JStorm第一个程序WordCount详解
Posted chen-kh
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JStorm第一个程序WordCount详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- nimbus是整个storm任务的管理者,并不实际进行工作。负责在集群中分发代码,对节点分配任务,并监视主机故障。
- supervisor是实际进行工作的节点,负责监听工作节点上已经分配的主机作业,启动和停止Nimbus已经分配的工作进程。
- Worker是具体处理Spout/Bolt逻辑的进程,worker数量由拓扑中的conf.setNumWorkers来定义,storm会在每个Worker上均匀分配任务,一个Worker只能执行一个topology,但是可以执行其中的多个任务线程。
- 一个worker是一个进程,被启动的时候表现为一个JVM进程(内存更改需要配置storm.yaml里面的worker.childopts: "-Xmx2048m"参数),里面可以同时运行多个线程,这些线程就是task。
- Tuple是spout与bolt、bolt与bolt之间传递消息(流)的基本单元,对于Storm来说是一个无边界的链表,每个值要事先声明它的域(field)
- task是spout和bolt执行的最小单元。
- 下面的结构图显示了各个component之间的关系

图片来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/foreach-break/p/storm_worker_executor_spout_bolt_simbus_supervisor_mk-assignments.html
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/cuihaolong/article/details/52652686(storm各个节点介绍和容错机制)
- 本地模式(Local Mode): 即Topology(相当于一个任务,后续会详细讲解) 运行在本地机器的单一JVM上,这个模式主要用来开发、调试。
- 远程模式(Remote Mode):在这个模式,我们把我们的Topology提交到集群,在这个模式中,Storm的所有组件都是线程安全的,因为它们都会运行在不同的Jvm或物理机器上,这个模式就是正式的生产模式。
- spout随机发送一个准备好的字符串数组里面的一个字符串(sentence)
- 第一层SplitBolt,负责对spout发过来的数据(sentence)进行split,分解成独立的单词,并按照一定的规则发往下一层bolt处理
- 第二层CountBolt,接收第一层bolt传过来的数据,并对各个单词进行数量计算
- spout数据源
- bolt1进行split操作
- bolt2进行count操作
- Topolgy运行程序
- setSpout,setBolt,shuffleGrouping——见代码注释和之后的Grouping方式介绍,
- setNumWorkers——设置worker数量,每个worker占用一个端口(storm.yaml里面的supervisor.slots.ports配置)
- setNumTasks——设置每个executor跑多少个task(本实例中没有配置这个参数,jstorm默认每个executor跑一个task[spout/bolt])
- setMaxTaskParallelism——设置此拓扑中组件允许的最大并行度。(此配置通常用于测试以限制所生成的线程数)

1 package act.chenkh.study.jstormPlay; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 5 import backtype.storm.Config; 6 import backtype.storm.LocalCluster; 7 import backtype.storm.StormSubmitter; 8 import backtype.storm.topology.TopologyBuilder; 9 import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields; 10 11 public class WordCountTopology { 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 13 /**第一步,设计一个Topolgy*/ 14 TopologyBuilder builder = new TopologyBuilder(); 15 /* 16 * 设置spout和bolt,完整参数为 17 * 1,spout的id(即name) 18 * 2,spout对象 19 * 3,executor数量即并发数,也就是设置多少个executor来执行spout/bolt(此项没有默认null) 20 */ 21 //setSpout 22 builder.setSpout("sentence-spout",new RandomSentenceSpout(),1); 23 //setBolt:SplitBolt的grouping策略是上层随机分发,CountBolt的grouping策略是按照上层字段分发 24 //如果想要从多个Bolt获取数据,可以继续设置grouping 25 builder.setBolt("split-bolt", new SplitBolt(),1) 26 .shuffleGrouping("sentence-spout"); 27 builder.setBolt("count-bolt", new CountBolt(),1) 28 .fieldsGrouping("split-bolt", new Fields("word")) 29 .fieldsGrouping("sentence-spout",new Fields("word")); 30 /**第二步,进行基本配置*/ 31 Config conf = new Config(); 32 //作用和影响??????????? 33 conf.setDebug(true); 34 if (args != null && args.length > 0) { 35 conf.setNumWorkers(1); 36 StormSubmitter.submitTopology(args[0], conf, builder.createTopology()); 37 } 38 else { 39 /* 40 * run in local cluster, for test in eclipse. 41 */ 42 conf.setMaxTaskParallelism(3); 43 LocalCluster cluster = new LocalCluster(); 44 cluster.submitTopology("Getting-Started-Toplogie", conf, builder.createTopology()); 45 Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE); 46 cluster.shutdown(); 47 } 48 } 49 }
- open——spout初始化调用
- nextTuple——系统不断调用
- declareOutputFields——声明输出tuple包含哪些字段

1 package act.chenkh.study.jstormPlay; 2 3 import java.util.Map; 4 import java.util.Random; 5 6 import org.apache.log4j.Logger; 7 import backtype.storm.spout.SpoutOutputCollector; 8 import backtype.storm.task.TopologyContext; 9 import backtype.storm.topology.IRichSpout; 10 import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer; 11 import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields; 12 import backtype.storm.tuple.Values; 13 import backtype.storm.utils.Time; 14 import backtype.storm.utils.Utils; 15 /* 16 * RandomSentenceSpout实现了IRichSpout接口 17 * Spout需要实现的接口可以是: 18 * 1,IRichSpout:最基本的Spout,继承自ISpout, IComponent,沒有任何特殊方法(一般用这个) 19 * 2,IControlSpout:继承自IComponent,包括open,close,activate,deactivate,nextTuple,ack(Object msgId),fail等方法 20 */ 21 public class RandomSentenceSpout implements IRichSpout { 22 23 /** 24 * 25 */ 26 private static final long serialVersionUID = 4058847280819269954L; 27 private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(RandomSentenceSpout.class); 28 SpoutOutputCollector _collector; 29 Random _rand; 30 String component; 31 /* 32 * Spout初始化的时候调用 33 */ 34 public void open(Map conf, TopologyContext context, SpoutOutputCollector collector){ 35 _collector = collector; 36 _rand = new Random(); 37 component = context.getThisComponentId(); 38 } 39 /* 40 * 系统框架会不断调用 41 */ 42 public void nextTuple() { 43 String[] sentences = new String[] { "Hello world! This is my first programme of JStorm", 44 "Hello JStorm,Nice to meet you!", "Hi JStorm, do you have a really good proformance", 45 "Goodbye JStorm,see you tomorrow" }; 46 String sentence = sentences[_rand.nextInt(sentences.length)]; 47 _collector.emit(new Values(sentence), Time.currentTimeSecs()); 48 Utils.sleep(1000); 49 } 50 @Override 51 public void ack(Object arg0) { 52 logger.debug("ACK!"); 53 } 54 55 public void activate() { 56 logger.debug("ACTIVE!"); 57 } 58 59 public void close() { 60 61 } 62 63 public void deactivate() { 64 65 } 66 67 public void fail(Object arg0) { 68 logger.debug("FAILED!"); 69 } 70 /* 71 * 声明框架有哪些输出的字段 72 */ 73 public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) { 74 declarer.declare(new Fields("word")); 75 } 76 77 public Map<String, Object> getComponentConfiguration() { 78 return null; 79 } 80 81 }
2,SplitBolt类:接收上层tuple,进行split,分发给下一层
重要方法和参数解释:
- cleanup,execute,prepare,declareOutputFields——见代码注释

1 package act.chenkh.study.jstormPlay; 2 3 import java.util.Map; 4 5 //import org.slf4j.Logger; 6 //import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 7 8 import org.apache.log4j.Logger; 9 10 import backtype.storm.task.TopologyContext; 11 import backtype.storm.topology.BasicOutputCollector; 12 import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer; 13 import backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseBasicBolt; 14 import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields; 15 import backtype.storm.tuple.Tuple; 16 import backtype.storm.tuple.Values; 17 /* 18 * 19 * IBasicBolt:继承自IComponent,包括prepare,execut,cleanup等方法 20 */ 21 public class SplitBolt extends BaseBasicBolt { 22 /** 23 * 24 */ 25 private static final long serialVersionUID = 7104767103420386784L; 26 private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(SplitBolt.class); 27 String component; 28 /* cleanup方法在bolt被关闭的时候调用, 它应该清理所有被打开的资源。(基本只能在local mode使用) 29 * 但是集群不保证这个方法一定会被执行。比如执行task的机器down掉了,那么根本就没有办法来调用那个方法。 30 * cleanup设计的时候是被用来在local mode的时候才被调用(也就是说在一个进程里面模拟整个storm集群), 31 * 并且你想在关闭一些topology的时候避免资源泄漏。 32 * (非 Javadoc) 33 * @see backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseBasicBolt#cleanup() 34 */ 35 public void cleanup() { 36 37 } 38 //接收消息之后被调用的方法 39 public void execute(Tuple input,BasicOutputCollector collector) { 40 String sentence = input.getString(0); 41 String[] words = sentence.split("[,|\\\\s+]"); 42 for(String word : words){ 43 word = word.trim(); 44 if(!word.isEmpty()){ 45 word = word.toLowerCase(); 46 collector.emit(new Values(word)); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 /* 51 * prepare方法在worker初始化task的时候调用. 52 * 53 * prepare方法提供给bolt一个Outputcollector用来发射tuple。 54 * Bolt可以在任何时候发射tuple — 在prepare, execute或者cleanup方法里面, 或者甚至在另一个线程里面异步发射。 55 * 这里prepare方法只是简单地把OutputCollector作为一个类字段保存下来给后面execute方法 使用。 56 */ 57 58 public void prepare(Map stromConf, TopologyContext context) { 59 component = context.getThisComponentId(); 60 } 61 62 /* 63 * declearOutputFields方法仅在有新的topology提交到服务器, 64 * 用来决定输出内容流的格式(相当于定义spout/bolt之间传输stream的name:value格式), 65 * 在topology执行的过程中并不会被调用. 66 * (非 Javadoc) 67 * @see backtype.storm.topology.IComponent#declareOutputFields(backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer) 68 */ 69 public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) { 70 declarer.declare(new Fields("word")); 71 } 72 }
3,CountBolt类:接收上层tuple,进行count,展示输出

1 package act.chenkh.study.jstormPlay; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 6 import org.apache.log4j.Logger; 7 8 import com.alibaba.jstorm.callback.AsyncLoopThread; 9 import com.alibaba.jstorm.callback.RunnableCallback; 10 11 import backtype.storm.task.TopologyContext; 12 import backtype.storm.topology.BasicOutputCollector; 13 import backtype.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer; 14 import backtype.storm.topology.base.BaseBasicBolt; 15 import backtype.storm.tuple.Fields; 16 import backtype.storm.tuple.Tuple; 17 import clojure.inspector__init; 18 19 public class CountBolt extends BaseBasicBolt { 20 Integer id; 21 String name; 22 Map<String, Integer> counters; 23 String component; 24 private static final Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(CountBolt.class); 25 private AsyncLoopThread statThread; 26 /** 27 * On create 28 */ 29 @Override 30 public void prepare(Map stormConf, TopologyContext context) { 31 this.counters = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 32 this.name = context.getThisComponentId(); 33 this.id = context.getThisTaskId(); 34 this.statThread = new AsyncLoopThread(new statRunnable()); 35 36 LOG.info(stormConf.get("abc")+"!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"); 37 component = context.getThisComponentId(); 38 } 39 40 public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) { 41 declarer.declare(new Fields("word","count")); 42 // declarer.declareStream("coord-"+"word-counter", new Fields("epoch","ebagNum")); 43 // LOG.info("set stream coord-"+component); 44 } 45 46 //接收消息之后被调用的方法 47 public void execute(Tuple input, BasicOutputCollector collector) { 48 // String str = input.getString(0); 49 String str = input.getStringByField("word"); 50 if(!counters.containsKey(str)){ 51 counters.put(str, 1); 52 }else{ 53 Integer c = counters.get(str) + 1; 54 counters.put(str, c); 55 } 56 } 57 class statRunnable extends RunnableCallback { 58 59 @Override 60 public void run() { 61 while(true){ 62 try { 63 Thread.sleep(10000); 64 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 65 66 } 67 LOG.info("\\n-- Word Counter ["+name+"-"+id+"] --"); 68 for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : counters.entrySet()){ 69 LOG.info(entry.getKey()+": "+entry.getValue()); 70 } 71 LOG.info(""); 72 } 73 74 } 75 } 76 77 }
参考:http://fireinwind.iteye.com/blog/2153699(第一个Storm应用)
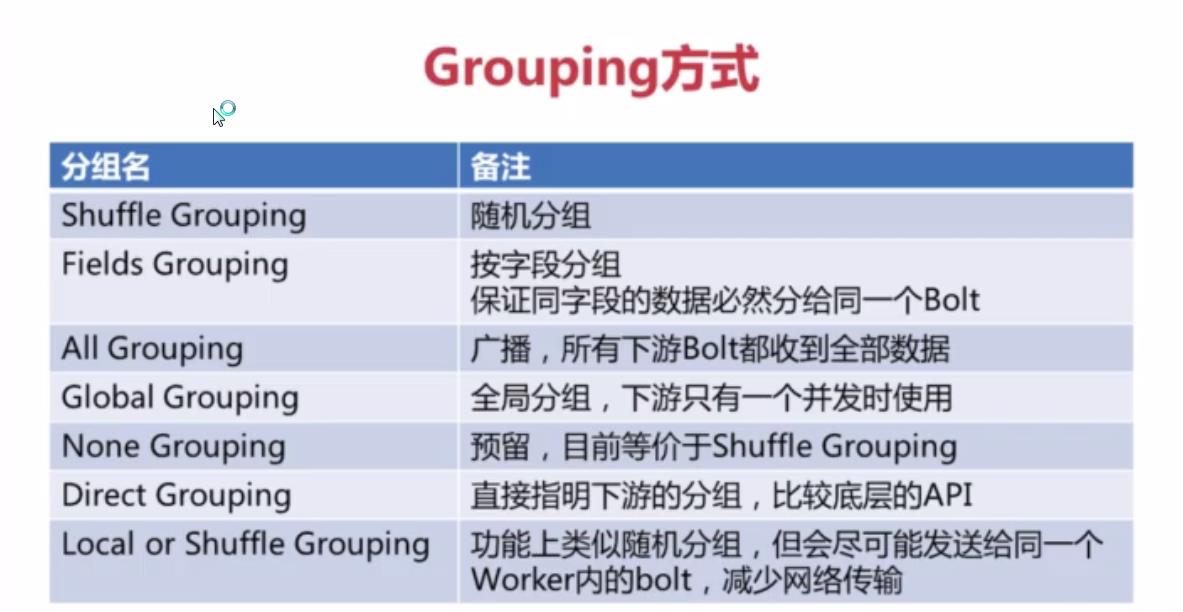
三、Grouping的几种方式
四、Bolt的声明周期
1、在定义Topology实例过程中,定义好Spout实例和Bolt实例
2、在提交Topology实例给Nimbus的过程中,会调用TopologyBuilder实例的createTopology()方法,以获取定义的Topology实例。在运行createTopology()方法的过程中,会去调用Spout和Bolt实例上的declareOutputFields()方法和getComponentConfiguration()方法,declareOutputFields()方法配置Spout和Bolt实例的输出,getComponentConfiguration()方法输出特定于Spout和Bolt实例的配置参数值对。Storm会将以上过程中得到的实例,输出配置和配置参数值对等数据序列化,然后传递给Nimbus。
3、在Worker Node上运行的thread,从Nimbus上复制序列化后得到的字节码文件,从中反序列化得到Spout和Bolt实例,实例的输出配置和实例的配置参数值对等数据,在thread中Spout和Bolt实例的declareOutputFields()和getComponentConfiguration()不会再运行。
4、在thread中,反序列化得到一个Bolt实例后,它会先运行Bolt实例的prepare()方法,在这个方法调用中,需要传入一个OutputCollector实例,后面使用该OutputCollector实例输出Tuple
5、接下来在该thread中按照配置数量建立task集合,然后在每个task中就会循环调用thread所持有Bolt实例的execute()方法
6、在关闭一个thread时,thread所持有的Bolt实例会调用cleanup()方法
不过如果是强制关闭,这个cleanup()方法有可能不会被调用到
五、Stream里面的Tuple

1 public List<Integer> emit(List<Object> tuple, Object messageId) { 2 return emit(Utils.DEFAULT_STREAM_ID, tuple, messageId); 3 }
这里的tuple, 实际上是List<Object> 对象,返回的是 List<Integer> 是要发送的tast的IdsList
在bolt接收的时候, 变成一个Tuple对象, 结构应该也是一个list, List<Field1, value1, Field2, value2..>这样的一个结构, FieldList ValueList, 我们根据对应的fieldname就可以取出对应的getIntegerByField方法
以上是关于JStorm第一个程序WordCount详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
