ARM/cacheDynamIQ架构及cache的替换策略
Posted 不积跬步无以至千里mmbb26
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ARM/cacheDynamIQ架构及cache的替换策略相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ARM的DynamIQ架构
ARM CPU的架构都基于big.LITTLE大小核技术。在big.LITTLE的基础上,又添加了DynamIQ。单一Cluster中最多可以有8个core,且支持不同架构的core,以及支持不同的clk。从而提升了工作效率和配置弹性。
使用以下图片来说明DynamIQ的工作原理:
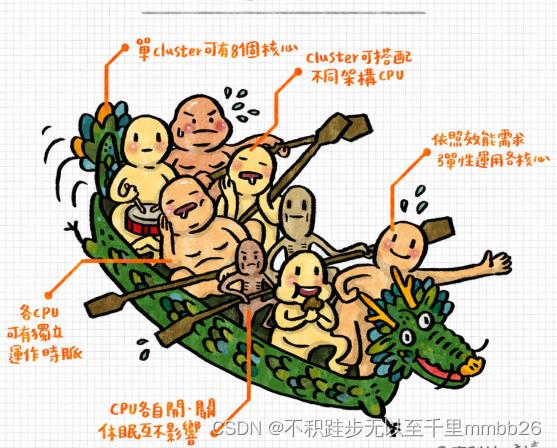
DynamIQ是ARM一个新的底层solution,用于连接在一个芯片上的不同core。
DynamIQ支持将不同类型的core放到一个cluster中。比如,将性能core,和能效core放进同一个cluster。如果没有DynamIQ,只能将性能core和能效core分别放在2个不同cluster中的。(结合上下文,此处有疑点,此处的放在一个cluster概念,我理解应该是指放在同一颗SOC中?)
最常见 4个Cortex-A72 核与4个Cortex-A53核,或者4个Cortex-A53与另外的4个Cortex-A53核配对。
把核心放在同一个cluster中能保证核与核之间更好的通信。
2、DynamIQ的cluster也可以与其他不同的DynamIQ cluster配对。DynamIQ cluster还可以应用ARMv8.2架构和DynamIQ Share Unit hardware,目前支持的平台有:Cortex-A76, Cortex-A75, Cortex-A55
比如:QCOM Krait385 Gold配合三星M3核集成至SDM845中;而三星Exynos9810则使用Cortex-A75作为base结构。海思麒麟980和SDM855使用Cortex-A76作为base结构。
DynamIQ 关键特性
1、Single cluster Design

大小核可以放在同一个簇里(上文中的疑点此处已阐明)。每个核可以按照各自需求工作在不同的频率,也可以单独的控制每个核开关。虽然可以有8个不同频率的核,但是实现起来,会带来更多的cost。
2、Power Saving Featues
把所有核到放到同一个簇里,可以降低memory latency(为啥?),并且简化了核与核之间的tasks sharing。LITTLE核是对memory latency非常敏感的。换句话说,就是在不增加功耗的前提下,提升性能。DynamIQ技术也让核能更快的下电,进一步省电了。
Meet the DynamIQ Shared Unit
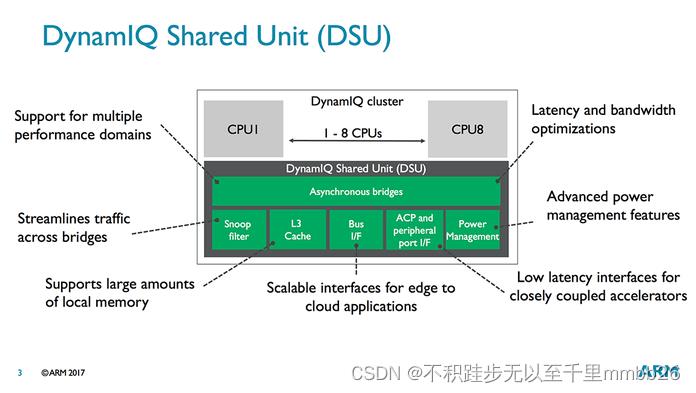
所有弹性的设计架构都仰仗着DynamIQ Shared Unit(DSU)。它构建了CPU、L3 cache、Snoop Filter、外围设备总线buses、power management features之间Asynchronous (异步)通信的桥梁。DSU的设计同时也起到了节省功耗和时间的作用。
1、DynamIQ中首次允许设计带有L3 cache的ARM SOC。这块memeory pool被簇中的所有核共享,它最大的好处是在于能简化big核与LITTLE核之间的task sharing,同时减少memory latency。
2、 L3 cache是16路相联的缓存,可以配置0KB~4MB大小。memory setup是高度专用的,仅有一小部分被L1、L2、L3共享。L3 cache最多可以分成4块partition,这样可以避免cache chrashing、不同进程使用同一块内存等。并且partition可以通过软件进行动态分配。
为了提高performance和充分利用新的memory子系统,ARM也在DSU中使用了cache stashing。它允许相近的coupled accelerators和I/O agents 对部分CPU memory进行direct access(direct读写每一个核的shared L3/L2 caches)。

思路是这样的:peripherals和accelerator的需要CPU进行快速处理的信息,可以以最小的latency,直接inject到CPU的memory中;而不是通过高latency的RAM读写或者prefetch。包括network系统的包处理,与DSP、虚拟加速器的通信,或者是VR应用所使用的视觉捕捉芯片的数据。这种就是基于特定应用的new feature,但能给SOC和designers更灵活、更强大的潜在性能提升。
回到功耗部分,不同CPU集成到一个cluster,这需要重新考虑一套通过DynamIQ来管理功耗和频率的方法。可选的异步bridges的使用,就可以在单个core的基础上配置的CPU clk domains;而之前只能基于单个cluster控制。Designer也可以选择core的频率与DSU的速度同步。
换句话说,通过DynamIQ,每个CPU理论上都可以跑在自己所需的频率上。而事实上,相同类型的core更多地是绑定到同一个domain group组,同步控制频率和电压,因此功耗是是按group组控制的,而非以单个core。ARM表示:big.LITTLE需要big cores和LITTLE cores分别动态的进行分频和分压。
以上内容摘抄自wiki:
DynamIQ扫盲文
DynamIQ技术详解
自2011年ARM big.LITTLE技术推出以来,它已经成为了目前运用非常广泛的多核架构技术。而全新推出的DynamIQ技术则是big.LITTLE技术的重要演进。
原有的big.LITTLE技术是将多个大核组成一个计算集群、多个小核组成另一个计算集群,然后进行协作运行。而全新的DynamIQ big.LITTLE将允许在单一计算集群上进行大小核配置,可以出现比如1+3、1+7、3+5等诸多类型(目前最多可以支持配置8核),将可配置性提升到了一个新的台阶。同时,DynamIQ big.LITTLE还可以对每一个处理器进行独立的频率控制以及开、关、休眠状态的控制,可以实现高效的、无缝的在不同任务间切换最合适的处理器。
此外,DynamIQ还对内存子系统进行了重新设计,可以对内存进行更细颗粒度的管理,实现更快的数据读取和全新的节能特性。
而DynamIQ的这些特性都将使得DynamIQ big.LITTLE在功耗上的表现也更为突出。
DynamIQ big.LITTLE不仅可以在单一计算集群上进行大小核配置,同时也可以通过结合Corelink等技术,实现多个计算集群的组合,而这也意味着,未来可能会出现一个(5+3)的大核计算集群+一个(2+6)小核计算集群或者更多的四五个计算集群的架构。
在智能手机这样的移动终端上,可能使用一个8核的DynamIQ计算集群就足够了(目前有哪些手机SOC芯片厂商在采用此类技术?),但是在企业级市场,确实可能会可能会用到多个DynamIQ计算集群,所以将会用到16核甚至更多核的情况,而这也是为什么说DynamIQ也非常适合企业级市场的原因。
DynamIQ技术仅在ARM V8.2及以后的内核版本才支持。同时在IP授权模式上也将会与ARM以往的策略一样。
以上内容摘抄自wiki:
ARM全新DynamIQ技术详解:真正的人工智能手机要来了!
DynamIQ的方案于2017年5月出现,它是基于big.LITTLE进行扩展和设计的,可视作是big.LITTLE技术的演进。但同原生的big.LITTLE不同的是,因为它采用了ARMv8.2中一些独有的特性,因此与之前的ARM架构不能完全兼容,所以只用在Cortex-A75和Cortex-A55及以后处理器上。
在DynamIQ中,“大核”和“小核”的概念依然存在,但构成一个cluster的cores可以属于不同的micro-architecture,因此其可扩展性比big.LITTLE要强。DynamIQ允许至多32个clusters,每个cluster支持最多8个cores,具体的配置可以配成"0+8", “1+7”, "2+2+4"等等。
DSU和L3
每个core有自己独立的L2 cache,同一cluster的所有core共享DSU(DynamIQ Shared Unit)单元中的L3 cache。任务在大小核之间的迁移可以在同一cluster内完成,不需要跨越不同的clusters,而且迁移过程中数据的传递可以借助L3 cache,而不是CCI,减少了总线竞争,因此更加高效。
L3 cache的大小从0KB到4MB不等,因为一个cluster中的CPU数目可能较多,为了减少维护cache一致性造成的cache thrashing问题,L3可被划分为至多4个groups,且这种划分可以在软件运行期间动态进行。
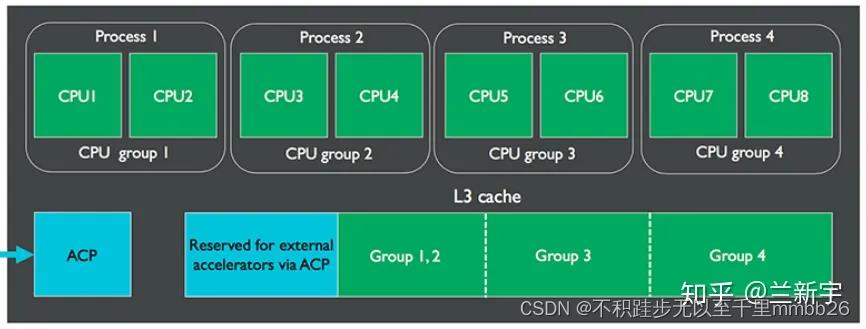
此外,当L3的使用率不高时,还可以group为单位,通过power-gating技术关闭L3中的部分存储空间,减小功耗,这已经被Energy Aware Scheduling所支持。
以上内容摘抄自wiki:
从big.LITTLE到DynamIQ [二]
经典的DynamIQ的cache架构如下:
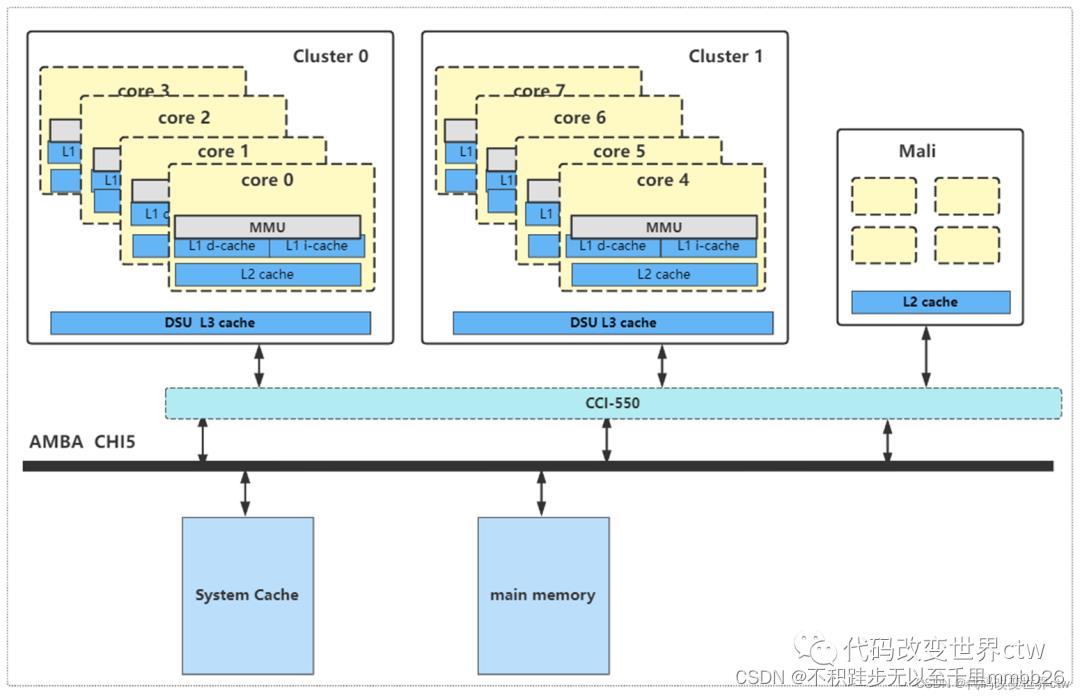
1、L1 / L2 cache直接的替换策略
DynamIQ架构中的cache中新增的几个概念:
.
(1) Strictly inclusive: 所有存在L1 cache中的数据,必然也存在L2 cache中
(2) Weakly inclusive: 当miss的时候,数据会被同时缓存到L1和L2,但在之后,L2中的数据可能会被替换
(3) Fully exclusive: 当miss的时候,数据只会缓存到L1
总结:inclusive/exclusive 描述的仅仅是 L1和L2之间的替换策略
查阅 ARMV9 cortex-A710 trm手册,查看该core的cache类型,得知:
L1 I-cache和L2之间是 weakly inclusive的
L1 D-cache和L2之间是 strictly inclusive的
也就是说:
当发生D-cache发生miss时,数据缓存到L1 D-cache的时候,也会被缓存到L2 Cache中,当L2 Cache被替换时,L1 D-cache也会跟着被替换
当发生I-cache发生miss时,数据缓存到L1 I-cache的时候,也会被缓存到L2 Cache中,当L2 Cache被替换时,L1 I- cache不会被替换
总结 :L1 和 L2之间的cache的替换策略,I-cache和D-cache可以是不同的策略,每一个core都有每一个core的做法,请查阅你使用core的手册。
2、core cache / DSU cache / memory 之间的替换策略
core cache/DSU cache/ 这个名字不太准确,叫 privatecache和share cache更好。
那么他们之间的替换策略是怎样的呢?
MMU的页表中的表项中,管理者每一块内存的属性,其实就是cache属性,也就是缓存策略。其中就有cacheable和shareable、Inner和Outer的概念。如下是针对 DynamIQ 架构做出的总结,注意哦,仅仅是针对 DynamIQ 架构的cache。
如果将block的内存属性配置成Non-cacheable,那么数据就不会被缓存到cache,那么所有observer看到的内存是一致的,也就说此时也相当于Outer Shareable。其实官方文档,也有这一句的描述:在B2.7.2章节 “Data accesses to memory locations are coherent for all observers in the system, and correspondingly are treated as being Outer Shareable”
如果将block的内存属性配置成write-through cacheable 或 write-back cacheable,那么数据会被缓存cache中。write-through和write-back是缓存策略。
如果将block的内存属性配置成 non-shareable, 那么core0访问该内存时,数据缓存的到Core0的L1 D-cache / L2 cache (即数据会缓存到core0的private cache),不会缓存到其它cache中。
如果将block的内存属性配置成 inner-shareable, 那么core0访问该内存时,数据只会缓存到core 0的L1 D-cache / L2 cache和 DSU L3 cache,不会缓存到System Cache中(当然如果有system cache的话 ) , (注意这里MESI协议其作用了)此时core0的cache TAG中的MESI状态是E, 接着如果这个时候core1也去读该数据,那么数据也会被缓存core1的L1 D-cache / L2 cache, 此时core0和core1的MESI状态都是S
如果将block的内存属性配置成 outer-shareable, 那么core0访问该内存时,数据会缓存到core 0的L1 D-cache / L2 cache 、cluster0的DSU L3 cache 、 System Cache中, core0的MESI状态为E。如果core1再去读的话,则也会缓存到core1的L1 D-cache / L2 cache,此时core0和core1的MESI都是S。这个时候,如果core7也去读的话,数据还会被缓存到cluster1的DSU L3 cache. 至于DSU0和DSU1之间的一致性,非MESI维护,具体怎么维护的请看DSU手册。
以上内容摘抄自wiki:
深度解读DynamIQ架构cache的替换策略
36 web系统架构及cache基础varnish4基础应用varnish状态引擎详解及vcl
02 varnish4基础应用
配置环境:
node1 CentOS7.2 192.168.1.131
[[email protected] ~]# yum -y install varnish
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/varnish/varnish.params
修改
VARNISH_STORAGE="file,/var/lib/varnish/varnish_storage.bin,1G"
为
VARNISH_STORAGE="malloc,256M"
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/varnish/default.vcl
修改backend default 段的内容为
backend default {
.host = "192.168.1.132";
.port = "80";
}
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl start varnish.service
访问测试页
[[email protected] ~]# curl 192.168.1.131:6081/test1.html
Page 1 on Web1
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
200
-----------------------------
Varnish Cache CLI 1.0
-----------------------------
Linux,3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64,x86_64,-smalloc,-smalloc,-hcritbit
varnish-4.0.3 revision b8c4a34
Type ‘help‘ for command list.
Type ‘quit‘ to close CLI session.
[[email protected] ~]# yum -y install httpd
[[email protected] ~]# for i in {1..10};do echo "Page $i on Web1" > /var/www/html/test$i.html;done
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl start httpd.service
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl enable httpd.service
03 varnish状态引擎详解
[[email protected] ~]# cd /etc/varnish/
[[email protected] varnish]# cp default.vcl test.vcl
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
修改sub vcl_recv段的内容为:
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.method == "PRI") {
/* We do not support SPDY or HTTP/2.0 */
return (synth(405));
}
if (req.method != "GET" &&
req.method != "HEAD" &&
req.method != "PUT" &&
req.method != "POST" &&
req.method != "TRACE" &&
req.method != "OPTIONS" &&
req.method != "DELETE") {
/* Non-RFC2616 or CONNECT which is weird. */
return (pipe);
}
if (req.method != "GET" && req.method != "HEAD") {
/* We only deal with GET and HEAD by default */
return (pass);
}
if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) {
/* Not cacheable by default */
return (pass);
}
return (hash);
}
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
200
-----------------------------
Varnish Cache CLI 1.0
-----------------------------
Linux,3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64,x86_64,-smalloc,-smalloc,-hcritbit
varnish-4.0.3 revision b8c4a34
Type ‘help‘ for command list.
Type ‘quit‘ to close CLI session.
vcl.load test1 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.list
200
active 0 boot
available 0 test1
vcl.use test1
200
VCL ‘test1‘ now active
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
在sub vcl_deliver 程序段添加
if (obj.hits>0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT";
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS";
}
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
vcl.load test2 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test2
200
VCL ‘test2‘ now active
测试
1)同一个地址测试3次,结果显示为HIT
[[email protected] ~]# curl http://192.168.1.131:6081/test5.html
Page 5 on Web1
[[email protected] ~]# curl http://192.168.1.131:6081/test5.html
Page 5 on Web1
[[email protected] ~]# curl http://192.168.1.131:6081/test5.html
Page 5 on Web1
[[email protected] ~]# curl -I http://192.168.1.131:6081/test5.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 19 Oct 2016 02:27:57 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS)
Last-Modified: Tue, 18 Oct 2016 08:59:47 GMT
ETag: "f-53f1fea1d7c0d"
Content-Length: 15
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
X-Varnish: 65556 65554
Age: 14
Via: 1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache: HIT
Connection: keep-alive
2)测试一次,结果显示为MISS
[[email protected] ~]# curl http://192.168.1.131:6081/test6.html
Page 6 on Web1
[[email protected] ~]# curl -I http://192.168.1.131:6081/test6.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 19 Oct 2016 02:39:41 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS)
Last-Modified: Tue, 18 Oct 2016 08:59:47 GMT
ETag: "f-53f1fea1d7ff5"
Content-Length: 15
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
X-Varnish: 12
Age: 0
Via: 1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache: MISS
Connection: keep-alive
显示客户端IP
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
修改sub vcl_deliver的内容为:
if (obj.hits>0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT from" + server.ip;
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS from" + server.ip;
}
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
vcl.load test3 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test3
200
VCL ‘test3‘ now active
[[email protected] ~]# curl -I http://192.168.1.131:6081/test6.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 19 Oct 2016 03:08:40 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS)
Last-Modified: Tue, 18 Oct 2016 08:59:47 GMT
ETag: "f-53f1fea1d7ff5"
Content-Length: 15
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
X-Varnish: 32770 3
Age: 5
Via: 1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache: HIT from 192.168.1.131
Connection: keep-alive
[[email protected] ~]# curl -I http://192.168.1.131:6081/test7.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 19 Oct 2016 03:09:11 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS)
Last-Modified: Tue, 18 Oct 2016 08:59:47 GMT
ETag: "f-53f1fea1d7ff5"
Content-Length: 15
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
X-Varnish: 5
Age: 0
Via: 1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache: MISS from 192.168.1.131
Connection: keep-alive
04 varnish状态引擎及vcl
#添加后端
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
在backend default段后添加
backend imgsrv {
.host = "192.168.1.133";
.port = "80";
}
#强制对某资源的请求,不检查缓存
#区分大小写(默认)
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
在sub vcl_recv段中添加
if (req.url ~ "^/test7.html$") {
return(pass);
}
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
vcl.load test4 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test4
200
VCL ‘test4‘ now active
[[email protected] ~]# curl -I http://192.168.1.131:6081/test7.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 19 Oct 2016 04:11:58 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS)
Last-Modified: Tue, 18 Oct 2016 08:59:47 GMT
ETag: "f-53f1fea1d7ff5"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 15
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
X-Varnish: 32791
Age: 0
Via: 1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache: MISS from 192.168.1.131
Connection: keep-alive
结果:不管测试几次,结果均为MISS
#不区分大小写,在url前面加(?i)
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
在sub vcl_recv段中添加
if (req.url ~ "(?i)^/login" || req.url ~ "(?i)^/admin") {
return(pass);
}
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
vcl.load test5 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test5
200
VCL ‘test5‘ now active
[[email protected] ~]# mkdir /var/www/html/admin
[[email protected] ~]# vim /var/www/html/admin/index.html
From Admin Page
[[email protected] ~]# curl -I http://192.168.1.131:6081/admin/index.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Wed, 19 Oct 2016 04:27:53 GMT
Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS)
Last-Modified: Wed, 19 Oct 2016 04:27:22 GMT
ETag: "10-53f3039b4f7b4"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Content-Length: 16
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
X-Varnish: 32794
Age: 0
Via: 1.1 varnish-v4
X-Cache: MISS from 192.168.1.131
Connection: keep-alive
结果:不论测试几次,结果均为MISS
对特定类型的资源取消其私有的cookie标识:
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
在vcl_backend_response段中添加
if (beresp.http.cache-control !~ "s-maxage") {
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i)\.jpg$") {
set beresp.ttl = 3600s;
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
}
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i)\.css$") {
set beresp.ttl = 600s;
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
}
}
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
vcl.load test6 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test6
200
VCL ‘test6‘ now active
[[email protected] ~]# cd /var/www/html/
上传两张图片1.jpg,2.jpg
示例:
[[email protected] ~]# cd /etc/varnish/
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
修改backend段的内容为:
backend websrv1 {
.host = "192.168.1.132";
.port = "80";
.probe = {
.url = "test1.html";
}
}
backend websrv2 {
.host = "192.168.1.133";
.port = "80";
}
在vcl_recv段内添加
if (req.url ~ "(?i)^\.(jpg|png|gif)$") {
set req.backend_hint = websrv1;
} else {
set req.backend_hint = websrv2;
}
[[email protected] ~]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082
vcl.load test7 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test7
200
VCL ‘test7‘ now active
backend.list
200
Backend name Refs Admin Probe
default(192.168.1.132,,80) 7 probe Healthy (no probe)
websrv1(192.168.1.132,,80) 2 probe Sick 0/8
websrv2(192.168.1.133,,80) 2 probe Healthy (no probe)
[[email protected] ~]# yum -y install httpd
[[email protected] ~]# for i in {1..10};do echo "<h1>Test Page $i Web2 </h1>" > /var/www/html/test$i.html;done
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl start httpd.service
示例2:
[[email protected] varnish]# vim test.vcl
添加
import directors;
sub vcl_init {
new mycluster = directors.round_robin();
mycluster.add_backend(websrv1);
mycluster.add_backend(websrv2);
}
在sub vcl_recv段内添加
if (req.url ~ "(?i)test1.html$") {
return(pass);
}
set req.backend_hint = mycluster.backend();
vcl.load test8 test.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test8
200
VCL ‘test8‘ now active
本文出自 “追梦” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://sihua.blog.51cto.com/377227/1863759
以上是关于ARM/cacheDynamIQ架构及cache的替换策略的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章