JavaEE实战——jsp入门El表达式JSTL标签库
Posted 李春春_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaEE实战——jsp入门El表达式JSTL标签库相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
本篇博客主要讲述JSP语法、EL技术和JSTL技术。
JSP复习
为什么sun推出 JSP技术?
Servlet 生成网页比较复杂,本身不支持html语法,html代码需要通过response输出流输出,JSP支持HTML语法,生成HTML方便。JSP技术与Servlet 技术区别和关系?
JSP和Servlet技术都是用来动态生成网页的,Servlet不支持HTML语法,生成网页麻烦,JSP支持HTML语法,生成网页方便,JSP运行是由服务器翻译成Servlet执行的。JSP 就是 Servlet。JSP运行原理是怎样的?
客户端访问编写JSP文件,服务器读取JSP文件,根据JSP生成Servlet ,Servlet编译运行 生成网页。

<%! %> 声明:定义翻译后Servlet程序的 全局变量或全局方法、内部类
<%= %> 表达式 输出内容到浏览器 效果等同于 out.print
<% %> 脚本代码块,嵌入java运行代码 ---- 不翻译
JSP翻译Servlet 存放tomcat/work 目录
注: JSP翻译为Servlet,页面当前所有HTML 翻译为out.write 输出
代码示例:
demo1.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JSP脚本元素</h1>
<%!
// JSP声明 定义成员变量、成员方法 、内部类
public static void m()
class A
%>
<!-- 表达式 等价于 会被翻译为 out.print -->
<%="abcd" %>
<%
// JSP 脚本代码块,嵌入任何java代码
String s = "abcdefg";
s = s.toUpperCase();
out.print(s);
%>
</body>
</html>demo1_jsp.java:
/*
* Generated by the Jasper component of Apache Tomcat
* Version: Apache Tomcat/7.0.42
* Generated at: 2016-09-03 12:18:11 UTC
* Note: The last modified time of this file was set to
* the last modified time of the source file after
* generation to assist with modification tracking.
*/
package org.apache.jsp;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
public final class demo1_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent
// JSP声明 定义成员变量、成员方法 、内部类
public static void m()
class A
private static final javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory _jspxFactory =
javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
private static java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> _jspx_dependants;
private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;
private org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_instancemanager;
public java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> getDependants()
return _jspx_dependants;
public void _jspInit()
_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();
_jsp_instancemanager = org.apache.jasper.runtime.InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(getServletConfig());
public void _jspDestroy()
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext;
javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null;
final javax.servlet.ServletContext application;
final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null;
final java.lang.Object page = this;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC \\"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\\" \\"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd\\">\\r\\n");
out.write("<html>\\r\\n");
out.write("<head>\\r\\n");
out.write("<meta http-equiv=\\"Content-Type\\" content=\\"text/html; charset=UTF-8\\">\\r\\n");
out.write("<title>Insert title here</title>\\r\\n");
out.write("</head>\\r\\n");
out.write("<body>\\r\\n");
out.write("<h1>JSP脚本元素</h1>\\r\\n");
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("<!-- 表达式 等价于 会被翻译为 out.print -->\\r\\n");
out.print("abcd" );
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("\\r\\n");
// JSP 脚本代码块,嵌入任何java代码
String s = "abcdefg";
s = s.toUpperCase();
out.print(s);
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("</body>\\r\\n");
out.write("</html>");
catch (java.lang.Throwable t)
if (!(t instanceof javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException))
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try out.clearBuffer(); catch (java.io.IOException e)
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
else throw new ServletException(t);
finally
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
JSP注释
JSP支持三种注释
1、JSP注释 <%-- --%> 只存在JSP文件源码中,在JSP翻译Servlet时,这类注释消失了* 该类注释得不到执行
2、Java注释 /** */文档注释、/* */多行注释、// 单行注释
文档注释 /** */ 生成javadoc 主要用来注释 包、类、成员变量、成员方法 ------ 代码功能使用者多行注释 和 单行注释 不会生成javadoc,注释代码实现逻辑 用于在方法内 ------ 程序员本身,读懂代码进行注释
* Java注释 在JSP翻译为Servlet时存在,在Servlet程序执行时,会被忽略,生成HTML网页源代码中不存在
* 在Servlet执行过程中被忽略
3、HTML注释 <!-- -->
* 在JSP翻译为Servlet时会被翻译 out.print 在生成HTML页面源代码中,该类注释也是存在的代码示例:
demo2.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JSP三种注释</h1>
<%-- JSP注释 --%>
<%!
/** 文档注释 肯定用在 JSP声明中*/
public void printInfo()
%>
<%
/** 多行注释*/
// 单行注释 存放JSP 脚本代码块
%>
<!-- HTML注释 -->
<%
String s = "abcd";
%>
<!-- 用HTML注释 注释 JSP或者java代码 <%=s%> -->
</body>
</html>demo2_jsp.java:
/*
* Generated by the Jasper component of Apache Tomcat
* Version: Apache Tomcat/7.0.42
* Generated at: 2016-09-17 09:21:24 UTC
* Note: The last modified time of this file was set to
* the last modified time of the source file after
* generation to assist with modification tracking.
*/
package org.apache.jsp;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
public final class demo2_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent
/** 文档注释 肯定用在 JSP声明中*/
public void printInfo()
private static final javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory _jspxFactory =
javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
private static java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> _jspx_dependants;
private javax.el.ExpressionFactory _el_expressionfactory;
private org.apache.tomcat.InstanceManager _jsp_instancemanager;
public java.util.Map<java.lang.String,java.lang.Long> getDependants()
return _jspx_dependants;
public void _jspInit()
_el_expressionfactory = _jspxFactory.getJspApplicationContext(getServletConfig().getServletContext()).getExpressionFactory();
_jsp_instancemanager = org.apache.jasper.runtime.InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(getServletConfig());
public void _jspDestroy()
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext;
javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null;
final javax.servlet.ServletContext application;
final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null;
final java.lang.Object page = this;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC \\"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\\" \\"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd\\">\\r\\n");
out.write("<html>\\r\\n");
out.write("<head>\\r\\n");
out.write("<meta http-equiv=\\"Content-Type\\" content=\\"text/html; charset=UTF-8\\">\\r\\n");
out.write("<title>Insert title here</title>\\r\\n");
out.write("</head>\\r\\n");
out.write("<body>\\r\\n");
out.write("<h1>JSP三种注释</h1>\\r\\n");
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write('\\r');
out.write('\\n');
/** 多行注释*/
// 单行注释 存放JSP 脚本代码块
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("<!-- HTML注释 -->\\r\\n");
String s = "abcd";
out.write("\\r\\n");
out.write("<!-- 用HTML注释 注释 JSP或者java代码 ");
out.print(s);
out.write(" -->\\r\\n");
out.write("</body>\\r\\n");
out.write("</html>");
catch (java.lang.Throwable t)
if (!(t instanceof javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException))
out = _jspx_out;
if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0)
try out.clearBuffer(); catch (java.io.IOException e)
if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t);
else throw new ServletException(t);
finally
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
结论:JSP注释在翻译阶段消失,Java注释在Servlet运行阶段消失,HTML注释不消失。
思考题:<%
String s = "abcd";
%>
<!-- 用HTML注释 注释 JSP或者java代码 <%=s%> -->
在页面结果源代码中 <!-- 用HTML注释 注释 JSP或者java代码 abcd -->
结论: HTML注释 无法阻止 JSP或者 Java代码执行的。
JSP指令
JSP指令又称为JSP Derective
功能:
用于指示JSP执行某些步骤用于指示JSP表现特定行为
语法:<%@ 指令名称 属性=值 属性=值 ... %>
分类:page指令
include指令taglib指令
page指令
page指令用来定义JSP文件的全局属性 <%@ page 属性=值 %>
在JSP页面中,只有import可以出现多次,其他属性都只能出现一次
1、language 只能为java2、extends 表示JSP翻译后的Servlet所继承的父类,这个属性一般不设置,因为服务器内部默认使jsp继承HttpJspBase类;如果非要设置,继承类必须是Servlet实现类
3、session 定义JSP中是否可以直接使用Session隐含对象,默认为true
如果属性设置为true,在JSP翻译Servlet时,生成以下两句代码:
HttpSession session = null;
session = pageContext.getSession();
* 如果jsp中想使用HttpSession对象,使用session属性默认值true
4、import 完成 JSP翻译后 Servlet 的导包
jsp在翻译为Servlet时,默认导入三个包:
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
jre默认导入 java.lang
* 在jsp中如果使用类 不属于以上四个包,就需要导包
5、buffer和autoFlush 设置 out隐含对象属性
buffer 设置缓冲区大小
autoFlush 设置当缓冲区满后,自动刷新
6、isELIgnored 设置JSP是否执行EL表达式
isELIgnored="false" 不忽略---执行解析
isELIgnored="true" 忽略 ---- 不解析
* 一般就是默认值false
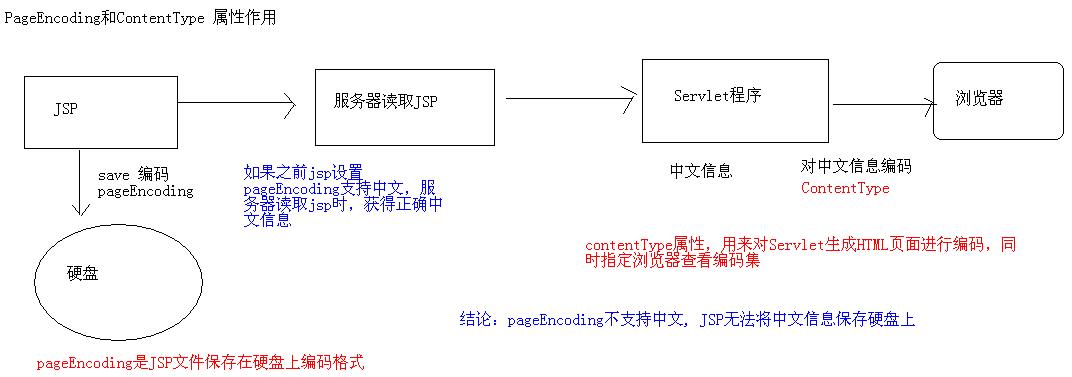
7、通过contentType和pageEncoding 设置 JSP页面编码
pageEncoding 是 JSP文件源代码在硬盘上编码集,如果设置支持中文的编码集,那么服务器就能正确读取jsp中的中文,并将翻译好的中文字符读取进内存(注意内存中保存的不是字节)contentType 在Servlet生成HTML、传递给浏览器时采用编码
* Java内存中,是没有编码集这一说的,存的都是字符
* 这两个属性设置成支持中文的编码集即可,互相之间不打架的
pageEncoding和contentType区别:
设置错误友好页面 ---- 当页面发生错误,不应该给用户看到含有代码错误页面,而应该看到一个友好页面
通过errorPage 指定 在页面发生错误跳转到哪个页面
注:IE 浏览器默认好友页面 ,如果想看到自己编写友好页面,关闭IE默认友好页面,方法是找到IE 工具栏 --- Internet选项 ----- 高级 -----显示友好HTTP错误信息 ,将钩去掉即可。
makeerror.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%--发生错误,想让用户看到友好页面 error.jsp--%>
<%@ page errorPage="/demo4/error.jsp" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 制作错误 -->
<%
int d = 1/0;
%>
</body>
</html>在错误友好页面中,可以通过设置isErrorPage属性,获得jsp内置对象exception,从而通过exception获得错误原因。
error.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%--当设置了当前页面是错误页面,则可以获得内置对象exception,从而获得错误信息 --%>
<%@page isErrorPage="true" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 错误友好信息页面 -->
<h4>对不起,服务器正在升级,请稍后访问!</h4>
<h5>错误原因:<%=exception.getMessage() %></h5>
</body>
</html>注:在实际开发中,一般不使用上面讲解错误处理方式,不然在每个发生错误的页面都要设置errorPage,指示发生错误时往哪里跳,太麻烦!
错误页面 第二种处理方式:配置web.xml
<error-page>
<error-code>500</error-code>
<location>/demo5/500.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/demo5/404.jsp</location>
</error-page>好处:不仅可以处理500 ,还可以处理404
示例:
mkeerror.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
// 制作 空指针异常
String s = null;
s.trim();
%>
</body>
</html>500.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>对不起,服务器发生内部错误,请稍后访问!</h1>
</body>
</html>404.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta content="3;url=/day08/index.jsp" http-equiv="refresh">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>对不起,你访问的资源不存在,网站将在3秒之后 自动跳转到主页面!</h1>
</body>
</html>
注:第二中处理错误页面的方式必须掌握!
page指令 代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"%>
<%@ page pageEncoding="gbk" %>
<%--如果编写 extends 属性,必须继承 Servlet实现类 ,这个属性一般不写--%>
<%--<%@ page extends="java.util.ArrayList" %>--%>
<%@page session="true" %>
<%@page import="java.util.List"%>
<%--通过 isELIgnored 控制 EL表达式是否解析 --%>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Page指令</h1>
<%
session.setAttribute("name","lichunchun");
%>
<%
// JSP 在翻译Servlet时 默认导入
/*import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
*/
// 如果 在jsp中使用 以上三个包类 不需要导包
Cookie cookie ;
List list ; //通过 alt+/ 回车快速生成导包 语句
%>
<%
request.setAttribute("address","安徽合肥");
%>
$requestScope.address
</body>
</html>include指令
include指令 ,用来静态包含页面 ----- 将页面公共部分提取出来,通过include完成页面布局。
语法:<%@ include file="文件路径" %>
include包含的是目标页面的整个内容,所以被包含页面,不需要是一个完整HTML,只要编写HTML片段就可以了。
代码示例:
index.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 主页面 -->
<!-- 通过 include 包含 logo.jsp -->
<%@ include file="/demo6/logo.jsp" %>
<h1>主页面其它内容</h1>
<%--包含页面必须存在的--%>
<%@ include file="/demo6/footer.jsp" %>
</body>
</html>logo.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<h1>这是系统LOGO</h1>footer.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String s = "computer@mail.ustc.edu.cn";
%>
<%=s %>
静态include原理
* 被包含的jsp文件本身不会被单独翻译成一个Servlet文件,而是把它们翻译成Servlet拼接到index_jsp.java这个Servlet文件中,所以我们在apache/work目录下只能看到index_jsp.java这一个Servlet文件。

* 在 JSP翻译为Servlet时,完成包含动作,此时Servlet程序并没有执行,包含路径不能用变量、不能含有?拼接参数,目标文件必须存在
* 存在特殊案例:被包含页面存在错误,只要包含后 组合在一起的Servlet没有错误,就可以执行

taglib指令
taglib指令 ,用来在jsp页面引用标签库文件
* 定义标签作用为了简化 jsp页面开发* 通过taglib 指令引入 jstl标签库,语法: <%@ taglib uri="" prefix="" %>
uri ---- 定义标签 唯一命名空间
prefixt ---- 命名空间前缀引用jstl时,在导入的jstl.jar中 META-INF/c.tld
<short-name>c</short-name> -------- 就是prefix属性<uri>http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core</uri> ----- 就是uri属性
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%--通过 taglib 指令 引用jstl ,必须导入jstl 的 jar包--%>
<%--在 javaee 5 libraries 存在 jstl-1.2.jar--%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
request.setAttribute("a",10);
%>
<c:if test="$requestScope.a>8">
<h1>a的值 大于8</h1>
</c:if>
</body>
</html>JSP 九个内置对象
什么是内置对象?
JSP翻译为Servlet代码时,有些对象是默认已经创建好的,这类对象可以直接在jsp中使用,称之为内置对象。JSP的九个内置对象分别是什么?
page、request、session、application、response、pageContext、out、config、exception

request HttpServletRequest ---- 请求对象
response HttpServletResponse ---- 响应对象
session HttpSession ------- 会话对象
application ServletContext ------ web应用全局唯一对象
config ServletConfig ------ 初始化数据
page this (HttpServlet)
pageContext PageContext
exception Throwable (所有exception异常的父类) ----- 当页面是一个错误页面,用exception获得异常信息 ---- jsp页面设置了isErrorPage,才会有这个内置对象
out JspWriter
下面具体解释一下这里面的几个没有见过的内置对象:
page对象
page 代表当前jsp生成的Servlet对象
* page 是 Object类型,只能使用Object中方法 ---- 这个对象在开发中不建议使用* 可以将page强制转换成HttpServlet对象
<%
HttpServlet httpServlet = (HttpServlet)page;
out.print(httpServlet.getServletContext().getRealPath("/"));
%>
JSP四种数据范围
Servlet 三种数据范围: request、session、servletcontext
JSP 四种数据范围: page、request、session、application
* JSP 在 Servlet 三种数据范围基础上,新添加page数据范围
* page数据范围存放数据,只在当前jsp内有效* 向page 范围保存数据,必须通过 pageContext对象 setAttribute方法
pageContext对象
pageContext 是当前“页面上下文”对象,代表的是当前页面运行的一些属性。
pageContext 对象提供了对JSP页面所有的对象及命名空间的访问。1、向page范围存取数据
pageContext.setAttribute("name","page");pageContext.getAttribute("name")
2、查找各个域中的属性
findAttribute 方法 依次在 page 、request 、session 、 application 四个数据范围进行数据查找注:若 EL中不加范围,直接写 $name,会调用 pageContext.findAttribute在四个范围中依次查找数据
3、pageContext 用来 获得其它八个隐含对象
* pageContext封装八个隐含对象意义:框架编写,得到PageContext对象 相当于得到 JSP九个内置对象
* 通过pageContext对象获得其他八个隐含对象

out对象
out 功能向浏览器输出信息,是JspWriter类型,内部使用PrintWriter实现,拥有独立缓冲区。
out创建:out对象通过pageContext对象获得,而在创建pageContext对象时,需指定out缓冲区大小以及是否自动flush* 通过 page指令 buffer autoFlush 设置out 缓存区大小 以及是否自动 flush,默认的缓冲区是8kb
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ page isErrorPage="true" %>
<%--通过 buffer和autoFlush 设置out 对象缓冲区--%>
<%--<%@page buffer="1kb" autoFlush="false" %>--%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JSP 九个内置对象</h1>
<%
// 非要使用page对象
HttpServlet httpServlet = (HttpServlet)page;
out.print(httpServlet.getServletContext().getRealPath("/"));
%>
<hr/>
<%
// 向四种数据范围保存数据
request.setAttribute("name","request");
session.setAttribute("name","session");
application.setAttribute("name","application");
// 向page 范围保存数据,必须通过 pageContext对象
pageContext.setAttribute("name","page");
%>
<%=request.getAttribute("name") %>
<%=session.getAttribute("name") %>
<%=application.getAttribute("name") %>
<%=pageContext.getAttribute("name") %>
<%
// 想在四个数据范围查询 指定名称数据
// 顺序按照 page -- request -- session -- application
Object value = pageContext.findAttribute("name");
%>
<h3>查找name属性 :<%=value %></h3>
<h1>通过EL 取得数据</h1>
$sessionScope.name
<!-- 如果直接写name 默认会调用 pageContext.findAttribute -->
$name
</body>
</html>通过查看Servlet翻译成的java代码,观察9个内置JSP对象:

out 向浏览器输出内容,response.getWriter 向浏览器输出内容 , 区别?
实验:在demo9.jsp加入如下内容out.println("aaa");
response.getWriter().println("bbb");
out.print("ccc");
结果:response.getWriter输出内容,在out输出内容之前
原因:JspWriter和response各自有独立的缓冲区,out中的内容会先刷新到response缓冲区中,然后一并输出到浏览器。
解惑:out 和 response.getWriter 区别
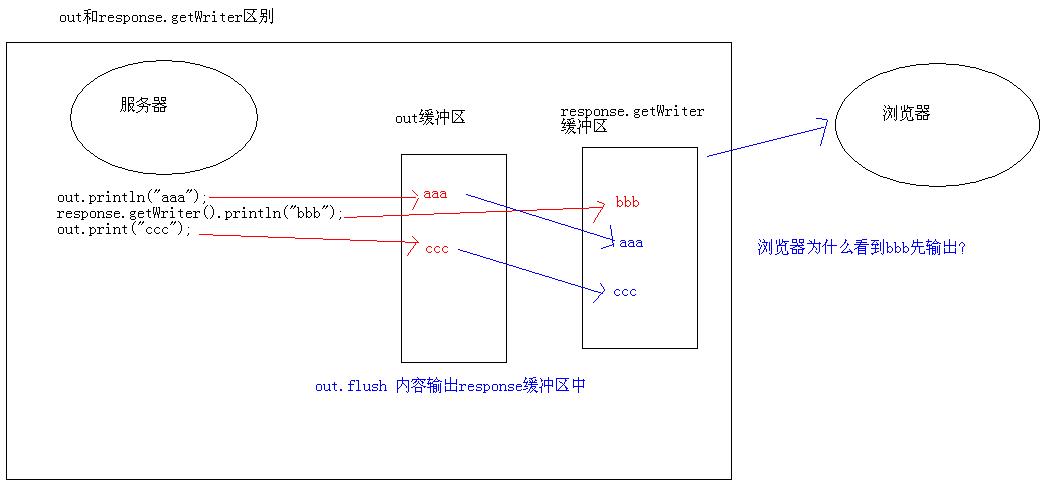
备注:out隐式对象的工作原理图
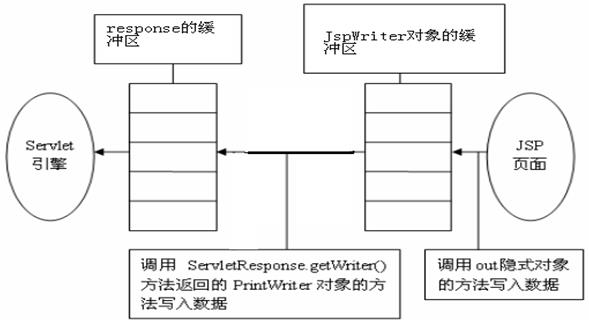
实验代码:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
out.println("aaa");//此时aaa写到了out缓冲区中
out.flush();//out的内容从out缓冲区输出到response缓冲区中
response.getWriter().println("bbb");
out.print("ccc");
//这之后先调用out.flush刷到response.getWriter缓冲区
//然后调用response.getWriter.flush刷到浏览器
%>
</body>
</html>exception对象
exception对象是java.lang.Trowable类的实例 (使用前需要在jsp页面设置page指令 isErrorPage=“true”)
exception对象用来处理JSP文件在执行时所有发生的错误和异常exception对象可以和page指令一起使用,通过指定某一个页面为错误处理页面,对错误进行处理
<%@ page isErrorPage="true"%>的页面内使用。(最好还是用第二种配置web.xml的方式)
再温习一下这9个JSP内置对象:
page、request、session、application、response、out、config、pageContext、exception
JSP标签
JSP标签也称之为Jsp Action (JSP动作) 元素,它用于在Jsp页面中提供业务逻辑功能,避免在JSP页面中直接编写java代码,造成jsp页面难以维护。注意,这些标签是默认存在的,不需要引入Jar包。
JSP指令和JSP标签 区分?JSP 指令 Directive
JSP 标签 Action
jsp中六个动作标签
<jsp:useBean>、<jsp:setProperty>、<jsp:getProperty> ----- 这三个标签与JavaBean 操作相关 下一篇博客阐述<jsp:include>、<jsp:forward>、<jsp:param >
<jsp:include> 效果 等价于 request.getRequestDispatcher().include
<jsp:forward> 效果 等价于 request.getRequestDispatcher().forward
<jsp:include>
<jsp:include> 标签功能等价于 <%@ include %>
原理:动态包含语法:<jsp:include page="文件路径" />
被包含页面不需要完整html,只需要编写html片段
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 使用 jsp:include 包含 logo.jsp -->
<jsp:include page="/demo10/logo.jsp"></jsp:include>
<h1>主页面其它内容</h1>
</body>
</html><%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<h1>页面 LOGO信息</h1>解惑:<jsp:include>标签动态包含原理:

jsp:include 和 @include 区别?
<%@ include%>:include指令,静态包含,在jsp翻译为Servlet时,执行包含动作,包含结果是目标页面翻译后的Servlet源代码,翻译为一个Servlet一起执行(包含的是Servlet源码)<jsp:include>:JSP标签,动态包含,在index servlet执行时,完成包含动作,包含结果是目标jsp翻译Servlet生成的html页面结果,每个被包含的jsp会翻译成单独Servlet进行执行(包含的是html结果)
原理:include动态包含

总结:
<jsp:include>标签是动态引入,<jsp:include>标签涉及到的2个JSP页面会被翻译成2个servlet,这2个servlet的内容在执行时进行合并。而<%@ include%>指令是静态引入,涉及到的2个JSP页面会被翻译成1个servlet,其内容是在源文件级别进行合并。
不管是<jsp:include>标签,还是include指令,它们都会把两个JSP页面内容合并输出,所以这两个页面不要出现重复的HTML全局架构标签,否则输出给客户端的内容将会是一个格式混乱的HTML文档。
*两种include用法的区别:
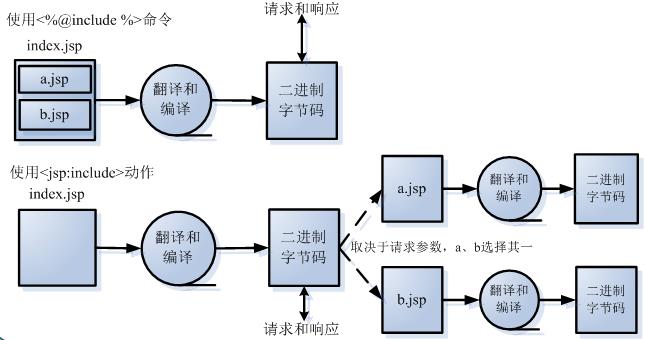
执行时间上:
<%@ include file="relativeURI"%>?是在 翻译阶段执行;
<jsp:include page="relativeURI" flush="true"?/>?在 请求处理阶段执行。
实验:

<jsp:forword>
<jsp:forward page="/demo11/b.jsp"></jsp:forward> 等价于 request.getRequestDispatcher("/demo11/b.jsp").forward(request,response);
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello A</h1>
<%
// 看不到Hello A,因为在跳转之前,会清空response 缓冲区
// request.getRequestDispatcher("/demo11/b.jsp").forward(request,response);
%>
<%
request.setAttribute("name", "lichunchun");
%>
<jsp:forward page="/demo11/b.jsp">
<jsp:param value="ustc" name="school"/>
</jsp:forward>
</body>
</html><%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello B</h1>
<%=request.getAttribute("name") %>
<%=request.getParameter("school") %>
</body>
</html><jsp:forward page="/demo11/b.jsp">
<jsp:param value="ustc" name="school"/></jsp:forward>
<%=request.getParameter("school") %>
上面写法表示用jsp传递一个参数
而实际上如果想用jsp传递一个参数,直接通过request.setAttribute(name,value)、getAttribute(name)就可以完成
注:<jsp:forward>之后的代码不执行
EL表达式语言
EL 表达式语言,来自民间 ,Servlet2.4 之后 EL 被纳入官方规范。
EL主要功能:
1、EL 获得 JSP四个范围中保存数据 (访问JavaBean的属性)2、EL 表达式支持运算
3、EL 内置 11个对象 --- web开发常用对象
4、EL 调用 java的方法
EL注意事项:
EL是从javaee1.4版本才被纳入规范,javaee1.3及以前版本,默认对EL不进行解析* 如果想javaee1.3以及之前版本解析 EL ------ 在JSP中加入page属性 <%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
1、使用EL获得JSP四个数据范围的数据
使用EL指定查找四个范围数据:
$pageScope.属性名称
$requestScope.属性名称
$sessionScope.属性名称
$applicationScope.属性名
如果不指定查找数据范围 $属性名称 ---- 会调用pageContext.findAttribute方法在page、request、session、application四个域范围依次查找如果查找属性不存在,返回是一个 "" 空串,而不是null
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" isELIgnored="false"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 通过el 获得四个数据范围 数据 page request session application-->
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("city","合肥");
request.setAttribute("name","李春春");
session.setAttribute("school","中国科学技术大学");
application.setAttribute("pnum",100);
%>
$pageScope.city
$requestScope.name
$sessionScope.school
$applicationScope.pnum
<h1>省略指定范围, 默认调用pageContext.findAttribute() 在四个范围依次查找</h1>
$name
$city
<h1>EL找不到数据返回""空串、传统表达式方式找不到数据返回null</h1>
<h3>abc: <%=request.getAttribute("abc") %></h3>
<h3>abc: $abc </h3>
</body>
</html>EL表达式也可以很轻松获取JavaBean的属性,或获取数组、Collection、Map类型集合的数据
代码示例:
package ustc.lichunchun.domain;
public class Person
private String name;
private int age;
private City city;
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
public int getAge()
return age;
public void setAge(int age)
this.age = age;
public City getCity()
return city;
public void setCity(City city)
this.city = city;
package ustc.lichunchun.domain;
public class City
private String name;
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@page import="ustc.lichunchun.domain.Person"%>
<%@page import="ustc.lichunchun.domain.City"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 通过EL 获得 存放在四个范围内的 java对象类型 -->
<%
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("李春春");
person.setAge(24);
City city = new City();
city.setName("合肥");
person.setCity(city);
pageContext.setAttribute("person", person);
%>
$pageScope.person.name
<!-- 上面写法等价于 pageContext.getAttribute("person").getName() -->
$pageScope.person.age
$pageScope.person["age"]
$pageScope["person"]["age"]
<!-- 获得person的city对象名称 -->
$pageScope.person.city.name
<!-- pageContext.getAttribute("person").getCity().getName() -->
$pageScope["person"]["city"]["name"]
</body>
</html>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@page import="java.util.List"%>
<%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%>
<%@page import="java.util.Map"%>
<%@page import="java.util.HashMap"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 通过EL 取得 List 或者 Map中数据 -->
<%
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("abc");
list.add("bcd");
list.add("efg");
// 将list 保存page范围
pageContext.setAttribute("list",list);
%>
$pageScope.list
取得list的第二个元素 :$pageScope.list[1] <br/>
<%
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("aaa","111");
map.put("bbb","222");
pageContext.setAttribute("map",map);
%>
取得 map 中 bbb对应 value : $pageScope.map.bbb 、$pageScope.map["bbb"] <br/>
</body>
</html>. 和 [ ] 有什么区别 ?
答案:. 和 [ ] 都可以用来取得EL 属性值,.可以实现的功能[ ] 也都可以!
例如: $pageScope.user.name 也可以写为 $pageScope.user["name"]
[ ] 可以使用特殊标识信息,但是. 不可以
例如:pageContext.setAttribute("0","itcast");
pageContext.setAttribute("aa.bb","春生泰克");
只能通过 [ ] 进行访问 ----- 注意:在使用[ ] 进行属性取值时,要加"" , 若不加"" 则认为是一个变量
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@page import="java.util.List"%>
<%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%>
<%@page import="java.util.Map"%>
<%@page import="java.util.HashMap"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 通过EL 取得 List 或者 Map中数据 -->
<%
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("abc");
list.add("bcd");
list.add("efg");
// 将list 保存page范围
pageContext.setAttribute("list",list);
%>
$pageScope.list
取得list的第二个元素 :$pageScope.list[1] <br/>
<%
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("aaa","111");
map.put("bbb","222");
pageContext.setAttribute("map",map);
%>
取得 map 中 bbb对应 value : $pageScope.map.bbb 、$pageScope.map["bbb"] <br/>
<h1>. 和 [] 区别</h1>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("0","itcast");
pageContext.setAttribute("aa.bb","特殊标识信息");
%>
特殊字符0 属性值:$pageScope["0"] <br/>
特殊字符 aa.bb 属性值 :$pageScope["aa.bb"] <br/>
<%
String ds = "aa.bb";
pageContext.setAttribute("s",ds);
%>
<!-- 在使用[] 进行属性取值时,要加"" , 若不加"" 则认为是一个变量 -->
特殊字符 aa.bb 属性值 :$pageScope[s] <br/><!-- 特殊标识信息 -->
特殊字符 aa.bb 属性值 :$pageScope["s"] <!-- aa.bb -->
<!-- 利用el表达式获取web应用的名称 -->
<a href="$pageContext.request.contextPath /demo1.jsp">点我</a>
</body>
</html>结论:在使用EL进行取值时,如果含有特使字符属性,尽量使用[ ] , 否则都使用 . 就可以了!
结合JSTL的foreach标签,使用EL表达式也可以很轻松迭代各种类型的数组或集合,如迭代数组、迭代collection类型集合、迭代map类型集合,后面jstl标签c:foreach时我会提及。
2、在EL 中执行 算术、比较、逻辑运算
在EL 执行运算时,运算语句必须写入 $ 中
* 在EL 获得属性值 执行算术运算,自动类型转换 ---- 执行算术运算时,进行运算参数,必须都是数字$"a"+"b" ---- 发生数字格式化错误
empty运算符
1) 判断一个属性是否存在 , 通常empty运算符都是结合c:if 一起使用2) 使用empty 判断List 或者 Map是否为空 (size==0)
二元表达式:$user!=null?user.name:"" ----- 三元运算符