app"> <p>Messages: {{ messages | json }}</p> <child-component></child-component> </div> <template id="child-component"> <input v-model="msg" /> <button v-on:click="notify">Dispatch Event</button> </template> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> // 注册子组件 Vue.component(‘child-component‘, { template: ‘#child-component‘, data: function() { return { msg: ‘‘ } }, methods: { notify: function() { if (this.msg.trim()) { this.$dispatch(‘child-msg‘, this.msg) this.msg = ‘‘ } } } }) // 初始化父组件 new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, data: { messages: [] }, events: { ‘child-msg‘: function(msg) { this.messages.push(msg) } } }) </script>
我们将这个示例分为几个步骤解读:
- 子组件的button元素绑定了click事件,该事件指向
notify方法 - 子组件的
notify方法在处理时,调用了$dispatch,将事件派发到父组件的child-msg事件,并给该该事件提供了一个msg参数 - 父组件的events选项中定义了
child-msg事件,父组件接收到子组件的派发后,调用child-msg事件。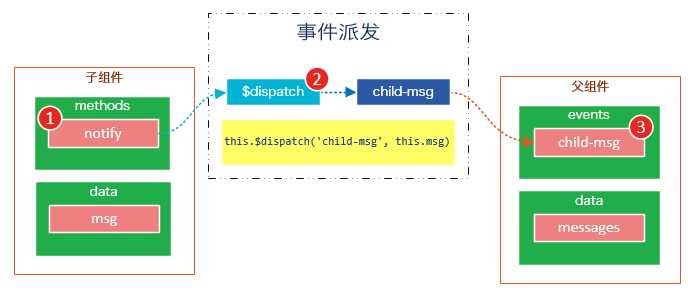
- 运行结果如下:

广播事件
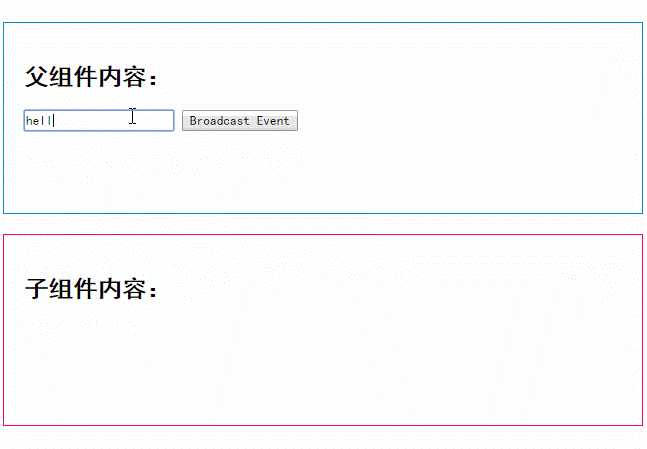
下面这段代码是一个简单的事件广播处理
<div id="app"> <input v-model="msg" /> <button v-on:click="notify">Broadcast Event</button> <child-component></child-component> </div> <template id="child-component"> <ul> <li v-for="item in messages"> 父组件录入了信息:{{ item }} </li> </ul> </template> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> // 注册子组件 Vue.component(‘child-component‘, { template: ‘#child-component‘, data: function() { return { messages: [] } }, events: { ‘parent-msg‘: function(msg) { this.messages.push(msg) } } }) // 初始化父组件 new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, data: { msg: ‘‘ }, methods: { notify: function() { if (this.msg.trim()) { this.$broadcast(‘parent-msg‘, this.msg) } } } }) </script>
我们将这个示例分为几个步骤解读:
- 父组件的button元素绑定了click事件,该事件指向
notify方法 - 父组件的
notify方法在处理时,调用了$broadcast,将事件派发到子组件的parent-msg事件,并给该该事件提供了一个msg参数 - 子组件的events选项中定义了
parent-msg事件,子组件接收到父组件的广播后,调用parent-msg事件。
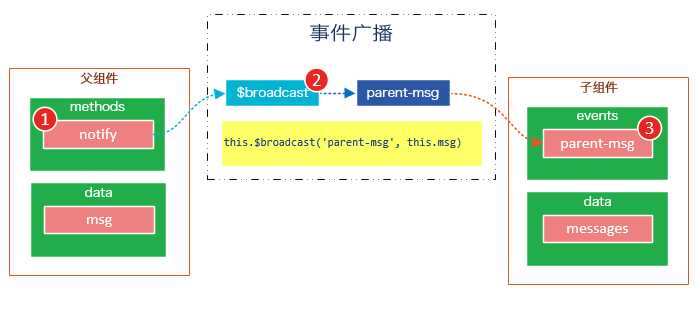
运行结果如下:
CURD示例
Vue.js组件的API来源于三部分——prop,slot和事件。
- prop 允许外部环境传递数据给组件;
- 事件 允许组件触发外部环境的 action;
- slot 允许外部环境插入内容到组件的视图结构内。
至此,这三部分我都已经介绍完了,接下来我就用这些知识来教大家一步一步完成一个CURD示例。
第1步——创建表格组件,添加查询和删除功能
创建表格组件,添加过滤,数据删除功能
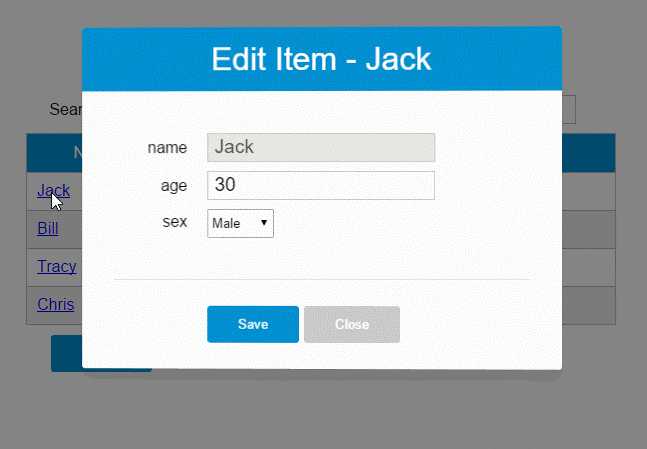
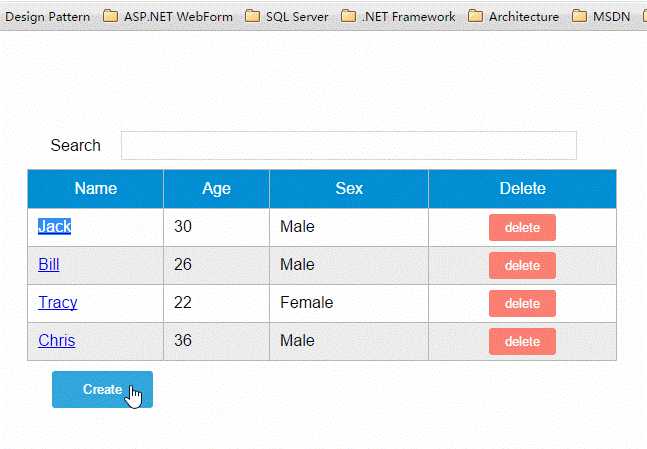
<div id="app"> <div class="container"> <div class="form-group"> <label>Search</label> <input type="text" class="search-input" v-model="searchQuery" /> </div> </div> <div class="container"> <simple-grid :data-list="people" :columns="columns" :search-key="searchQuery"> </simple-grid> </div> </div> <template id="grid-template"> <table> <thead> <tr> <th v-for="col in columns"> {{ col.name | capitalize}} </th> <th> Delete </th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr v-for="(index,entry) in dataList | filterBy searchKey"> <td v-for="col in columns"> {{entry[col.name]}} </td> <td class="text-center"> <button @click="deleteItem(index)">delete</button> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </template> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component(‘simple-grid‘, { template: ‘#grid-template‘, props: [‘dataList‘, ‘columns‘, ‘searchKey‘], methods: { deleteItem: function(index) { this.dataList.splice(index, 1); }, } }) var demo = new Vue({ el: ‘#app‘, data: { searchQuery: ‘‘, columns: [{ name: ‘name‘ }, { name: ‘age‘ }, { name: ‘sex‘ }], people: [{ name: ‘Jack‘, age: 30, sex: ‘Male‘ }, { name: ‘Bill‘, age: 26, sex: ‘Male‘ }, { name: ‘Tracy‘, age: 22, sex: ‘Female‘ }, { name: ‘Chris‘, age: 36, sex: ‘Male‘ }] } }) </script>
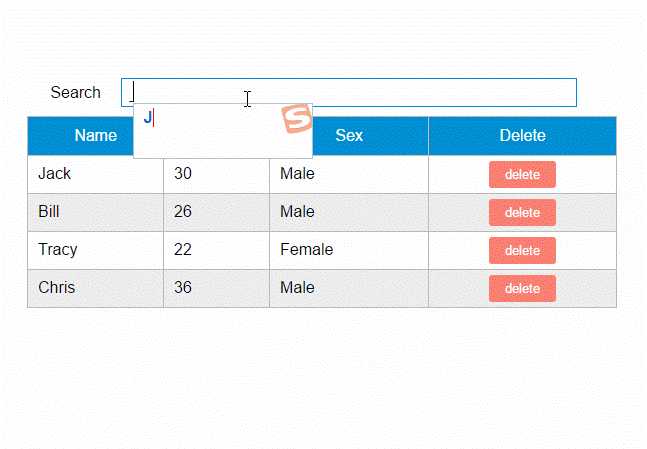
使用知识点
1. 使用Vue.component语法糖
Vue.component是创建并注册组件的语法糖,使用Vue.component注册的组件是全局的。
2. 使用prop将父组件数据传递给子组件
#app元素是父组件,simple-grid是子组件。
在simple-grid组件中定义选项props: [‘dataList‘, ‘columns‘, ‘searchKey‘]
在#app下使用<simple-grid :data-list="people" :columns="columns" :search-key="searchQuery"> 将数据传递给simple-grid组件
3. 使用过滤器
{{ col.name | capitalize}}使用了capitalize过滤器,将字符串的首字母转换为大写后输出。filterBy filterKey使用了filterBy过滤器,根据指定条件过滤数组元素,filterBy返回过滤后的数组。
4. 使用数组索引别名
数组默认的索引名称为$index,v-for="(index,entry) in dataList使用了数组索引别名。
括号中的第一个参数index是$index的别名,第二个参数是遍历的数组元素。
5. 使用了v-bind和v-on指令的缩写
<simple-grid :data-list="people" :columns="columns" :search-key="searchQuery"> 使用了v-bind指令的缩写。:data-list是v-bind:data-list的缩写,:columns是v-bind:columns的缩写,:search-key是v-bind:search-key的缩写。
<button @click="deleteItem(index)">delete</button> 使用了v-on指令的缩写,@click是v-on:click的缩写。
第2步——创建对话框组件
表格数据的添加和修改,我们使用模态对话框来实现。
模态对话框有两种模式,新建模式和修改模式,分别用于新建一条数据和修改指定的数据。
由于对话框的内容来源于具体的数据,所以我们可以考虑将对话框作为simple-grid组件的一个子组件。
modal-dialog组件的模板内容:
<template id="dialog-template"> <div class="dialogs"> <div class="dialog" v-bind:class="{ ‘dialog-active‘: show }"> <div class="dialog-content"> <header class="dialog-header"> <h1 class="dialog-title">{{ title }}</h1> </header> <footer class="dialog-footer"> <div class="form-group"> <label></label> <button v-on:click="save">Save</button> <button v-on:click="close">Close</button> </div> </footer> </div> </div> <div class="dialog-overlay"></div> </div> </template>
modal-dialog组件在simple-grid组件中注册:
Vue.component(‘simple-grid‘, { // ...已省略 data: function() { return { mode: 0, item: {} titie: ‘‘ } }, components: { ‘modal-dialog‘: { template: ‘#dialog-template‘, data: function() { return { // 对话框默认是不显示的 show: false } }, /* * mode = 1是新增数据模式,mode = 2是修改数据模式 * title表示对话框的标题内容 * fields表示对话框要显示的数据字段数组 * item是由simple-dialog传下来,用于绑定表单字段的 */ props: [‘mode‘, ‘title‘, ‘fields‘, ‘item‘], methods: { close: function() { this.show = false }, save: function() { } } } } // ...已省略 }) 由于modal-dialog组件是simple-grid的子组件,所以它应该在simple-grid的template中使用: <template id="grid-template"> <!--...前面的内容已省略 --> <modal-dialog :mode="mode" :title="title" :fields="columns" :item="item"> </modal-dialog> <!--...后面的内容已省略 --> </template>
modal-dialog组件的props选项,追加了3个元素:
- title表示对话框的标题内容
- fields表示对话框要显示的数据字段数组
- item用于绑定表单字段,它是一个对象
注意:由于modal-dialog是一个子组件,它仅用于simple-grid组件的新增或修改模式,所以modal-dialog的template没有使用
使用知识点
1. 使用组件的局部注册
modal-dialog组件没有使用Vue.component进行全局注册,使用simple-grid组件components选项实现了局部注册。
2. 使用组件的data选项
组件的data选项必须以函数的方式返回。
第3步——实现数据新建功能
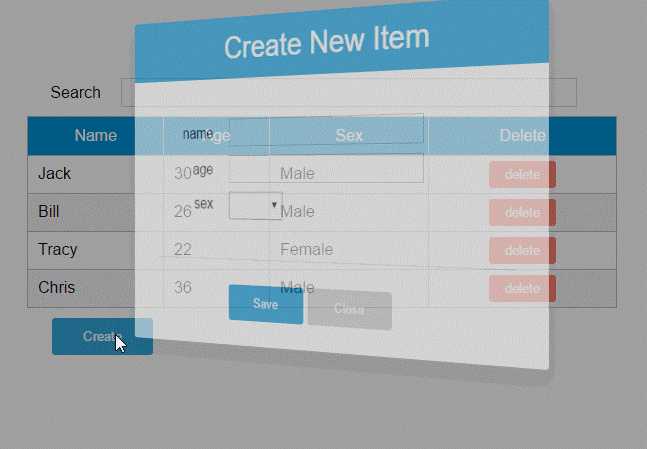
1. 修改Vue实例的data选项的columns:
var demo = new Vue({
// ...已省略
columns: [{
name: ‘name‘,
isKey: true
}, {
name: ‘age‘
}, {
name: ‘sex‘,
dataSource: [‘Male‘, ‘Female‘]
}]
// ...已省略
})
为’name’列追加一个isKey属性,并设置为true,表示该列为主键列。
为’sex’列追加一个dataSoruce属性,并设置为[‘Male’, ‘Female’],表示新增或修改数据时选择性别的下拉框数据源。
2. 修改modal-dialog的template:
<template id="dialog-template"> <div class="dialogs"> <div class="dialog" v-bind:class="{ ‘dialog-active‘: show }"> <div class="dialog-content"> <header class="dialog-header"> <h1 class="dialog-title">{{ title }}</h1> </header> <div v-for="field in fields" class="form-group" > <label>{{ field.name }}</label> <select v-if="field.dataSource" v-model="item[field.name]"> <option v-for="opt in field.dataSource" :value="opt">{{ opt }}</option> </select> <input v-else type="text" v-model="item[field.name]"> </div> <footer class="form-group"> <label></label> <button v-on:click="save">Save</button> <button v-on:click="close">Close</button> </footer> </div> </div> <div class="dialog-overlay"></div> </div> </template>
在modal-dialog组件的模板中遍历fields,然后显示field的名称。
在渲染表单时,根据是否有dataSource判定表单是下拉框还是文本框。
(由于示例较为简陋,所以只提供了input和select两种表单类型)
注意modal-dialog组件的fields是由Vue实例传递给simple-grid,然后再由simple-grid传递过来的。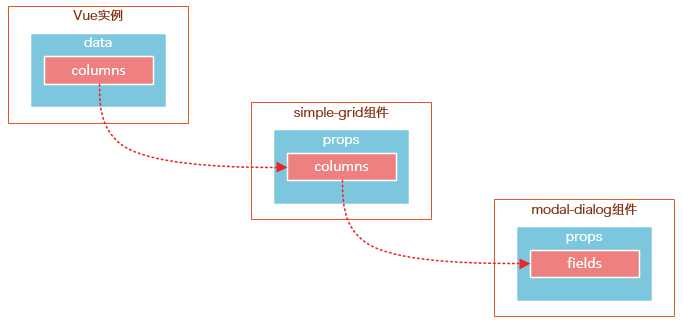
3. 修改simple-grid的template
<template id="grid-template"> <!--...已省略 --> <div class="container"> <button class="btn" @click="openNewItemDialog(‘Create new item‘)">Create</button> </div> <modal-dialog :mode="mode" :title="title" :fields="columns" :item="item" v-on:create-item="createItem"> </modal-dialog> </template>
添加一个Create按钮,绑定click事件到openNewItemDiaolog()方法,该方法用于打开modal-dialog组件,并将模式设置为新建模式。 在<modal-dialog>标签上给sample-grid绑定一个自定义事件create-item,后面在$dispatch派发事件时会用到。 4. 修改simple-grid的methods选项
Vue.component(‘simple-grid‘, {
// ...已省略
methods: {
openNewItemDialog: function(title) {
// 对话框的标题
this.title = title
// mode = 1表示新建模式
this.mode = 1
// 初始化this.item
this.item = {}
// 广播事件,showDialog是modal-dialog组件的一个方法,传入参数true表示显示对话框
this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, true)
},
createItem: function() {
// 将item追加到dataList
this.dataList.push(this.item)
// 广播事件,传入参数false表示隐藏对话框
this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, false)
// 新建完数据后,重置item对象
this.item = {}
},
deleteItem: function(index) {
this.dataList.splice(index, 1);
},
},
// ...已省略
})
追加了两个方法:opeNewItemDialog和createItem方法。
opeNewItemDialog方法用于打开对话框,this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, true) 调用子组件modal-dialog的showDialog事件,传入参数true表示显示对话框。
createItem方法用于保存新建的数据,this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, false) 调用子组件modal-dialog的showDialog事件,传入参数false表示隐藏对话框。
5. 修改modal-grid的methods和events选项
Vue.component(‘simple-grid‘, {
// ...已省略
components: {
‘modal-dialog‘: {
// ...已省略
methods: {
close: function() {
this.show = false
},
save: function() {
//新建模式
if (this.mode === 1){
// 使用$dispatch调用simple-grid的create-item方法
this.$dispatch(‘create-item‘)
}
}
},
events: {
// 显示或隐藏对话框
‘showDialog‘: function(show) {
this.show = show
}
}
}
}
// ...已省略
})
修改methods选项的save方法,由于保存按钮是在子组件modal-dialog中的,而createItem方法是在父组件simple-grid中的,所以这里使用this.$dispatch(‘create-item‘) 派发到父组件的自定义事件create-item。
追加events选项,添加showDialog事件,用于显示或隐藏对话框。
请将4和5结合起来看,我们既用到了$broadcast广播事件,又用到了$dispatch派发事件。
下面这幅图有助于理解simple-grid和modal-dialog组件之间的通信: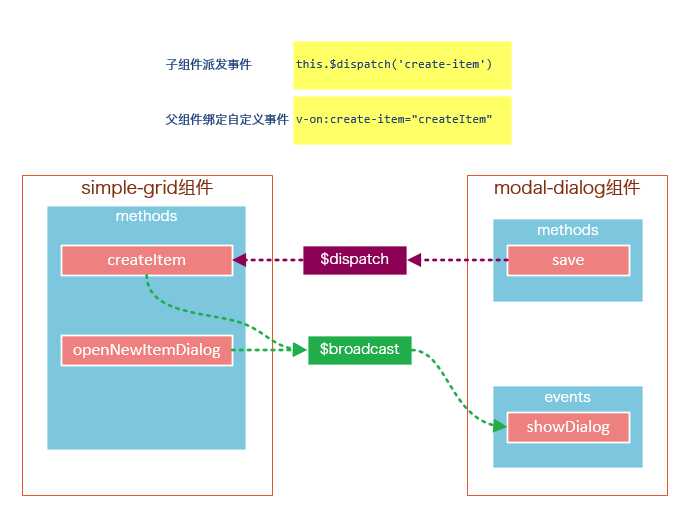
create-item是一个自定义事件,由子组件modal-dialog调用this.$dispatch(‘create-item‘) 派发到自定义事件create-item,自定义事件create-item是绑定在父组件simple-grid上的,该事件会执行createItem方法。
第4步——实现数据修改功能
1. 修改sample-grid的template
<template id="grid-template"> <!--...已省略--> <tbody> <tr v-for="(index,entry) in dataList | filterBy searchKey"> <td v-for="col in columns"> <span v-if="col.isKey"><a href="javascript:void(0)" @click="openEditItemDialog(index, ‘Edit item ‘ + entry[col.name])">{{entry[col.name]}}</a></span> <span v-else>{{entry[col.name]}}</span> </td> </tr> </tbody> <!--...已省略--> <modal-dialog :mode="mode" :title="title" :item="item" :fields="columns" v-on:create-item="createItem" v-on:update-item="updateItem"> </modal-dialog> </template>
遍历列表数据时,使用v-if指令判断当前列是否为主键列,如果是主键列,则给主键列添加链接,然后给链接绑定click事件,click事件用于打开修改数据的对话框。
在<modal-dialog>标签上,给sample-grid绑定自定义事件update-item,update-item事件指向sample-grid的方法updateItem。
2. 修改modal-dialog的template
<div v-for="field in fields" class="form-group"> <label>{{ field.name }}</label> <select v-if="field.dataSource" v-model="item[field.name]" :disabled="mode === 2 && field.isKey"> <option v-for="opt in field.dataSource" :value="opt">{{ opt }}</option> </select> <input v-else type="text" v-model="item[field.name]" :disabled="mode === 2 && field.isKey"> </div>
在修改模式下(mode = 2),如果当前字段是主键字段,则禁止修改。
3. 修改sample-grid的methods选项
// 弹出修改数据的对话框时,使用对象的深拷贝 initItemForUpdate: function(p) { var c = c || {}; for (var i in p) { // 属性i是否为p对象的自有属性 if (p.hasOwnProperty(i)) { if (typeof p[i] === ‘object‘) { c[i] = Array.isArray(p[i]) ? [] : {} deepCopy(p[i], c[i]) } else { // 属性是基础类型时,直接拷贝 c[i] = p[i] } } } return c; }, findItemByKey: function(key){ var keyColumn = this.keyColumn for(var i = 0; i < this.dataList.length; i++){ if(this.dataList[i][keyColumn] === key){ return this.dataList[i] } } }, createItem: function() { // 将item追加到dataList this.dataList.push(this.item) // 广播事件,传入参数false表示隐藏对话框 this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, false) // 新建完数据后,重置item对象 this.item = {} }, updateItem: function() { // 获取主键列 var keyColumn = this.keyColumn for (var i = 0; i < this.dataList.length; i++) { // 根据主键查找要修改的数据,然后将this.item数据更新到this.dataList[i] if (this.dataList[i][keyColumn] === this.item[keyColumn]) { for (var j in this.item) { this.dataList[i][j] = this.item[j] } break; } } // 广播事件,传入参数false表示隐藏对话框 this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, false) // 修改完数据后,重置item对象 this.item = {} }
追加的内容:调用内置的ready()函数,openEditDialog、updateItem、findItemByKey和initItemForUpdate方法。
ready()函数会在编译结束和 $el 第一次插入文档之后调用,你可以将其理解为jQuery中的document.ready()。
在ready()函数中,初始化keyColumn,keyColumn表示主键列,调用updateItem方法时,会根据主键数据找到dataList中匹配的元素。
opeEditItemDialog方法用于打开对话框,this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, true) 调用子组件modal-dialog的showDialog事件,传入参数true表示显示对话框。
ready()函数没有特别的业务逻辑,主要是获取主键列,调用updateItem方法时,会根据主键数据找到dataList中匹配的元素。
updateItem方法用于保存修改的数据,this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, false) 调用子组件modal-dialog的showDialog事件,传入参数false表示隐藏对话框。
initItemForUpdate方法用于将选中的数据this.dataList[index]深拷贝到this.item。为什么要使用深拷贝呢?因为this.dataList[index]是一个引用对象,它有一些属性也是引用类型的,如果使用浅拷贝可能得到一些超出预期的效果。

4.修改modal-dialog的methods选项
save: function() {
//新建模式
if (this.mode === 1) {
// 使用$dispatch调用simple-grid的create-item事件
this.$dispatch(‘create-item‘)
}else if(this.mode === 2){
// 使用$dispatch调用simple-grid的update-item事件
this.$dispatch(‘update-item‘)
}
}
修改methods选项中的save方法,this.mode === 2时,将事件派发到父组件的update-item事件。
第5步——修改数据新建功能
修改sample-grid的methods选项,追加itemExists方法,然后修改createItem方法。
itemExists: function(keyColumn) { for (var i = 0; i < this.dataList.length; i++) { if (this.item[keyColumn] === this.dataList[i][keyColumn]) return true; } return false; }, createItem: function() { var keyColumn = this.getKeyColumn() if (!this.itemExists(keyColumn)) { // 将item追加到dataList this.dataList.push(this.item) // 广播事件,传入参数false表示隐藏对话框 this.$broadcast(‘showDialog‘, false) // 新建完数据后,重置item对象 this.item = {} } else { alert(keyColumn + ‘ "‘ + this.item[keyColumn] + ‘" is already exists‘) } }
由于主键列数据是不能重复的,所以在新增数据时需要判断主键列数据是否已经存在。
总结
说到底,组件的API主要来源于以下三部分:
- prop 允许外部环境传递数据给组件;
- 事件 允许组件触发外部环境的 action;
- slot 允许外部环境插入内容到组件的视图结构内。
这三大知识点在上下两篇文章中都体现出来了,限于篇幅和个人知识的匮乏,我并不能将组件的所有特性都描述出来,这还需要靠各位花一些时间去多多了解官网的API,并付诸实践。
如果要构建一些大型的应用,基于组件的开发模式是一个不错的选择,我们将整个系统拆分成一个一个小组件,就像乐高一样,然后将这些组件拼接起来。
原文出处:Web前端开发 » http://www.ujiuyeweb.com/archives/419
以上是关于Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章