js中的异步与同步,解决由异步引起的问题
Posted lin_zone
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了js中的异步与同步,解决由异步引起的问题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
之前在项目中遇到过好多次因为异步引起的变量没有值,所以意识到了认识js中同步与异步机制的重要性
在单线程的js中,异步代码会被放入一个事件队列,等到所有其他代码执行后再执行,而不会阻塞线程。
下面是js几种最常见的异步情况:
- 异步函数 setTimeout和setInterval
异步函数,如setTimeout和setInterval,被压入了称之为Event Loop的队列。
setTimeout:在指定的毫秒数后,将定时任务处理的函数添加到执行队列的队尾。所以有时候也可以使用setTimeout解决异步带来的问题
setInterval:按照指定的周期(以毫秒数计时),将定时任务处理函数添加到执行队列的队尾。
Event Loop是一个回调函数队列。当异步函数执行时,回调函数会被压入这个队列。javascript引擎直到异步函数执行完成后,才会开始处理事件循环。这意味着JavaScript代码不是多线程的,即使表现的行为相似。事件循环是一个先进先出(FIFO)队列,这说明回调是按照它们被加入队列的顺序执行的。 - ajax
- node.js中的许多函数也是异步的
解决由的js异步引起的问题办法:
- 命名函数
清除嵌套回调的一个便捷的解决方案是简单的避免双层以上的嵌套。传递一个命名函数给作为回调参数,而不是传递匿名函数
例:1 var fromLatLng, toLatLng; 2 var routeDone = function( e ){ 3 console.log( "ANNNND FINALLY here\'s the directions..." ); 4 // do something with e 5 }; 6 var toAddressDone = function( results, status ) { 7 if ( status == "OK" ) { 8 toLatLng = results[0].geometry.location; 9 map.getRoutes({ 10 origin: [ fromLatLng.lat(), fromLatLng.lng() ], 11 destination: [ toLatLng.lat(), toLatLng.lng() ], 12 travelMode: "driving", 13 unitSystem: "imperial", 14 callback: routeDone 15 }); 16 } 17 }; 18 var fromAddressDone = function( results, status ) { 19 if ( status == "OK" ) { 20 fromLatLng = results[0].geometry.location; 21 GMaps.geocode({ 22 address: toAddress, 23 callback: toAddressDone 24 }); 25 } 26 }; 27 GMaps.geocode({ 28 address: fromAddress, 29 callback: fromAddressDone 30 });
async.js 库可以帮助我们处理多重Ajax requests/responses,如:
1 async.parallel([ 2 function( done ) { 3 GMaps.geocode({ 4 address: toAddress, 5 callback: function( result ) { 6 done( null, result ); 7 } 8 }); 9 }, 10 function( done ) { 11 GMaps.geocode({ 12 address: fromAddress, 13 callback: function( result ) { 14 done( null, result ); 15 } 16 }); 17 } 18 ], function( errors, results ) { 19 getRoute( results[0], results[1] ); 20 });
- 使用promise
promise在异步执行的流程中,把执行代码和处理结果的代码清晰地分离了: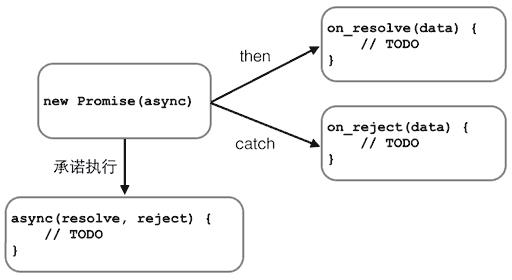
promise还可以做若干个异步的任务,例:有一个异步任务,需要先做任务1,如果任务成功后再做任务2,任何任务失败则不再继续并执行错误处理函数。
例:job1.then(job2).then(job3).catch(handleError); //job1、job2和job3都是Promise对象
1 \'use strict\'; 2 3 var logging = document.getElementById(\'test-promise2-log\'); 4 while (logging.children.length > 1) { 5 logging.removeChild(logging.children[logging.children.length - 1]); 6 } 7 8 function log(s) { 9 var p = document.createElement(\'p\'); 10 p.innerhtml = s; 11 logging.appendChild(p); 12 } 13 // 0.5秒后返回input*input的计算结果: 14 function multiply(input) { 15 return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 16 log(\'calculating \' + input + \' x \' + input + \'...\'); 17 setTimeout(resolve, 500, input * input); 18 }); 19 } 20 21 // 0.5秒后返回input+input的计算结果: 22 function add(input) { 23 return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 24 log(\'calculating \' + input + \' + \' + input + \'...\'); 25 setTimeout(resolve, 500, input + input); 26 }); 27 } 28 29 var p = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 30 log(\'start new Promise...\'); 31 resolve(123); 32 }); 33 34 p.then(multiply) 35 .then(add) 36 .then(multiply) 37 .then(add) 38 .then(function (result) { 39 log(\'Got value: \' + result); 40 });
关于promise的两个方法
1 var p1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 2 setTimeout(resolve, 500, \'P1\'); 3 }); 4 var p2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 5 setTimeout(resolve, 600, \'P2\'); 6 }); 7 // 同时执行p1和p2,并在它们都完成后执行then: 8 Promise.all([p1, p2]).then(function (results) { 9 console.log(results); // 获得一个Array: [\'P1\', \'P2\'] 10 });
1 var p1 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 2 setTimeout(resolve, 500, \'P1\'); 3 }); 4 var p2 = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 5 setTimeout(resolve, 600, \'P2\'); 6 }); 7 Promise.race([p1, p2]).then(function (result) { 8 console.log(result); // \'P1\' 9 });
//由于p1执行较快,Promise的then()将获得结果\'P1\'。p2仍在继续执行,但执行结果将被丢弃。
本文参考:
以上是关于js中的异步与同步,解决由异步引起的问题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章