故障诊断用于轴承故障诊断的性能增强时变形态滤波方法及用于轴承断层特征提取的增强数学形态算子研究(Matlab代码实现)
Posted 我爱Matlab编程
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了故障诊断用于轴承故障诊断的性能增强时变形态滤波方法及用于轴承断层特征提取的增强数学形态算子研究(Matlab代码实现)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
形态学滤波是从集合论推导出的典型非线性信号处理方法。在这种方法中,可以通过与指定的结构元件(SE)相互作用来挖掘信号中的脉冲特征。SE的参数(即形状、高度和长度)选择对形态过滤结果有重要影响。针对该问题,该文提出一种自适应时变形态滤波(ATVMF)方法。ATVMF可以根据待分析信号的固有特性自适应地确定SE的形状和尺度,有效提高瞬态特征提取能力和计算效率。此外,还提出了广义形态产物算子(GMPO)的定义,可以构造新的形态积算子进行特征提取。
📚2 运行结果
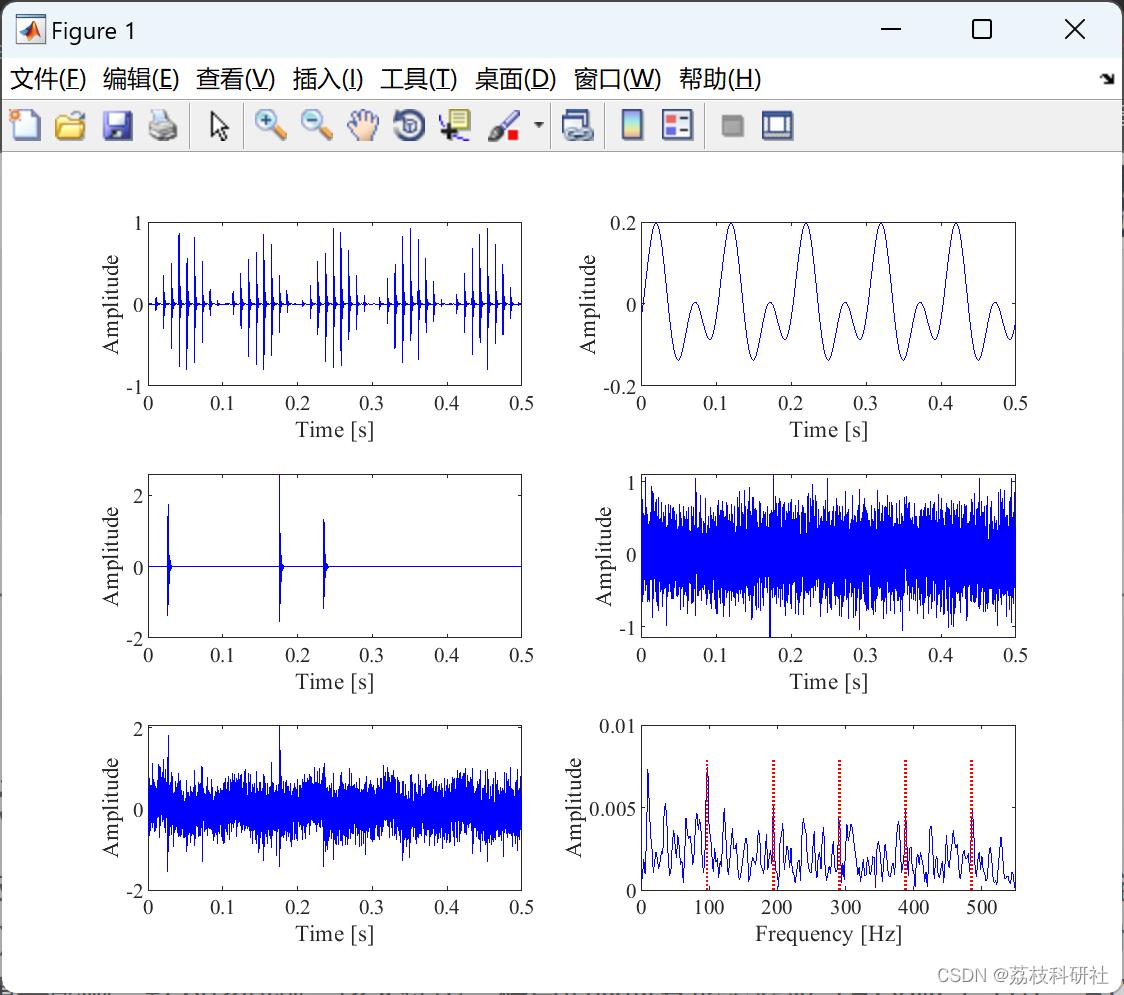
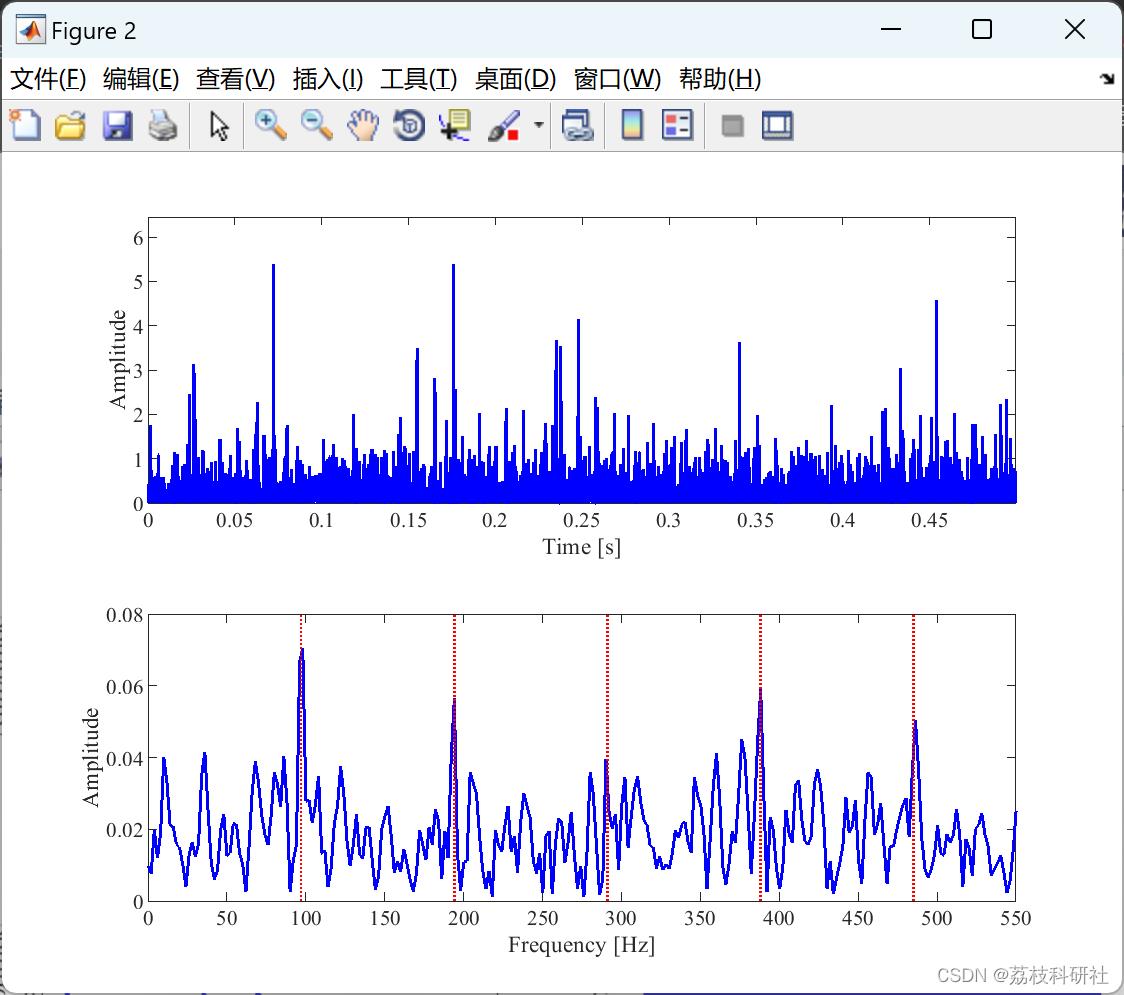
部分代码:
function [ y ] = ATVMF( x, interp_method, operator )
% Algorithm name: Adaptive Time-Varying Morphological Filtering (ATVMF)
%
% Algorithm description: This method can achieve adaptive morphological filtering,
% in which a time-varying structure element (TVSE) is adaptively designed
% based on the characteristics of a signal and is no longer fixed.
%
% Input:
% x: signal to be analyzed (a vector)
% interp_method: selected interpllation method, such as 'spline', 'pchip',
% 'linear' and 'nearest', in which 'spline' is recommended.
% 'spline' -- cubic spline interpolation
% 'pchip' -- cubic Hermitian interpolation
% 'linear' -- piecewise linear interpolation
% 'nearest' -- nearest neighbor interpolation
% operator: selected morphological operator, see sub-function 'MF_operator'
%
% Output:
% y: morphological filtered signal
x = x(:)-mean(x); % a vector
N = length(x);
[indmin, indmax] = extreme_points(x); % Determine the location of local minima and maxima
% indmin -- the position of the local minimum point in the sequence x
% indmax -- the position of the local maximum point in the sequence x
tmin = indmin;
tmax = indmax;
xmin = x(tmin); % The magnitude of the local minimum point
xmax = x(tmax); % The magnitude of the local maximum point
% Sorting of local minimum and maximum points
textra = zeros(1,length(tmin)+length(tmax));
xextra = zeros(1,length(xmin)+length(xmax));
if tmin(1) < tmax(1) % The first extreme point is the minimum point
if tmin(end) > tmax(end) % The last extreme point is the minimum point
textra(1) = tmin(1);
xextra(1) = xmin(1);
for i = 1:length(tmax)
textra(2*i) = tmax(i);
textra(2*i+1) = tmin(i+1);
xextra(2*i) = xmax(i);
xextra(2*i+1) = xmin(i+1);
end
else % The last extreme point is the maximum point
for i = 1:length(tmax)
textra(2*i-1) = tmin(i);
textra(2*i) = tmax(i);
xextra(2*i-1) = xmin(i);
xextra(2*i) = xmax(i);
end
end
else % The first extreme point is the maximum point
if tmin(end) < tmax(end) % The last extreme point is the maximum point
textra(1) = tmax(1);
xextra(1) = xmax(1);
for i = 1:length(tmin)
textra(2*i) = tmin(i);
textra(2*i+1) = tmax(i+1);
xextra(2*i) = xmin(i);
xextra(2*i+1) = xmax(i+1);
end
else % The last extreme point is the minimum point
for i = 1:length(tmin)
textra(2*i-1) = tmax(i);
textra(2*i) = tmin(i);
xextra(2*i-1) = xmax(i);
xextra(2*i) = xmin(i);
end
end
end
% Selection of 'interp_method'
env = interp1(textra,xextra,textra(1):textra(end),interp_method);
delta = textra(1)-1;
S = length(indmin)-1; % number of SE
y = []; % output initialization
for s = 1:S
xnew = x(indmin(s)+1:indmin(s+1));
g = env(indmin(s)+1-delta:indmin(s+1)-delta);
g = g-min(g);
% the morphological filtering result
ynew = MF_operator( xnew, g, operator );
y = [y; ynew];
end
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% sub-function
function d = dilation(f,g)
% Morphological dilation operation
N = length(f);
M = length(g);
dtmp = f;
for i = 1:N
for j = 1:M
if (i-j) >= 1 && (i-j) <= N
tmp = f(i-j) + g(j);
if tmp > dtmp(i)
dtmp(i) = tmp;
end
end
end
end
d = dtmp;
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% sub-function
function e = erosion(f,g)
% Morphological erosion operation
N = length(f);
M = length(g);
dtmp = f;
for i = 1:N
for j = 1:M
if (i+j) >= 1 && (i+j) <= N
tmp = f(i+j) - g(j);
if tmp < dtmp(i)
dtmp(i) = tmp;
end
end
end
end
e = dtmp;
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% sub-function
function y = MF_operator( x, g, operator )
% Morphological operators
%
a1 = dilation(x,g); % dilation
a2 = erosion(a1,g); % closing
a3 = erosion(a2,g);
a4 = dilation(a3,g); % closing-opening
%
b1 = erosion(x,g); % erosion
b2 = dilation(b1,g); % opening
b3 = dilation(b2,g);
b4 = erosion(b3,g); % opening-closing
if strcmp(operator,'Gde') == 1
y = a1-b1;
elseif strcmp(operator,'Gco') == 1
y = a2-b2;
elseif strcmp(operator,'Gcooc') == 1
y = a4-b4;
elseif strcmp(operator,'AHde') == 1
y = x-(a1+b1)/2;
elseif strcmp(operator,'AHco') == 1
y = x-(a2+b2)/2;
elseif strcmp(operator,'AHcooc') == 1
y = x-(a4+b4)/2;
elseif strcmp(operator,'MGPO1') == 1
y = (a1-b1).*(a2-b2);
elseif strcmp(operator,'MGPO2') == 1
y = (a1-b1).*(a4-b4);
elseif strcmp(operator,'MGPO3') == 1
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]陈斌, 宋大鹏, 张伟, 程彦, 王志, 一种用于轴承故障诊断的性能增强时变形态滤波方法, 测量学报 (2021) 109163.
[2]陈斌, 程彦, 张文, 梅国, 用于轴承断层特征提取的增强数学形态算子研究, ISA Trans. (2021)
[3]B. Chen, D. Song, W. Zhang, Y. Cheng, Z. Wang, A performance enhanced time-varying morphological filtering method for bearing fault diagnosis, Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 176 (2021) 109163.
[4]B. Chen, Y. Cheng, W. Zhang, G. Mei, Investigation on enhanced mathematical morphological operators for bearing fault feature extraction, ISA Trans. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2021.07.027.
🌈4 Matlab代码实现
故障诊断分析基于matlab滚动轴承故障诊断系统含Matlab源码 1679期
一、小波语音降噪简介
对于噪声频谱遍布于语音信号频谱之中的宽带噪声,如果噪声振幅比大部分的语音信号振幅低,则削去低幅度成分也就削去了宽带噪声。基于这种思路,可以在频域中采取中心限幅的方法,即让带噪语音信号通过一限幅滤波器,高幅度频谱可以通过而低幅成分不允许通过,从而实现噪声抑制。需要注意的是中心削波不可避免地要损害语音质量,通常只在频域中进行,而一般不在时域中实施。
小波降噪的原理类似于中心削波法。小波降噪最初是由Donoho和Johnstone提出的, 其主要理论依据是,小波变换具有很强的去数据相关性,它能够使信号的能量在小波域集中在一些大的小波系数中;而噪声的能量却分布于整个小波域内。因此,经小波分解后,信号的小波系数幅值要大于噪声的系数幅值。因此,幅值比较大的小波系数一般以信号为主,而幅值比较小的系数在很大程度上是噪声。于是,采用阈值的办法可以把信号系数保留,而使大部分噪声系数减小至0。小波降噪的具体处理过程为:将含噪信号在各尺度上进行小波分解,设定一个阈值,幅值低于该阈值的小波系数置为0,高于该阈值的小波系数或者完全保
留, 或者做相应的“收缩”(shrinkage) 处理。最后; 将处理后获得的小波系数用逆小波变换进行重构,得到去噪后的信号。
阈值去噪中,阈值函数体现了对超过和低于阈值的小波系数的不同处理策略,是阈值去噪中关键的一步。设w表示小波系数, T为给定阈值, sgn(*) 为符号函数, 常见的阈值函数主要有:

二、部分源代码
H=figure('color',[0.82,0.82421875,0.832],'position',[250,100,800,500],...
'Name','滚动轴承故障诊断系统','NumberTitle','off',...
'MenuBar','None');
uicontrol(H,'style','Text','position',[0.2,0.2,0.55,0.05],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center',...
'String','制作人:**学院','fontsize',16,...
'backgroundcolor',[0.82,0.82421875,0.832]);
uicontrol(H,'style','Text','position',[0.2,0.15,0.55,0.05],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center',...
'String','机械1班 紫极神光','fontsize',16,...
'backgroundcolor',[0.82,0.82421875,0.832]);
uicontrol(H,'style','Pushbutton','position',[0.7,0.66,0.2,0.06],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center',...bg
'String','进入系统','fontsize',15,'call','STYM');
uicontrol(H,'style','Pushbutton','position',[0.7,0.45,0.2,0.06],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center',...
'String','退出系统','fontsize',15,'call','close(H)');
load mtlb;
a=axes('parent',H,'position',[-0.16 0 1 1.1]);
imshow('11.jpg');
hold on;
axis off;
%mnxh.m文件
uiheight=0.05;
uiweith=0.12;
uilow=0.08;
uileft=0.85;
dif=0.08;
uicontrol(f,'style','Text','Position',...
[uileft-10*dif uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight uiweith/2 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','幅值1','tag','fuz1data','backgroundcolor',[0.8,0.9,0.8]);
uicontrol(f,'style','edit','Position',...
[uileft-10*dif+uiweith/2 uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight 2*uiweith/3 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','tag','fuz1ed','fontsize',10,'String',11);
uicontrol(f,'style','Text','Position',...
[uileft-8*dif uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight 2*uiweith/2 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','频率1','tag','pl1data','backgroundcolor',[0.8,0.9,0.8]);
uicontrol(f,'style','edit','Position',...
[uileft-7.6*dif+uiweith/2 uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight 2*uiweith/3 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','tag','pl1ed','fontsize',10,'String',12);
uicontrol(f,'style','Text','Position',...
[uileft-10*dif uilow+2*dif+11*uiheight uiweith/2 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','幅值3','tag','fuz3data','backgroundcolor',[0.8,0.9,0.8]);
uicontrol(f,'style','edit','Position',...
[uileft-10*dif+uiweith/2 uilow+2*dif+11*uiheight 2*uiweith/3 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','tag','fuz3ed','fontsize',10,'String',35);
uicontrol(f,'style','Text','Position',...
[uileft-8*dif uilow+2*dif+11*uiheight 2*uiweith/2 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','频率3','tag','pl3data','backgroundcolor',[0.8,0.9,0.8]);
uicontrol(f,'style','edit','Position',...
[uileft-7.6*dif+uiweith/2 uilow+2*dif+11*uiheight 2*uiweith/3 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','tag','pl3ed','fontsize',10,'String',40);
uicontrol(f,'style','Text','Position',...
[uileft-5*dif uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight uiweith/2 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','幅值2','tag','fuz2data','backgroundcolor',[0.8,0.9,0.8]);
uicontrol(f,'style','edit','Position',...
[uileft-5*dif+uiweith/2 uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight 2*uiweith/3 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','tag','fuz2ed','fontsize',10,'String',15);
uicontrol(f,'style','Text','Position',...
[uileft-3*dif uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight 2*uiweith/2 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','频率2','tag','pl2data','backgroundcolor',[0.8,0.9,0.8]);
uicontrol(f,'style','edit','Position',...
[uileft-2.6*dif+uiweith/2 uilow+2*dif+13*uiheight 2*uiweith/3 uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','tag','pl2ed','fontsize',10,'String',5);
uicontrol(f,'style','Pushbutton','position',...
[uileft-4.5*dif uilow+2*dif+11*uiheight uiweith uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','无噪音信号','call','wzy');
uicontrol(f,'style','Pushbutton','position',...
[uileft-2.3*dif uilow+2*dif+11*uiheight uiweith uiheight],...
'Units','normalized','Horizontal','center','fontsize',12,...
'String','加噪音信号','call','jzy');
三、运行结果

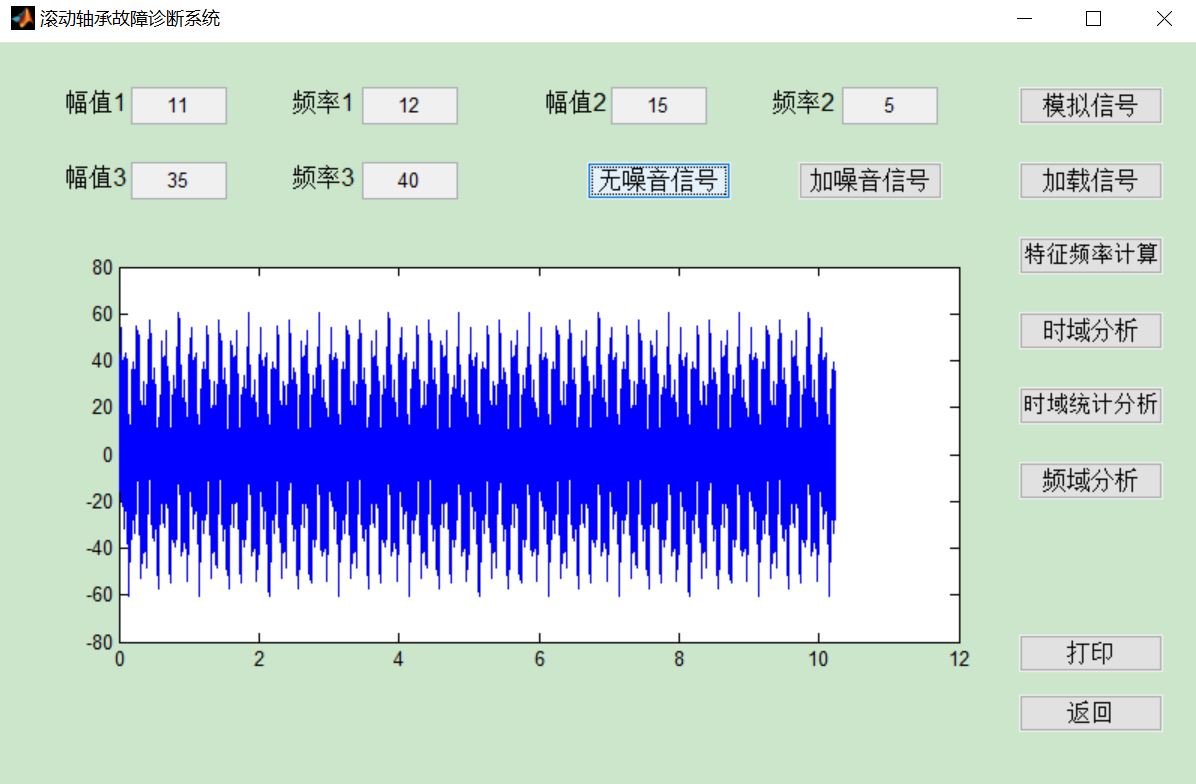
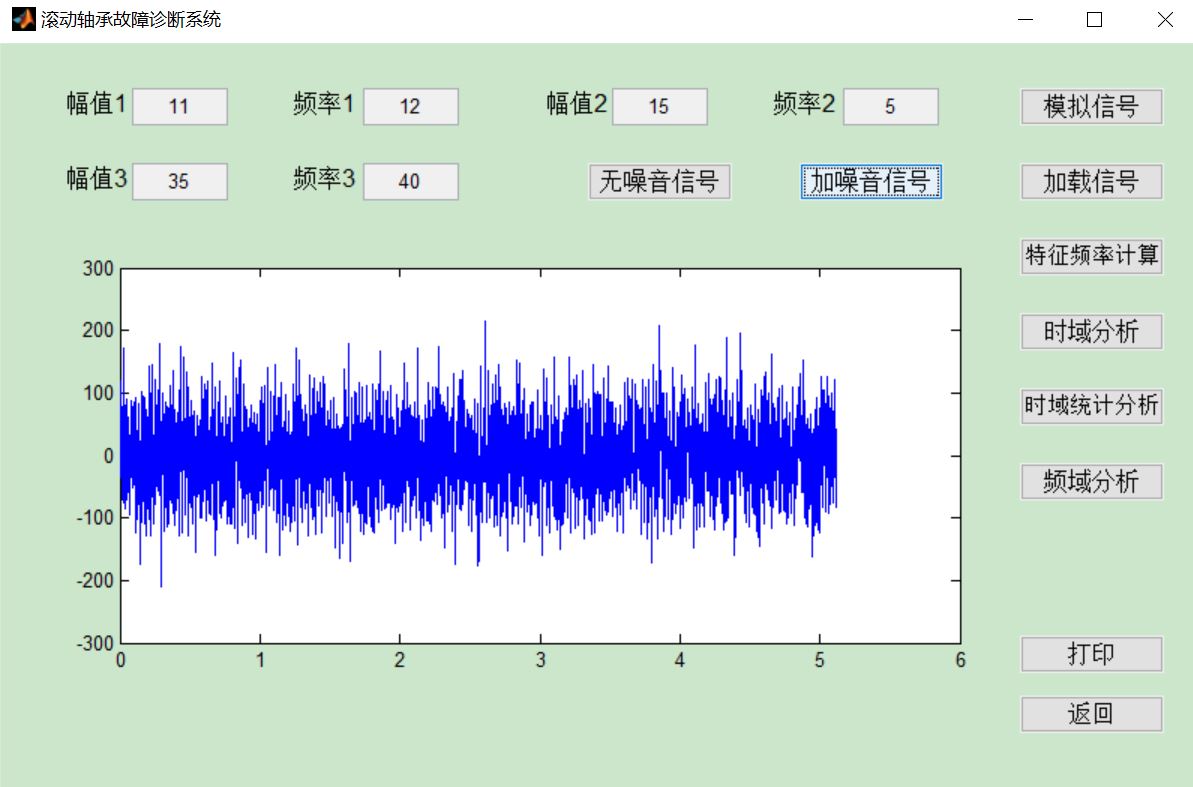
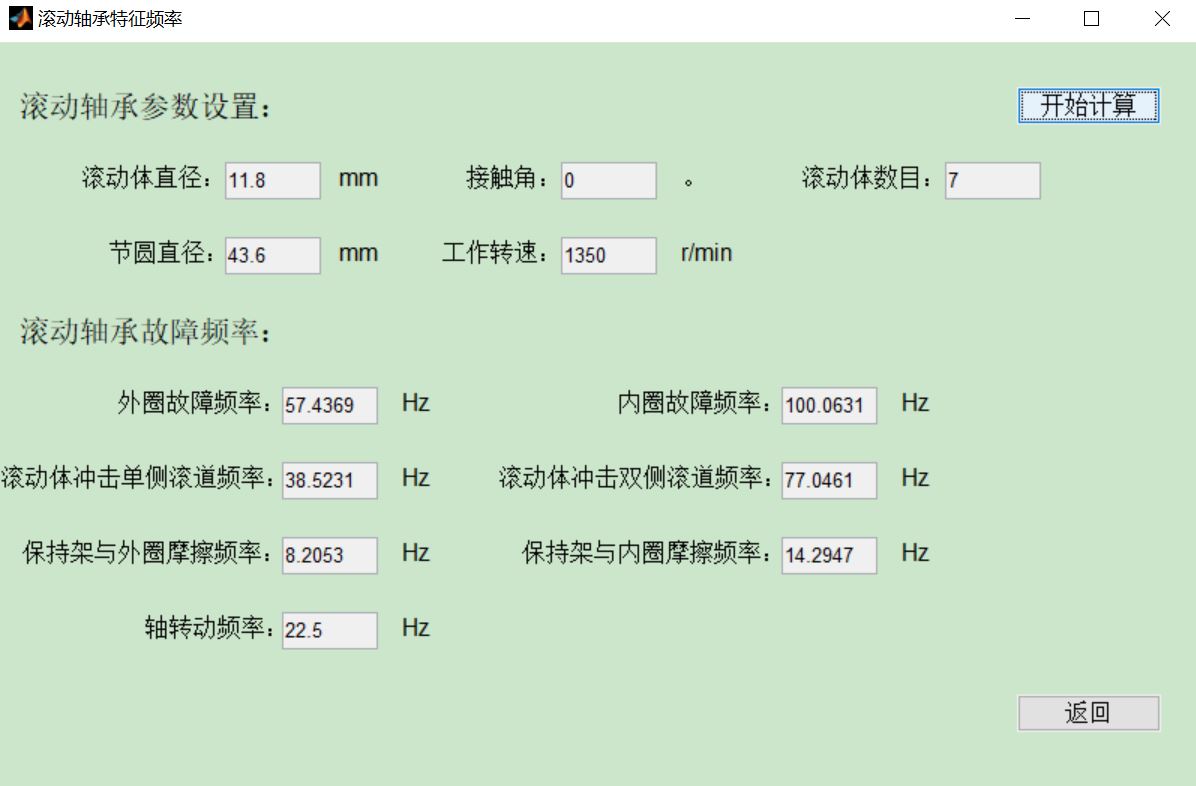
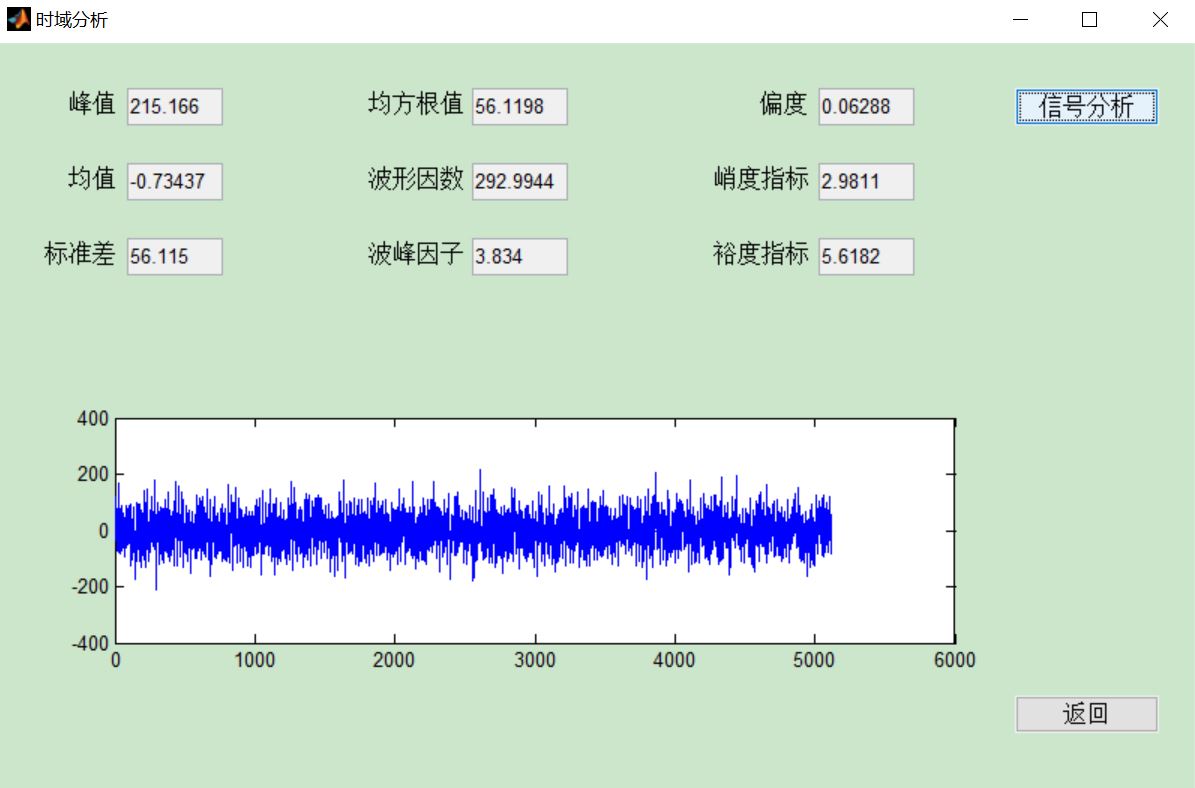
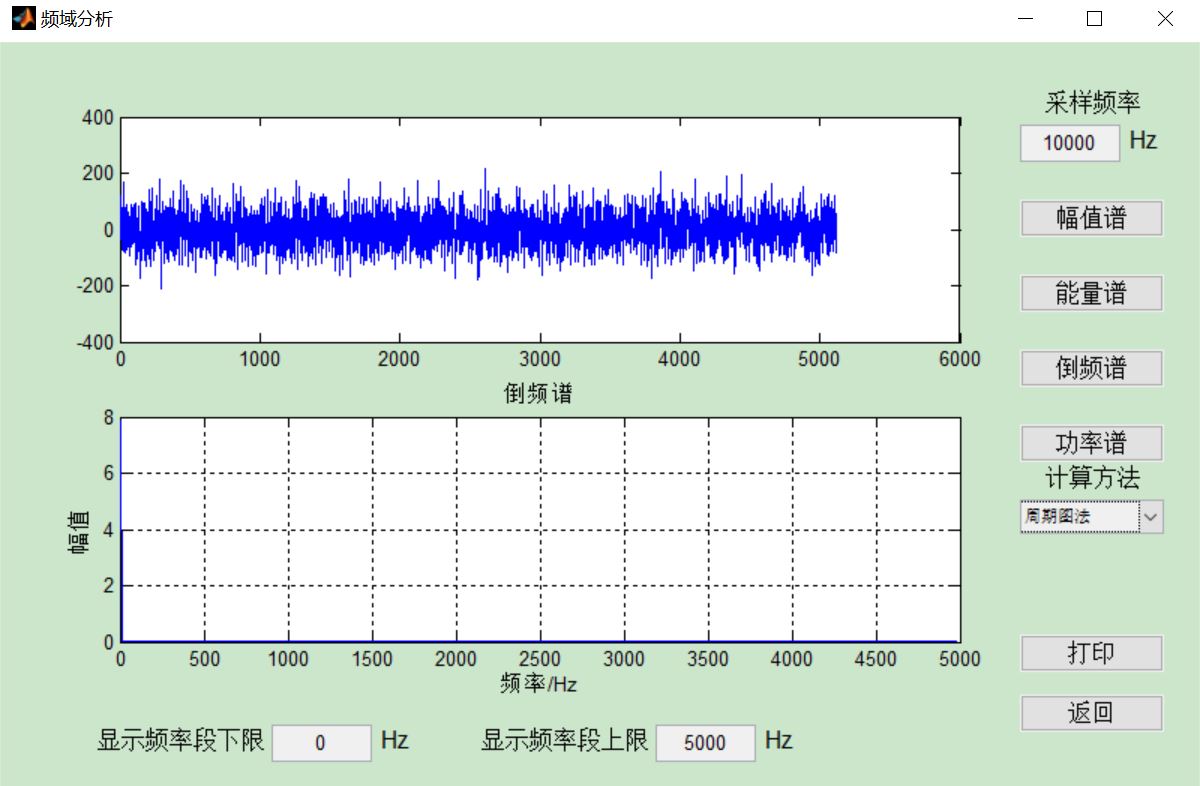
四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1] 沈再阳.精通MATLAB信号处理[M].清华大学出版社,2015.
[2]高宝建,彭进业,王琳,潘建寿.信号与系统——使用MATLAB分析与实现[M].清华大学出版社,2020.
[3]王文光,魏少明,任欣.信号处理与系统分析的MATLAB实现[M].电子工业出版社,2018.
以上是关于故障诊断用于轴承故障诊断的性能增强时变形态滤波方法及用于轴承断层特征提取的增强数学形态算子研究(Matlab代码实现)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
